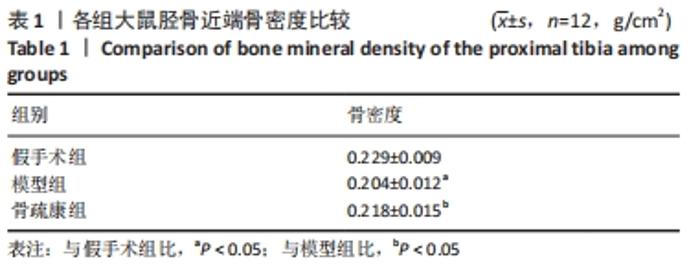
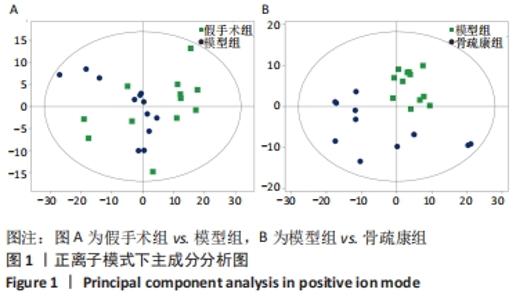
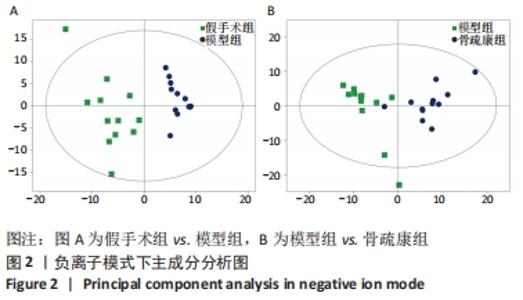
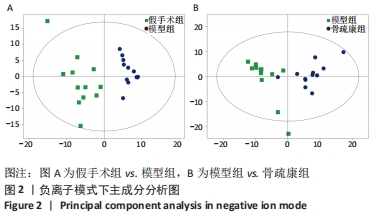
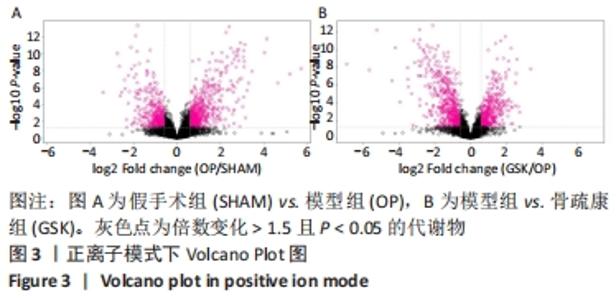
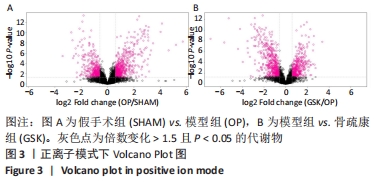
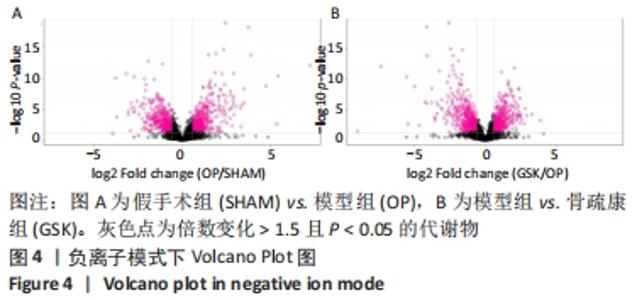
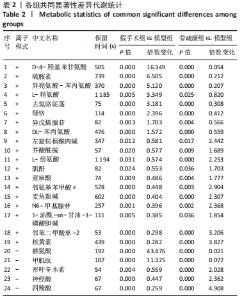
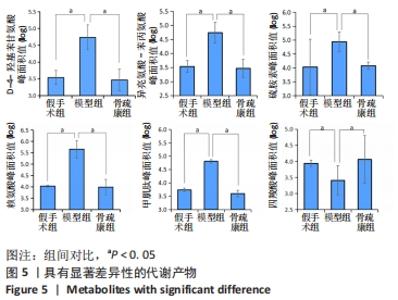
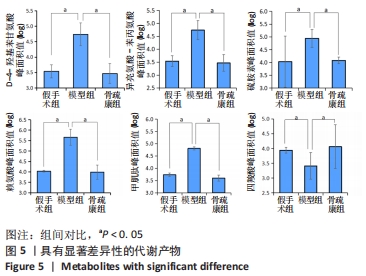
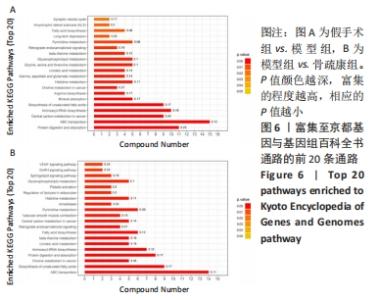
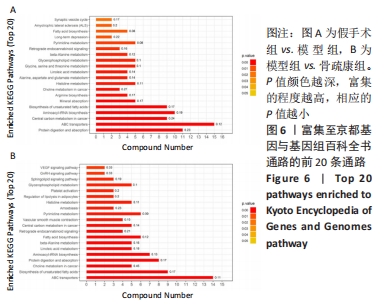
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (32): 5185-5190.doi: 10.12307/2022.937
Previous Articles Next Articles
Anti-osteoporosis effect of Gushukang in ovariectomized rats: a lumbar metabonomic analysis
Zhang Haiyong1, Huang Jingwen2, Xie Bingying2, Chen Sainan2, Xie Lihua2, Chen Xuan2, Li Shengqiang2, Ge Jirong2
- 1Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350003, Fujian Province, China; 2Basic Research Institute, Fujian Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Fuzhou 350003, Fujian Province, China
-
Received:2022-01-04Accepted:2022-02-11Online:2022-11-18Published:2022-05-12 -
Contact:Li Shengqiang, MD, Associate researcher, Basic Research Institute, Fujian Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Fuzhou 350003, Fujian Province, China -
About author:Zhang Haiyong, Master candidate, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350003, Fujian Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81774350 (to LSQ); the Fundamental Scientific Research Project of Fujian Provincial Public Welfare Scientific Research Institutes of Fujian Provincial Department of Science and Technology, No. 2019R1003-1 (to LSQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Haiyong, Huang Jingwen, Xie Bingying, Chen Sainan, Xie Lihua, Chen Xuan, Li Shengqiang, Ge Jirong. Anti-osteoporosis effect of Gushukang in ovariectomized rats: a lumbar metabonomic analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(32): 5185-5190.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] 原发性骨质疏松症诊治指南(2011年)[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2011,4(1):2-17. [2] YOSHIMURA N, MURAKI S, NAKAMURA K, et al.Epidemiology of the locomotive syndrome: The research on osteoarthritis/osteoporosis against disability study 2005-2015. Mod Rheumatol. 2017;27(1):1-7. [3] 中国骨质疏松症流行病学调查及“健康骨骼”专项行动结果发布[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2019,12(4):317-318. [4] 吕遐,扶琼.原发性骨质疏松症的研究进展与最新指南解读[J].临床内科杂志,2020,37(5):319-322. [5] 许荣权,苏再发.骨质疏松症中医疗法的研究概况[J].中国医药导刊,2020,22(11):772-775. [6] 葛继荣,王和鸣,郑洪新,等.中医药防治原发性骨质疏松症专家共识(2020)[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(12):1717-1725. [7] 郭宁,宫明,于大鹏.绝经后骨质疏松症应用骨疏康治疗的临床效果研究[J].中外医疗,2015,34(15):156-157. [8] 张鉴,王亦璜,王文超,等.中药骨舒康治疗绝经后骨质疏松患者的临床效果观察[J].临床合理用药杂志,2017,10(29):56-57. [9] NICHOLSON JK, LINDON JC, HOLMES E. ‘Metabonomics’: understanding the metabolic responses of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli via multivariate statistical analysis of biological NMR spectroscopic data. Xenobiotica. 1999;29(11):1181-1189. [10] 陈赛楠,吴华嵩,程佑民,等.续苓健骨方对去卵巢骨质疏松模型大鼠血液钙磷代谢的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(4):528-532. [11] 陈勇.骨疏康胶囊治疗绝经后骨质疏松性转子间骨折的临床效果分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(11):1571-1575. [12] 成洁,王颖,吉健华,等.骨疏康胶囊治疗肾阳虚型骨质疏松症疗效及对患者骨代谢影响[J].陕西中医,2019,40(9):1232-1234+1250. [13] 韩国瑞,董卫兵,明海武.骨疏康胶囊辅助治疗绝经后骨质疏松性股骨转子间骨折的临床效果分析[J].中国合理用药探索,2021,18(6): 86-91. [14] WANG Q, ZHAO YG, SHA NN, et al. The systemic bone protective effects of Gushukang granules in ovariectomized mice by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis and stimulating osteoblastogenesis. J Pharmacol Sci. 2018;136(3):155-164. [15] LI WT, ZHOU XQ, JIANG TJ, et al. Positive Effect of Gushukang on Type-H Vessel and Bone Formation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:265. [16] 郑志坚,舒冰,赵世天,等.骨疏康颗粒对去卵巢小鼠骨质疏松模型骨丢失和破骨细胞凋亡的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2020,35(7): 3647-3651. [17] LI XL, WANG L, BI XL, et al. Gushukang exerts osteopreserve effects by regulating vitamin D and calcium metabolism in ovariectomized mice. J Bone Miner Metab. 2019;37(2):224-234. [18] IDE T, ORIGUCHI I. An Oil Rich in γ-Linolenic Acid Differently Affects Hepatic Fatty Acid Oxidation in Mice and Rats. Biol Pharm Bull. 2020; 43(9):1382-1392. [19] Ide T, ORIGUCHI I. Physiological effects of an oil rich in γ-linolenic acid on hepatic fatty acid oxidation and serum lipid levels in genetically hyperlipidemic mice. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2019;64(2):148-157. [20] 伍海艳,吴荣艳,钟凤元,等.雌激素代谢紊乱对老年女性骨质疏松患者的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2021,41(12):2567-2569. [21] 梁胡贞,贲吕金,钟雪群.绝经后骨质疏松症患者血清雌激素水平与前脂肪因子-1及瘦素水平的相关性分析[J].中国实用医药,2020, 15(29):104-106. [22] 张倩,杨旭,王媛,等.二仙汤对去势大鼠骨微结构及ALP、OPG、IL-6的影响[J].世界中西医结合杂志,2020,15(11):2053-2057+2061. [23] XUE LM, WANG Y, LIU L, et al. A HNMR-based metabonomics study of postmenopausal osteoporosis and intervention effects of Er-Xian Decoction in ovariectomized rats. Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(11):7635-7651. [24] DAI L, FENG Z, ZHA R, et al. Discovery of Novel Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor α (PPARα) Agonists by Virtual Screening and Biological Evaluation. J Chem Inf Model. 2020;60(3):1717-1727. [25] 赵晓杰,韩晓群,邓琴,等.PPARγ在结核分枝杆菌感染小鼠脂质代谢中的作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2021,37(5):849-856. [26] TORU Y, TOSHITSUG S, SHOZO Y, et al. Plasma Lipids and Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women. Endocr J. 2002;49(2):211-217. [27] KRESS BJ, KIM DH, MAYO JR, et al. Synthesis and Evaluation of PPARδ Agonists That Promote Osteogenesis in a Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Culture and in a Mouse Model of Human Osteoporosis. J Med Chem. 2021;64(10):6996-7032. [28] SMITH P, OWEN DM, LORENZ CD, et al. Asymmetric glycerophospholipids impart distinctive biophysical properties to lipid bilayers. Biophys J. 2021;120(9):1746-1754. [29] SHE Y, SONG J, YANG E, et al. Rapid identification of glycerophospholipids from RAW264.7 cells by UPLC/ESI -QTOF-MS. Biomed Chromatogr. 2014;28(12):174417-174455. [30] LIU XY, LIU YQ, CHENG MC, et al. A metabolomics study of the inhibitory effect of 17-beta-estradiol on osteoclast proliferation and differentiation. Mol Biosyst. 2015;11(2):635-646. [31] LIU XY, ZHANG SS, LU XM, et al. Metabonomic study on the anti-osteoporosis effect of Rhizoma Drynariae and its action mechanism using ultra-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012;139(1):311-317. [32] FERNANDES DA SJ, ALVES JV, SILVANETO JA, et al. Lysophosphatidylcholine induces oxidative stress in human endothelial cells via NOX5 activation - implications in atherosclerosis. Clin Sci (London, England : 1979). 2021;135(15):1845-1858. [33] 彭涛,李爱国,何培亮.绝经后骨质疏松与氧化应激相关研究进展[J].中外医学研究,2020,18(10):186-188. [34] SOOHO L, HUYNH LN, DONGCHUL K. Melatonin alleviates oxidative stress-inhibited osteogenesis of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells through AMPK activation. Int J Med Sci. 2018; 15(10):1083-1091. [35] XIAO W, BIN C, JING YS, et al. Iron-induced oxidative stress stimulates osteoclast differentiation via NF-κB signaling pathway in mouse model. Metabolism. 2018;83:167-176. [36] ZHANG AH, MA ZM, SUN H, et al. High-Throughput Metabolomics Evaluate the Efficacy of Total Lignans From Acanthophanax Senticosus Stem Against Ovariectomized Osteoporosis Rat. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:553. [37] HE W, LIU M, HUANG XN, et al. The influence of vitamin D receptor genetic variants on bone mineral density and osteoporosis in Chinese postmenopausal women. Dis Markers. 2015;2015:760313 [38] DEYAMA Y, KIKUIRI T, OHNISHI GI, et al. Histamine stimulates production of osteoclast differentiation factor/receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand by osteoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;298(2):240-246. [39] NAKAMURA M, KURODA H, NARITA K, et al. Parathyroid hormone induces a rapid increase in the number of active osteoclasts by releasing histamine from mast cells. Life Sci. 1996;58(21):1861-1868. [40] FITZPATRICK LA, BUZAS E, GAGNE TJ, et al. Targeted Deletion of Histidine Decarboxylase Gene in Mice Increases Bone Formation and Protects against Ovariectomy-Induced Bone Loss. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(10):6027-6032. [41] LIU YZ, DVORNYK V, LU Y, et al. A novel pathophysiological mechanism for osteoporosis suggested by an in vivo gene expression study of circulating monocytes. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(32):29011-20916. [42] YAMAGUCHI M. beta-Alanyl-L-histidinato zinc and bone resorption. Gen Pharmacol. 1995;26(6):1179-1183. |
| [1] | Nong Fuxiang, Jiang Zhixiong, Li Yinghao, Xu Wencong, Shi Zhilan, Luo Hui, Zhang Qinglang, Zhong Shuang, Tang Meiwen. Bone cement augmented proximal femoral nail antirotation for type A3.3 intertrochanteric femoral fracturalysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10. |
| [2] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Zhu Guangyu, Wang Rongtian, Wang Jian, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Changes of lower limb force line and knee function after high tibial osteotomy in osteoporotic medial ventricular knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [3] | Jiang Xiaocheng, Shi Lu, Wang Yinbin, Li Qiujiang, Xi Chuangzhen, Ma Zefeng, Cai Lijun. Systematical evaluation of bone fusion rate after interbody fusion in patients with osteoporosis and lumbar degenerative disease treated with teriparatide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1427-1433. |
| [4] | Sun Jiajia, Zhu Haidi, Lu Yun, Zhang Kai. Comparison of bone metabolism markers between type 2 diabetes mellitus and non-type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with hip fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1156-1160. |
| [5] | Ruan Ling, Wang Guanghua, Wu Rongping, Jin Zhan, Lyu Zhenqing, Zhang Nan, Li Shoubang. Correlation between exercise intensity and lipid metabolism disorder and oxidative stress in a high-diet rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1149-1155. |
| [6] | Long Yanming, Xie Mengsheng, Huang Jiajie, Xue Wenli, Rong Hui, Li Xiaojie. Casein kinase 2-interaction protein-1 regulates the osteogenic ability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in osteoporosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 878-882. |
| [7] | Wang Jinling, Huang Xiarong, Qu Mengjian, Huang Fujin, Yin Lingwei, Zhong Peirui, Liu Jin, Sun Guanghua, Liao Yang, Zhou Jun. Effects of exercise training on bone mass and bone microstructure in aged osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 676-682. |
| [8] | Zhang Min, Zhang Xiaoming, Liu Tongbin. Application potential of naringin in bone tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 787-792. |
| [9] | Cheng Yunzhong, Liu Yuzeng, Hai Yong, Guan Li, Pan Aixing, Zhang Xinuo, Tao Luming, Li Yue. Bibliometric and visual analysis of the research status and development trend of cortical bone trajectory screws [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 513-519. |
| [10] | Liu Hao, Yang Hongsheng, Zeng Zhimou, Wang Liping, Yang Kunhai, Hu Yongrong, Qu Bo. Lumbar MRI vertebral bone quality score to evaluate the severity of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 606-611. |
| [11] | Chen Feng, Ren Guowu, Zhang Xiaoyun, Chen Yueping, Shi Rusheng. Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand signal transduction mechanism and osteoclast activation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 293-299. |
| [12] | Lin Shi, Yuan Jiayao, Lin Xiancan, Yang Binbin, Wu Jianjun, Dongzhi Zhuoma, Tang Zijia, Yang Zhijie, Wan Lei, Huang Hongxing. Diagnostic value of peripheral blood interferon-gamma and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 165-170. |
| [13] | Gao Xu, Xing Wenhua. Application of finite element analysis in spine surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(18): 2921-2927. |
| [14] | Jiang Guozheng, Feng Ningning, Yu Xing, Zhao He, Yang Yongdong, Qu Yi, Wang Fengxian. Correlation between hand feeling and torque of screw insertion in lumbar pedicle system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(18): 2861-2865. |
| [15] | Wu Ruiqi, Cui Wei, Yang Qipei, Zhou Yi, Zhang Xuan. Therapeutic mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of hormone-induced necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(17): 2763-2771. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||