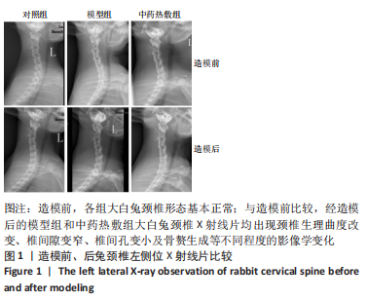
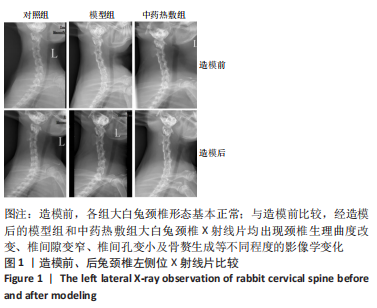
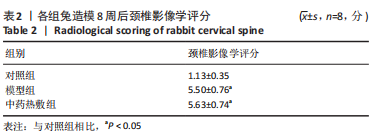
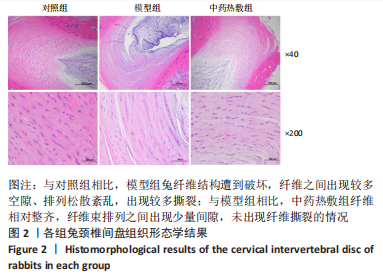
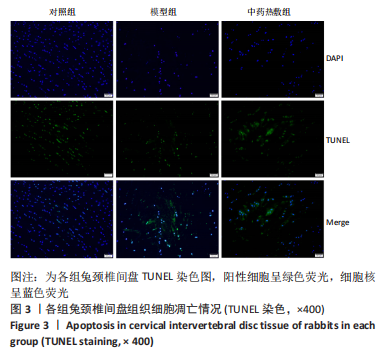
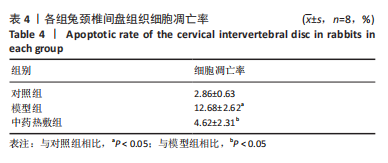
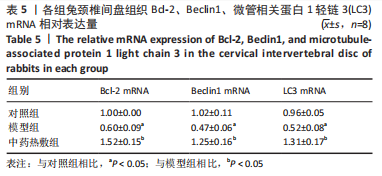
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (26): 4181-4186.doi: 10.12307/2023.445
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of traditional Chinese medicine hot compress on autophagy and expression of apoptosis related factors in the intervertebral disc of rabbits with cervical spondylosis
Chen Jiali1, Gao Hang1, Zhao Ziying1, Wang Guangyi2
- 1Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2022-05-16Accepted:2022-07-09Online:2023-09-18Published:2023-01-28 -
Contact:Wang Guangyi, Master, Professor, Chief physician, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Chen Jiali, Master candidate, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the Guiyang Municipal Science and Technology Plan Program, No. (2019)9-1-4 (to WGY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Jiali, Gao Hang, Zhao Ziying, Wang Guangyi. Effect of traditional Chinese medicine hot compress on autophagy and expression of apoptosis related factors in the intervertebral disc of rabbits with cervical spondylosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(26): 4181-4186.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] 岳寿伟,魏慧,邵山.颈椎病评估与康复治疗进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2019,34(11):1273-1277. [2] HOY D, MARCH L, WOOLF A, et al. The global burden of neck pain: estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(7):1309-1315. [3] HURWITZ EL, LI D, GUILLEN J, et al. Variations in Patterns of Utilization and Charges for the Care of Neck Pain in North Carolina, 2000 to 2009: A Statewide Claims’ Data Analysis. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2016; 39(4):240-251. [4] SKILLGATE E, PICO-ESPINOSA OJ, HALLQVIST J, et al. Healthy lifestyle behavior and risk of long duration troublesome neck pain or low back pain among men and women: results from the Stockholm Public Health Cohort. Clin Epidemiol. 2017;9:491-500. [5] DING F, SHAO ZW, YANG SH, et al. Role of mitochondrial pathway in compression-induced apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells. Apoptosis. 2012;17(6):579-590. [6] HE R, WANG Z, CUI M, et al. HIF1A Alleviates compression-induced apoptosis of nucleus pulposus derived stem cells via upregulating autophagy. Autophagy. 2021;17(11):3338-3360. [7] GONG C, ZHANG HH. Autophagy as a potential therapeutic target in intervertebral disc degeneration. Life Sci. 2021;273:119266. [8] WANG D, HE X, WANG D, et al. Quercetin Suppresses Apoptosis and Attenuates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration via the SIRT1-Autophagy Pathway. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:613006. [9] ZHANG S, LIANG W, ABULIZI Y, et al. Quercetin Alleviates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Modulating p38 MAPK-Mediated Autophagy. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:6631562. [10] ZHENG Z, WANG ZG, CHEN Y, et al. Spermidine promotes nucleus pulposus autophagy as a protective mechanism against apoptosis and ameliorates disc degeneration. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(6):3086-3096. [11] JIANG W, ZHANG X, HAO J, et al. SIRT1 protects against apoptosis by promoting autophagy in degenerative human disc nucleus pulposus cells. Sci Rep. 2014;4:7456. [12] 杨帏勋,李威廷,苏菲德.中医针灸结合中药热敷治疗颈椎病疼痛的效果[J].中医临床研究,2019,11(31):50-51. [13] 张桂平.中药热敷治疗颈椎病的临床疗效及护理观察[J]. 中国医药指南,2019,17(28):208-209. [14] 余家阔,吴毅文,戴先进,等.颈椎病生物力学发病机制实验研究[J]. 安徽医科大学学报,1990(1):47-51. [15] 徐银琴,高航,王光义.通痹方热敷对颈椎病家兔颈部痛阈和椎间盘退变的影响[J].贵州医科大学学报,2020,45(3):298-303. [16] MASUDA K, AOTA Y, MUEHLEMAN C, et al. A novel rabbit model of mild, reproducible disc degeneration by an anulus needle puncture: correlation between the degree of disc injury and radiological and histological appearances of disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(1):5-14. [17] 李跃兵,王焕梅.向贤德教授针药结合治疗神经根型颈椎病临床经验撷菁[J]. 湖南中医药大学学报,2019,39(12):1503-1506. [18] 丁明明,陈文莉,戴益辉,等.简述中药热奄包的临床应用近况[J].江西中医药,2019,50(8):72-74. [19] 牛明镜,王顺云.中医综合疗法治疗神经根型颈椎病97例[J].中医正骨,2012,24(3):61-62. [20] 常献,陈斌,李长青.髓核细胞老化机制研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(1):40-42. [21] 孟祥宇,夏建龙,杨挺,等.椎间盘退变的机制及修复[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(11):1768-1773.. [22] 李文举, 李亦梅. 椎间盘退变机制研究现状及生物治疗展望[J]. 中国骨与关节外科,2014,7(1):66-69. [23] PENG B, DEPALMA MJ. Cervical disc degeneration and neck pain. J Pain Res. 2018;11:2853-2857. [24] 苏树燕,黄瑞滨,周晓柔,等.颈椎曲度变直对青年人颈椎间盘早期退变的影响:基于56例磁共振T2-mapping[J]. 分子影像学杂志, 2020,43(2):296-299. [25] 李沅骋,李开平,宋子琪,等.长期低头位与寒湿刺激建立颈型颈椎病动物模型的研究[J].中华中医药学刊:1-20[2022-05-14]. [26] HASCHTMANN D, STOYANOV JV, GEDET P, et al. Vertebral endplate trauma induces disc cell apoptosis and promotes organ degeneration in vitro. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(2):289-299. [27] 邹璟,姜梦雅,李解,等.细胞凋亡参与电针对退变椎间盘保护作用的研究[J]. 时珍国医国药,2017,28(9):2271-2273. [28] AVIN-WITTENBERG T. Autophagy and its role in plant abiotic stress management. Plant Cell Environ. 2019;42(3):1045-1053. [29] HU YX, HAN XS, JING Q. Autophagy in Development and Differentiation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1206:469-487. [30] MIZUSHIMA N, KOMATSU M. Autophagy: renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. 2011;147(4):728-741. [31] D’ARCY MS. Cell death: a review of the major forms of apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy. Cell Biol Int. 2019;43(6):582-592. [32] RYTER SW, MIZUMURA K, CHOI A. The Impact of Autophagy on Cell Death Modalities. Int J Cell Biol. 2014;2014(1):502676. [33] HE C, ZHU H, LI H, et al. Dissociation of Bcl-2–Beclin1 Complex by Activated AMPK Enhances Cardiac Autophagy and Protects Against Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis in Diabetes. Diabetes. 2013;62(4):1270-1281. [34] NAKASHIMA A, AOKI A, KUSABIRAKI T, et al. Role of autophagy in oocytogenesis, embryogenesis, implantation, and pathophysiology of pre-eclampsia. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2017;43(4):633-643. [35] GRILO AL, MANTALARIS A. Apoptosis: A mammalian cell bioprocessing perspective. Biotechnol Adv. 2019;37(3):459-475. [36] GARCÍA-SÁEZ AJ. The secrets of the Bcl-2 family. Cell Death Differ. 2012; 19(11):1733-1740. [37] SUN T, LI X, ZHANG P, et al. Acetylation of Beclin 1 inhibits autophagosome maturation and promotes tumour growth. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7215. [38] ZHANG TW, LI ZF, DONG J, et al. The circadian rhythm in intervertebral disc degeneration: an autophagy connection. Exp Mol Med. 2020; 52(1):31-40. [39] 孙忠人,栾逸先,尹洪娜,等. 夹脊电针通过调控细胞死亡治疗脊髓损伤的相关机制研究进展[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2021,36(4):2213-2215. [40] 赵军,师建平,党赢.椎动脉型颈椎病的血管内皮细胞自噬与血瘀气虚关系探讨[J]. 中医学报,2021,36(6):1184-1186. [41] LIU Y, SHI L, QIU W, et al. Ferulic acid exhibits anti-inflammatory effects by inducing autophagy and blocking NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Mol Cell Toxicol. 2022;18(4):509-519. [42] WU C, CHEN H, ZHUANG R, et al. Betulinic acid inhibits pyroptosis in spinal cord injury by augmenting autophagy via the AMPK-mTOR-TFEB signaling pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(4):1138-1152. [43] 蔡慧倩, 粟胜勇, 张熙, 等. 温和灸对神经根型颈椎病大鼠脊髓Beclin-1/Bcl-2表达的影响[J]. 针刺研究,2020,45(10):799-805. [44] ZHAO K, ZHANG Y, LIANG K, et al. Methylation of microRNA-129-5P modulates nucleus pulposus cell autophagy by targeting Beclin-1 in intervertebral disc degeneration. Oncotarget. 2017;8(49):86264-86276. [45] 徐银琴, 史红美, 王光义. 通痹方热敷联合针刺治疗对退变椎间盘细胞凋亡相关基因Caspase-3、Bcl-2 mRNA的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(5):713-718. [46] 徐银琴,王光义.通痹方热奄包外敷对家兔退变颈椎间盘细胞凋亡相关基因Caspase-3和Bcl-2 mRNA的影响[J].贵州医科大学学报, 2020,45(4):438-443. |
| [1] | Fang Xingyan, Tian Zhenli, Zhao Zheyi, Wen Ping, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and sphingosine kinases 1/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling axis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | Cao Sheng, Kong Lingwei, Xu Kun, Sun Zhijie. Correlation of cervical sagittal force line parameters with degenerative segment and Pfirrmann classification in patients with cervical intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1319-1324. |
| [3] | Wang Yanjin, Zhou Yingjie, Chai Xubin, Zhuo Hanjie. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of 3D printed porous titanium alloy fusion cage in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1434-1440. |
| [4] | Lian Shilin, Zhang Yan, Jiang Qiang, Zhang Hanshuo, Li Tusheng, Ding Yu. Interventional effects of whole blood and platelet-rich plasma with different preparation methods on nucleus pulposus cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1199-1204. |
| [5] | Nie Chenchen, Su Kaiqi, Gao Jing, Fan Yongfu, Ruan Xiaodi, Yuan Jie, Duan Zhaoyuan, Feng Xiaodong. The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| [6] | Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Lu Dahong, Xu Junrong, Liu Xiaocui, Wang Bingyun. Clinical-grade human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells affect the improvement of neurological function in rats with traumatic brain injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 835-839. |
| [7] | Li Qicheng, Deng Jin, Fu Xiaoyang, Han Na. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on hypoxia-treated myoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 853-859. |
| [8] | Zhang Qing, Gao Chunlan, Yu Feifei, Zhang Zhenghao, Ma Fang, Gao Yuan, Li Guizhong, Jiang Yideng, Ma Shengchao. Ephrin A receptor 2 DNA methylation increases in pancreatic beta cell apoptosis induced by homocysteine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 714-719. |
| [9] | Li Long, Li Guangdi, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 751-757. |
| [10] | Li Zhichao, Tan Guoqing, Su Hui, Xu Zhanwang, Xue Haipeng. Regulatory role of non-coding RNAs as potential therapeutic targets in spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 758-764. |
| [11] | Wu Yujie, Wan Xiaofang, Wei Mianxing, Peng Shiyuan, Xu Xiaomei. Correlation between autophagy and the Hippo-YAP protein pathway in periodental ligament cells on the pressure side of a mouse model of orthodontic tooth movement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 683-689. |
| [12] | Zhao Siqi, Du Juan, Qu Haifeng, Li Jianmin, Zhang Yuxin, Liu Junjie. Effects of enriched environment combined with melatonin on learning and memory function and brain neuron apoptosis in SAMP8 mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 701-706. |
| [13] | Chen Chao, Wang Xuenan, Zhan Enyu, Lyu Zhengpin, Zhang Fan. Mechanism underlying the mutual regulation between circadian rhythm and autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(29): 4696-4703. |
| [14] | Chen Cai, Zeng Ping, Liu Jinfu. Long non-coding RNAs regulate osteoarthritis by mediating chondrocyte-related mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(29): 4729-4735. |
| [15] | Xu Guangming, Liang Ziyang, Wang Hongbo, Zhang Zhen, Xiao Qinghua, Yang Jiyong, Lin Xiaosheng. Mechanical effect of oblique-pulling manipulation on triarticular complex after human lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4277-4282. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||