Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (26): 4113-4119.doi: 10.12307/2023.435
Previous Articles Next Articles
Astragaloside IV can reduce interleukin-1beta-induced chondrocyte inflammation
Huang Shaoshuo1, Li Jiacheng1, Luo Di2, Zhu Kai1, Xu Bo2, Xue Yuanliang1, Yan Bozhao1, Li Gang1
- 1The First Clinical Medical College of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China; 2The Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2022-04-27Accepted:2022-06-29Online:2023-09-18Published:2023-01-20 -
Contact:Li Gang, MD, Professor, Chief physician, The First Clinical Medical College of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Huang Shaoshuo, Master candidate, The First Clinical Medical College of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82074453 (to LG); Shandong Medical and Health Science and Technology Development Project, No. 202004071045 (to XB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Shaoshuo, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Zhu Kai, Xu Bo, Xue Yuanliang, Yan Bozhao, Li Gang. Astragaloside IV can reduce interleukin-1beta-induced chondrocyte inflammation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(26): 4113-4119.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
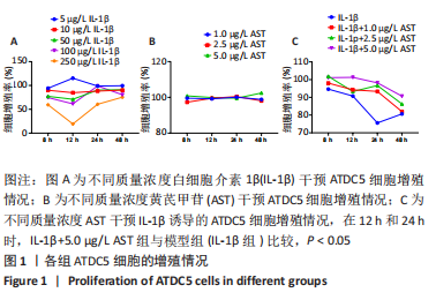
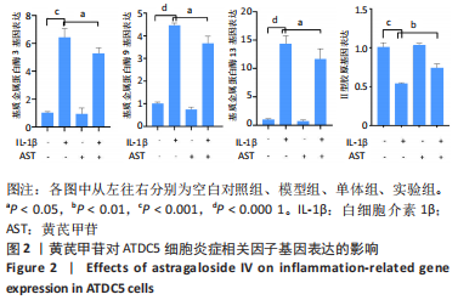
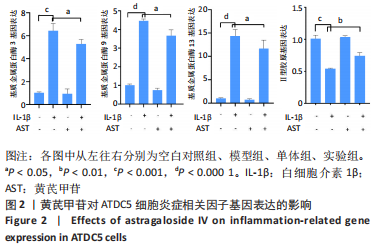
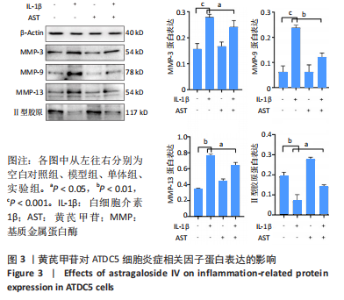
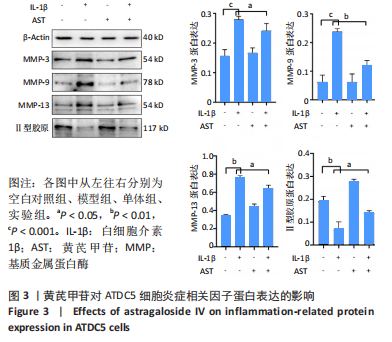
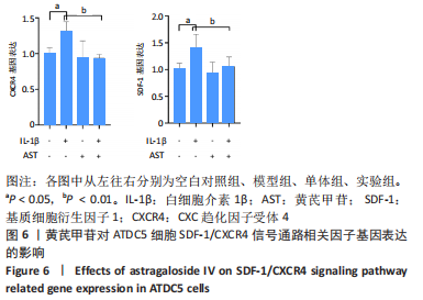
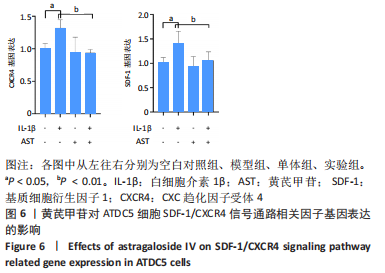
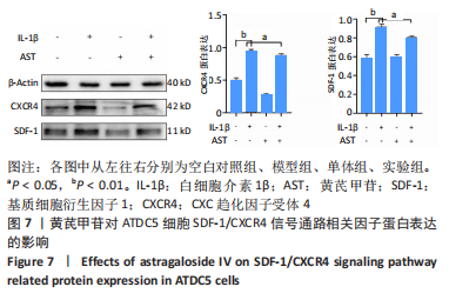
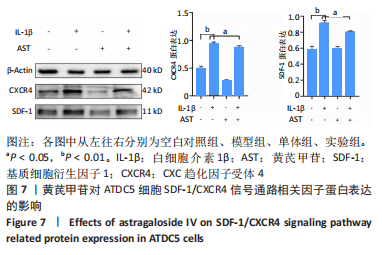
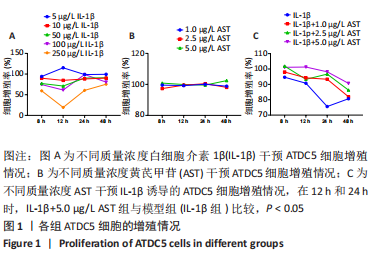
2.1 黄芪甲苷能减轻白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞炎症反应 2.1.1 黄芪甲苷能提高白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞活力 采用CCK-8法分析黄芪甲苷对白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞活力的影响,见图1。图1A显示白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞活性较空白对照组明显降低,且细胞活性与白细胞介素1β的浓度呈反比,考虑含250 μg/L白细胞介素1β的培养基中培养基的比例过低,为避免实验干扰,选择100 μg/L白细胞介素1β进行造模。图1B显示单独使用黄芪甲苷(1,2.5,5 μg/L)后细胞增殖率均接近100%,认为黄芪甲苷对细胞存活率没有明显影响。图1C显示白细胞介素1β诱导后的软骨细胞中加入黄芪甲苷(1,2.5,5 μg/L)干预后细胞存活率较模型组有所改善,其中改善效果最佳的黄芪甲苷质量浓度是5 μg/L,且药物起效时间在12-24 h之间,实验药物干预时间设定为18 h。"
| [1] 郑晓芬.骨关节炎发病机制和治疗的最新进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(20):3255-3262. [2] 潘炳,周颖芳,方芳,等.骨性关节炎的国内外研究现状及治疗进展[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2021,27(5):861-865. [3] JIMÉNEZ G, COBO-MOLINOS J, ANTICH C, et al. Osteoarthritis: Trauma vs Disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1059:63-83. [4] 中华中医药学会骨伤科分会膝痹病(膝骨关节炎)临床诊疗指南制定工作组.中医骨伤科临床诊疗指南·膝痹病(膝骨关节炎)[J].康复学报,2019,29(3):1-7. [5] YANO F, OHBA S, MURAHASHI Y, et al. Runx1 contributes to articular cartilage maintenance by enhancement of cartilage matrix production and suppression of hypertrophic differentiation. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):7666. [6] HEINEGÅRD D, SAXNE T. The role of the cartilage matrix in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(1):50-56. [7] RAHMATI M, NALESSO G, MOBASHERI A, et al. Aging and osteoarthritis: Central role of the extracellular matrix. Ageing Res Rev. 2017;40:20-30. [8] 范重山,孙明帅,韩文朝.促炎因子及基质金属蛋白酶在骨关节炎发病机制及相关治疗中的地位和作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(32):5162-5170. [9] 汪国翔,章晓云.骨关节炎病变过程中炎症细胞因子及相关信号通路的作用机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(14):2266-2273. [10] LI H, PENG Y, WANG X, et al. Astragaloside inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammatory response in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes and ameliorates the progression of osteoarthritis in mice. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2019;41(4):497-503. [11] LU W, SHI J, ZHANG J, et al. CXCL12/CXCR4 Axis Regulates Aggrecanase Activation and Cartilage Degradation in a Post-Traumatic Osteoarthritis Rat Model. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(10):1522. [12] BOER CG, HATZIKOTOULAS K, SOUTHAM L, et al. Deciphering osteoarthritis genetics across 826,690 individuals from 9 populations. Cell. 2021;184(18):4784-4818.e17. [13] 曹向昱,刘雨曦,曹永平.老年退行性骨关节炎治疗进展[J].中国临床保健杂志,2022,25(1):25-29. [14] CHAN CM, MACDONALD CD, LITHERLAND GJ, et al. Cytokine-induced MMP13 Expression in Human Chondrocytes Is Dependent on Activating Transcription Factor 3 (ATF3) Regulation. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(5):1625-1636. [15] DENG Z, LIN Z, ZHONG Q, et al. Interleukin 1 beta-induced chloride currents are important in osteoarthritis onset: an in vitro study. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021;53(4):400-409. [16] VINCENT TL. IL-1 in osteoarthritis: time for a critical review of the literature. F1000Res. 2019;8:F1000 Faculty Rev-934. [17] NA HS, PARK JS, CHO KH, et al. Interleukin-1-Interleukin-17 Signaling Axis Induces Cartilage Destruction and Promotes Experimental Osteoarthritis. Front Immunol. 2020;11:730. [18] 肖勇洪,毕翊鹏,阮莹艺,等.彭江云辨治骨关节炎经验总结[J].辽宁中医杂志,2017,44(7):1371-1372. [19] AUYEUNG KK, HAN QB, KO JK. Astragalus membranaceus: A Review of its Protection Against Inflammation and Gastrointestinal Cancers. Am J Chin Med. 2016;44(1):1-22. [20] FU J, WANG Z, HUANG L, et al. Review of the botanical characteristics, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Astragalus membranaceus (Huangqi). Phytother Res. 2014;28(9):1275-1283. [21] ZHANG J, WU C, GAO L, et al. Astragaloside IV derived from Astragalus membranaceus: A research review on the pharmacological effects. Adv Pharmacol. 2020;87:89-112. [22] SHAN H, ZHENG X, LI M. The effects of Astragalus Membranaceus Active Extracts on Autophagy-related Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(8):1904. [23] JIANG H, FAN C, LU Y, et al. Astragaloside regulates lncRNA LOC100912373 and the miR‑17‑5p/PDK1 axis to inhibit the proliferation of fibroblast‑like synoviocytes in rats with rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Mol Med. 2021;48(1):130. [24] WANG B, CHEN MZ. Astragaloside IV possesses antiarthritic effect by preventing interleukin 1β-induced joint inflammation and cartilage damage. Arch Pharm Res. 2014;37(6):793-802. [25] LIU J, MENG Q, JING H, et al. Astragaloside IV protects against apoptosis in human degenerative chondrocytes through autophagy activation. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(3):3269-3275. [26] MALEMUD CJ. Inhibition of MMPs and ADAM/ADAMTS. Biochem Pharmacol. 2019;165:33-40. [27] MEHANA EE, KHAFAGA AF, EL-BLEHI SS. The role of matrix metalloproteinases in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: An updated review. Life Sci. 2019;234:116786. [28] JARECKI J, MAŁECKA-MASALSKA T, KOSIOR-JARECKA E, et al. Concentration of Selected Metalloproteinases and Osteocalcin in the Serum and Synovial Fluid of Obese Women with Advanced Knee Osteoarthritis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(6):3530. [29] LIU CX, GAO G, QIN XQ, et al. Correlation Analysis of C-terminal telopeptide of collagen type II and Interleukin-1β for Early Diagnosis of Knee Osteoarthritis. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(1):286-294. [30] FIRNER S, ZAUCKE F, MICHAEL J, et al. Extracellular Distribution of Collagen II and Perifibrillar Adapter Proteins in Healthy and Osteoarthritic Human Knee Joint Cartilage. J Histochem Cytochem. 2017;65(10):593-606. [31] STANCKER TG, VIEIRA SS, SERRA AJ, et al. Can photobiomodulation associated with implantation of mesenchymal adipose-derived stem cells attenuate the expression of MMPs and decrease degradation of type II collagen in an experimental model of osteoarthritis? Lasers Med Sci. 2018;33(5):1073-1084. [32] KANBE K, CHIBA J, INOUE Y, et al. SDF-1 and CXCR4 in synovium are associated with disease activity and bone and joint destruction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with golimumab. Mod Rheumatol. 2016;26(1):46-50. [33] QIN HJ, XU T, WU HT, et al. SDF-1/CXCR4 axis coordinates crosstalk between subchondral bone and articular cartilage in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Bone. 2019;125:140-150. [34] NAGASAWA T. CXC chemokine ligand 12 (CXCL12) and its receptor CXCR4. J Mol Med (Berl). 2014;92(5):433-439. [35] KANBE K, TAKAGISHI K, CHEN Q. Stimulation of matrix metalloprotease 3 release from human chondrocytes by the interaction of stromal cell-derived factor 1 and CXC chemokine receptor 4. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46(1):130-137. [36] KITAORI T, ITO H, SCHWARZ EM, et al. Stromal cell-derived factor 1/CXCR4 signaling is critical for the recruitment of mesenchymal stem cells to the fracture site during skeletal repair in a mouse model. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(3):813-823. [37] VILLALVILLA A, GOMEZ R, ROMAN-BLAS JA, et al. SDF-1 signaling: a promising target in rheumatic diseases. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014;18(9):1077-1087. [38] KANBE K, TAKEMURA T, TAKEUCHI K, et al. Synovectomy reduces stromal-cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) which is involved in the destruction of cartilage in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86(2):296-300. [39] WANG K, LI Y, HAN R, et al. T140 blocks the SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling pathway and prevents cartilage degeneration in an osteoarthritis disease model. PLoS One. 2017;12(4):e0176048. [40] QIN H, LIU P, LIN S. Effects of Astragaloside IV on the SDF-1/CXCR4 Expression in Atherosclerosis of apoE(-/-) Mice Induced by Hyperlipaemia. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015; 2015:385154. |
| [1] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Zhu Guangyu, Wang Rongtian, Wang Jian, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Changes of lower limb force line and knee function after high tibial osteotomy in osteoporotic medial ventricular knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [2] | Huang Linke, Wei Linhua, Jiang Jie, Liu Qian, Chen Weiwei. Effects of estrogen combined with treadmill exercise on bone mass and articular cartilage in ovariectomized mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [3] | Li Long, Li Guangdi, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 751-757. |
| [4] | Shao Zichen, Li Huanan, Gu Bing, Zhang Xiaoyun, Sun Weikang, Liu Yongqian, Gan Bin. MicroRNA, long non-coding RNA and circular RNA mediate the mechanism of decreasing uric acid, anti-inflammation and regulating bone metabolism in gout [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 765-771. |
| [5] | Yuan Changshen, Guan Yanbing, Li Zhe, Rong Weiming, Liao Shuning, Chen Lewei, Mei Qijie, Duan Kan. Screening and verification of key genes of necroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 695-700. |
| [6] | Lu Huixiu, Cao Haiyu, Lou Dan, Li Jianying, Liu Hongyuan, Sun Jing. Imiquimod combined with photodynamic therapy for hypertrophic scars: immune response and prognosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 690-694. |
| [7] | Wan Guoli, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan, Li Ang, Shi Xunda, Cai Yi. Retrospective analysis of the influencing factors of chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 558-564. |
| [8] | Gu Mingxi, Wang Bo, Tian Fengde, An Ning, Hao Ruihu, Wang Changcheng, Guo Lin. Comparison of early efficacy and safety of simultaneous and staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 565-571. |
| [9] | Yu He, Zheng Jiafa, Song Xiufeng, Guan Shengyi. Tibiotalocalcaneal arthrodesis with blood supplied fibular flap combined with hollow screw in the treatment of end-stage ankle osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 588-593. |
| [10] | Guo Yingqi, Gong Xianxu, Zhang Yan, Xiao Han, Wang Ye, Gu Wenguang. Meniscus extrusion and patellofemoral joint cartilage injury and bone marrow lesions: MRI semi-quantitative score [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 600-605. |
| [11] | Yu Jiaan, Liu Xinwei, Lian Hongyu, Liu Kexin, Li Zitao. Medial open-wedge tibial osteotomy versus lateral closed-wedge tibial osteotomy for unicompartmental knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 632-639. |
| [12] | Ma Wei, Pang Jian, Zhang Jiefan, Xu Kun, Wang Yongyu, Zhang Min, Chen Bo, Shi Ying, Zhan Hongsheng. Analysis of influencing factors of fear of falling in patients with knee osteoarthritis and construction of nomogram model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(29): 4690-4695. |
| [13] | Chen Cai, Zeng Ping, Liu Jinfu. Long non-coding RNAs regulate osteoarthritis by mediating chondrocyte-related mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(29): 4729-4735. |
| [14] | Wei Zongbo, Su Yunyu, Zhang Xiaoyun, Huang Wei, Xu Hang, Liu Rongfa. Role and mechanism by which long non-coding RNAs regulate subchondral bone homeostasis in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(29): 4736-4744. |
| [15] | Zhou Guangzhi, Tai Dongxu. Research advances in animal models of ankle osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(29): 4745-4750. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||