[1] NAKASHIMA H, YUKAWA Y, SUDA K, et al. Cervical Disc Protrusion Correlates With the Severity of Cervical Disc Degeneration: A Cross-Sectional Study of 1211 Relatively Healthy Volunteers. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(13):E774-E779.
[2] AL-RYALAT NT, SALEH SA, MAHAFZA WS, et al. Myelopathy associated with age-related cervical disc herniation: a retrospective review of magnetic resonance images. Ann Saudi Med. 2017;37(2):130-137.
[3] MU W, SHANG Y, ZHANG C, et al. Analysis of the depression and anxiety status and related risk factors in patients with lumbar discherniation. Pak J Med Sci. 2019;35(3):658-662.
[4] 李龙,张春霖,邵成龙,等.三维体积法评价内镜下微创颈椎管成形术后不同退变程度突出颈椎间盘的自然吸收[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(36): 5832-5837.
[5] 鲁攀,张春霖,王永魁,等.三维体积法定量评价单开门颈椎管成形与保守治疗突出椎间盘的体积变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(9):1395-1401.
[6] 张春霖,赵晓,严旭,等.三维体积法定量评估内镜下微创颈椎管成形和保守治疗后突出椎间盘的再吸收现象[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(30): 4774-4780.
[7] 吴彦禹,张春霖,邵成龙,等.二维距离法和三维体积法对内镜下微创颈椎管成形后突出椎间盘再吸收的定量测量[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(21): 3390-3394.
[8] 张春霖,张银鹤,严旭,等.内镜下颈椎管成形术治疗脊髓型颈椎病[J].中华骨科杂志,2017,37(2):89-95.
[9] 王经宇,张春霖,翟福英,等.微型钛板置入颈椎管成形与单开门椎管扩大治疗脊髓型颈椎病的对比[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(9):1380-1385.
[10] 张春霖,刘洋,尚利杰,等.基于 PACS 软件定量体积测量“监控”的突出颈椎间盘体积观察[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(18):2888-2892.
[11] 王在先,韦沽涌,李维坚.后纵韧带椎间盘三角[J].广东解剖学通报,1995, 17(2):114.
[12] CHOI BW, HUM TW. Significance of Intramedullary High Signal Intensity on Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Cervical Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament. Clin Orthop Surg. 2015;7(4):465.
[13] GU Y, JUEQIAN S, PENG C, et al. Clinical and Imaging Predictors of Surgical Outcome in Multilevel Cervical Ossification of Posterior Longitudinal Ligament: An Analysis of 184 Patients. PloS One. 2015;10(9):e136042.
[14] 张春霖,曾昭峰,唐恒涛,等.标本模拟微创颈椎管成形后椎管容积变化及临床意义[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(26):4849-4856.
[15] GUINTO F. CT demonstration of disk regression after conserva-tive therapy. AJR. 1984;5(2):832-834.
[16] GEZICI AR, ERGÜN R. Spontaneous regression of a huge sub-ligamentous extruded disc herniation: short report of an illus-trative case. Acta Neurochir. 2009;5(12):1299-1300.
[17] 陈其昕,刘耀升,李方财,等.游离型腰椎间盘突出的组织学观察[J].中华骨科杂志,2006,26(8):539-543.
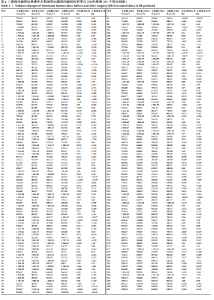
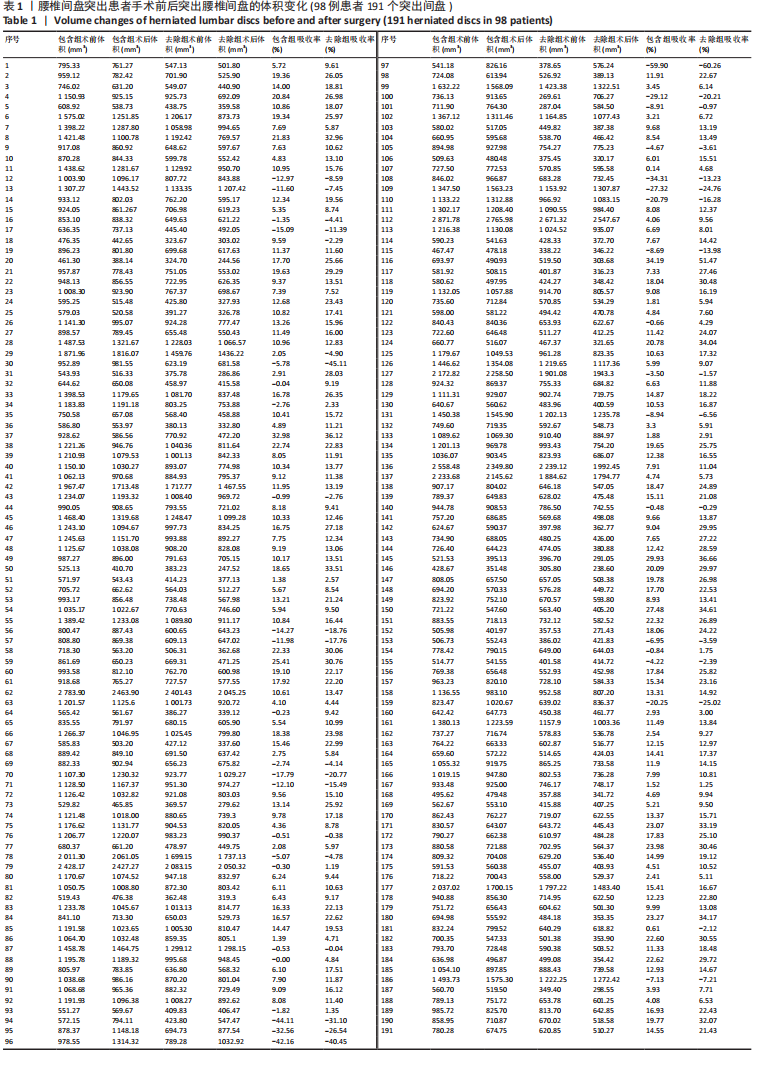
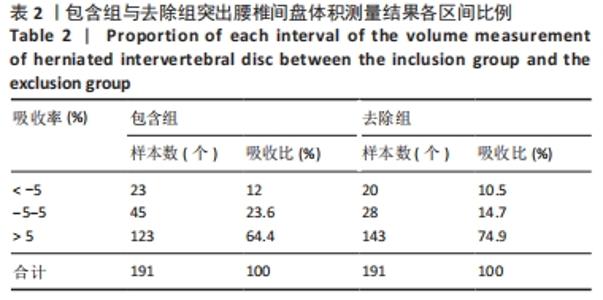
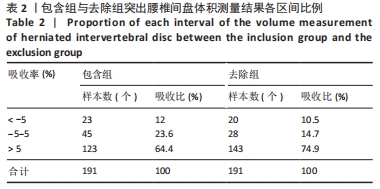
|