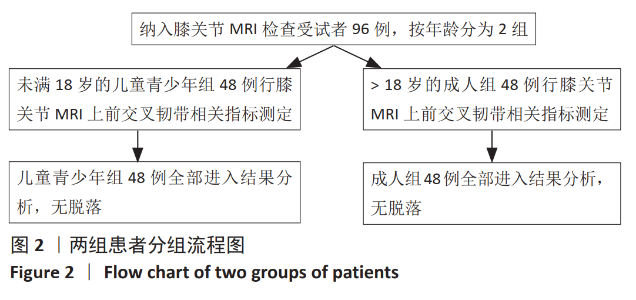
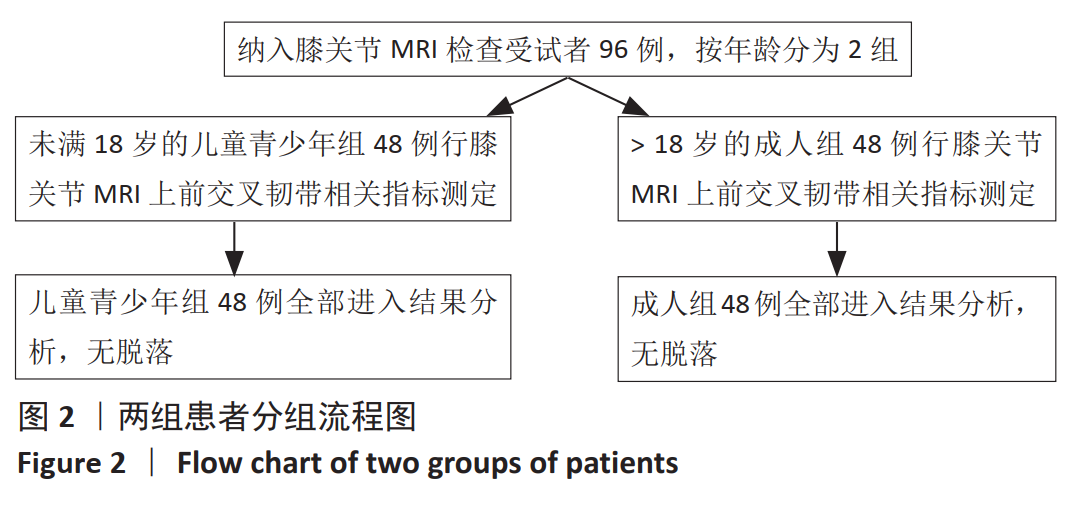
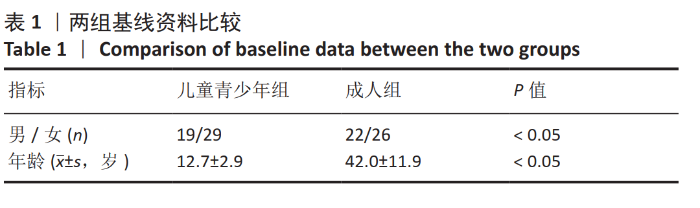
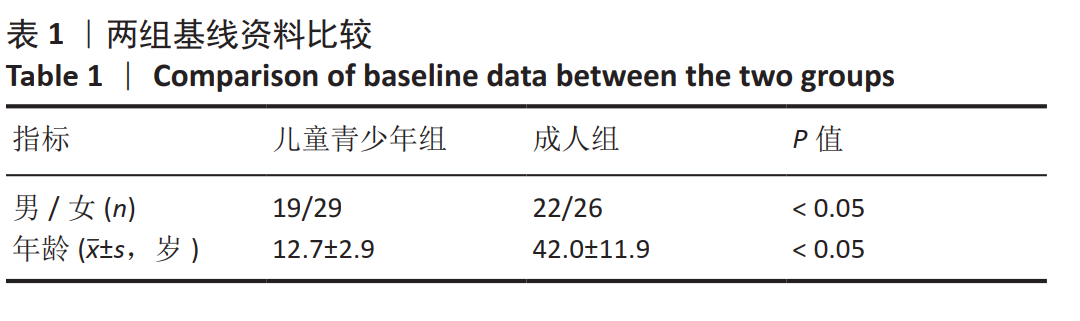
[1] BURNHAM JM, WRIGHT V. Update on anterior cruciate ligament rupture and care in the female athlete. Clin Sports Med. 2017;36(4):703-715.
[2] CHEUNG EC, BOGUSZEWSKI DV, JOSHI NB, et al. Anatomic factors that may predispose female Athletes to anterior cruciate ligament injury. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2015;14(5):368-372.
[3] SUGIMOTO D, MYER GD, MICHELI LJ, et al. ABCs of evidence-based anterior cruciate ligament injury prevention strategies in female Athletes. Curr Phys Med Rehabil Rep. 2015;3(1):43-49.
[4] UHORCHAK JM, SCOVILLE CR, WILLIAMS GN, et al. Risk factors associated with noncontact injury of the anterior cruciate ligament: a prospective four-year evaluation of 859 West Point cadets. Am J Sports Med. 2003;31(6): 831-842.
[5] WERNER BC, YANG S, LOONEY AM, et al. Trends in pediatric and adolescent anterior cruciate ligament injury and reconstruction. J Pediatr Orthop. 2016; 36(5):447-452.
[6] DODWELL ER, LAMONT LE, GREEN DW, et al. 20 years of pediatric anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in New York State. Am J Sports Med. 2014; 42(3):675-680.
[7] CRAWFORD R, WALLEY G, BRIDGMAN S, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging versus arthroscopy in the diagnosis of knee pathology, concentrating on meniscal lesions and ACL tears: a systematic review. Br Med Bull. 2007;84:5-23.
[8] NAKAYAMA Y, SHIRAI Y, NARITA T, et al. The accuracy of MRI in assessing graft integrity after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Nippon Ika Daigaku Zasshi. 2001;68(1):45-49.
[9] 陈文栋,李彦林,许鹏,等.基于MRI建立膝关节前交叉韧带三维数字化模型[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(52):9725-9728.
[10] LABELLA CR, HENNRIKUS W, HEWETT TE, et al. Anterior cruciate ligament injuries: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Pediatrics. 2014;133(5): e1437-e1450.
[11] GAUSDEN EB, CALCEI JG, FABRICANT PD, et al. Surgical options for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in the young child. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2015;27(1):82-91.
[12] XEROGEANES JW, FOX RJ, TAKEDA Y, et al. A functional comparison of animal anterior cruciate ligament models to the human anterior cruciate ligament. Ann Biomed Eng. 1998;26(3):345-352.
[13] AHN JH, LEE YS, JEONG HJ, et al. Comparison of transtibial and retrograde outside-in techniques of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in terms of graft nature and clinical outcomes: a case control study using 3T MRI. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017;137(3):357-365.
[14] BREITENSEHER MJ, MAYERHOEFER ME. Oblique MR imaging of the anterior cruciate ligament based on three-dimensional orientation. J Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 2007;26(3):794-798.
[15] MALL NA, CHALMERS PN, MORIC M, et al. Incidence and Trends of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction in the United States. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(10):2363-2370.
[16] VAN ECK CF, WIDHALM H, MURAWSKI C, et al. Individual¬ized anatomic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Phys Sports Med. 2015;43(1):87-92.
[17] MOKSNES H, ENGEBRETSEN L, RISBERG MA. Prevalence and incidence of new meniscus and cartilage injuries after a nonoperative treatment algorithm for ACL tears in skel-etally immature children: a prospective MRI study. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(8):1771-1779.
[18] FERRETTI M, EKDAHL M, SHEN W, et al. Osseous landmarks of the femoral attachment of the anterior cruciate ligament: an anatomic study. Arthroscopy. 2007;23(11):1218-1225.
[19] AHN JH, LEE SH , YOO JC, et al. Measurement of the graft angles for the anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with transtibial technique using postoperative magnetic resonance imaging in comparative study. Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy. 2007;15(11):1293-1300.
[20] KOPF S, POMBO MW, SZCZODRY M, et al. Size Variability of the Human Anterior Cruciate Ligament Insertion Sites. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(1): 108-113.
[21] VAN ECK CF, LESNIAK BP, SCHREIBER VM, et al. Anatomic Single- and Double-Bundle Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Flowchart. Arthroscopy. 2010;26(2):258-268.
[22] FUJIMAKI Y, THORHAUER E, SASAKI Y, et al. Quantitative in situ analysis of the anterior cruciate ligament: length, midsubstance cross-sectional area, and insertion site areas. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(1):118-125.
[23] LYSENS R, STEVERLYNCK A, VANDEN AUWEELE YU, et al. The predictability of sports injuries. Sports Medicine. 1984;5(S1):S153-S155.
[24] BAHR R, HOLME I. Risk factors for sports injuries - a methodological approach. Br J Sports Med. 2003;37(5):384-392.
[25] BRIGHT RW, BURSTEIN AH, ELMORE SM. Epiphyseal-plate cartilage. A biomechanical and histological analysis of failure modes. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974;56(4):688.
[26] MORSCHER E. Strength and morphology of growth cartilage under hormonal influence of puberty. Animal experiments and clinical study on the etiology of local growth disorders during puberty. Reconstr Surg Traumatol. 1968;10:3-104.
[27] FLACHSMANN R, BROOM ND, HARDY AE, et al. Why Is the Adolescent Joint Particularly Susceptible to Osteochondral Shear Fracture? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;381(381):212-221.
[28] BACKOUS DD, FRIEDL KE, SMITH NJ, et al. Soccer injuries and their relation to physical maturity. Am J Dis Child. 1988;142(8):839.
[29] GÓMEZ JE, ROSS SK, CALMBACH WL, et al. Body Fatness and Increased Injury Rates in High School Football Linemen. Clin J Sport Med. 1998;8(2): 115-120.
[30] EMERY CA. Injury prevention and future research. Med Sports Sci. 2005; 49:170-191.
[31] AGEL J, ARENDT EA, BERSHADSKY B. Anterior cruciate ligament injury in national collegiate athletic association basketball and soccer: a 13-year review. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(4):524-530.
[32] POWELL JW, BARBER-FOSS KD. Sex-related injury patterns among selected high school sports. Am J Sports Med. 2000;28(1):385-391.
[33] ARENDT E, DICK R. Knee injury patterns among men and women in collegiate basketball and soccer. NCAA data and review of literature. Am J Sports Med. 1995;23(6):694-701.
[34] DOMZALSKI M, GRZELAK P, GABOS P. Risk factors for anterior cruciate ligament injury in skeletally immature patients: analysis of intercondylar notch width using magnetic resonance imaging. Int Orthop. 2010;34(5):703-707.
[35] LINDENFELD TN, SCHMITT DJ, HENDY MP, et al. Incidence of injury in indoor soccer. Am J Sports Med. 1994;22(3):364-371.
[36] RUE JP, GHODADRA N, LEWIS PB, et al. Femoral and tibial t unnel position using atranstibial drilled anterior cruciate ligament reconstru- ction technique. J Knee Surg. 2008;21(3):246-249.
[37] ROBERTS CC,TOWERS JD,SPANGEHL MJ,et al.Advanced MR imaging of the cruciate ligaments. Radiol Clin North Am. 2007;45(6):1003-1016. |