Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (13): 2104-2109.doi: 10.12307/2023.245
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application and progress of finite element analysis in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures with pedicle screw fixation
Zheng Xiaobo, Yang Sheng, Wang Fengyun
- Zhongshan Hospital Affiliated to Dalian University, Dalian 116000, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2022-02-14Accepted:2022-04-18Online:2023-05-08Published:2022-08-12 -
Contact:Yang Sheng, MD, Chief physician, Zhongshan Hospital Affiliated to Dalian University, Dalian 116000, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Zheng Xiaobo, Master candidate, Zhongshan Hospital Affiliated to Dalian University, Dalian 116000, Liaoning Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zheng Xiaobo, Yang Sheng, Wang Fengyun. Application and progress of finite element analysis in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures with pedicle screw fixation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(13): 2104-2109.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
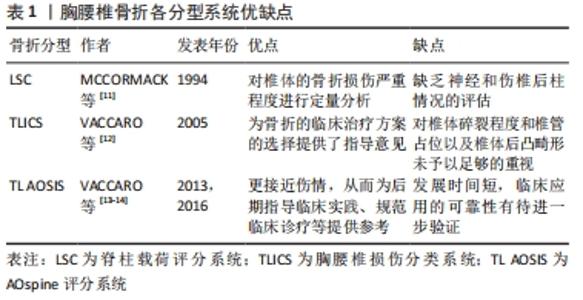
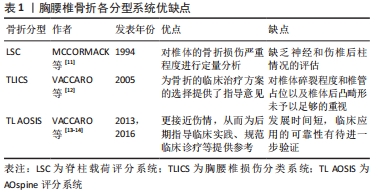
由于胸腰椎骨折的有限元模拟是基于原有骨折分型标准上的模拟,所以作者首先简要介绍并比较常用的3种分型标准以及适于伤椎有限元模拟的骨折分型标准,主要从以下几个方面进行阐述。 2.1 胸腰椎骨折分型及评分系统 目前普遍认可的分型有脊柱载荷评分系统(LSC)、胸腰椎损伤分类系统(TLICS)、AOspine评分系统。 2.1.1 脊柱载荷评分系统[11] 该系统从伤椎椎体损伤程度、CT轴位椎体碎骨移位程度、椎体后凸矫正角3个方面进行评分。每项根据损伤严重程度分为1-3分,总分最高为9分(脊柱载荷评分≥7分为重度骨折),从而评估脊柱骨折的稳定性。但脊柱载荷评分系统缺乏神经和伤椎后柱情况的评估。 2.1.2 胸腰椎损伤分类及严重度评分系统[12] 该系统对骨折形态、后纵韧带复合体完整性、神经功能状态进行评分,分数越高表示骨折损伤越严重,此系统为骨折的临床治疗方案选择提供了指导意见,缺点是对椎体碎裂程度和椎管占位以及椎体后凸畸形未予以足够的重视。 2.1.3 AOspine评分系统(TL AOSIS)[13-14] 该分型包括了骨折的形态、神经功能以及临床修正参数,并对原AO分型的骨折形态描述进行了简化。该系统整合了Magerl分类系统和胸腰椎损伤分类系统的优势,使分类更接近伤情,从而为后期指导临床实践、规范临床诊疗等提供参考。因其具体评分情况较为复杂,不在此过多赘述。以上3种分型优缺点见表1。 "
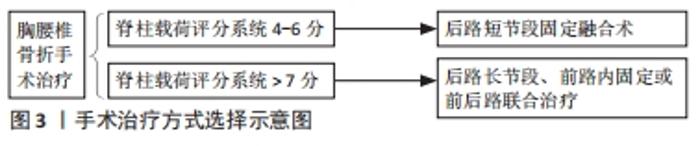
迄今为止,脊柱载荷评分系统和AOspine评分系统已获得普遍认同。脊柱载荷评分系统分型对椎体的骨折损伤严重程度进行定量分析,在临床中预测后路短节段椎弓根钉内固定断钉风险以及手术方法的选择中有重要意义[11]。AOspine评分系统分型虽然是在AO分型和胸腰椎损伤分类系统分型上的改进,对椎体爆裂骨折程度进行了更为细化分类,但其发展时间短,临床应用的可靠性有待进一步验证。先前的一项研究表明,这两种分类相互补充,在临床上它们的组合可用于确定胸腰椎爆裂型骨折的最佳治疗方案[33]。 2.2 胸腰椎骨折的治疗 2.2.1 保守治疗 适用于脊柱载荷系统评分< 4分、胸腰椎损伤分类系统评分≤ 3分及AOspine评分系统评分≤3分的骨折。治疗方法主要有支具保护下功能锻炼、促骨生长及对症止疼。 2.2.2 手术治疗 适用于胸腰椎损伤分类系统评分≥5分或AOspine评分系统评分> 5分的骨折。手术方式有前路、后路和前后路联合等。脊柱载荷评分系统4-6分的骨折患者多采用后路短节段固定融合术;脊柱载荷评分系统评分> 7分的患者常常需要后路长节段、前路内固定或前后路联合治疗,见图3。 "
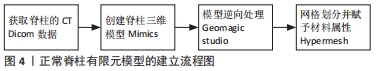
2018-2021年以来YANG等[21,34-36]发表了胸腰椎骨折系列的临床和有限元分析研究后提出:脊柱载荷系统评分> 7分的A型爆裂骨折使用临近上下椎Schanz椎弓根钉固定联合胸腰骶支具就能获得良好的疗效。 2.3 有限元方法的应用 2.3.1 有限元分析介绍 有限元分析是将复杂的结构看成由有限个单元仅在节点处连接的整体,再根据几何材料的特性和应力情况,集合不同类型的小单元,得出每个小单元的作用方程,然后将整个自由连续体的单元组合成系统方程,最终求解系统方程问题[37-41]。有限元分析已经成为骨科生物力学中不可缺少的重要研究方法,特别是在脊柱内固定植入物中具有无可比拟的优势[42-44]。有限元分析可以帮助外科医生更好地了解健康和病理条件下的生物力学[45]。它还有一个额外的好处,可以预测螺钉植入区域周围机械应力分布的变化,有助于防止由于错误的植入位置而导致的相关并发症[46]。 2.3.2 正常脊柱有限元模型的建立 正常胸腰段脊柱有限元模型的建立一般选取经临床检查及X射线片检查无脊柱相关疾病的健康青年男性志愿者。使用CT对全腰椎进行薄层扫描,将采集的DICOM影像数据导入MIMICS中,通过设定合适的灰度值,再通过阈值分割、动态区域增长、Mask编辑以及3D calculate等功能,得到最初的骨性三维几何模型;在Geomagic studio软件中对原始三维模型表面孔状或钉状结构进行填充、修复与光滑,经点阶段、多边形阶段和精确曲面阶段,转化为NURBS曲面,以IGES格式保存;将保存的模型导入Hypermesh软件中进行网格划分(包括骨组织网格),并对不合格网格进行修复,控制其质量;对椎间盘、韧带、关节软骨等软组织进行建立并网格划分;在椎间盘和相邻的椎体之间以及对应的关节软骨之间建立接触对,椎间盘与椎体间设为绑定关系,临近关节软骨间设为摩擦接触关系;根据前人的研究,建立合适的材料及属性,并分配到每个对应的结构中,见图4。 "
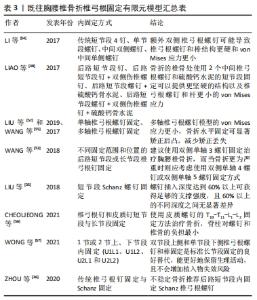
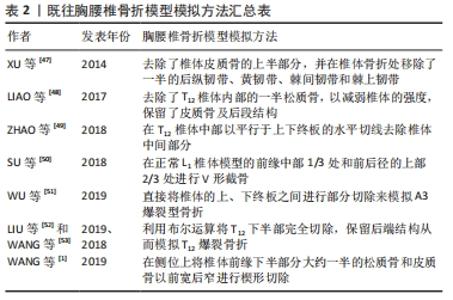
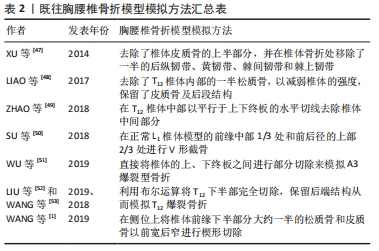
XU等[47]为了模拟T12椎骨的轻度骨折,去除了椎体皮质骨的上半部分,同时将松质骨的上半部分弹性模量降为正常的10%,并在椎体骨折处移除了一半的后纵韧带、黄韧带、棘间韧带和棘上韧带。LIAO等[48]去除了T12椎体内部的一半松质骨,以减弱椎体的强度,保留了皮质骨及后段结构。这些模型相对简化且与临床实际脱离,对伤椎真实情况不能进行准确地展现,可重复性差。ZHAO等[49]在T12椎体中部以平行于上下终板的水平切线去除椎体中间部分,形成一条0.5 mm宽的骨折线,以此来模拟T12椎体压缩型骨折模型。SU等[50]通过在正常L1椎体模型的前缘中部1/3处和前后径的上部2/3处进行V形截骨创建了胸腰椎稳定性爆裂骨折有限元模型。这类模型相对简化,与临床实际情况不一致。 WU等[51]则直接将椎体的上、下终板之间进行部分切除来模拟A3爆裂型骨折,与之类似LIU等[52]和WANG等[53]利用布尔运算将T12下半部完全切除,保留后端结构从而模拟T12爆裂骨折。WANG等[1]在侧位上将椎体前缘下半部分大约一半的松质骨和皮质骨以前宽后窄进行楔形切除从而获得不稳定的胸腰椎爆裂骨折有限元模型。这些模型直接简单机械去除椎体中下部,而临床骨折常常为前上部压缩,严重时中部爆裂、终板碎裂。手术复位后中下部压缩骨折仍然存在,但局部有骨质缺损区,此类模型与实际术后伤椎情况有一定差异,并且难以分析伤椎骨质缺损区活动/位移情况。 目前为止,LIU等[35]的骨折模型最为接近临床实际情况,其随机选取了1例L1爆裂型骨折患者经后路短节段Schanz钉固定复位后的CT影像,计算出伤椎椎体前柱和中柱的缺损体积,然后在L1椎体有限元模型上等效去除前柱和中柱缺损区的骨质来建立伤椎有限元模型。 尽管胸腰段骨折有限元方面的研究有很多,但目前鲜有基于脊柱载荷评分系统的中度和重度骨折的有限元模型报道。LIU等[34]和ZHOU等[36]基于脊柱载荷评分系统分型给予中、重度骨折模型参数标准化设定:中度骨折模型(脊柱载荷评分系统5-6分),该模型椎体前缘高度压缩45%,伤椎完全复位后,侧视图上骨质缺损区前缘高度占椎体高度30%,骨质缺损区上端前缘高度占15%,骨质缺损区下端前缘高度占55%,后凸矫正角为6°,同时伤椎终板粉碎性骨折;重度骨折模型(脊柱载荷评分系统≥7分),该模型椎体前缘高度压缩65%,伤椎完全复位后,侧视图上骨质缺损区前缘高度占椎体高度50%,骨质缺损区上端前缘高度占15%,骨质缺损区下端前缘高度占35%,后凸矫正角为12°,终板粉碎性骨折。作者认为,脊柱载荷评分系统能够很好地指导建立更符合实际情况胸腰段骨折模型,因其进行量化评估的椎体损伤程度、骨折块范围及移位程度、伤椎后凸畸形矫正度都能通过有限元方法很好地模拟出来。 2.3.4 胸腰椎骨折椎弓根固定有限元模型 胸腰段脊柱骨折后的手术方式要根据其评分情况来综合选择,一般可分为前路、后路和前后路联合,其中后路又包括后路短节段椎弓根钉固定、后路长节段椎弓根钉固定和后路经皮椎弓根钉固定,既往研究不同内固定方式见表3。 "
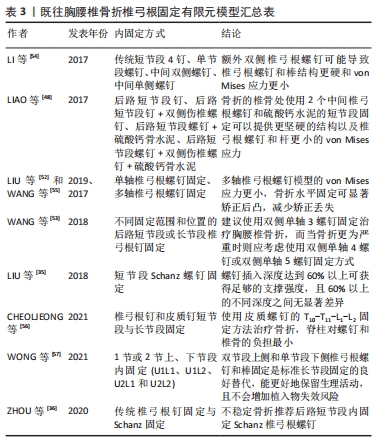

SU等[50]通过有限元方法表明后路短节段内固定联合单侧椎弓根短钉内固定是治疗稳定型胸腰椎骨折最简单的方法。与之类似LI等[54]通过有限元方法创建了4种T12不稳定性骨折后路短节段椎弓根螺钉内固定模型:传统短节段4椎弓根螺钉固定、单节段椎弓根螺钉固定、中间双侧椎弓根螺钉固定、中间单侧椎弓根螺钉固定,然后通过施加不同的载荷模拟前屈、后伸、侧弯和旋转等活动,结果表明在上述4种固定方式中传统短节段4椎弓根螺钉固定组、单节段椎弓根螺钉固定组上椎弓根螺钉最大应力大于下椎弓根螺钉,传统短节段4椎弓根螺钉固定组、单节段椎弓根螺钉固定组上椎弓根螺钉von Mises应力最大,而中间双侧椎弓根螺钉固定组、中间单侧椎弓根螺钉固定组下椎弓根螺钉von Mises应力最大,双侧椎弓根螺钉在传统短节段4椎弓根螺钉固定骨折水平上的附加可使椎弓根螺钉和棒的结构更坚固,von Mises应力更小。LIAO等[48]同样创建了4种不同的T12不稳定性骨折后内固定模型:后路短节段椎弓根钉、后路短节段椎弓根钉+双侧伤椎椎弓根钉、后路短节段椎弓根钉+硫酸钙骨水泥、后路短节段椎弓根钉+双侧伤椎椎弓根钉+硫酸钙骨水泥,然后通过施加不同的载荷模拟前屈、后伸、侧弯和旋转等活动,结果表明在上述4种固定方式中,后路短节段椎弓根钉+双侧伤椎椎弓根钉+硫酸钙骨水泥的承重能力最强,椎弓根钉所受最大应力最小,而后路短节段椎弓根钉的螺钉应力最大,可能会导致固定失败。 LIU等[52]和WANG等[55]研究发现与单轴椎弓根螺钉固定脊柱模型相比,多轴椎弓根螺钉模型的von Mises应力更小,相邻节段的椎间盘内压力更低,骨折水平固定可显著矫正后凸,减少矫正丢失,中间多轴椎弓根螺钉固定组不太可能出现邻近节段退变。 ZHAO等[49]则模拟了骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折骨水泥椎体成形术后不同椎体高度的有限元模型,推测出术后椎体高度在一定范围内越高,其所承受的最大负荷越小,尽管该技术不能完全恢复椎体高度到解剖学标准。 WANG等[53]使用有限元法模拟了T12不稳定性骨折后不同固定范围和位置的后路短节段或长节段椎弓根钉固定模型,提出当选择短节段椎弓根螺钉固定治疗胸腰椎骨折时,建议使用从T11-L1的双侧单轴3螺钉固定,而当骨折更为严重时则应考虑使用从T10-L1的双侧单轴4螺钉或从T11-L2的双侧单轴5螺钉固定方式。LIU等[35]使用有限元模型模拟了L1爆裂型骨折后使用Schanz螺钉固定的不同螺钉插入深度对椎体强度和螺钉应力的影响,结果表明,插入深度达到60%以上可获得足够的支撑强度,且60%以上的不同深度之间无显著差异。 CHEOLJEONG等[56]采用有限元方法创建了T11-L1、T10-T11-L1、T11-L1-L2、T10-T11-L1-L2四种T12胸腰椎骨折固定融合模型,考虑螺钉类型:椎弓根钉和皮质钉,计算螺钉、种植体周围骨和椎间盘所受的应力和活动范围,结果表明在T10-T11-L1-L2固定模型中腰椎活动范围最低,而使用椎弓根钉的T11-L1-L2固定模型获得了最接近完整的情况;在T10-T11-L1-L2固定模型中,螺钉和种植体周围骨应力最低。与之固定方式类似WONG等[57]通过有限元方法创建了4种L1爆裂骨折后路椎弓根螺钉内固定模型:包括1节或2节上、下节段内固定(U1L1、U1L2、U2L1和U2L2),结果显示2节段下位固定(U1L2和U2L2)导致了更大的整体运动减少,范围为66.0%-87.3%,而1节段下位固定(U1L1和U2L1)则是32.0%-47.3%;与U1L1和U1L2相比,U2L1和U2L2椎弓根螺钉的von Mises应力平均减少25.3%和24.8%,U2L1结构能更好地保留脊柱的生理运动,同时在骨折水平提供足够的运动复位范围。 ZHOU等[36]使用有限元方法创建了4种L1骨折后内固定模型:传统椎弓根螺钉中度骨折组(MC),Schanz螺钉中度骨折组(MS),传统椎弓根螺钉不稳定/严重骨折组(UC),Schanz螺钉不稳定/严重骨折(US)组,结果表明相同骨折情况下,传统椎弓根螺钉(MC/UC)最大von Mises应力大于Schanz椎弓根螺钉(MS/US),Schanz椎弓根螺钉(MS/US)L1位移/微动大于常规椎弓根螺钉(MC/UC);在相同螺钉下,不稳定骨折(UC/US)的最大von Mises应力和位移/微动均大于中度骨折(MC/MS)。 "

| [1] Wang W, Pei B, Pei Y, et al. Biomechanical effects of posterior pedicle fixation techniques on the adjacent segment for the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures: a biomechanical analysis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2019;22(13):1083-1092. [2] Aono H, Tobimatsu H, Ariga K, et al. Surgical outcomes of temporary short-segment instrumentation without augmentation for thoracolumbar burst fractures. Injury. 2016;47(6):1337-1344. [3] Mi J, Sun XJ, Zhang K, et al. Prediction of MRI findings including disc injury and posterior ligamentous complex injury in neurologically intact thoracolumbar burst fractures by the parameters of vertebral body damage on CT scan. Injury. 2018;49(2):272-278. [4] Aono H, Ishii K, Tobimatsu H, et al. Temporary short-segment pedicle screw fixation for thoracolumbar burst fractures: comparative study with or without vertebroplasty. Spine J. 2017;17(8):1113-1119. [5] Haiyun Y, Rui G, Shucai D, et al. Three-column reconstruction through single posterior approach for the treatment of unstable thoracolumbar fracture. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(8):E295-302. [6] Lin B, Chen ZW, Guo ZM, et al. Anterior Approach Versus Posterior Approach With Subtotal Corpectomy, Decompression, and Reconstruction of Spine in the Treatment of Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Study. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012;25(6):309-317. [7] De Iure F, Lofrese G, De Bonis P, et al. Vertebral body spread in thoracolumbar burst fractures can predict posterior construct failure. Spine J. 2018;18(6):1005-1013. [8] Ding S, Lu X, Liu Z, et al. Reduce the fractured central endplate in thoracolumbar fractures using percutaneous pedicle screws and instrumentational maneuvers: Technical strategy and radiological outcomes. Injury. 2021;52(4):1060-1064. [9] Lee KY, Kim MW, Seok SY, et al. The Relationship between Superior Disc-Endplate Complex Injury and Correction Loss in Young Adult Patients with Thoracolumbar Stable Burst Fracture. Clin Orthop Surg. 2017;9(4):465-471. [10] Liao JC,Chen WJ. Short-Segment Instrumentation with Fractured Vertebrae Augmentation by Screws and Bone Substitute for Thoracolumbar Unstable Burst Fractures. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019: 4780426. [11] McCormack T, Karaikovic E,Gaines RW. The load sharing classification of spine fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994;19(15):1741-1744. [12] Vaccaro AR, Zeiller SC, Hulbert RJ, et al. The thoracolumbar injury severity score: a proposed treatment algorithm. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005;18(3):209-215. [13] Vaccaro AR, Schroeder GD, Kepler CK, et al. The surgical algorithm for the AOSpine thoracolumbar spine injury classification system. Eur Spine J. 2016;25(4):1087-1094. [14] Vaccaro AR, Oner C, Kepler CK, et al. AOSpine thoracolumbar spine injury classification system: fracture description, neurological status, and key modifiers. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(23):2028-2037. [15] Richardson B, Paulzak A, Rusyniak WG, et al. Anterior Lumbar Corpectomy with Expandable Titanium Cage Reconstruction: A Case Series of 42 Patients. World Neurosurg. 2017;108:317-324. [16] Li C, Pan J, Gu Y, et al. Minimally invasive pedicle screw fixation combined with percutaneous vertebroplasty for the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fracture. Int J Surg. 2016;36(Pt A):255-260. [17] Saglam N, Dogan S, Ozcan C, et al. Comparison of Four Different Posterior Screw Fixation Techniques for the Treatment of Thoracolumbar Junction Fractures. World Neurosurg. 2019;123:e773-e780. [18] Kwon WK, Park WB, Lee GY, et al. Decompression with Lateral Pediculectomy and Circumferential Reconstruction for Unstable Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures: Surgical Techniques and Results in 18 Patients. World Neurosurg. 2018; 20:e53-e62. [19] Lindtner RA, Mueller M, Schmid R, et al. Monosegmental anterior column reconstruction using an expandable vertebral body replacement device in combined posterior-anterior stabilization of thoracolumbar burst fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2018;138(7): 939-951. [20] Liao JC,Fan KF. Posterior short-segment fixation in thoracolumbar unstable burst fractures - Transpedicular grafting or six-screw construct. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2017;153:56-63. [21] Yang S, Shang DP, Lu JM, et al. Modified Posterior Short-Segment Pedicle Screw Instrumentation for Lumbar Burst Fractures with Incomplete Neurological Deficit. World Neurosurg. 2018;119: e977-e985. [22] Smits AJ, Noor A, Bakker FC, et al. Thoracoscopic anterior stabilization for thoracolumbar fractures in patients without spinal cord injury: quality of life and long-term results. Eur Spine J. 2018;27(7):1593-1603. [23] Hao D, Wang W, Duan K, et al. Two-year follow-up evaluation of surgical treatment for thoracolumbar fracture-dislocation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(21):E1284-1290. [24] Liang C, Liu B, Zhang W, et al. Clinical Effects of Posterior Limited Long-Segment Pedicle Instrumentation for the Treatment of Thoracolumbar Fractures. J Invest Surg. 2020;33(1):25-30. [25] Kapoen C, Liu Y, Bloemers FW, et al. Pedicle screw fixation of thoracolumbar fractures: conventional short segment versus short segment with intermediate screws at the fracture level-a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2020;29(10):2491-2504. [26] Xiong C, Huang B, Wei T, et al. Effect of the short-segment internal fixation with intermediate inclined-angle polyaxial screw at the fractured vertebra on the treatment of Denis type B thoracolumbar fracture. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):182. [27] Basaran R, Efendioglu M, Kaksi M, et al. Finite Element Analysis of Short- Versus Long-Segment Posterior Fixation for Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture. World Neurosurg. 2019;128:e1109-e1117. [28] Dobran M, Nasi D, Brunozzi D, et al. Treatment of unstable thoracolumbar junction fractures: short-segment pedicle fixation with inclusion of the fracture level versus long-segment instrumentation. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2016;158(10):1883-1889. [29] Kocanli O, Komur B, Duymuş TM, et al. Ten-year follow-up results of posterior instrumentation without fusion for traumatic thoracic and lumbar spine fractures. J Orthop. 2016;13(4):301-305. [30] D’Oro A, Spoonamore MJ, Cohen JR, et al. Effects of fusion and conservative treatment on disc degeneration and rates of subsequent surgery after thoracolumbar fracture. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;24(3): 476-482. [31] Ankomah F, Ikpeze T, Mesfin A. The Top 50 Most-Cited Articles on Thoracolumbar Fractures. World Neurosurg. 2018;118:e699-e706. [32] Sensale M, Vendeuvre T, Schilling C, et al. Patient-Specific Finite Element Models of Posterior Pedicle Screw Fixation: Effect of Screw’s Size and Geometry. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:643154. [33] Machino M, Yukawa Y, Ito K, et al. The complement of the load-sharing classification for the thoracolumbar injury classification system in managing thoracolumbar burst fractures. J Orthop Sci. 2013;18(1):81-86. [34] Liu J, Yang S, Zhou F, et al. The feasibility of short-segment Schanz screw implanted in an oblique downward direction for the treatment of lumbar 1 burst fracture: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):537. [35] Liu J, Yang S, Lu J, et al. Biomechanical effects of USS fixation with different screw insertion depths on the vertebrae stiffness and screw stress for the treatment of the L1 fracture. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2018;31(2):285-297. [36] Zhou F, Yang S, Liu J, et al. Finite element analysis comparing short-segment instrumentation with conventional pedicle screws and the Schanz pedicle screw in lumbar 1 fracture. Neurosurg Rev. 2020; 43(12):301-312. [37] Welch-Phillips A, Gibbons D, Ahern DP, et al. What Is Finite Element Analysis? Clin Spine Surg. 2020;33(8):323-324. [38] Ye Y, You W, Zhu W, et al. The Applications of Finite Element Analysis in Proximal Humeral Fractures. Comput Math Methods Med. 2017;2017:4879836. [39] Goel VK, Nyman E. Computational Modeling and Finite Element Analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41 Suppl 7:S6-7. [40] Quah C, Yeoman MS, Cizinauskas A, et al. Finite element investigation of the effect of a bifid arch on loading of the vertebral isthmus. Spine J. 2014;14(4):675-682. [41] Webb JD, Blemker SS, Delp SL. 3D finite element models of shoulder muscles for computing lines of actions and moment arms. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2014;17(8):829-837. [42] Benca E, Amini M, Pahr DH. Effect of CT imaging on the accuracy of the finite element modelling in bone. Eur Radiol Exp. 2020;4(1):51. [43] Kulduk A, Altun NS, Senkoylu A. Biomechanical comparison of effects of the Dynesys and Coflex dynamic stabilization systems on range of motion and loading characteristics in the lumbar spine: a finite element study. Int J Med Robot. 2015;11(4):400-405. [44] Han Y, Wang X, Wu J, et al. Biomechanical finite element analysis of vertebral column resection and posterior unilateral vertebral resection and reconstruction osteotomy. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):88. [45] Eggermont F, van der Wal G, Westhoff P, et al. Patient-specific finite element computer models improve fracture risk assessments in cancer patients with femoral bone metastases compared to clinical guidelines. Bone. 2020;130:115101. [46] Widmer J, Fasser MR, Croci E, et al. Individualized prediction of pedicle screw fixation strength with a finite element model. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2020;23(4):155-167. [47] Xu G, Fu X, Du C, et al. Biomechanical comparison of mono-segment transpedicular fixation with short-segment fixation for treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: a finite element analysis. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2014;228(10):1005-1013. [48] Liao JC, Chen WP, Wang H. Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by short-segment pedicle screw fixation using a combination of two additional pedicle screws and vertebroplasty at the level of the fracture: a finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017; 18(1):262. [49] Zhao WT, Qin DP, Zhang XG, et al. Biomechanical effects of different vertebral heights after augmentation of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):32. [50] Su Y, Wang X, Ren D, et al. A finite element study on posterior short segment fixation combined with unilateral fixation using pedicle screws for stable thoracolumbar fracture. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018; 97(34):e12046. [51] Wu Y, Chen CH, Tsuang FY, et al. The stability of long-segment and short-segment fixation for treating severe burst fractures at the thoracolumbar junction in osteoporotic bone: A finite element analysis. PLoS One. 2019;14(2):e0211676. [52] Liu H, Wang H, Liu J, et al. Biomechanical comparison of posterior intermediate screw fixation techniques with hybrid monoaxial and polyaxial pedicle screws in the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fracture: a finite element study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):122. [53] Wang H, Mo Z, Han J, et al. Extent and location of fixation affects the biomechanical stability of short- or long-segment pedicle screw technique with screwing of fractured vertebra for the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures: An observational study using finite element analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(26):e11244. [54] Li C, Zhou Y, Wang H, et al. Treatment of unstable thoracolumbar fractures through short segment pedicle screw fixation techniques using pedicle fixation at the level of the fracture: a finite element analysis. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e99156. [55] Wang H, Zhao Y, Mo Z, et al. Comparison of short-segment monoaxial and polyaxial pedicle screw fixation combined with intermediate screws in traumatic thoracolumbar fractures: a finite element study and clinical radiographic review. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2017;72(10):609-617. [56] CheolJeong K, Min SS, Hoon CS, et al. Numerical Evaluation of Spinal Stability after Posterior Spinal Fusion with Various Fixation Segments and Screw Types in Patients with Osteoporotic Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture Using Finite Element Analysis. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(7):3243. [57] Wong CE, Hu HT, Tsai CH, et al. Comparison of Posterior Fixation Strategies for Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture: A Finite Element Study. J Biomech Eng. 2021;143(7):071007. |
| [1] | Nong Fuxiang, Jiang Zhixiong, Li Yinghao, Xu Wencong, Shi Zhilan, Luo Hui, Zhang Qinglang, Zhong Shuang, Tang Meiwen. Bone cement augmented proximal femoral nail antirotation for type A3.3 intertrochanteric femoral fracturalysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10. |
| [2] | Peng Zhixin, Yan Wengang, Wang Kun, Zhang Zhenjiang. Finite element analysis and structural optimization design of 3D printed forearm braces [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1340-1345. |
| [3] | Wu Tianliang, Tao Xiuxia, Xu Hongguang. Influence of different bone mineral densities on cage subsidence after stand-alone oblique lateral interbody fusion: three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1352-1358. |
| [4] | Liu Jinyu, Zhang Hanshuo, Cui Hongpeng, Pan Lingzhi, Zhao Boran, Li Fei, Ding Yu. Finite element biomechanical analysis of minimally invasive treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy and accurate exercise rehabilitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1359-1364. |
| [5] | He Yujie, Kang Zhijie, Xue Mingming, Jin Feng, Li Zhijun, Wang Xing, Xu Yangyang, Gao Mingjie, Li Jiawei, Li Xiaohe, Wang Haiyan. Finite element analysis of transarticular screw fixation of adolescent thoracic vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1365-1370. |
| [6] | Wen Xinghua, Ding Huanwen, Cheng Kai, Yan Xiaonan, Peng Yuanhao, Wang Yuning, Liu Kang, Zhang Huiwu. Three-dimensional finite element model analysis of intramedullary nailing fixation design for large femoral defects in Beagle dogs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1371-1376. |
| [7] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [8] | Cai Zhihao, Xie Zhaoyong. Femoral neck anteversion measurement assessment: how to establish a unified method and standard [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1448-1454. |
| [9] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [10] | Wang Ji, Zhang Min, Yang Zhongya, Zhang Long. A review of physical activity intervention in type 2 diabetes mellitus with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1272-1277. |
| [11] | Nie Chenchen, Su Kaiqi, Gao Jing, Fan Yongfu, Ruan Xiaodi, Yuan Jie, Duan Zhaoyuan, Feng Xiaodong. The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| [12] | Gao Yu, Han Jiahui, Ge Xin. Immunoinflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [13] | Zhu Lin, Gu Weiping, Wang Can, Chen Gang. Biomechanical analysis of All-on-Four and pterygomaxillary implants under different maxillary bone conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 985-991. |
| [14] | Sun Jiangwei, Wang Junxiang, Baibujiafu·Yellisi, Dai Huijuan, Nijati·Turson. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of stress distribution in different smooth collar implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1004-1011. |
| [15] | Jiang Yifang, Cai Qimin, Chu Zhengyi, Qin Min, Shen Yurong, Gu Yuanping. Simulation analysis of stress distribution of NRT FILES in curved root canals [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1038-1042. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||