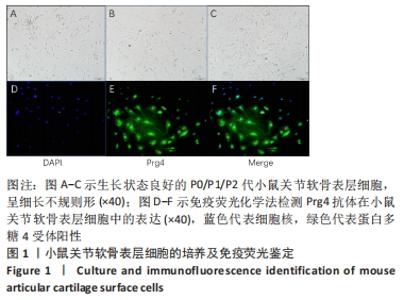
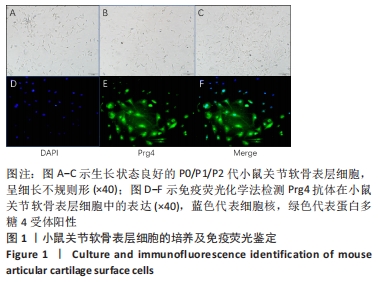
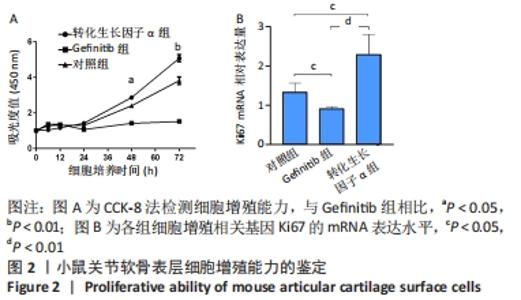
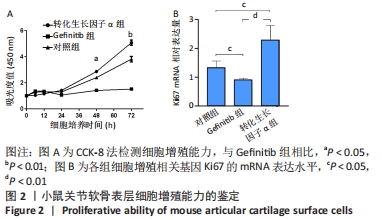
[1] MURRAY CJ, VOS T, LOZANO R, et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2197-2223.
[2] LOTZ M, LOESER RF. Effects of aging on articular cartilage homeostasis. Bone. 2012;51(2):241-248.
[3] GOLDRING MB. Chondrogenesis, chondrocyte differentiation, and articular cartilage metabolism in health and osteoarthritis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2012;4(4):269-285.
[4] STOCKWELL RA. The cell density of human articular and costal cartilage. J Anat. 1967;101(Pt 4):753-763.
[5] KHAN IM, GILBERT SJ, SINGHRAO SK, et al. Cartilage integration: evaluation of the reasons for failure of integration during cartilage repair. A review. Eur Cell Mater. 2008;16:26-39.
[6] HUNZIKER EB, MICHEL M, STUDER D. Ultrastructure of adult human articular cartilage matrix after cryotechnical processing. Microsc Res Tech. 1997;37(4): 271-284.
[7] DOWTHWAITE GP, BISHOP JC, REDMAN SN, et al. The surface of articular cartilage contains a progenitor cell population. J Cell Sci. 2004;117(Pt 6):889-897.
[8] LI L, NEWTON PT, BOUDERLIQUE T, et al. Superficial cells are self-renewing chondrocyte progenitors, which form the articular cartilage in juvenile mice. FASEB J. 2017;31(3):1067-1084.
[9] PACIFICI M, KOYAMA E, IWAMOTO M. Mechanisms of synovial joint and articular cartilage formation: recent advances, but many lingering mysteries. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2005;75(3):237-248.
[10] FRANCIS-WEST PH, PARISH J, LEE K, et al. BMP/GDF-signalling interactions during synovial joint development. Cell Tissue Res. 1999;296(1):111-119.
[11] YARDEN Y, SHILO BZ. SnapShot: EGFR signaling pathway. Cell. 2007;131(5):1018.
[12] JIA H, MA X, TONG W, et al. EGFR signaling is critical for maintaining the superficial layer of articular cartilage and preventing osteoarthritis initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(50):14360-14365.
[13] SUN H, WU Y, PAN Z, et al. Gefitinib for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Activated Osteoarthritis Subpopulation Treatment. EBioMedicine. 2018;32:223-233.
[14] BRACHMANN R, LINDQUIST PB, NAGASHIMA M, et al. Transmembrane TGF-alpha precursors activate EGF/TGF-alpha receptors. Cell. 1989;56(4):691-700.
[15] ZHANG X, TAMASI J, LU X, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor plays an anabolic role in bone metabolism in vivo. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(5):1022-1034.
[16] USMANI SE, APPLETON CT, BEIER F. Transforming growth factor-alpha induces endothelin receptor A expression in osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2012;30(9):1391-1397.
[17] GRIFFIN R, RAMIREZ RA. Molecular Targets in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Ochsner J. 2017;17(4): 388-392.
[18] PINILLA-MACUA I, GRASSART A, DUVVURI U, et al. EGF receptor signaling, phosphorylation, ubiquitylation and endocytosis in tumors in vivo. Elife. 2017;6: e31993.
[19] JIANG Y, TUAN RS. Origin and function of cartilage stem/progenitor cells in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(4):206-212.
[20] CANDELA ME, YASUHARA R, IWAMOTO M, et al. Resident mesenchymal progenitors of articular cartilage. Matrix Biol. 2014;39:44-49.
[21] ZHANG X, ZHU J, LI Y, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling regulates epiphyseal cartilage development through β-catenin-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(45):32229-32240.
[22] CHANDRA A, LAN S, ZHU J, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling promotes proliferation and survival in osteoprogenitors by increasing early growth response 2 (EGR2) expression. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(28):20488-20498.
[23] KOZHEMYAKINA E, ZHANG M, IONESCU A, et al. Identification of a Prg4-expressing articular cartilage progenitor cell population in mice. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67(5):1261-1273.
[24] ROUBILLE C, PELLETIER JP, MARTEL-PELLETIER J. New and emerging treatments for osteoarthritis management: will the dream come true with personalized medicine. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2013;14(15):2059-2077.
[25] JIANG Z, DERRICK-ROBERTS A, REICHSTEIN C, et al. Cell cycle progression is disrupted in murine MPS VII growth plate leading to reduced chondrocyte proliferation and transition to hypertrophy. Bone. 2020;132:115195.
[26] GÓMEZ-LECHÓN MJ, O’CONNOR E, CASTELL JV, et al. Sensitive markers used to identify compounds that trigger apoptosis in cultured hepatocytes. Toxicol Sci. 2002;65(2):299-308.
[27] WALLER KA, ZHANG LX, ELSAID KA, et al. Role of lubricin and boundary lubrication in the prevention of chondrocyte apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013; 110(15):5852-5857.
[28] 葛心慈, 徐岩, 吴琼, 等. 左、右归丸及其拆方对去卵巢大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化的影响[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2016,22(10):1324-1328.
[29] 吴顺义, 张晓蓉. Runx2在成骨细胞和软骨细胞分化中作用的研究进展[J]. 医学综述,2019,25(7):1302-1307.
[30] 陈臻浩, 赵广雷, 石晶晟, 等. Sox9对软骨细胞分化和基质产生的调控机制[J]. 复旦学报(医学版),2019,46(6):824-828.
[30] 欧阳宏伟,主编. 医学分子细胞生物学研究策略与技术原理[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2012.
[32] ZHANG YW, SU Y, LANNING N, et al. Targeted disruption of Mig-6 in the mouse genome leads to early onset degenerative joint disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(33):11740-11745.
|