Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (25): 4038-4044.doi: 10.12307/2023.177
Previous Articles Next Articles
Carbon dot Prussian blue nanoenzyme antioxidative stress delays intervertebral disc degeneration
Cao Zhipeng1, 2, Shi Yu1, 2, Li Ke1, 2, Lin Wenzheng1, Jiang Letao1, Bu Wenzhen1, 2, Zhu Hai3, Du Jianwei1, Wang Huihui2, Chen Hao1, 2
- 1Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225000, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Institute of Translational Medicine, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225000, Jiangsu Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, First People’s Hospital, Huai’an 223001, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2022-02-28Accepted:2022-05-26Online:2023-09-08Published:2023-01-17 -
Contact:Chen Hao, PhD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225000, Jiangsu Province, China; Institute of Translational Medicine, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225000, Jiangsu Province, China Wang Huihui, MD, Lecturer, Master’s supervisor, Institute of Translational Medicine, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Cao Zhipeng, Master candidate, Physician, Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225000, Jiangsu Province, China; Institute of Translational Medicine, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:General Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 8217090346 (to CH); Jiangsu Basic Research Program (Natural Science Foundation) (General Project), No. SBK2021022619 (to CH); Basic Science of Jiangsu Province Universities (Natural Science) Research Project, No. 21KJB320009 (to CH); Huaian Natural Science Research Program, No. HAB202023 (to ZH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cao Zhipeng, Shi Yu, Li Ke, Lin Wenzheng, Jiang Letao, Bu Wenzhen, Zhu Hai, Du Jianwei, Wang Huihui, Chen Hao. Carbon dot Prussian blue nanoenzyme antioxidative stress delays intervertebral disc degeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(25): 4038-4044.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
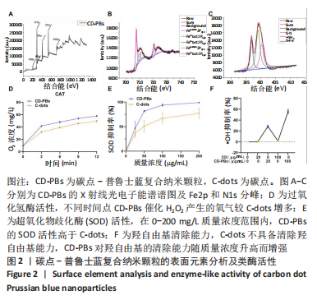
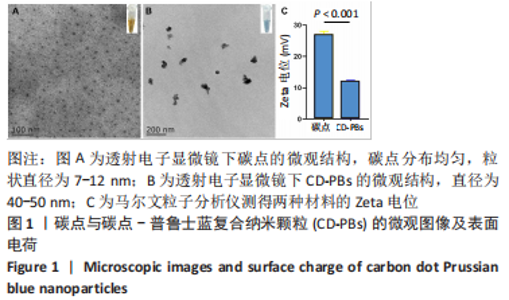
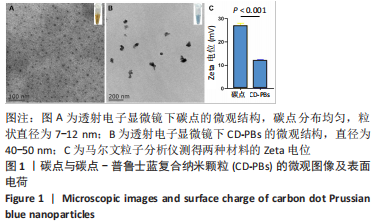
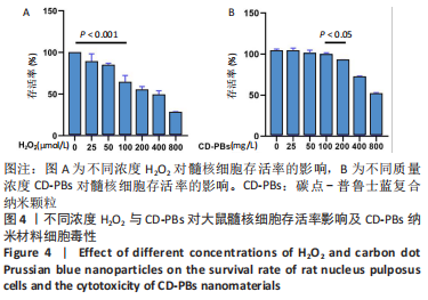
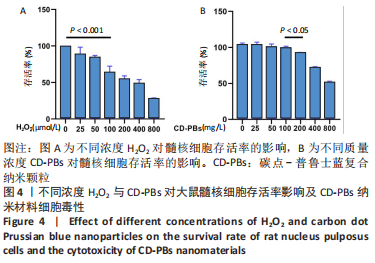
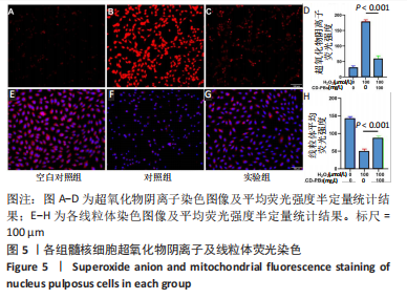
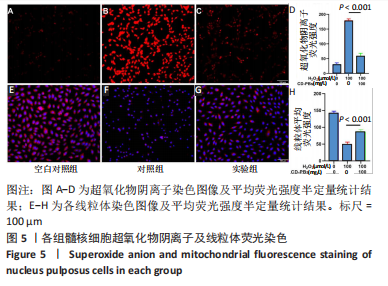
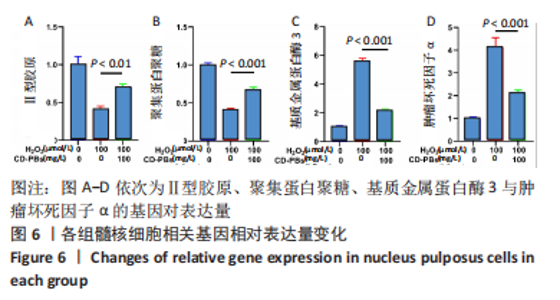
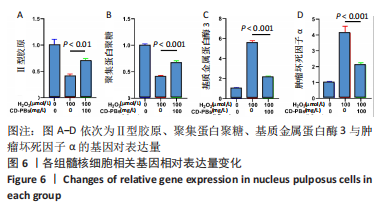
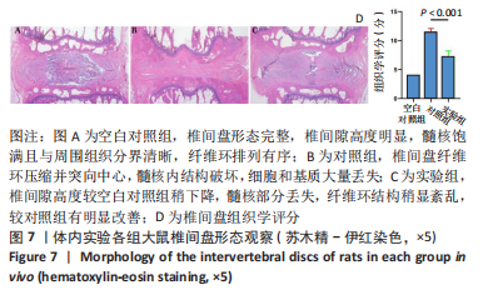
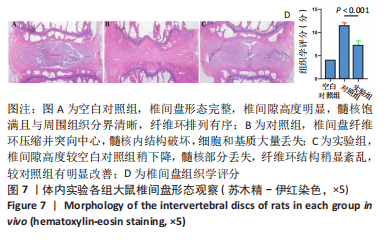
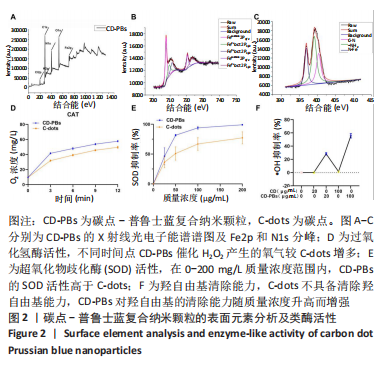
2.1.2 CD-PBs表面元素组成 如图2A-C所示,CD-PBs表面有明显的Fe-C峰(707.6,720.5 eV)、Fe-N峰(396.9 eV)和C-N峰(400.4 eV)。该结果显示碳点表面存在普鲁士蓝的特征峰,提示普鲁士蓝在碳点表面成功合成。 2.1.3 碳点及CD-PBs的类酶活性 如图2D-F所示,类酶活性检测结果显示,不同时间点CD-PBs催化H2O2产生的氧气较碳点显著增多;在0-200 mg/L质量浓度范围内,同质量浓度的CD-PBs相比碳点的超氧化物歧化酶活性高10%-30%;碳点不具备清除羟自由基能力,在其表面原位合成普鲁士蓝之后对羟自由基的清除能力随浓度升高而增强。"
| [1] EKRAM S, KHALID S, SALIM A, et al. Regulating the fate of stem cells for regenerating the intervertebral disc degeneration. World J Stem Cells. 2021;13(12):1881-1904. [2] ISA ILM, MOKHTAR SA, ABBAH SA, et al. Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering Strategies Towards Precision Medicine. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(13):e2102530. [3] ZHANG GZ, LIU MQ, CHEN HW, et al. NF-κB signalling pathways in nucleus pulposus cell function and intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(7):e13057. [4] FENG C, YANG M, LAN M, et al. ROS: Crucial Intermediators in the Pathogenesis of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:5601593. [5] APEL K, HIRT H. Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2004;55:373-399. [6] LENNICKE C, COCHEMé HM. Redox metabolism: ROS as specific molecular regulators of cell signaling and function. Mol Cell. 2021; 81(18):3691-3707. [7] CAO G, YANG S, CAO J, et al. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022: 2166817. [8] CORMODE DP, GAO L, KOO H. Emerging Biomedical Applications of Enzyme-Like Catalytic Nanomaterials. Trends Biotechnol. 2018;36(1): 15-29. [9] AN Z, YAN J, ZHANG Y, et al. Applications of nanomaterials for scavenging reactive oxygen species in the treatment of central nervous system diseases. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(38):8748-8767. [10] DIXON AR, WARREN JP, CULBERT MP, et al. Review of in vitro mechanical testing for intervertebral disc injectable biomaterials. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021;123:104703. [11] ÐORĐEVIĆ L, ARCUDI F, PRATO M. Preparation, functionalization and characterization of engineered carbon nanodots. Nat Protoc. 2019; 14(10):2931-2953. [12] LI X, ZHAO S, LI B, et al. Advances and perspectives in carbon dot-based fluorescent probes: Mechanism, and application. Coord Chem Rev. 2021;431:213686. [13] WANG H, LIU C, LIU Z, et al. Specific Oxygenated Groups Enriched Graphene Quantum Dots as Highly Efficient Enzyme Mimics. Small. 2018;14(13):e1703710. [14] LI F, LI T, SUN C, et al. Selenium-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Free-Radical Scavenging. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2017;56(33):9910-9914. [15] RIZZO C, ARCUDI F, ĐORĐEVIĆ L, et al. Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanodots-Ionogels: Preparation, Characterization, and Radical Scavenging Activity. ACS Nano. 2018;12(2):1296-1305. [16] ZHANG W, ZHANG Y, CHEN Y, et al. Prussian blue modified ferritin as peroxidase mimetics and its applications in biological detection. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2013;13(1):60-67. [17] ZHANG W, MA D, DU J. Prussian blue nanoparticles as peroxidase mimetics for sensitive colorimetric detection of hydrogen peroxide and glucose. Talanta. 2014;120:362-367. [18] ESTELRICH J, BUSQUETS MA. Prussian Blue: A Nanozyme with Versatile Catalytic Properties. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(11):5993. [19] WANG H, CHENG L, MA S, et al. Self-Assembled Multiple-Enzyme Composites for Enhanced Synergistic Cancer Starving-Catalytic Therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(18):20191-20201. [20] BIAN J, CAI F, CHEN H, et al. Modulation of Local Overactive Inflammation via Injectable Hydrogel Microspheres. Nano Lett. 2021; 21(6):2690-2698. [21] MASUDA K, AOTA Y, MUEHLEMAN C, et al. A novel rabbit model of mild, reproducible disc degeneration by an anulus needle puncture: correlation between the degree of disc injury and radiological and histological appearances of disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(1):5-14. [22] JI ML, JIANG H, ZHANG XJ, et al. Preclinical development of a microRNA-based therapy for intervertebral disc degeneration. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):5051. [23] NASTO LA, ROBINSON AR, NGO K, et al. Mitochondrial-derived reactive oxygen species (ROS) play a causal role in aging-related intervertebral disc degeneration. %J Journal of Orthopaedic Research. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(7):1150-1157. [24] DIMOZI A, MAVROGONATOU E, SKLIROU A, et al. Oxidative stress inhibits the proliferation, induces premature senescence and promotes a catabolic phenotype in human nucleus pulposus intervertebral disc cells. Eur Cell Mater. 2015;30:89-102. [25] WANG J, XIA D, LIN Y, et al. Oxidative stress-induced circKIF18A downregulation impairs MCM7-mediated anti-senescence in intervertebral disc degeneration. Exp Mol Med. 2022;54(3):285-297. [26] QUINLAN CL, PEREVOSHCHIKOVA IV, HEY-MOGENSEN M, et al. Sites of reactive oxygen species generation by mitochondria oxidizing different substrates. Redox Biol. 2013;1:304-312. [27] ZIEGLER DV, WILEY CD, VELARDE MC. Mitochondrial effectors of cellular senescence: beyond the free radical theory of aging. Aging Cell. 2015; 14(1):1-7. [28] QI JH, DONG FX. The relevant targets of anti-oxidative stress: a review. J Drug Target. 2021;29(7):677-686. [29] JUAN CA, PéREZ DE LA LASTRA JM, PLOU FJ, et al. The Chemistry of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Revisited: Outlining Their Role in Biological Macromolecules (DNA, Lipids and Proteins) and Induced Pathologies. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(9):4642. [30] XU X, WANG D, ZHENG C, et al. Progerin accumulation in nucleus pulposus cells impairs mitochondrial function and induces intervertebral disc degeneration and therapeutic effects of sulforaphane. Theranostics. 2019;9(8):2252-2267. [31] YANG L, RONG Z, ZENG M, et al. Pyrroloquinoline quinone protects nucleus pulposus cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis by inhibiting the mitochondria-mediated pathway. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(8): 1702-1710. [32] KANG L, LIU S, LI J, et al. The mitochondria-targeted anti-oxidant MitoQ protects against intervertebral disc degeneration by ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction and redox imbalance. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(3): e12779. [33] DAI S, SHI X, QIN R, et al. Sodium Tanshinone IIA Sulfonate Ameliorates Injury-Induced Oxidative Stress and Intervertebral Disc Degeneration in Rats by Inhibiting p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:5556122. [34] SEOL D, COLEMAN MC, MARTIN JA, et al. Targeting Oxidative Stress with Amobarbital to Prevent Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Spine J. 2021;21(6):1021-1030. [35] LIN J, DU J, WU X, et al. SIRT3 mitigates intervertebral disc degeneration by delaying oxidative stress-induced senescence of nucleus pulposus cells. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(9):6441-6456. [36] ZHAO H, ZHANG R, YAN X, et al. Superoxide dismutase nanozymes: an emerging star for anti-oxidation. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(35):6939-6957. [37] GAO L, ZHUANG J, NIE L, et al. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol. 2007;2(9):577-583. [38] REN X, CHEN D, WANG Y, et al. Nanozymes-recent development and biomedical applications. J Nanobiotechnol. 2022;20(1):92. [39] LIU X, GAO Y, CHANDRAWATI R, et al. Therapeutic applications of multifunctional nanozymes. Nanoscale. 2019;11(44):21046-21060. [40] CHEN R, LIU G, SUN X, et al. Chitosan derived nitrogen-doped carbon dots suppress osteoclastic osteolysis via downregulating ROS. Nanoscale. 2020;12(30):16229-16244. [41] HOU W, YE C, CHEN M, et al. Excavating bioactivities of nanozyme to remodel microenvironment for protecting chondrocytes and delaying osteoarthritis. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(8):2439-2451. |
| [1] | Li Huayuan, Li Chun, Liu Junwei, Wang Ting, Li Long, Wu Yongli. Effect of warm acupuncture on PINK1/Parkin pathway in the skeletal muscle of rats with chronic fatigue syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1618-1625. |
| [2] | Zhu Hanmin, Wang Song, Xiao Wenlin, Zhang Wenjing, Zhou Xi, He Ye, Li Wei, . Mitophagy regulates bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1676-1683. |
| [3] | Chi Wenxin, Zhang Cunxin, Gao Kai, Lyu Chaoliang, Zhang Kefeng. Mechanism by which nobiletin inhibits inflammatory response of BV2 microglia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1321-1327. |
| [4] | Liu Lingyun, He Guixin, Qin Weibin, Song Hui, Zhang Liwen, Tang Weizhi, Yang Feifei, Zhu Ziyi, Ou Yangbin . Improvement of myocardial injury by traditional Chinese medicine: mitochondrial calcium homeostasis mediates macrophage autophagy and pyroptosis pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1276-1284. |
| [5] | Qian Kun, Li Ziqing, Sun Shui . Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the occurrence and development of common degenerative bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1285-1295. |
| [6] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [7] | He Bo, Chen Wen, Ma Suilu, He Zhijun, Song Yuan, Li Jinpeng, Liu Tao, Wei Xiaotao, Wang Weiwei, Xie Jing . Pathogenesis and treatment progress of flap ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1230-1238. |
| [8] | Xiang Pan, Che Yanjun, Luo Zongping. Compressive stress induces degeneration of cartilaginous endplate cells through the SOST/Wnt/beta-catenin pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 951-957. |
| [9] | Lu Ranran, Zhou Xu, Zhang Lijie, Yang Xinling. Dimethyl fumarate alleviates nerve damage in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 989-994. |
| [10] | Ding Zhili, Huang Jie, Jiang Qiang, Li Tusheng, Liu Jiang, Ding Yu. Constructing rabbit intervertebral disc degeneration models by different methods under X-ray guidance: a comparative study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 995-1002. |
| [11] | Gao Xilin, Wu Si Zhang Chao Zhu Liguo, Fu Bifeng, Wang Ping. Mechanotransduction proteins in intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 579-589. |
| [12] | Li Haishan, Wu Yuheng, Liang Zixuan, Zhang Shiyin, Zhang Zhen, Mai Bin, Deng Wei, Li Yongxian, Tang Yongchao, , Zhang Shuncong, , Yuan Kai, . Carnosic acid inhibits osteoclast differentiation by inhibiting mitochondrial activity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 245-253. |
| [13] | Wu Ao, Yu Peng, Teng Jiawen, Kong Peng, Bian Sishan. Analysis of oxidative stress-related genes and immune infiltration in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 302-311. |
| [14] | Liu Zhongyuan, Li Yang, Zhang Zhiwen . Mechanism by which KRT18 interacts with mRNA and long non-coding RNA to regulate intervertebral disc nucleus pulposus cell injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 312-321. |
| [15] | Huang Renjun, Yang Jingyan, Ma She, Wang Chaoyi, Zhao Yuyang, Yu Dong. Causal relationship between sedentary and physical activity levels in the Oswestry disability index score and intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 322-330. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||