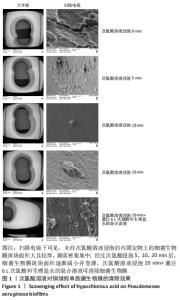
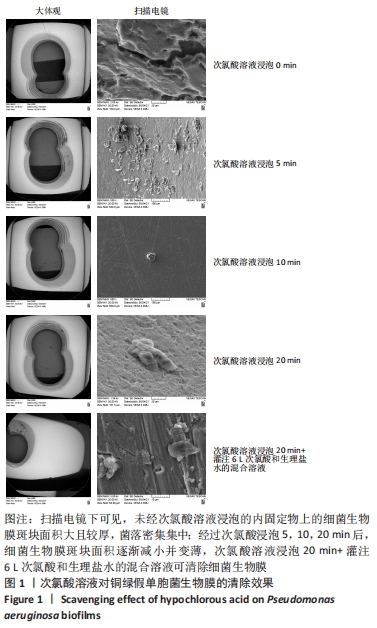
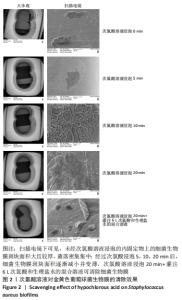
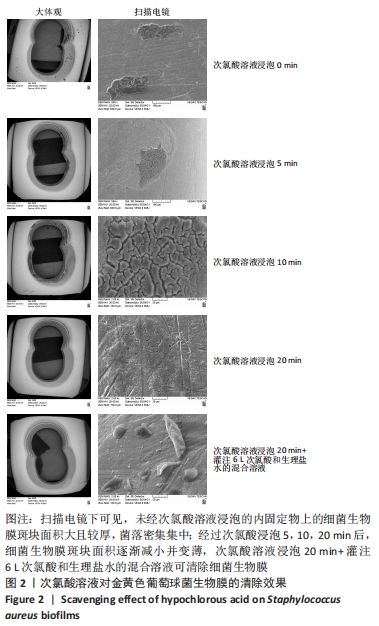
[1] 刘浩,李静.骨折内固定术后感染的药物治疗[J].中华创伤杂志,2020,36(6): 567-573.
[2] 姜楠,余斌.骨折内固定术后感染的诊治最新进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2020,22(12):1098-1104.
[3] CHEN C, CHEN C, DING S. Effectiveness of Hypochlorous Acid to Reduce the Biofilms on Titanium Alloy Surfaces in Vitro. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(7):1161.
[4] 中华医学会骨科学分会创伤骨科学组,中华医学会骨科学分会外固定与肢体重建学组,中国医师协会创伤外科医师分会创伤感染专家委员会,等.中国骨折内固定术后感染诊断与治疗专家共识(2018版)[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2018,20(11):929-936.
[5] BOSCH-NICOLAU P, RODRIGUEZ-PARDO D, PIGRAU C, et al. Acute spinal implant infection treated with debridement: does extended antibiotic treatment improve the prognosis? Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019;38(5):951-958.
[6] MACIEJCZAK A, WOLAN-NIERODA A, WALASZEK M, et al. Antibiotic prophylaxis in spine surgery: a comparison of single-dose and 72-hour protocols. J Hosp Infect. 2019;103(3): 303-310.
[7] ZIMMERLI W. Clinical presentation and treatment of orthopaedic implant-associated infection. J Intern Med. 2014;276(2):111-119.
[8] MORGENSTERN M, KÜHL R, ECKARDT H, et al. Diagnostic challenges and future perspectives in fracture-related infection. Injury. 2018;49:S83-S90.
[9] METSEMAKERS W, MORGENSTERN M, SENNEVILLE E, et al. General treatment principles for fracture-related infection: recommendations from an international expert group. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020;140(8):1013-1027.
[10] GOVAERT GAM, KUEHL R, ATKINS BL, et al. Diagnosing Fracture-Related Infection: Current Concepts and Recommendations. J Orthop Trauma. 2020;34(1):8-17.
[11] ALAEE F, ANGERAME M, BRADBURY T, et al. General Assembly, Prevention, Operating Room - Surgical Technique: Proceedings of International Consensus on Orthopedic Infections. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(2):S139-S146.
[12] PUETZLER J, ZALAVRAS C, MORIARTY TF, et al. Clinical practice in prevention of fracture-related infection: An international survey among 1197 orthopaedic trauma surgeons. Injury. 2019;50(6):1208-1215.
[13] FOSTER AL, MORIARTY TF, TRAMPUZ A, et al. Fracture-related infection: current methods for prevention and treatment. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2020;18(4): 307-321.
[14] SCHÖMIG F, PUTZIER M. Clinical presentation and diagnosis of delayed postoperative spinal implant infection. J Spine Surg. 2020;6(4):772-776.
[15] JIANG N, ZHAO X, WANG L, et al. Single-stage debridement with implantation of antibiotic-loaded calcium sulphate in 34 cases of localized calcaneal osteomyelitis. Acta Orthop. 2020;91(3):353-359.
[16] 唐良华,王爱民,杜全印,等.四肢骨折内固定术后感染的细菌分布、耐药分析及防治措施[J].四川医学,2008,29(6):679-682.
[17] 王宇强,冯世庆,王小华,等.脊柱手术术后感染的病原菌和药敏分析及血清炎症因子的辅助诊断价值[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2017,27(1):147-150.
[18] PULIDO L, GHANEM E, JOSHI A, et al. Periprosthetic Joint Infection: The Incidence, Timing, and Predisposing Factors. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(7):1710-1715.
[19] AGGARWAL V, BAKHSHI H, ECKER N, et al. Organism Profile in Periprosthetic Joint Infection: Pathogens Differ at Two Arthroplasty Infection Referral Centers in Europe and in the United States. J Knee Surg. 2014;27(5):399-406.
[20] 施绒舟,胡奇哲,裘情密.骨折内固定术后感染的病原菌分析及防治措施[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2013,23(1):71-72.
[21] HARJAI K, KUMAR R, SINGH S. Garlic blocks quorum sensing and attenuates the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2010; 58(2):161-168.
[22] MASTERS EA, TROMBETTA RP, de MESY BK, et al. Evolving concepts in bone infection: redefining “biofilm”, “acute vs. chronic osteomyelitis”, “the immune proteome” and “local antibiotic therapy”. Bone Res. 2019;7(15):20.
[23] BJARNSHOLT T. The role of bacterial biofilms in chronic infections. APMIS Suppl. 2013;121(136): 1-51.
[24] ZIMMERLI W, SENDI P. Orthopaedic biofilm infections. APMIS. 2017;125(4):353-364.
[25] 费军.载去甲万古霉素钢板的研制及防治兔胫骨感染的实验研究[D].重庆:第三军医大学外科学(骨外),2008.
[26] STEWART PS, FRANKLIN MJ. Physiological heterogeneity in biofilms. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008;6(3):199-210.
[27] BLOCK MS, ROWAN BG. Hypochlorous Acid: A Review. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020;78(9):1461-1466.
[28] 顾峥嵘,陈晓,翁蔚宗,等.次氯酸临床研究及使用进展[J].世界复合医学, 2015,1(4):336-339.
[29] SELKON JB, CHERRY GW, WILSON JM, et al. Evaluation of hypochlorous acid washes in the treatment of chronic venous leg ulcers. J Wound Care. 2006;15(1):33-37.
[30] WANG L, BASSIRI M, NAJAFI R, et al. Hypochlorous acid as a potential wound care agent: part I. Stabilized hypochlorous acid: a component of the inorganic armamentarium of innate immunity. J Burns Wounds. 2007;6(12):e5.
[31] LEBWOHL MG, DEL RJ, ABRAMOVITS W, et al. Pathways to managing atopic dermatitis: consensus from the experts. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2013;6(7 Suppl):S2-S18.
[32] SAKARYA S, GUNAY N, KARAKULAK M, et al. Hypochlorous Acid: an ideal wound care agent with powerful microbicidal, antibiofilm, and wound healing potency. Wounds. 2014;26(12):342-350.
[33] 王凡,郭建新,李明新,等.0.01%次氯酸局部滴眼治疗细菌性角膜溃疡的临床分析[J]. 国际眼科杂志,2019,19(12):2131-2134.
[34] 于佳,李志夫,张静,等.医院环境空气及物表次氯酸雾化消毒效果[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2021,31(4):616-619.
[35] 钱麟,史庆丰,许华,等.一种新型次氯酸消毒剂对纤维支气管镜的消毒效果[J].中国感染控制杂志,2020,19(7):662-665.
[36] ISHIHARA M, MURAKAMI K, FUKUDA K, et al. Stability of Weakly Acidic Hypochlorous Acid Solution with Microbicidal Activity. Biocontrol Sci. 2017;22(4): 223-227.
[37] 崔孔蛟,张玉发.彻底清创保留钉棒系统治疗腰椎内固定术后早期感染的临床观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(3):262-264.
[38] 俞国雨,徐杰,林院,等.保留内固定清创术治疗脊柱术后早期深部感染的临床疗效[J].中国医药指南,2018,16(36):148-149.
[39] MYERS TG, LIPOF JS, CHEN AF, et al. Antibiotic Stewardship for Total Joint Arthroplasty in 2020. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2020;28(18):e793-e802.
[40] 吴宇黎,王继芳,卢世璧,等.大剂量灌注冲洗对感染性假体表面生物膜中细胞外多粘质物质(ESS)的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2001,8(8):63-64.
|