Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (24): 3826-3832.doi: 10.12307/2022.561
Previous Articles Next Articles
CD1d-mediated inhibition of the nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3 inflammatory factor expression via signal regulatory protein-alpha
Xiang Mingzhi1, 2, Yuan Zilin2, 3, Wang Gang2, 3, Cheng Jie2, 4, Diao Bo2, 3, Liu Yueping2, 3
- 1Medical College, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430081, Hubei Province, China; 2Basic Medical Laboratory, General Hospital of Central Theater Command, Wuhan 430070, Hubei Province, China; 3Hubei Key Laboratory of Central Nervous System Tumor and Intervention, Wuhan 430070, Hubei Province, China; 4First School of Clinical Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangzhou Province, China
-
Received:2021-01-28Accepted:2021-03-04Online:2022-08-28Published:2022-01-24 -
Contact:Diao Bo, MD, Associate professor, Basic Medical Laboratory, General Hospital of Central Theater Command, Wuhan 430070, Hubei Province, China; Hubei Key Laboratory of Central Nervous System Tumor and Intervention, Wuhan 430070, Hubei Province, China Liu Yueping, Master, Associate chief technician, Basic Medical Laboratory, General Hospital of Central Theater Command, Wuhan 430070, Hubei Province, China; Hubei Key Laboratory of Central Nervous System Tumor and Intervention, Wuhan 430070, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Xiang Mingzhi, Master candidate, Physician, Medical College, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430081, Hubei Province, China; Basic Medical Laboratory, General Hospital of Central Theater Command, Wuhan 430070, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81971478, No. 81771691 (to DB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xiang Mingzhi, Yuan Zilin, Wang Gang, Cheng Jie, Diao Bo, Liu Yueping. CD1d-mediated inhibition of the nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3 inflammatory factor expression via signal regulatory protein-alpha[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3826-3832.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

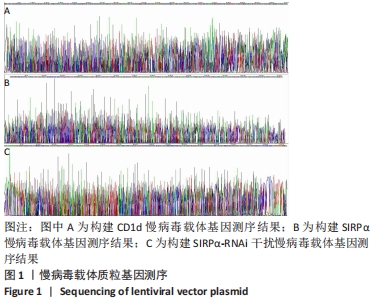
2.1 慢病毒构建及验证 2.1.1 慢病毒载体构建及病毒包装 将目的基因CD1d、SIRPα和SIRPα-RNAi干扰序列克隆至pHBLV-CMV-MCS-3FLAG-EF1-ZsGreen-T2A-puromycin、pHBLV-CMV-MCS-EF1-Zsgreen1-T2A-puromycin、GV493载体质粒。如图1A所示,质粒pHBLV-CMV-MCS-3FLAG-EF1-ZsGreen-T2A-puromycin在1-952的位置与CD1d目的基因序列完全一致;如图1B所示,质粒pHBLV-CMV-MCS-3FLAG-EF1-ZsGreen-T2A-puromycin在1-1288位置与SIRPα目的基因序列完全一致;如图1C所示,GV493质粒序列中含有与设计的SIRPα-RNAi干扰序列(CCG GGC AAG CAT TGA GAC AGG CAA ACT CGA GTT TGC CTG TCT CAA TGC TTG CTT TTT g)完全一致。以上说明慢病毒载体构建成功,可用于后续实验。"

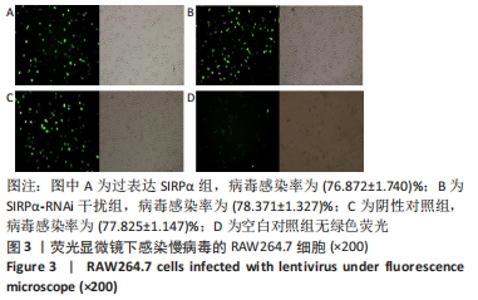
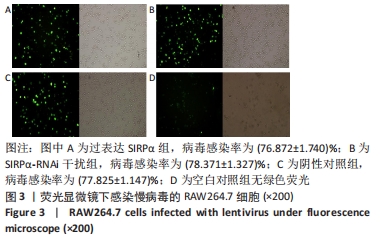
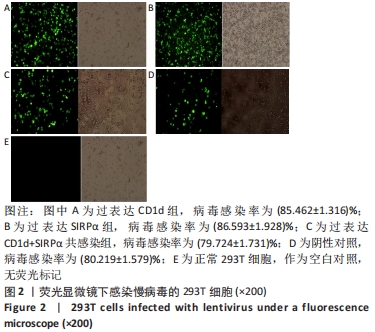
2.1.2 慢病毒构建验证 (1)荧光显微镜下观察慢病毒感染细胞的GFP荧光标记情况:生长状态良好的293T细胞、RAW264.7细胞,慢病毒感染48 h后,荧光显微镜下观察结果:添加目的基因实验组及阴性载体对照组,因有GFP标记,所以镜下可见绿色荧光。根据公式(病毒感染率=荧光细胞数/明视野细胞数×100% )计算感染率。①如图2所示,过表达CD1d组病毒感染率为(85.462±1.316)%;过表达SIRPα组病毒感染率为(86.593±1.928)%;过表达CD1d+SIRPα共感染组病毒感染率为(79.724±1.731)%;阴性对照组病毒感染率为(80.219±1.579)%。空白对照组因未添加目的基因片段,无荧光标记,所以荧光显微镜下无绿色荧光。②如图3所示,过表达SIRPα组病毒感染率为(76.872±1.740)%;SIRPα-RNAi干扰组病毒感染率为(78.371±1.327)%;阴性对照组病毒感染率为(77.825±1.147)%。空白对照组无绿色荧光。结果提示目的基因成功感染至细胞中,可以进行下一步实验。"
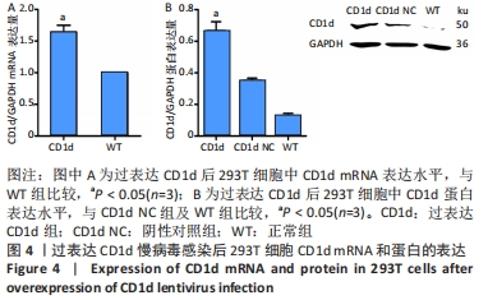
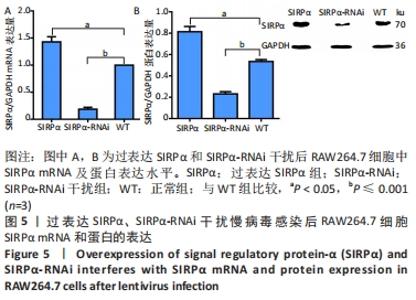
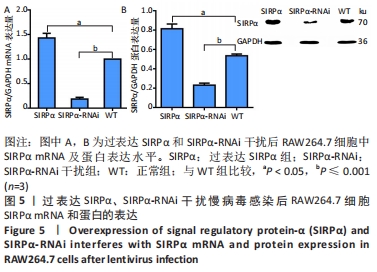
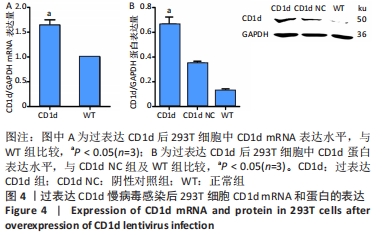
(2)RT-qPCR和Western blot检测基因及蛋白表达验证慢病毒感染情况:过表达CD1d、过表达SIRPα和SIRPα-RNAi干扰慢病毒感染细胞72 h后,结果如图4所示,过表达CD1d组CD1d mRNA及蛋白表达水平较对照组明显升高(mRNA:P < 0.001;蛋白:P < 0.001);如图5所示,过表达SIRPα组SIRPα mRNA及蛋白表达水平较对照组显著升高(mRNA:P=0.002;蛋白:P=0.001);SIRPα-RNAi干扰组SIRPα mRNA及蛋白表达水平较对照组显著下降(mRNA:P < 0.001;蛋白:P=0.001)。综上所述,慢病毒转染后达到靶向调控目的基因及蛋白的作用,成功构建过表达CD1d、过表达SIRPα和SIRPα-RNAi干扰慢病毒。"
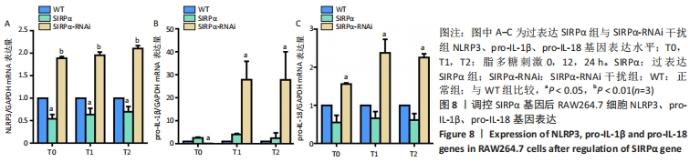
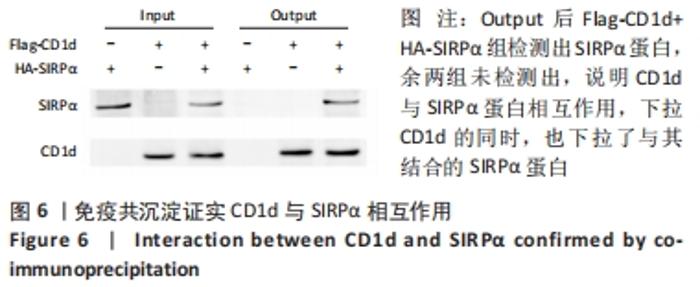
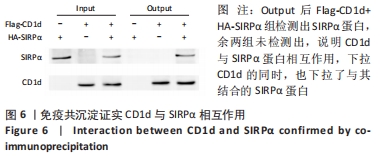
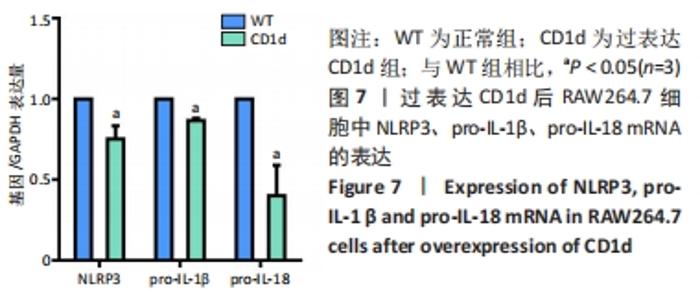
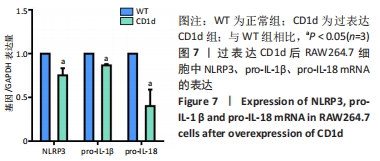
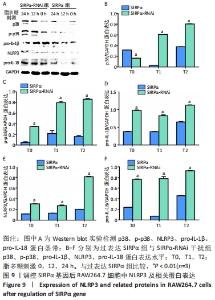
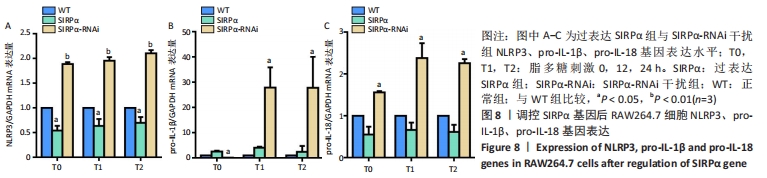
2.4 调控SIRPα基因表达后对下游基因及蛋白的影响 RT-qPCR实验结果显示,脂多糖刺激后,SIRPα-RNAi干扰组NLRP3、pro-IL-1β、pro-IL-18基因表达水平较对照组明显升高(NLRP3:P < 0.001; pro-IL-1β:P=0.019;pro-IL-18:P=0.001);过表达SIRPα组NLRP3基因表达水平较对照组明显降低(P=0.011),但pro-IL-1β、pro-IL-18基因表达水平较对照组无明显差异(pro-IL-1β:P=0.728;pro-IL-18:P=0.064),见图8,说明SIRPα基因能负向调控NLRP3、pro-IL-1β、pro-IL-18基因。琼脂糖凝胶电泳实验结果显示RT-qPCR扩增产物电泳条带位置与目的产物长度相符。"
| [1] KELLEY N, JELTEMA D, DUAN Y, et al. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: An Overview of Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(13):3328. [2] ZHANG T, DU H, FENG S, et al. NLRP3/ASC/Caspase-1 axis and serine protease activity are involved in neutrophil IL-1β processing during Streptococcus pneumoniae infection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;513(3):675-680. [3] THEOFANI E, SEMITEKOLOU M, MORIANOS I, et al. Targeting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Severe Asthma. J Clin Med. 2019;8(10):1615. [4] YAO ST, CAO F, CHEN JL, et al. NLRP3 is Required for Complement-Mediated Caspase-1 and IL-1beta Activation in ICH. J Mol Neurosci. 2017;61(3):385-395. [5] ZHEN Y, ZHANG H. NLRP3 Inflammasome and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front Immunol. 2019;10:276. [6] GUO S, YANG C, DIAO B, et al. The NLRP3 Inflammasome and IL-1beta Accelerate Immunologically Mediated Pathology in Experimental Viral Fulminant Hepatitis. PLoS Pathog. 2015;11(9):e1005155. [7] MELUM E, JIANG X, BAKER KD, et al. Control of CD1d-restricted antigen presentation and inflammation by sphingomyelin. Nat Immunol. 2019;20(12):1644-1655. [8] INUKI S, HIRATA N, KASHIWABARA E, et al. Polar functional group-containing glycolipid CD1d ligands modulate cytokine-biasing responses and prevent experimental colitis. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):15766. [9] LEE C, HONG SN, KIM YH. A glycolipid adjuvant, 7DW8-5, provides a protective effect against colonic inflammation in mice by the recruitment of CD1d-restricted natural killer T cells. Intest Res. 2020;18(4):402-411. [10] CUI S, WANG C, BAI W, et al. CD1d1 intrinsic signaling in macrophages controls NLRP3 inflammasome expression during inflammation. Sci Adv. 2020;6(43): eaaz7290. [11] BARCLAY AN, BROWN MH. The SIRP family of receptors and immune regulation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6(6):457-464. [12] DE VOS AF, VAN DER POLL T. SIRP-α instructs alveolar macrophages to stop eating after pneumonia. Nat Immunol. 2020;21(6):601-603. [13] ZHANG W, HUANG Q, XIAO W, et al. Advances in Anti-Tumor Treatments Targeting the CD47/SIRPalpha Axis. Front Immunol. 2020;11:18. [14] LOGTENBERG MEW, SCHEEREN FA, SCHUMACHER TN. The CD47-SIRPalpha Immune Checkpoint. Immunity. 2020;52(5):742-752. [15] VEILLETTE A, TANG Z. Signaling Regulatory Protein (SIRP)α-CD47 Blockade Joins the Ranks of Immune Checkpoint Inhibition. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(12):1012-1014. [16] HE Y, ZENG MY, YANG D, et al. NEK7 is an essential mediator of NLRP3 activation downstream of potassium efflux. Nature. 2016;530(7590):354-357. [17] BRIARD B, FONTAINE T, SAMIR P, et al. Galactosaminogalactan activates the inflammasome to provide host protection. Nature. 2020;588(7839):688-692. [18] MAGUPALLI VG, NEGRO R, TIAN Y, et al. HDAC6 mediates an aggresome-like mechanism for NLRP3 and pyrin inflammasome activation. Science. 2020; 369(6510):eaas8995. [19] YOUM YH, NGUYEN KY, GRANT RW, et al. The ketone metabolite β-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory disease. Nat Med. 2015;21(3):263-269. [20] CAMILLI G, BOHM M, PIFFER AC, et al. β-Glucan-induced reprogramming of human macrophages inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in cryopyrinopathies. J Clin Invest. 2020;130(9):4561-4573. [21] YU X, LAN P, HOU X, et al. HBV inhibits LPS-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation and IL-1β production via suppressing the NF-κB pathway and ROS production. J Hepatol. 2017;66(4):693-702. [22] WARD R, LI W, ABDUL Y, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition with MCC950 improves diabetes-mediated cognitive impairment and vasoneuronal remodeling after ischemia. Pharmacol Res. 2019;142:237-250. [23] LIU D, CHEN C, WANG D, et al. Effect of sericin on the p38MAPK signaling pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome in the kidney of type 2 diabetic rats. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(6):267. [24] SHAO BZ, XU ZQ, HAN BZ, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome and its inhibitors: a review. Front Pharmacol. 2015;6:262. [25] RAMESH A, KUMAR S, NANDI D, et al. CSF1R- and SHP2-Inhibitor-Loaded Nanoparticles Enhance Cytotoxic Activity and Phagocytosis in Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Adv Mater. 2019;31(51):e1904364. [26] RAY M, LEE YW, HARDIE J, et al. CRISPRed Macrophages for Cell-Based Cancer Immunotherapy. Bioconjug Chem. 2018;29(2):445-450. [27] HAYAT SMG, BIANCONI V, PIRRO M, et al. CD47: role in the immune system and application to cancer therapy. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020;43(1):19-30. [28] ORONSKY B, CARTER C, REID T, et al. Just eat it: A review of CD47 and SIRP-alpha antagonism. Semin Oncol. 2020;47(2-3):117-124. [29] HUANG CY, YE ZH, HUANG MY, et al. Regulation of CD47 expression in cancer cells. Transl Oncol. 2020;13(12):100862. [30] KONG XN, YAN HX, CHEN L, et al. LPS-induced down-regulation of signal regulatory protein {alpha} contributes to innate immune activation in macrophages. J Exp Med. 2007;204(11):2719-2731. [31] LI XJ, GOODWIN CB, NABINGER SC, et al. Protein-tyrosine phosphatase Shp2 positively regulates macrophage oxidative burst. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(7):3894-3909. [32] LI X, ZHOU W, LIANG Y, et al. The Immunotherapeutic Effect of SIRPα-Silenced DCs against Cervical Cancer. J Immunol Res. 2020;2020:1705187. [33] KRISHNAN SM, SOBEY CG, LATZ E, et al. IL-1beta and IL-18: inflammatory markers or mediators of hypertension? Br J Pharmacol. 2014;171(24):5589-5602. [34] HARA K, SENGA T, BISWAS MH, et al. Recovery of anoikis in Src-transformed cells and human breast carcinoma cells by restoration of the SIRP α1/SHP-2 signaling system. Cancer Res. 2011;71(4):1229-1234. [35] BRUTKIEWICZ RR, YUNES-MEDINA L, Liu J. Immune evasion of the CD1d/NKT cell axis. Curr Opin Immunol. 2018;52:87-92. [36] SHYANTI RK, SEHRAWAT A, SINGH SV, et al. Zerumbone modulates CD1d expression and lipid antigen presentation pathway in breast cancer cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 2017;44:74-84. [37] NI C, WU P, WU X, et al. Thymosin alpha1 enhanced cytotoxicity of iNKT cells against colon cancer via upregulating CD1d expression. Cancer Lett. 2015;356(2 Pt B):579-588. [38] KOHLGRUBER AC, DONADO CA, LAMARCHE NM, et al. Activation strategies for invariant natural killer T cells. Immunogenetics. 2016;68(8):649-663. |
| [1] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [2] | Tang Wenjing, Wu Siyuan, Yang Chen, Tao Xi. Inflammatory responses in post-stroke depression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1278-1285. |
| [3] | Gao Yujin, Peng Shuanglin, Ma Zhichao, Lu Shi, Cao Huayue, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. Osteogenic ability of adipose stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 999-1004. |
| [4] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [5] | Wang Jifang, Bao Zhen, Qiao Yahong. miR-206 regulates EVI1 gene expression and cell biological behavior in stem cells of small cell lung cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1027-1031. |
| [6] | Liu Jin, Li Zhen, Hao Huiqin, Wang Ze, Zhao Caihong, Lu Wenjing. Ermiao san aqueous extract regulates proliferation, migration, and inflammatory factor expression of fibroblast-like synovial cells in collagen-induced arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 688-693. |
| [7] | Li Weiming, Xu Qingwen, Li Yijun, Sun Yanbo, Cui Jin, Xu Pengyuan . Deep seawater promotes wound healing in diabetic mice by activating PI3K/Akt pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 724-729. |
| [8] | Li Jiajun, Xia Tian, Liu Jiamin, Chen Feng, Chen Haote, Zhuo Yinghong, Wu Weifeng. Molecular mechanism by which icariin regulates osteogenic signaling pathways in the treatment of steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 780-785. |
| [9] | Liu Yiyi, Qiu Junqiang, Yi Longyan, Zhou Cailiang. Effect of resistance training on interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in middle-age and elderly people: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 804-812. |
| [10] | Mo Weibin, Huang Tianchang, Zeng Zhiwei, Yan Linbo. Effects of Pueraria lobata flavonoids on expressions of beta-catenin and glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in the brain of rats undergoing exhaustive exercise after long endurance exercise [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 736-741. |
| [11] | Jin Ke, Wu Xiaoling, Luo Xiaoling, Xu Pengfei, Xu Xiaomei. Osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells under estrogen and crosstalk between the two pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3886-3891. |
| [12] | Chen Qiaoling, Bai Yiguang, Liu Kang, Lin Tao, Luo Xuwei. Osteoblast differentiation after conditional knockout of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 gene from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3785-3789. |
| [13] | Cai Zhiguo, Du Shasha, Yang Kun, Zhao Na, Liu Qi. Lipopolysaccharides mediate autophagy of mouse insulinoma βtc6 cells in high glucose state [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(20): 3127-3132. |
| [14] | Yang Lin, Wu Yao, Zhou Binbin. Interaction of Nogo-A/NgR signaling pathway and NGF/TrkA signaling pathway during the regeneration of injured spinal cord nerve axons [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(20): 3220-3224. |
| [15] | Lyu Yuhu, Cheng Lin, Lin Wentao, Peng Fenglin. Role and regulatory mechanism of glycophagy in glycogen metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(20): 3243-3249. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||