Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (17): 2713-2719.doi: 10.12307/2022.540
Previous Articles Next Articles
Establishment and evaluation of neurogenic bladder model in rats with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Han Xuke1, 2, Chen Yiding1, 2, Chen Huizhen1, 2, Yang Xiaomei1. 2, Hong Peipei1, 2, Chen Qiu1, 2
- 1Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610072, Sichuan Province, China; 2Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2021-03-29Revised:2021-05-07Accepted:2021-09-27Online:2022-06-18Published:2021-12-24 -
Contact:Chen Qiu, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610072, Sichuan Province, China; Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Han Xuke, MD candidate, Physician, Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610072, Sichuan Province, China; Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:Chengdu Major Science and Technology Application Demonstration Project, No. 2019-YF09-00094-SN (to CQ); Central Medical Service and Guarantee Capability Improvement Subsidy Fund, No. CYW2019079 (to CQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Han Xuke, Chen Yiding, Chen Huizhen, Yang Xiaomei, Hong Peipei, Chen Qiu. Establishment and evaluation of neurogenic bladder model in rats with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(17): 2713-2719.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
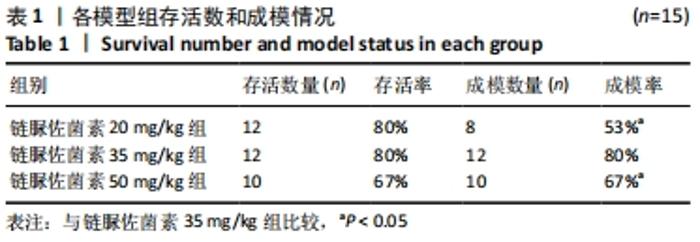
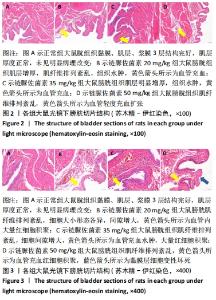
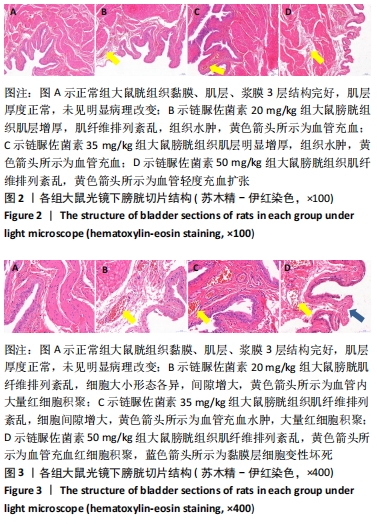
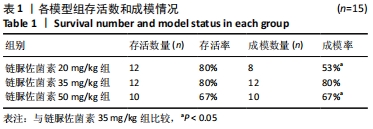
2.1 实验动物数量分析 选取雄性SD大鼠55只,分为4组,其中正常组10只,在整个实验过程中无脱失;链脲佐菌素20,35,50 mg/kg分别15只,用于2型糖尿病建模。其中链脲佐菌素20,35 mg/kg组在造模过程中分别死亡3只,链脲佐菌素50 mg/kg组在造模过程中死亡5只,剩余34只全部纳入实验结果进行分析。 2.2 不同剂量链脲佐菌素对成模率和存活率的影响 3个模型组入组各15只大鼠,在第4周链脲佐菌素注射后,链脲佐菌素20 mg/kg组分别于第5,6,7周死亡大鼠1只,至第8周检测时存活12只;链脲佐菌素35 mg/kg组于第5周死亡大鼠2只,第7周死亡1只,至第8周检测时存活12只;链脲佐菌素50 mg/kg组于第5周死亡大鼠3只,第6,7周各死亡1只,至第8周检测时存活10只。相较于链脲佐菌素35 mg/kg组(中间剂量),链脲佐菌素50 mg/kg组(高剂量)大鼠存活率较低(P < 0.05)。而成模率方面,相较于链脲佐菌素35 mg/kg组,链脲佐菌素20 mg/kg组(低剂量)大鼠的成模率较低(P < 0.05),见表1。通过统计分析发现,链脲佐菌素35 mg/kg组成模率和存活率均较高,稳定性较好。"
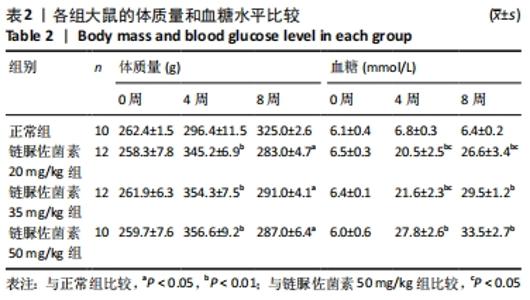
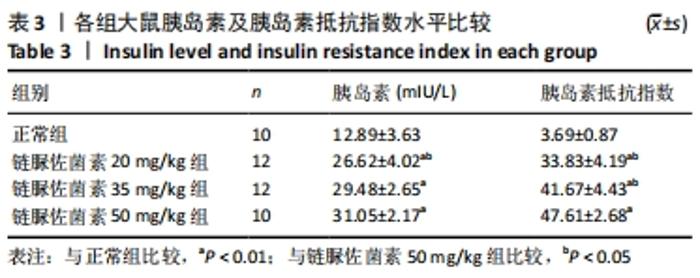
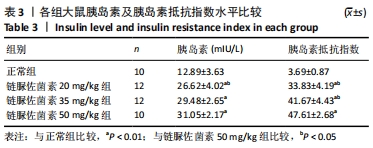
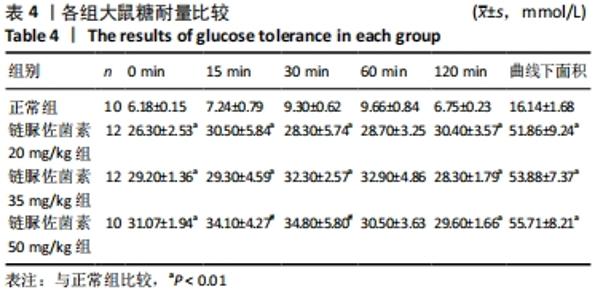
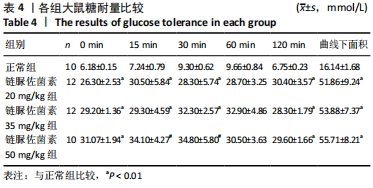
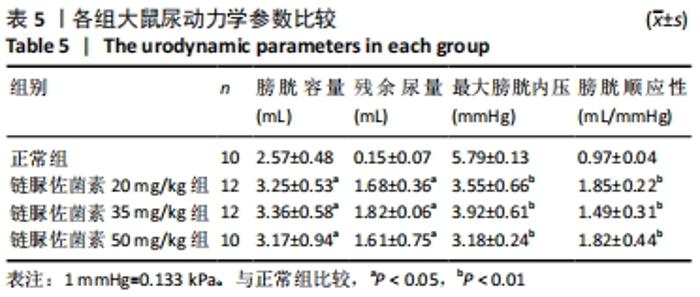
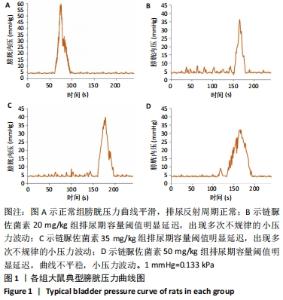
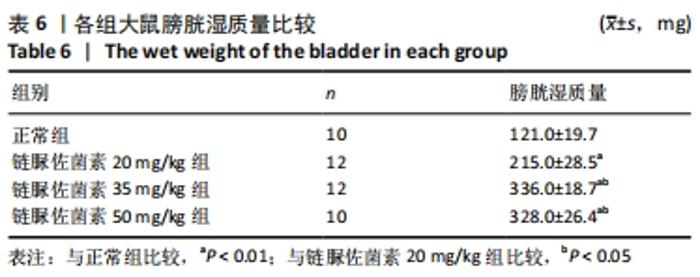
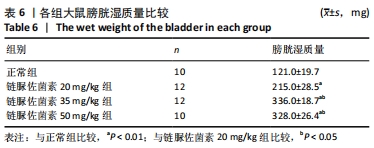
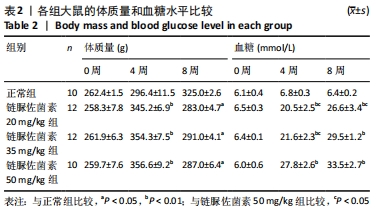
2.3 一般情况 与正常组相比,模型组大鼠建模前初始体质量无明显差异。正常组大鼠体质量增加,血糖平稳;模型组大鼠在链脲佐菌素注射3 d后,出现多饮、多尿、多食的典型糖尿病症状。第4 周时模型组大鼠精神萎靡,活动度降低,体质量明显升高(P < 0.01),空腹血糖升高(P < 0.01);与正常组大鼠相比,第8周时模型组大鼠皮毛光泽度晦暗,活动度及精神状态明显变差,体质量下降(P < 0.05),空腹血糖明显升高(P < 0.01),均≥16.7 mmol/L。链脲佐菌素20,35,50 mg/kg组间体质量相比,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);但在第4周时,链脲佐菌素50 mg/kg组的血糖明显高于另外两组(P < 0.05);第8周时,链脲佐菌素35 mg/kg组血糖水平上升,与链脲佐菌素50 mg/kg组相比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),仅链脲佐菌素20 mg/kg组血糖水平明显低于链脲佐菌素50 mg/kg组(P < 0.05),见表2。"
| [1] COLE JB, FLOREZ JC. Genetics of diabetes mellitus and diabetes complications. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020;16(7):377-390. [2] Ramirez AVG, Filho DR, de Sá LBPC. Melatonin and its relationships with diabetes and obesity: a literature review. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2021; 17(7):e072620184137. [3] AMERICAN DIABETES ASSOCIATION. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2019. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(Suppl 1):S13-S28. [4] HAN X, GAO Y, WANG S, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on diabetic neurogenic bladder: A randomized controlled trial protocol. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(17):e19843. [5] DANESHGARI F, MOORE C. Diabetic uropathy. Semin Nephrol. 2006; 26(2):182-185. [6] 陈蓉琼,方克伟. 糖尿病膀胱的发病机制及临床诊疗进展[J]. 临床荟萃,2018,33(7):641-644. [7] YUAN Z, TANG Z, HE C, et al. Diabetic cystopathy: A review. J Diabetes. 2015;7(4):442-447. [8] LIFFORD KL, CURHAN GC, HU FB, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and risk of developing urinary incontinence. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005;53(11): 1851-1857. [9] 彭茜,李舍予,安振梅,等. 美国泌尿协会症状指数评分在女性2型糖尿病神经性膀胱患者中的应用价值研究[J]. 四川大学学报(医学版),2019,50(4):566-570. [10] LIANG CC, SHAW SS, HUANG YH, et al. Improvement in bladder dysfunction after bladder transplantation of amniotic fluid stem cells in diabetic rats. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):2105. [11] OGER-ROUSSEL S, BEHR-ROUSSEL D, CAISEY S, et al. Bladder and erectile dysfunctions in the Type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2014;306(2):R108-R117. [12] ISLAM MS, LOOTS DT. Experimental rodent models of type 2 diabetes: a review. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2009;31(4):249-261. [13] DONG K, NI H, WU M, et al. ROS-mediated glucose metabolic reprogram induces insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;476(4):204-211. [14] REED MJ, MESZAROS K, ENTES LJ, et al. A new rat model of type 2 diabetes: the fat-fed, streptozotocin-treated rat. Metabolism. 2000; 49(11):1390-1394. [15] KLEE NS, MORELAND RS, KENDIG DM. Detrusor contractility to parasympathetic mediators is differentially altered in the compensated and decompensated states of diabetic bladder dysfunction. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019;317(2):F388-F398. [16] 曹石金,何朝辉,李逊,等. 糖尿病大鼠膀胱结构与功能的改变[J]. 广东医学,2012,33(16):2372-2375. [17] 陈潮江,周兴,孔桃红,等. 链脲佐菌素复制大鼠糖尿病神经源性膀胱模型[J]. 中国现代医学杂志,2013,23(32):18-21. [18] 方元龙,周兴,陈潮江,等. 链尿佐菌素制备糖尿病神经源性膀胱大鼠模型[J]. 解剖学研究,2013,35(6):439-442. [19] TSOUNAPI P, HONDA M, HIKITA K, et al. Oxidative Stress Alterations in the Bladder of a Short-period Type 2 Diabetes Rat Model: Antioxidant Treatment Can Be Beneficial for the Bladder. In Vivo. 2019;33(6): 1819-1826. [20] LI XF, ZHANG SH, LIU GF, et al. miR-363 Alleviates Detrusor Fibrosis via the TGF-beta1/Smad Signaling Pathway by Targeting Col1a2 in Rat Models of STZ-Induced T2DM. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;22: 1142-1153. [21] 刘玉琳,李国泰. 高压氧、振动训练与虾青素联合干预糖尿病骨质疏松模型大鼠骨密度、糖代谢及氧化应激的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(20):3117-3124. [22] LE FLOCH JP, ESCUYER P, BAUDIN E, et al. Blood glucose area under the curve. Methodological aspects. Diabetes Care. 1990;13(2):172-175. [23] 王梅,刘杰. 2型糖尿病患者慢性并发症现状调查及影响因素[J]. 中国卫生工程学,2020,19(2):228-229. [24] LIN TL, CHEN GD, CHEN YC, et al. Aging and recurrent urinary tract infections are associated with bladder dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2012;51(3):381-386. [25] MANACK A, MOTSKO SP, HAAG-MOLKENTELLER C, et al. Epidemiology and healthcare utilization of neurogenic bladder patients in a US claims database. Neurourol Urodyn. 2011;30(3):395-401. [26] 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2017年版)[J]. 中国实用内科杂志,2018, 38(4):292-344. [27] LIN M, AI J, HARDEN SW, et al. Impairment of baroreflex control of heart rate and structural changes of cardiac ganglia in conscious streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic mice. Auton Neurosci. 2010; 155(1-2):39-48. [28] GHEIBI S, KASHFI K, GHASEMI A. A practical guide for induction of type-2 diabetes in rat: Incorporating a high-fat diet and streptozotocin. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;95:605-613. [29] 刘丽娟,张会凯,李辉,等. 丹芪缩尿方结合西医常规疗法对糖尿病神经源性膀胱尿流动力学的影响[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘, 2019,19(92):11-12. [30] 王云汉,杨进. 糖尿病膀胱病研究进展[J]. 现代临床医学,2012,38(2): 83-84. [31] DING L, SONG T, YI C, et al. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) improves the diabetic cytopathy (DCP) via up-regulation of CGRP and cAMP. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57477. [32] HAN X, GAO Y, YIN X, et al. Effect of Electroacupuncture on Bladder Dysfunction via Regulation of MLC and MLCK Phosphorylation in a Rat Model of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021:5558890. [33] GOU X, WU J, HUANG M, et al. microRNA-128 mediates CB1 expression and regulates NF-KB/p-JNK axis to influence the occurrence of diabetic bladder disease. J Transl Med. 2020;18(1):284. [34] YI CR, WEI ZQ, DENG XL, et al. Effects of coffee and caffeine on bladder dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2006;27(8):1037-1043. [35] 汪悦,杨阳,邬颖华. 高能量饮食联合STZ诱导2型糖尿病肾病动物模型研究进展[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘,2018,18(92):84-86. [36] KLEE NS, MORELAND RS, KENDIG DM. Detrusor contractility to parasympathetic mediators is differentially altered in the compensated and decompensated states of diabetic bladder dysfunction. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019;317(2):F388-F398. [37] 肖艳红,谷佳琦,杨晔娟,等. 高脂高糖饲料联合STZ诱导2型糖尿病大鼠模型STZ最佳剂量探讨[J]. 承德医学院学报,2015,32(5): 376-378. [38] 唐艺丹,王鲜忠,张姣姣. Ⅱ型糖尿病动物模型构建的研究进展[J]. 中国实验动物学报,2020,28(6):870-876. [39] LEIRIA LO, SOLLON C, CALIXTO MC, et al. Role of PKC and CaV1.2 in detrusor overactivity in a model of obesity associated with insulin resistance in mice. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e48507. [40] WINZELL MS, AHREN B. The high-fat diet-fed mouse: a model for studying mechanisms and treatment of impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2004;53 Suppl 3:S215-S219. [41] ZHANG H, QIU X, SHINDEL AW, et al. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells ameliorate diabetic bladder dysfunction in a type II diabetic rat model. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(9):1391-1400. [42] ZHANG M, LV XY, LI J, et al. The characterization of high-fat diet and multiple low-dose streptozotocin induced type 2 diabetes rat model. Exp Diabetes Res. 2008;2008:704045. [43] 段丽君,郭洪涛,商书霞,等. 膀胱残余尿量测定联合IPSS初步筛查糖尿病神经源性膀胱[J]. 中国医药导报,2020,17(12):76-79. [44] 张祥,许天源,夏磊磊,等. 原位膀胱癌大鼠建模方法比较及超声鉴定方法[J]. 现代泌尿生殖肿瘤杂志,2015,7(2):99-103. [45] 冯建华,邓丽萍,曾祥建. 糖尿病大鼠膀胱逼尿肌超微结构的改变[J]. 中国热带医学,2012,12(1):15-17. [46] ELLENBROEK JH, ARIOGLU IE, MICHEL MC. A systematic review of urinary bladder hypertrophy in experimental diabetes: Part 2. Comparison of animal models and functional consequences. Neurourol Urodyn. 2018;37(8):2346-2360. [47] YESILYURT ZE, ERDOGAN BR, KARAOMERLIOGLU I, et al. Urinary Bladder Weight and Function in a Rat Model of Mild Hyperglycemia and Its Treatment With Dapagliflozin. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:911. [48] KENDIG DM, ETS HK, MORELAND RS. Effect of type II diabetes on male rat bladder contractility. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016;310(9): F909-F922. |
| [1] | Chen Xianghe, Liu Bo, Yang Kang, Lu Pengcheng, Yu Huilin. Treadmill exercise improves the myocardial fibrosis of spontaneous type 2 diabetic mice: an exploration on the functional pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1210-1215. |
| [2] | Zeng Xinyu, Chen Xianghe, Liu Bo, Lu Pengcheng, Jin Shengjie, Li Wenxiu, Tian Zhikai, Sun Changliang. Mechanism of exercise improving bone metabolism in type 2 diabetics mellitus based on "Muscle-Bone" Crosstalk [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 289-295. |
| [3] | Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| [4] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [5] |
Li Ying, Lin Wentao, Weng Xiquan.
Effects of different exercise intensities on visfatin level and glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4196-4200. |
| [6] |
Liu Huimin, Leng Jun, Guo Wen, Fang Xiaolei, Zhang Chen, Wei Fangyue.
The rules of acupoint selection in the treatment of neurogenic bladder after spinal cord injury with acupuncture and moxibustion: based on data mining technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4237-4242. |
| [7] | Liu Yuetong, Wang Qin, Yang Ye, Zhu Jun, Abulikemu•Tuerdi. Effects of 1,25(OH)2D3 on microRNA-130b and transforming growth factor beta 1 in renal tissue of rat models of diabetic nephropathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(2): 248-253. |
| [8] | Liang Min, Wang Hainiu, Huang Peng, Zhu Weihua, Li Shunchang . Systematic review and meta-analysis of effect of resistance exercise on glucose and lipid metabolism disorder in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(35): 5718-5726. |
| [9] | Zhao Dalin1, Li Jing1, Ma Tie1, Gao Haining1, Liu Haopeng1, Zhang Shicheng1, Xu Sitong1, Xiao Jiayu1, Li Yiran1, Yan Shengnan1, Chang Bo1, 2. Changes of phosphoinositide 3-kinase-protein kinase B signaling pathway in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes rat models after 8-week aerobic exercise [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(23): 3660-3666. |
| [10] | Jin Shanhu, Hu Yazhe. Effect of early different intensities of exercise on the modelling rate and blood glucose level of rats with late-stage type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(19): 3092-3096. |
| [11] | Wang Li-xin, Ji Jun, Gao Jia-shuo, Xiao Hong. Uroflowmeter calibration device: standard water flow and its stability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(22): 3569-3574. |
| [12] | Liu Wen-qi, Dai Hong-yan, Xing Ming-qing, Guan Jun, Wang Yan-ping. Establishment of animal models of diabetic cardiomyopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(27): 4265-4270. |
| [13] | Ding Liu-cheng, Huang Yi, Wei Zhong-qing . Research and application of urethral sling placement on neurogenic incontinence [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(44): 7791-7796. |
| [14] | Wang Fang, Li Yong, Su Ying-jun, Wang Na, Xu Chen, Zhou Bo. Application of low-dose insulin in diabetes refractory wound healing: Epithelialization, collagen deposition and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(20): 3650-3657. |
| [15] | Xu Jin-hua1, Pan Wen2, Gong Jian, Lu Suo-xing, Guan Shu-hui, Wang Dong-xia, Piao Zhe, Li Ning, Li Jing-shu. Bariatric surgery for non-obese type 2 diabetes mellitus in Mainland China: A meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(15): 2843-2850. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||