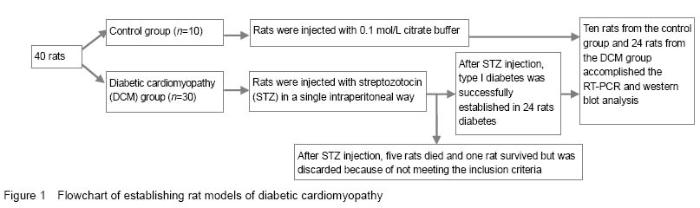
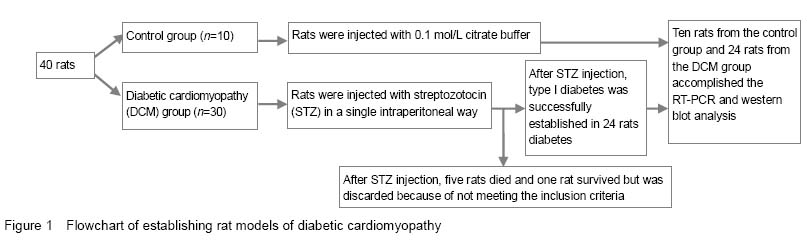
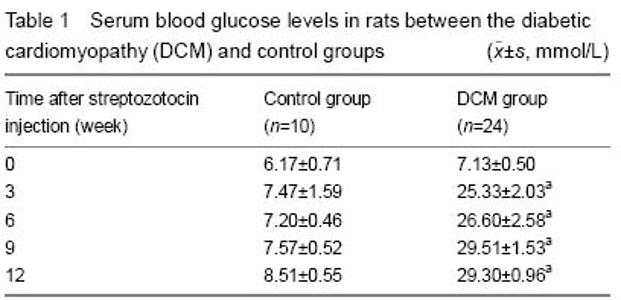
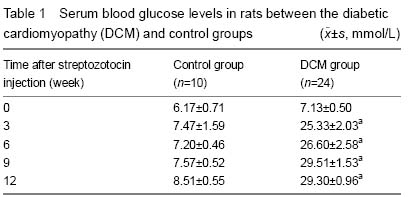
| [1] |
Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang.
High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211.
|
| [2] |
Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei.
Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001.
|
| [3] |
Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang.
Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031.
|
| [4] |
Nie Huijuan, Huang Zhichun.
The role of Hedgehog signaling pathway in transforming growth factor beta1-induced myofibroblast transdifferentiation
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 754-760.
|
| [5] |
Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao.
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993.
|
| [6] |
Xie Wenjie, Zhou Gang, Xie Jinmei, Liu Jiao, Li Pengfei, Yang Fan, Cui Di.
Mechanism of myocardial oxidative damage in a rat model of one-time exhaustive exercise
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 247-252.
|
| [7] |
Zhang Lei, Yan Yu, Liu Yin, Xu Long, Yang Xinglei, Liu Yujia.
An 8-week aerobic exercise improves obesity-induced myocardial fibrosis: role of nuclear factor-erythroid 2 p45-related factor 2 pathway
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2650-2656.
|
| [8] |
Hu Sheng, Yuan Haiyan, Hu Meng, Jin Shanhu.
Effects of moderate treadmill exercise on alpha-smooth muscle actin and type IV collagen in the liver of type 2 diabetic rats
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1723-1727.
|
| [9] |
Wang Hongshu, Han Shen, Liu Zu, Li Xiaofang, Zhong Chongbin, Li Lifeng, Li Yaxiong, Jiang Lihong.
Transcription factor NKX2-5: molecular structure and biological function in regulating cardiovascular precursor cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 108-115.
|
| [10] |
Li Xuan, Lu Min, Li Mingxing, Ao Meng, Tang Linmei, Zeng Zhen, Hu Jingwei, Huang Zhiqiang, Xuan Jiqing.
In vitro multi-modal imaging of magnetic
targeted nanoparticles and their targeting effect on hepatic stellate cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 566-571.
|
| [11] |
Zhu Shoulei, Yang Jiandong, Cai Jun, Zhang Yujie, Tian Yuan.
Mechanism by which allicin inhibits proliferation and migration but promotes apoptosis of human fibroblasts
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(35): 5662-5667.
|
| [12] |
Cheng Xue, Fang Hong, Zhang Yunke, Wu Yingen.
Interventional mechanism of Feibi prescription on extracellular matrix transformation in a mouse model of pulmonary fibrosis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 5038-5043.
|
| [13] |
Li Qinwen, Liang Jie, Wang Dongmei, Shang Zhenghui.
Fibrotic changes in rat dorsal root ganglion following chronic sciatic nerve compression
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(29): 4686-4691.
|
| [14] |
Li Ying, Lin Wentao, Weng Xiquan.
Effects of different exercise intensities on visfatin level and glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetic rats
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4196-4200.
|
| [15] |
Wu Zhen, Ma Wei, Zang Chenghao, Liu Kuangpin, Liu Wei, Liu Jie, Liang Yu, Li Chunyan, Chen Zhiming, Ru Jin, Fan Chuming, Yang Jinwei, Guo Jianhui, Li Liyan.
Protective effect of notoginsenoside R1 on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in rats
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4213-4217.
|