Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (19): 2997-3003.doi: 10.12307/2022.377
Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparison of biological characteristics of two kinds of primary isolated human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells under three-dimensional culture
Chen Siming, Hu Jiawei, Li Lili, Wu Yongqiang, Peng Weijie
- Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China
-
Received:2021-03-10Revised:2021-04-17Accepted:2021-08-04Online:2022-07-08Published:2021-12-28 -
Contact:Peng Weijie, MD, Professor, Master, Doctoral supervisor, Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China -
About author:Chen Siming, Master candidate, Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81860327 (to PWJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Siming, Hu Jiawei, Li Lili, Wu Yongqiang, Peng Weijie. Comparison of biological characteristics of two kinds of primary isolated human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells under three-dimensional culture[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 2997-3003.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
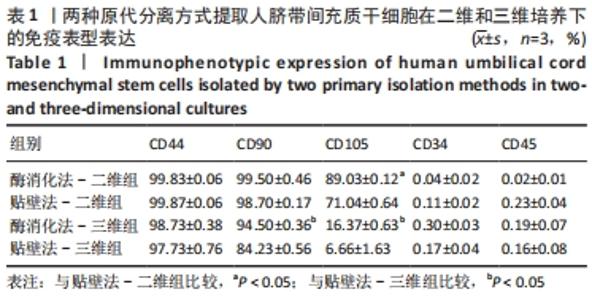
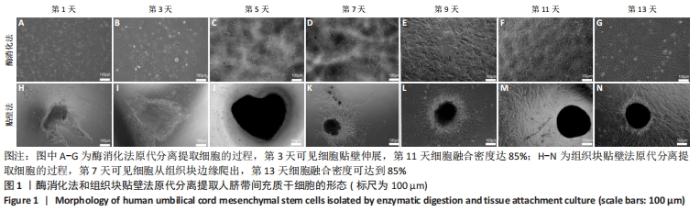
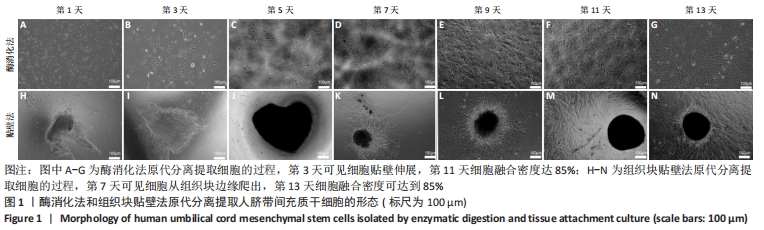
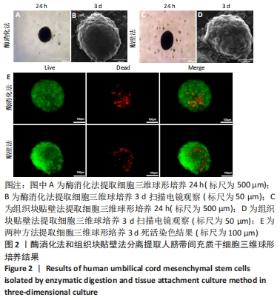
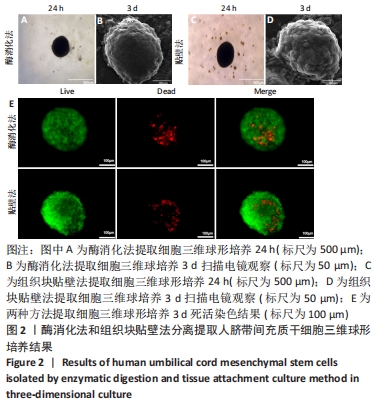
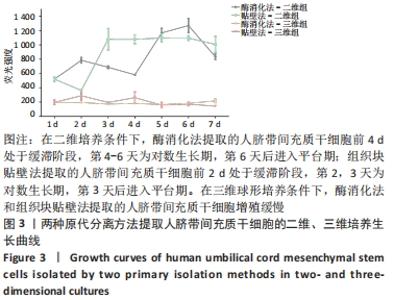
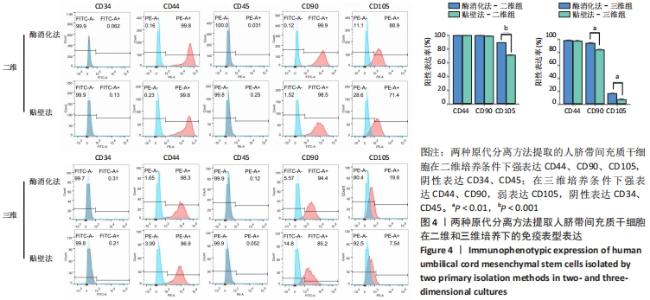
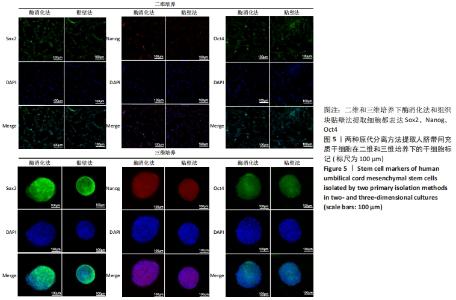
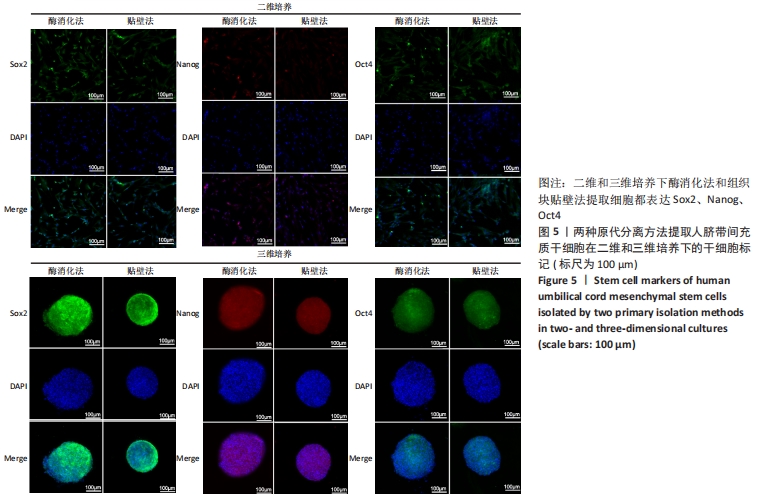
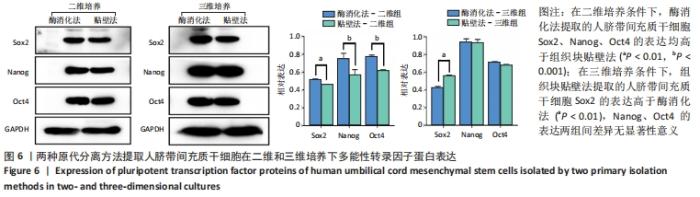
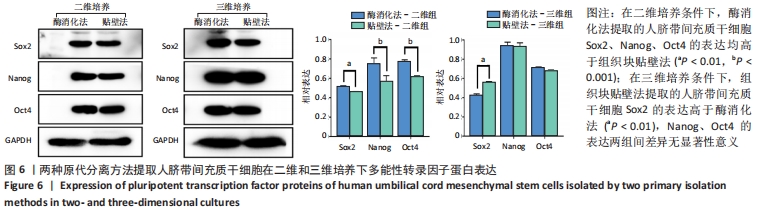
2.3 人脐带间充质干细胞免疫表型表达 两种原代分离方法提取的人脐带间充质干细胞在二维培养条件下强表达CD44、CD90、CD105,阴性表达CD34、CD45。二维培养下CD44、CD90的表达无差异;酶消化法CD105的表达(89.03±0.12)%高于组织块贴壁法(71.04±0.64)%,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。在三维培养条件下强表达CD44、CD90,弱表达CD105,阴性表达CD34、CD45。三维培养下CD44的表达无差异;酶消化法CD90的表达(94.50±0.36)%高于组织块贴壁法(84.23±0.56)%,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);酶消化法CD105的表达(16.37±0.63)%高于组织块贴壁法(6.66±1.63)%,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表1,图4。"
| [1] ULLAH M, LIU DD, THAKOR AS. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Homing: Mechanisms and Strategies for Improvement. iScience. 2019;15:421-438. [2] ZAKRZEWSKI W, DOBRZYŃSKI M, SZYMONOWICZ M, et al. Stem cells: past, present, and future. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):68. [3] GURUSAMY N, ALSAYARI A, RAJASINGH S, et al. Adult Stem Cells for Regenerative Therapy. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2018;160:1-22. [4] CLEVERS H. STEM CELLS. What is an adult stem cell? Science. 2015; 350(6266): 1319-1320. [5] WITKOWSKA-ZIMNY M, WROBEL E. Perinatal sources of mesenchymal stem cells: Wharton’s jelly, amnion and chorion. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2011;16(3):493-514. [6] ABBASPANAH B, MOMENI M, EBRAHIMI M, et al. Advances in perinatal stem cells research: a precious cell source for clinical applications. Regen Med. 2018; 13(5):595-610. [7] MUSHAHARY D, SPITTLER A, KASPER C, et al. Isolation, cultivation, and characterization of human mesenchymal stem cells. Cytometry A. 2018;93(1):19-31. [8] SALEHINEJAD P, ALITHEEN NB, ALI AM, et al. Comparison of different methods for the isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord Wharton’s jelly. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2012;48(2): 75-83. [9] HAN YF, TAO R, SUN TJ, et al. Optimization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell isolation and culture methods. Cytotechnology. 2013;65(5):819-827. [10] GUILAK F, COHEN DM, ESTES BT, et al. Control of stem cell fate by physical interactions with the extracellular matrix. Cell Stem Cell. 2009; 5(1):17-26. [11] KNIGHT E, PRZYBORSKI S. Advances in 3D cell culture technologies enabling tissue-like structures to be created in vitro. J Anat. 2015; 227(6):746-756. [12] LEE YB, KIM EM, BYUN H, et al. Engineering spheroids potentiating cell-cell and cell-ECM interactions by self-assembly of stem cell microlayer. Biomaterials. 2018;165:105-120. [13] IMAMURA A, KAJIYA H, FUJISAKI S, et al. Three-dimensional spheroids of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells promote osteogenesis by activating stemness and Wnt/beta-catenin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020; 523(2):458-464. [14] 王菲,周洪,郭昱成,等.原代人脐带间充质干细胞培养方法的研究[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(19):3042-3047. [15] JENSEN AR, DRUCKER NA, FERKOWICZ MJ, et al. Umbilical mesenchymal stromal cells provide intestinal protection through nitric oxide dependent pathways. J Surg Res. 2018;224:148-155. [16] ZHANG H, ZHANG B, TAO Y, et al. Isolation and characterization of mesenchymal stem cells from whole human umbilical cord applying a single enzyme approach. Cell Biochem Funct. 2012;30(8):643-649. [17] NAGAMURA-INOUE T, MUKAI T. Umbilical Cord is a Rich Source of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells for Cell Therapy. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;11(8):634-642. [18] CHANDRAVANSHI B, BHONDE RR. Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Stem Cells: Isolation, Characterization, Differentiation, and Application in Treating Diabetes. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2018;46(5):399-412. [19] ERTL J, PICHLSBERGER M, TUCA AC, et al. Comparative study of regenerative effects of mesenchymal stem cells derived from placental amnion, chorion and umbilical cord on dermal wounds. Placenta. 2018; 65:37-46. [20] ZHANG J, LV S, LIU X, et al. Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Treatment for Crohn’s Disease: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Gut Liver. 2018;12(1):73-78. [21] WU KC, CHANG YH, LIU HW, et al. Transplanting human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells and hyaluronate hydrogel repairs cartilage of osteoarthritis in the minipig model. Ci Ji Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019;31(1):11-19. [22] REYHANI S, ABBASPANAH B, MOUSAVI SH. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in neurodegenerative disorders: from literature to clinical practice. Regen Med. 2020;15(4):1561-1578. [23] ZHANG Y, WANG WT, GONG CR, et al. Combination of olfactory ensheathing cells and human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promotes sciatic nerve regeneration. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(10):1903-1911. [24] WANG X, LIU C, LI S, et al. Effects of continuous passage on immunomodulatory properties of human adipose-derived stem cells. Cell Tissue Bank. 2015;16(1): 143-150. [25] KIM HJ, SUNG IY, CHO YC, et al. Three-Dimensional Spheroid Formation of Cryopreserved Human Dental Follicle-Derived Stem Cells Enhances Pluripotency and Osteogenic Induction Properties. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;16(5):513-523. [26] EL OMAR R, BEROUD J, STOLTZ JF, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: the new gold standard for mesenchymal stem cell-based therapies? Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2014;20(5):523-544. [27] HUA J, GONG J, MENG H, et al. Comparison of different methods for the isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord matrix: proliferation and multilineage differentiation as compared to mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood and bone marrow. Cell Biol Int. 2013;38(2):198-210. [28] YU S, LONG J, YU J, et al. Analysis of differentiation potentials and gene expression profiles of mesenchymal stem cells derived from periodontal ligament and Wharton’s jelly of the umbilical cord. Cells Tissues Organs. 2013;197(3):209-223. [29] RANJBARAN H, ABEDIANKENARI S, MOHAMMADI M, et al. Wharton’s Jelly Derived-Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Isolation and Characterization. Acta Med Iran. 2018;56(1):28-33. [30] AUNG SW, ABU KASIM NH, RAMASAMY TS. Isolation, Expansion, and Characterization of Wharton’s Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cell: Method to Identify Functional Passages for Experiments. Methods Mol Biol. 2019;2045:323-335. [31] BOYER LA, LEE TI, COLE MF, et al. Core transcriptional regulatory circuitry in human embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2005;122(6):947-956. [32] CHAN YS, YANG L, NG HH. Transcriptional regulatory networks in embryonic stem cells. Prog Drug Res. 2011;67:239-252. [33] NOVAK D, HÜSER L, ELTON JJ, et al. SOX2 in development and cancer biology. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020;67(Pt 1):74-82. [34] GRUBELNIK G, BOŠTJANČIČ E, PAVLIČ A, et al. NANOG expression in human development and cancerogenesis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020;245(5):456-464. [35] PATRA SK. Roles of OCT4 in pathways of embryonic development and cancer progression. Mech Ageing Dev. 2020;189:111286. [36] BEERAVOLU N, KHAN I, MCKEE C, et al. Isolation and comparative analysis of potential stem/progenitor cells from different regions of human umbilical cord. Stem Cell Res. 2016;16(3):696-711. [37] HUANG GS, DAI LG, YEN BL, et al. Spheroid formation of mesenchymal stem cells on chitosan and chitosan-hyaluronan membranes. Biomaterials. 2011;32(29):6929-6945. |
| [1] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [2] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [3] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [4] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [5] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [6] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [7] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [8] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [9] | Zhou Ying, Zhang Huan, Liao Song, Hu Fanqi, Yi Jing, Liu Yubin, Jin Jide. Immunomodulatory effects of deferoxamine and interferon gamma on human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1012-1019. |
| [10] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [11] | Wang Jifang, Bao Zhen, Qiao Yahong. miR-206 regulates EVI1 gene expression and cell biological behavior in stem cells of small cell lung cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1027-1031. |
| [12] | Liu Feng, Peng Yuhuan, Luo Liangping, Wu Benqing. Plant-derived basic fibroblast growth factor maintains the growth and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1032-1037. |
| [13] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [14] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [15] | Luo Xiaoling, Zhang Li, Yang Maohua, Xu Jie, Xu Xiaomei. Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||