Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (19): 2964-2969.doi: 10.12307/2022.372
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism by which bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve cognitive function in APP/PS1 double transgenic mice
Gu Qingfang1, Guo Minfang1, Liu Xiaoqin1, Mu Bingtao1, Li Weimei1, Song Lijuan2, Chai Zhi2, Ma Cungen1, 2, Yu Jiezhong1
- 1Shanxi Key Laboratory of Inflammatory Neurodegenerative Diseases, Shanxi Datong University, Datong 037009, Shanxi Province, China; 2Research Center of Neurobiology, Key Laboratory of Multiple Sclerosis, Nourishing Qi and Activating Blood of State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Taiyuan 030629, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2021-01-07Revised:2021-02-10Accepted:2021-07-22Online:2022-07-08Published:2021-12-28 -
Contact:Yu Jiezhong, MD, Professor, Shanxi Key Laboratory of Inflammatory Neurodegenerative Diseases, Shanxi Datong University, Datong 037009, Shanxi Province, China Ma Cungen, MD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Shanxi Key Laboratory of Inflammatory Neurodegenerative Diseases, Shanxi Datong University, Datong 037009, Shanxi Province, China; Research Center of Neurobiology, Key Laboratory of Multiple Sclerosis, Nourishing Qi and Activating Blood of State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Taiyuan 030629, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Gu Qingfang, Master, Lecturer, Shanxi Key Laboratory of Inflammatory Neurodegenerative Diseases, Shanxi Datong University, Datong 037009, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the Open Project of the Key Laboratory of Medical Resources and Natural Medicine Chemistry of the Ministry of Education, No. 2019004 (to MCG); the Neurodegenerative Disease Project of Key Laboratory of Shanxi Province, No. 201805D111009 (to MCG), No. 201805D131005 (to YJZ); the Basic Research Program of Datong Science and Technology Bureau, Shanxi Province, No. 2017136 (to GQF); the Applied Basic Research Project of Shanxi Province, No. 201901D111334 (to SLJ), No. 2018TD-012 (to CZ); the Open Project of the State Key Laboratory of Molecular Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, No. 2020-MDB-KF-09 (to SLJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gu Qingfang, Guo Minfang, Liu Xiaoqin, Mu Bingtao, Li Weimei, Song Lijuan, Chai Zhi, Ma Cungen, Yu Jiezhong. Mechanism by which bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve cognitive function in APP/PS1 double transgenic mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 2964-2969.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
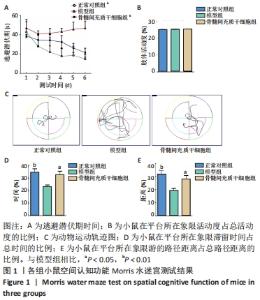
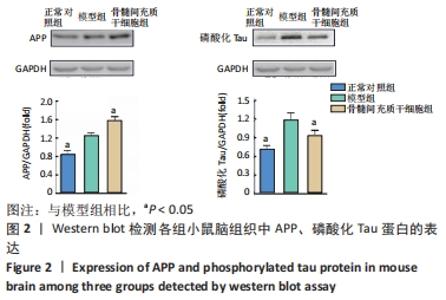
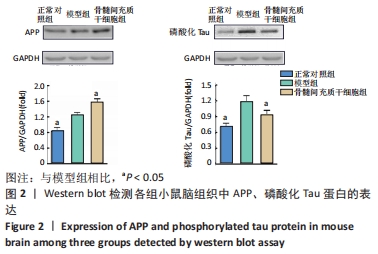
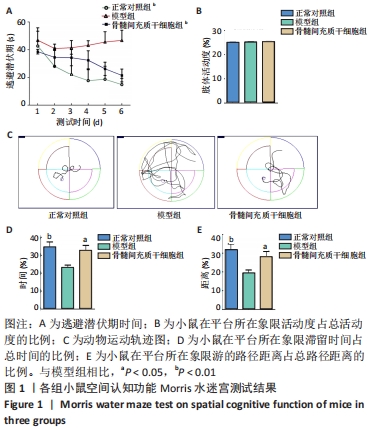
2.1 骨髓间充质干细胞改善APP/PS1双转基因小鼠认知功能障碍 通过Morris水迷宫实验比较3组小鼠的学习记忆能力和空间认知能力。在定位航行实验中,3组小鼠在测试期间的逃避潜伏期各不相同,见图1A:正常对照组小鼠逃避潜伏期时间逐渐减少;与正常对照组相比,模型组小鼠在初期(第1天)较容易找到隐藏的平台,但是在后期(第4-6天)迅速忘记(P < 0.01),表明模型组小鼠记忆巩固受损,认知功能较正常对照组下降,阿尔茨海默病模型建立成功[22]。经过连续治疗2个月,与模型组相比,骨髓间充质干细胞组小鼠逃避潜伏期时间明显缩短(P < 0.01),结果提示骨髓间充质干细胞可改善阿尔茨海默病APP/PS1转基因小鼠的学习记忆能力。3组小鼠游泳速度相当,表明它们在水下平台定位的时间不同与运动能力无关,见图1B。在空间探索实验中,正常对照组小鼠的游泳路径高度集中在目标象限,模型组小鼠经常在每个象限随机游动,没有任何目的,而骨髓间充质干细胞组小鼠在水池较大的区域进行搜索,但仍倾向于集中在目标象限,见图1C。对于小鼠在平台所在象限滞留时间占总时间的比例以及小鼠在平台所在象限游的路径距离占总路径距离的比例,骨髓间充质干细胞组均高于模型组(P < 0.05),见图1D,E,结果表明骨髓间充质干细胞可有效改善APP/PS1转基因小鼠的空间记忆能力。"
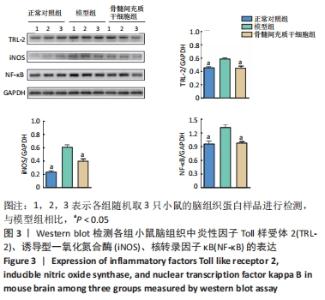
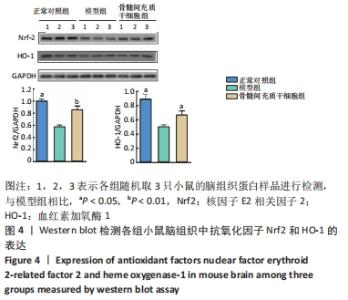
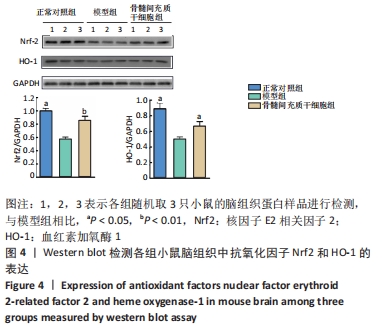
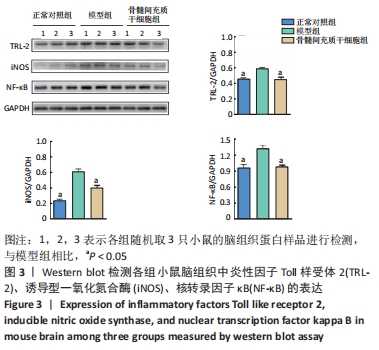
2.3 骨髓间充质干细胞抑制APP/PS1转基因小鼠脑内神经炎症反应 如图3所示,与正常对照组相比,模型组小鼠脑组织中Toll样受体2、诱导型一氧化氮合酶、核转录因子κB的表达水平显著增加,是正常对照组的1.3倍、2.7倍、1.4倍(均P < 0.05),然而经过骨髓间充质干细胞治疗后,小鼠脑内Toll样受体2的表达从模型组的0.58±0.02减少到骨髓间充质干细胞组的0.44±0.12(P < 0.05),减少了24%;诱导型一氧化氮合酶的表达从模型组的0.60±0.14减少到骨髓间充质干细胞组的 0.39±0.04(P < 0.05),减少了35%;核转录因子κB的表达从模型组的1.31±0.07减少到骨髓间充质干细胞组的0.97±0.03(P < 0.05),减少了26%。以上结果表明骨髓间充质干细胞治疗可抑制APP/PS1小鼠脑内神经炎症反应。"
| [1] PRINCE M, COMASHERRERA A, ADELINA K, et al. World Alzheimer Report 2016: Improving Healthcare for People Living with Dementia: Coverage, Quality and Costs Now and in the Future. London, UK: Alzheimer’s Disease International.2016. [2] 谷青芳,尉杰忠,吴昊,等.FSD-C10调节阿尔茨海默病双转基因小鼠炎性微环境[J].中国病理生理杂志,2017,33(10):1729-1737. [3] GLASS CK, SAIJO K, WINNER B, et al. Mechanisms underlying inflammation in neurodegeneration. Cell. 2010;140(6):918-934. [4] NDISANG JF. Synergistic Interaction Between Heme Oxygenase (HO) and Nuclear-Factor E2- Related Factor-2 (Nrf2) against Oxidative Stress in Cardiovascular Related Diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(10): 1465-1470. [5] JI H, XIAO F, LI S, et al. GRP78 effectively protect hypoxia/reperfusion-induced myocardial apoptosis via promotion of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(2):1228-1236. [6] XU Y, YANG Y, HUANG Y, et al. Inhibition of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway by Dextran Sulfate suppresses angiogenesis of Gastric Cancer. J Cancer. 2021;12(4):1042-1060. [7] LIN HY, YEH WL, HUANG BR, et al. Desipramine protects neuronal cell death and induces heme oxygenase-1 expression in Mes23.5 dopaminergic neurons. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50138. [8] CHEN XQ, WU SH, ZHOU Y, et al. Lipoxin A4-induced heme oxygenase-1 protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury via p38 MAPK activation and Nrf2/ARE complex. PLoS One. 2013;8(6):e67120. [9] WYSE RD, DUNBAR GL, ROSSIGNOL J. Use of genetically modified mesenchymal stem cells to treat neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(2):1719-1745. [10] SALEM AM, AHMED HH, ATTA HM, et al. Potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in management of Alzheimer’s disease in female rats. Cell Biol Int. 2014;38(12):1367-1383. [11] 尉杰忠,闫玉清,谷青芳,等.法舒地尔通过促进APP/PS1双转基因小鼠神经再生改善认知功能[J].中国病理生理杂志,2018,34(7): 1153-1161. [12] YUE W, LI Y, ZHANG T, et al. ESC-Derived Basal Forebrain Cholinergic Neurons Ameliorate the Cognitive Symptoms Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease in Mouse Models. Stem Cell Reports. 2015;5(5): 776-790. [13] HUNSBERGER JG, RAO M, KURTZBERG J, et al. Accelerating stem cell trials for Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15(2):219-230. [14] SADATPOOR SO, SALEHI Z, RAHBAN D, et al. Manipulated Mesenchymal Stem Cells Applications in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int J Stem Cells. 2020;13(1):24-45. [15] YU J, YAN Y, GU Q, et al. Fasudil in Combination With Bone Marrow Stromal Cells (BMSCs) Attenuates Alzheimer’s Disease-Related Changes Through the Regulation of the Peripheral Immune System. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018;10:216. [16] EFTEKHARZADEH M, NOBAKHT M, ALIZADEH A, et al. The effect of intrathecal delivery of bone marrow stromal cells on hippocampal neurons in rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015;18(5):520-525. [17] LI YH, FENG L, ZHANG GX, et al. Intranasal delivery of stem cells as therapy for central nervous system disease. Exp Mol Pathol. 2015; 98(2):145-151. [18] YANG J, YAN Y, CIRIC B, et al. Evaluation of bone marrow- and brain-derived neural stem cells in therapy of central nervous system autoimmunity. Am J Pathol. 2010;177(4):1989-2001. [19] LI YH, XIE C, ZHANG Y, et al. FSD-C10, a Fasudil derivative, promotes neuroregeneration through indirect and direct mechanisms. Sci Rep. 2017;7:41227. [20] 宋国斌,席国萍,李艳花,等.Fasudil 联合骨髓源神经干细胞对 EAE小鼠的神经保护作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2017,33(12):2113-2120. [21] YU JZ, LI YH, LIU CY, et al. Multitarget Therapeutic Effect of Fasudil in APP/PS1transgenic Mice. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2017;16(2): 199-209. [22] FAN Y, LIU M, WU X, et al. Aquaporin-4 promotes memory consolidation in Morris water maze. Brain Struct Funct. 2013;218(1):39-50. [23] ROJAS-GUTIERREZ E, MUÑOZ-ARENAS G, TREVIÑO S, et al. Alzheimer’s disease and metabolic syndrome: A link from oxidative stress and inflammation to neurodegeneration. Synapse. 2017;71(10):e21990. [24] ZHANG FQ, JIANG JL, ZHANG JT, et al. Current status and future prospects of stem cell therapy in Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(2):242-250. [25] CIOFFI F, ADAM RHI, BROERSEN K. Molecular Mechanisms and Genetics of Oxidative Stress in Alzheimer’s Disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019;72(4):981-1017. [26] 谷青芳,尉杰忠,郭敏芳,等.新型Rho激酶抑制剂 FSD-C10对阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠的神经保护作用[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2019,35(12):2227-2234. [27] ZUO L, PRATHER ER, STETSKIV M, et al. Inflammaging and Oxidative Stress in Human Diseases: From Molecular Mechanisms to Novel Treatments. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(18):4472. [28] VALKO M, LEIBFRITZ D, MONCOL J, et al. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39(1):44-84. [29] BO H, KANG W, JIANG N, et al. Exercise-induced neuroprotection of hippocampus in APP/PS1 transgenic mice via upregulation of mitochondrial 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014:834502. [30] ZHAO L, LIU S, WANG Y, et al. Effects of Curculigoside on Memory Impairment and Bone Loss via Anti-Oxidative Character in APP/PS1 Mutated Transgenic Mice. PLoS One. 2015;10(7):e0133289. [31] KIM DC, QUANG TH, OH H, et al. Steppogenin Isolated from Cudrania tricuspidata Shows Antineuroinflammatory Effects via NF-kappaB and MAPK Pathways in LPS-Stimulated BV2 and Primary Rat Microglial Cells. Molecules. 2017;22(12):2130. [32] MOLTENI M, ROSSETTI C. Neurodegenerative diseases: The immunological perspective. J Neuroimmunol. 2017;313:109-115. [33] HONG Y, AN Z. Hesperidin attenuates learning and memory deficits in APP/PS1 mice through activation of Akt/Nrf2 signaling and inhibition of RAGE/NF-κB signaling. Arch Pharm Res. 2018;41(6):655-663. [34] PRASAD KN. Simultaneous activation of Nrf2 and elevation of antioxidant compounds for reducing oxidative stress and chronic inflammation in human Alzheimer’s disease. Mech Ageing Dev. 2016; 153:41-47. [35] JOSHI G, GAN KA, JOHNSON DA, et al. Increased Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology in the APP/ PS1ΔE9 mouse model lacking Nrf2 through modulation of autophagy. Neurobiol Aging. 2015;36(2):664-679. [36] CHIANG MC, NICOL CJ, CHENG YC, et al. Rosiglitazone activation of PPARγ-dependent pathways is neuroprotective in human neural stem cells against amyloid-beta-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress. Neurobiol Aging. 2016;40:181-190. [37] YANG H, YUE C, YANG H, et al. Intravenous Administration of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improves Cognitive Impairments and Reduces Amyloid-Beta Deposition in an AβPP/PS1 Transgenic Mouse Model. Neurochem Res. 2013:12(38):2474-2482. |
| [1] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [2] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [3] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [4] | Gao Yujin, Peng Shuanglin, Ma Zhichao, Lu Shi, Cao Huayue, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. Osteogenic ability of adipose stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 999-1004. |
| [5] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [6] | Zhou Ying, Zhang Huan, Liao Song, Hu Fanqi, Yi Jing, Liu Yubin, Jin Jide. Immunomodulatory effects of deferoxamine and interferon gamma on human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1012-1019. |
| [7] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [8] | Wang Jifang, Bao Zhen, Qiao Yahong. miR-206 regulates EVI1 gene expression and cell biological behavior in stem cells of small cell lung cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1027-1031. |
| [9] | Liu Feng, Peng Yuhuan, Luo Liangping, Wu Benqing. Plant-derived basic fibroblast growth factor maintains the growth and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1032-1037. |
| [10] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [11] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [12] | Luo Xiaoling, Zhang Li, Yang Maohua, Xu Jie, Xu Xiaomei. Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| [13] | Wen Xiaoyu, Sun Yuhao, Xia Meng. Effects of serum containing Wuzang Wenyang Huayu Decoction on phosphorylated-tau protein expression in Alzheimer’s disease cell model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1068-1073. |
| [14] | Wang Xinmin, Liu Fei, Xu Jie, Bai Yuxi, Lü Jian. Core decompression combined with dental pulp stem cells in the treatment of steroid-associated femoral head necrosis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1074-1079. |
| [15] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||