Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (16): 2602-2607.doi: 10.12307/2022.264
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation and biological properties of zinc-doped hydroxyapatite
Tang Yanan, Gao Teng, Ren Guiyun
- Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Stomatology, Hebei Medical University, Hebei Provincial Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Hebei Clinical Medical Research Center of Oral Diseases, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2020-10-12Revised:2020-10-14Accepted:2020-11-19Online:2022-06-08Published:2021-12-23 -
Contact:Ren Guiyun, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Stomatology, Hebei Medical University, Hebei Provincial Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Hebei Clinical Medical Research Center of Oral Diseases, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Tang Yanan, Master candidate, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Stomatology, Hebei Medical University, Hebei Provincial Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Hebei Clinical Medical Research Center of Oral Diseases, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:Key Research and Development Plan of Hebei Provincial Department of Science and Technology, No. 20377747D (to RGY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tang Yanan, Gao Teng, Ren Guiyun. Preparation and biological properties of zinc-doped hydroxyapatite[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2602-2607.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
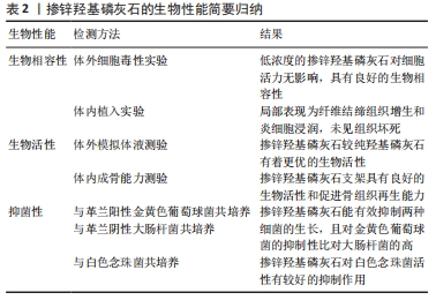
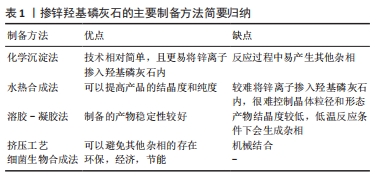
2.1.1 化学沉淀法 化学沉淀法是保持一定pH值、温度在连续搅拌下将一种试剂滴加到另一种试剂中进行反应,然后经洗涤、过滤、干燥后得到沉淀产物。 THIAN等[13]在室温下以氢氧化钙[Ca(OH)2]、正磷酸(H3PO4)和六水合硝酸锌[Zn(NO3)2?6H2O]为原料通过沉淀法合成了锌含量为1.6%的掺锌羟基磷灰石颗粒。化学沉淀法是在连续搅拌条件下将正磷酸溶液滴加到氢氧化钙和六水合硝酸锌混合液中,同时用氨水使pH值保持在10.5以上。上述溶液完全混合后持续搅拌18 h,然后静置2周,经离心去除产物中的水后在124 ℃下高压灭菌2 h便制得掺锌羟基磷灰石。此法合成的掺锌羟基磷灰石实际掺锌量为1.5%,接近期望值1.6%。 PREDOI等[10]通过改进的化学沉淀法合成了含锌浓度分别为1%,3%,5%的掺锌羟基磷灰石,原料选用了四水合硝酸钙[Ca(NO3)2?4H2O]、磷酸氢铵[(NH4)2HPO4]和六水合硝酸锌,反应温度变为80 ℃,最终合成的掺锌羟基磷灰石具有与纯羟基磷灰石一样的晶体结构,说明改进后的化学沉淀法可以提高产物的纯度。另有研究表明,改进的化学沉淀法可以提高羟基磷灰石的结晶度[2]。化学沉淀技术相对简单,且较水热法更易将锌离子掺入羟基磷灰石内[15],但是反应过程中易产生其他杂相。MARDZIAH等[14]应用化学沉淀法制备的掺锌羟基磷灰石产物中出现由羟基磷灰石和β-磷酸三钙相组成的双相混合物,并且随着锌含量的增加,β-磷酸三钙相的含量也增加;此外还观察到制得的产物形状不规则,出现结块现象。因此应用化学沉淀法制备时应严格控制反应条件,进一步改善工艺以提高产物的品质。 2.1.2 水热合成法 水热合成法是一种简便而经济的制备方法[16],是将反应物按一定顺序放入特定的容器内,在高温高压条件下进行充分反应后,经冷却、干燥后得到相应的羟基磷灰石材料或者掺有其他微量元素的羟基磷灰石材料。此法主要优点是可以提高产品的结晶度和纯度,主要缺点是很难控制晶体粒径和形态[10]。 LI等[15]通过水热法制备含不同摩尔浓度的掺锌羟基磷灰石粉末,以硝酸钙[Ca(NO3)2],磷酸铵[(NH4)3PO4]和硝酸锌[Zn(NO3)2]为试剂,用量是假设锌可以取代钙来进行计算的。反应过程中分别通过加入氨水或氢氧化钠溶液来控制pH值,反应8 h后将所得沉淀物过滤,100 ℃干燥过夜,之后分别在400 ℃和800 ℃处理1 h。结果显示,合成样品中锌的含量低于起始添加量,反应完成后溶液中仍有大量的锌离子,说明水热法较难将锌离子掺入羟基磷灰石内。 肖胜杰[17]以磷酸二氢钙[Ca(H2PO4)2?H2O]、磷酸二氢锌[Zn(H2P2PO4)3?H2O]和氢氧化钙为原料,利用水热法制备出了掺锌浓度为0.13%的掺锌羟基磷灰石粉末,并且反应副产物只有H2O生成。此外,YU等[12]和SUN等[18]分别应用该法合成了Zn/(Zn+Ca)摩尔比为0.02的掺锌介孔羟基磷灰石和超长羟基磷灰石纳米材料,该两种材料较未添加锌的产物有着更粗糙的表面形态和表面积,从而利于成骨细胞的吸附增殖和新骨的形成。 2.1.3 溶胶-凝胶法 溶胶-凝胶法以无机物或金属醇盐作前驱体,将原料分散在溶剂中,在一定温度和pH值条件下经过水解、缩合化学反应成为溶胶,溶胶经陈化胶粒间缓慢聚合,形成具有一定空间结构的凝胶,最后经过干燥和热处理制备出所需材料。 ICONARU等[19]通过溶胶-凝胶法制备了掺锌羟基磷灰石溶胶-凝胶,并经加热干燥制备了掺锌羟基磷灰石粉末。首先将亚磷酸三乙酯[P(C2H5O)3]和六水合硝酸锌溶于乙醇制成含磷和锌溶液,将四水合硝酸钙溶于乙醇制成含钙溶液,分别在40 ℃下搅拌24 h;然后向上述含磷和锌溶液中加入氢氧化铵(NH4OH)溶液,再逐滴加入上述含钙溶液,接着在40 ℃下连续搅拌1周便制得掺锌羟基磷灰石溶胶-凝胶;再经100 ℃干燥60 min后得到掺锌羟基磷灰石粉末。作者通过此法制得了掺锌量为1.67%的掺锌羟基磷灰石粉末,但经傅里叶红外光谱观察到,低温条件下反应时样品中会含有一定数量的碳酸盐杂相。之后PREDOI等[20]通过升高反应温度,将所有反应溶液混合后于100 ℃下连续搅拌24 h,再经洗涤、分散,制得掺锌羟基磷灰石胶体,经X射线衍射物相分析发现,方法改进后合成的掺锌羟基磷灰石只具有羟基磷灰石单相空间结构,未见其他杂相结构的存在。同样,BI等[21]首先在60 ℃下连续搅拌30 min,然后在700 ℃连续加热90 min,经陈化后得到了掺锌量为1%(摩尔百分比)的掺锌羟基磷灰石胶体,经X射线衍射物相分析发现,掺锌羟基磷灰石与羟基磷灰石有着相同特征的衍射峰,未见其他杂相衍射峰的存在。由此可见,适当升高反应温度可以缩短制备周期,提高反应产物的纯度。 另外,NEGRILA等[22]首次应用超声波测量了采用溶胶-凝胶法合成的羟基磷灰石和掺锌羟基磷灰石分散液的稳定性,结果发现两种分散液都有良好的稳定性,且掺锌羟基磷灰石分散液更加稳定。说明溶胶-凝胶法可以制备稳定性较好的羟基磷灰石复合物,且锌的掺入可以提高产物的稳定性。 2.1.4 挤压工艺 PINC等[23]首次采用挤压法制备了掺锌量为8%的羟基磷灰石复合材料(Zn/HA8),并进行表征。采用的原料为锌粉和羟基磷灰石粉,按照质量比取92%锌粉和8%羟基磷灰石粉,放入特定容器混合20 min后压制成直径20 mm、高15 mm的片剂,再将两者挤压成直径6 mm的圆柱棒,最后经水冷却制得复合材料。此复合材料中的羟基磷灰石与锌并没有发生化学反应,而是机械地结合在一起,避免了化学反应过程中其他物质的生成。 2.1.5 细菌生物合成法 AHMADZADEH等[24]首次利用细菌生物合成法制备了碳酸盐羟基磷灰石和锌镁取代羟基磷灰石纳米颗粒。实验分3步,首先是产气肠杆菌的培养和矿化液的制备,第2步是将细菌接种至矿化液用来合成碳酸盐羟基磷灰石,第3步是在矿化液中加入氯化锌和氯化镁,然后在室温下进行搅拌、静置、沉淀、过滤,最后经高温煅烧得到锌-镁取代的羟基磷灰石。细菌生物合成法是一种环保、节能、经济的生产方法,可以在常温和大气压力下在水介质中进行,此外此法还可以精确地调整和控制过程参数。 2.2 掺锌羟基磷灰石的形态结构 羟基磷灰石晶体结构属于六角晶系,形态为长10-60 nm、宽2-6 nm的针状晶体,目前用来分析掺锌羟基磷灰石形态结构的常用方法有透射电子显微镜、X射线衍射、扫描电子显微镜和傅里叶变换红外光谱等。 THIAN等[13]、LI等[15]用透射电子显微镜对掺锌羟基磷灰石进行精析发现,其有着与天然羟基磷灰石相似的形态,呈棒状,保持着羟基磷灰石典型的六角晶系结构特性。ICONARU等[19]用X射线衍射对低浓度锌掺杂的羟基磷灰石进行分析,结果未见除羟基磷灰石外其他任何杂质特征的峰,这说明锌离子的进入并没有改变羟基磷灰石原有的结构,仍保持着与纯羟基磷灰石一样的六角晶体结构。NEGRILA等[22]用Rietveld分析了用溶胶-凝胶法制得的掺锌羟基磷灰石粉末,发现在P6(3/m)空间内掺锌羟基磷灰石具有与羟基磷灰石一样的六角晶体结构,佐证了ICONARU等的研究结果。LI等[15]通过X射线衍射观察到,当锌含量低于20%(摩尔百分比)时,掺锌羟基磷灰石衍射峰符合羟基磷灰石的衍射峰;当锌含量为40%(摩尔百分比)时,除了羟基磷灰石相衍射峰外,还出现了第二相的衍射峰-水合磷酸锌钙峰,这说明过高浓度的锌会导致混合相的出现。 有研究表明,Zn离子是通过取代Ca离子而在结构上结合到羟基磷灰石晶体中的,由于Zn离子半径小于Ca离子半径,所以Zn离子的取代会导致晶格参数的改变[13]。PREDOI等[10]的研究结果显示,随掺锌量的增加,晶格参数“a”和“c”均减小,这导致单位晶胞体积的变小,进一步导致了掺锌羟基磷灰石晶体体积的减小。但OFUDJE等[25]的X射线衍射果显示,随着掺锌量的增加,掺锌羟基磷灰石晶格参数“a”增大、晶格参数“c”减小,与羟基磷灰石相比,掺锌羟基磷灰石的晶体体积最终都是减小的。CRISTINA等[26]的扫描电子显微镜结果也显示,随着掺锌量的增加,掺锌羟基磷灰石的晶体颗粒尺寸减小,并且傅立叶变换红外光谱结果显示,随着掺锌量的增加,样品的结晶度也降低。 由以上结果可知,锌离子掺入后不会导致羟基磷灰石晶体结构的改变,但是会对其尺寸和结晶度产生影响。 2.3 掺锌羟基磷灰石的生物相容性 生物相容性是衡量生物材料价值的一个重要指标,植入体内的生物材料必须具有无毒性、无刺激性、无致敏性、无致畸性等。检测材料生物相容性常用的方法是细胞毒性检测,包括体外细胞毒性实验和体内植入实验。体外细胞毒性实验,即在生物材料表面进行细胞培养,观察细胞黏附生长情况,推测这种生物材料生物相容性。体内植入实验是指将生物材料或者医疗器械埋入动物体内某些部位,观察埋入不同时间材料对局部组织的病理改变。 多数研究表明,复合材料内掺杂适当锌离子后可以增强骨髓间充质干细胞的附着和增殖能力[27-28],但掺杂过量锌时则会导致细胞毒性[29-30]。ITO等[31]的研究结果显示,掺锌量在0.6%-1.2%时对成骨细胞的增殖有促进作用,当掺锌量超过1.2%时则表现出细胞毒性。 但近期有研究表明,当掺锌量超过1.2%时,掺锌羟基磷灰石仍具有较好的生物相容性。MARTINEZ-ZELAYA等[32]用小鼠前成骨细胞(MC3T3)对掺锌量为3.2%的掺锌碳酸盐羟基磷灰石微球进行了体外细胞毒性实验,通过PrestoBlue细胞活力剂测定生物材料表面的细胞活力,以评估掺锌碳酸盐羟基磷灰石和碳酸盐羟基磷灰石样品的生物相容性。结果显示与阴性对照组相比,上述两种样品的细胞代谢活性均有所增加,掺锌碳酸盐羟基磷灰石组和碳酸盐羟基磷灰石组的细胞活力无差异,两者均具有较好的生物相容性,并表示这可能与材料中锌的释放率有关。同时他还研究了掺锌碳酸盐羟基磷灰石和碳酸盐羟基磷灰石的体内生物相容性,结果发现植入1个月后,两组骨缺损处均观察到大量纤维结缔组织生成和散在炎细胞浸润,并在掺锌碳酸盐羟基磷灰石组缺损边缘处观察到新骨形成;植入3个月后,两组缺损中心区可见大量纤维结缔组织和少量炎细胞浸润,在缺损边缘处均观察到新骨形成和大量散在生物材料;植入6个月末,在缺损中心可见富含胶原纤维的结缔组织,在缺损边缘处发现大量的新骨与少量生物材料。由此可见,生物材料的植入对机体产生的反应是炎症性而非组织坏死性的。 CUOZZO等[33]研究了纳米结构藻酸钙-羟基磷灰石和藻酸钙-含锌羟基磷灰石的体内生物相容性,同样是将上述生物材料植入大鼠颅骨缺损处,1,3,6个月后的组织学结果与MARTINEZ-ZELAYA等[32]一致,即在缺损中心区以炎性反应为主,在缺损边缘区可见新骨形成;与阴性对照组相比,在观察期间内两组的细胞活力均无差异。以上两个研究结果都证实了掺锌羟基磷灰石生物材料具有良好的体内生物相容性,并且从上述研究中得知新骨形成始于缺损边缘区域,而缺损中心区域以纤维结缔组织和炎细胞为主。 RESENDE等[34]研究了含锌量为0.5%(摩尔百分比)的掺锌羟基磷灰石的体内降解情况,结果显示,植入26周时掺锌组与未掺锌组微粒大小无明显差异,但26周后含锌羟基磷灰石微球直径减小,纯羟基磷灰石直径大小没有明显变化,说明含锌羟基磷灰石具有更显著的生物降解性和生物相容性。LYTKINA等[35]进一步研究了掺锌浓度(0,0.1,0.5,0.9 mol)对机体生物相容性的影响,并与阴性对照组(未植入任何材料)和阳性对照组(植入羟基磷灰石)进行比较,组织学检查显示两对照组均表现为少量纤维化变性,而所有实验组内均为大量纤维结缔组织增生,并且掺锌量越多纤维结缔组织增生越明显,其中掺锌量为0.9 mol的掺锌羟基磷灰石组中纤维结缔组织增生最多,这表明掺锌浓度越大毒性反应越大,但总体上这种毒性反应也主要是炎症占主导而非坏死,所有实验动物的器官都没有受到毒性损伤的痕迹。 以上研究结果都表明,低浓度的掺锌羟基磷灰石有着良好的生物相容性,高浓度掺杂时会出现细胞毒性,但关于这个临界值目前尚无定论,仍需大量研究来确定。 2.4 掺锌羟基磷灰石的生物活性 生物活性主要指生物材料与活体骨产生化学键合的能力,即材料与骨组织之间形成有骨引导或骨诱导作用的能力,是衡量生物材料的一个重要指标。掺锌羟基磷灰石的生物活性,见表2。"
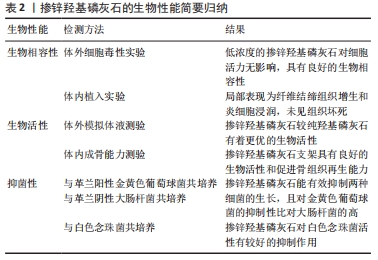

2.4.1 体外生物活性 一般是通过材料表面在人体模拟体液中形成磷灰石的能力来反映材料在体内的生物活性,此评价方法可以减少实验所需动物数量。BHATTACHARJEE等[36]将烧结后的羟基磷灰石和掺锌羟基磷灰石团块浸泡在模拟体液内,4周后观察到两样品质量均增加,增加量分别为羟基磷灰石增加了0.54%,掺锌羟基磷灰石增加了0.97%,并且在掺锌羟基磷灰石样品表面观察到了多层磷灰石。BI等[21]分别将羟基磷灰石和掺锌羟基磷灰石涂层钛支架浸泡在模拟体液中,7 d后羟基磷灰石和掺锌羟基磷灰石涂层表面都观察到了磷灰石的沉积,但羟基磷灰石涂层表面的沉积物形态不规则,而掺锌羟基磷灰石涂层表面的沉积物呈规则的球形。DITTLER等[37]将掺锌羟基磷灰石生物活性玻璃支架在模拟体液中浸泡7 d后,观察到支架表面有规则的菜花状磷酸钙结构致密层形成。由上可以看出,锌掺入后可以加速磷灰石的形成,并较未掺锌产物的形态更加规则,由此证实了掺锌羟基磷灰石较纯羟基磷灰石有着更优的生物活性。 2.4.2 体内生物活性 将生物材料植入体内能直观地评价材料的生物活性。CUOZZO等[33]评价了纳米藻酸钙-羟基磷灰石微球和含锌纳米藻酸钙-羟基磷灰石复合微球的体内生物活性,植入体内6个月后,未掺锌组在骨缺损边缘区域可见少量新骨和较多的结缔组织形成,但在骨缺损中心区域未见有新骨形成;含锌组的骨缺损中心区域及边缘区域都观察到有大量的新骨形成。此研究证明,两种生物材料都具有良好的体内生物活性,但锌掺入后可显著提高羟基磷灰石的成骨能力,从而进一步促进新骨形成。 BHATTACHARJEE等[36]将羟基磷灰石和掺锌羟基磷灰石植入小鼠体内2个月后便观察到了有新骨形成,并且掺锌羟基磷灰石组的骨形成较羟基磷灰石组快;组织学也显示与羟基磷灰石组比较,掺锌羟基磷灰石组在植入物和骨组织间形成了大量的血管和骨基质,并且骨基质显示出良好的矿化;扫描电子显微镜结果显示,羟基磷灰石组植入物和骨骼之间有明显的间隙,但掺锌羟基磷灰石组整个缺损界面几乎被新生的骨组织充满,仅余留一些散在的小间隙。BEGAM等[38]观察了植入新西兰兔体内2个月后的成骨情况,结果与PROMITA等的一致。由此可见,掺锌羟基磷灰石具有更好的骨形成能力。 MARTINEZ-ZELAYA等[32]的动物体内植入实验发现,植入1个月后掺锌组和未掺锌组骨缺损区均观察到了大量纤维结缔组织,而且在掺锌组骨缺损边缘观察到了新骨形成,说明锌可以促进早期骨组织的形成。 以上研究说明,羟基磷灰石和掺锌羟基磷灰石均不会引起机体的不良反应,皆具有良好的生物相容性,并且锌掺入后可以显著改善羟基磷灰石的成骨速率和成骨量,有利于早期骨组织的形成[39]。由此可见,掺锌羟基磷灰石较羟基磷灰石有着更好的生物活性。 2.5 掺锌羟基磷灰石的抑菌性 用于组织修复的植入物易受葡萄球菌感染,特别是金黄色葡萄球菌感染,因此应用于骨组织工程中的人工骨支架材料应该具备良好的抑菌性能。TURLYBEKULY等[40]采用共同培养法评价了羟基磷灰石-氧化锌和羟基磷灰石-海藻酸钠-双相氧化锌多相纳米复合材料对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌性能,结果显示培养24 h后,对照组羟基磷灰石和羟基磷灰石-海藻酸钠材料的细菌死亡率没有任何变化,而实验组羟基磷灰石-氧化锌和羟基磷灰石-海藻酸钠-双相氧化锌复合材料的细菌死亡率达100%,表明掺入锌的复合材料能有效抑制细菌的生长。 ZHOU等[41]研究了纳米羟基磷灰石和氧化锌纳米羟基磷灰石对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制作用,结果与TURLYBEKULY等[40]的一致;并进一步解释了ZnO的抑菌机制,即ZnO在光照下尤其是紫外线照射下会产生活性氧,活性氧与呼吸酶或细菌核酸的巯基结合使细菌呼吸受到抑制;此外,当活性氧与细胞接触时可能会破坏细胞膜,或与蛋白质硫基相互作用使细胞质流失并氧化细胞核,最终导致细菌死亡,这与STANNIC等[42]提出的抑菌机制相一致。OFUDJE等[25]研究了掺锌量在20%(摩尔百分比)以下时锌浓度对金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌活性的影响,结果显示羟基磷灰石缺乏抑菌活性,而各个浓度的掺锌羟基磷灰石均显示出抑菌性能,并且抑菌活性随Zn离子浓度的增加而增加,其中掺锌量为20%(摩尔百分比)的羟基磷灰石抑菌活性最强。SWETHA等[43]的抑菌性实验结果与OFUDJE等的一致,并且在掺锌量为1%(摩尔百分比)时掺锌羟基磷灰石对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌就表现出明显的生长抑制作用。但有研究表明,当锌含量超过一定限值时抑菌活性会随锌浓度增高而降低[44-45],这可能跟金属的细胞毒性及金属和细菌相互作用的方式有关。另外,观察到掺锌羟基磷灰石涂层对革兰阳性金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制性比对革兰阴性大肠杆菌的高,这可能跟细菌的细胞膜结构有关。 GROZA等[46]用白色念珠菌对掺锌羟基磷灰石-聚二甲基硅氧烷复合材料的抗真菌性进行了体外实验,培养24, 48 h后与对照组相比,掺锌羟基磷灰石-聚二甲基硅氧烷复合材料上的白色念珠菌生长速率随培养时间的延长而降低,72 h后白色念珠菌生长速率明显降低,证明掺锌羟基磷灰石-聚二甲基硅氧烷复合材料对白色念珠菌有抑制作用。ALIOUI等[47]的抑白色念珠菌实验结果与GROZA等[46]一致,表明掺锌羟基磷灰石纳米材料对黑曲霉菌也有很强的抑菌活性。 由上可见,掺锌羟基磷灰石对细菌及真菌有着良好的抑菌活性,在一定掺锌浓度范围内抑菌活性与掺锌浓度呈正比;超过一定浓度后,因金属的毒性反应,抑菌活性随锌浓度增加反而降低。另外,抑菌活性也与细菌种类和细胞膜结构有关,如掺锌羟基磷灰石对革兰阳性菌的抑制性比对革兰阴性菌高。"

| [1] 叶利远,王会丹,孟增东.二价阳离子掺杂羟基磷灰石的基础研究进展[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2017,14(3):62-66,69. [2] CIOBANU CS, MASSUYEAU F, CONSTANTIN LV, et al. Structural and physical properties of antibacterial Ag-doped nano-hydroxyapatite synthesized at 100 ℃. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2011;6(1):613. [3] LANDI E, LOGROSCINO G, PROIETTI L, et al. Biomimetic Mg-substituted hydroxyapatite: from synthesis to in vivo behaviour. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2008;19(1):239-247. [4] DENG L, LI D, YANG Z, et al. Repair of the calvarial defect in goat model using magnesium-doped porous hydroxyapatite combined with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2. Biomed Mater Eng. 2017;28(4):361-377. [5] PIETAK AM, REID JW, STOTT MJ, et al. Silicon substitution in the calcium phosphate bioceramics. Biomaterials. 2007;28(28):4023-4032. [6] COX SC, JAMSHIDI P, GROVER LM, et al.Preparation and characterisation of nanophase Sr, Mg, and Zn substituted hydroxyapatite by aqueous precipitation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;35:106-114. [7] DHIVYA S, SARAVANAN S, SASTRY TP, et al. Nanohydroxyapatite-reinforced chitosan composite hydrogel for bone tissue repair in vitro and in vivo. J Nanobiotechnology. 2015;13:40. [8] YANG H, QU X, LIN W, et al. In vitro and in vivo studies on zinc-hydroxyapatite composites as novel biodegradable metal matrix composite for orthopedic applications. Acta Biomater. 2018;71:200-214. [9] YAMAGUCHI M, WEITZMANN MN. Zinc stimulates osteoblastogenesis and suppresses osteoclastogenesis by antagonizing NF-κB activation. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011;355(1-2):179-186. [10] PREDOI D, ICONARU SL, DENIAUD A, et al. Textural, Structural and Biological Evaluation of Hydroxyapatite Doped with Zinc at Low Concentrations. Materials (Basel). 2017;10(3):229. [11] WANG X, ITO A, SOGO Y, et al. Zinc-containing apatite layers on external fixation rods promoting cell activity. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(3):962-968. [12] YU W, SUN TW, QI C, et al. Evaluation of zinc-doped mesoporous hydroxyapatite microspheres for the construction of a novel biomimetic scaffold optimized for bone augmentation. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017; 12:2293-2306. [13] THIAN ES, KONISHI T, KAWANOBE Y, et al. Zinc-substituted hydroxyapatite: a biomaterial with enhanced bioactivity and antibacterial properties. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2013;24(2):437-445. [14] MARDZIAH CM, RAMESH S, ABDUL WAHID MF, et al. Effect of zinc ions on the structural characteristics of hydroxyapatite bioceramics. J Ceramics International. 2020;46(9):13945-13952. [15] LI M, XIAO X, LIU R, et al. Structural characterization of zinc-substituted hydroxyapatite prepared by hydrothermal method. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2008;19(2):797-803. [16] HUANG YZ, HE SK, GUO ZJ, et al. Nanostructured titanium surfaces fabricated by hydrothermal method: Influence of alkali conditions on the osteogenic performance of implants. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;94:1-10. [17] 肖胜杰.微量元素掺杂羟基磷灰石制备与生物学性能研究[D].北京:中国科学院大学(中国科学院上海硅酸盐研究所),2018. [18] SUN TW, YU WL, ZHU YJ, et al. Porous Nanocomposite Comprising Ultralong Hydroxyapatite Nanowires Decorated with Zinc-Containing Nanoparticles and Chitosan: Synthesis and Application in Bone Defect Repair. Chemistry. 2018;24(35):8809-8821. [19] ICONARU SL, PRODAN AM, BUTON N, et al. Structural Characterization and Antifungal Studies of Zinc-Doped Hydroxyapatite Coatings. Molecules. 2017;22(4):604. [20] PREDOI D, ICONARU SL, PREDOI MV, et al. Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of Zinc-Doped Hydroxyapatite Colloids and Dispersion Stability Using Ultrasounds. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019;9(4):515. [21] BI Q, SONG X, CHEN Y, et al. Zn-HA/Bi-HA biphasic coatings on Titanium: Fabrication, characterization, antibacterial and biological activity. J Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;189:110813. [22] NEGRILA CC, PREDOI MV, ICONARU SL, et al. Development of Zinc-Doped Hydroxyapatite by Sol-Gel Method for Medical Applications. J Molecules. 2018;23(11):2986. [23] PINC J, ČAPEK J, HYBASEK V, et al. Characterization of Newly Developed Zinc Composite with the Content of 8 wt.% of Hydroxyapatite Particles Processed by Extrusion. J Materials (Basel). 2020;13(7):1716. [24] AHMADZADEH E, TALEBNIA F, TABATABAEI M, et al. Osteoconductive composite graft based on bacterial synthesized hydroxyapatite nanoparticles doped with differentions: From synthesis to in vivo studies. J Nanomedicine. 2016;12(5):1387-1395. [25] OFUDJE EA, ADEOGUN AI, IDOWU MA, et al. Synthesis and characterization of Zn-Doped hydroxyapatite: scaffold application, antibacterial and bioactivity studies. J Heliyon. 2019;5(5):e01716. [26] CRISTINA LP, AURELIEN D, ISABELLE MS, et al. Structural and Biological Assessment of Zinc Doped Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles. J Nanomater. 2016;2016:1-10. [27] GHORBANI FM, KAFFASHI B, SHOKROLLAHI P, et al. PCL/chitosan/Zn-doped nHA electrospun nanocomposite scaffold promotes adipose derived stem cells adhesion and proliferation. Carbohydr Polym. 2015; 118:133-142. [28] BOSTANCIOGLU RB, GURBUZ M, AKYUREKLI AG, et al. Adhesion profile and differentiation capacity of human adipose tissue derived mesenchymal stem cells grown on metal ion (Zn, Ag and Cu) doped hydroxyapatite nano-coated surfaces. J Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;155:415-428. [29] HAIMI S, GORIANC G, MOIMAS L, et al. Characterization of zinc-releasing three-dimensional bioactive glass scaffolds and their effect on human adipose stem cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation. Acta Biomater. 2009;5(8):3122-3131. [30] ISHIKAWA K, MIYAMOTO Y, YUASA T, et al. Fabrication of Zn containing apatite cement and its initial evaluation using human osteoblastic cells. Biomaterials. 2002;23(2):423-428. [31] ITO A, OJIMA K, NAITO H, et al. Preparation, solubility, and cytocompatibility of zinc-releasing calcium phosphate ceramics. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000;50(2):178-183. [32] MARTINEZ-ZELAYA VR, ZARRANZ L, HERRERA EZ, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluations of nanocrystalline Zn-doped carbonated hydroxyapatite/alginate microspheres: zinc and calcium bioavailability and bone regeneration. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:3471-3490. [33] CUOZZO RC, SARTORETTO SC, RESENDE RFB, et al. Biological evaluation of zinc-containing calcium alginate-hydroxyapatite composite microspheres for bone regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020;108(6):2610-2620. [34] RESENDE RF, FERNANDES GV, SANTOS SR, et al. Long-term biocompatibility evaluation of 0.5 % zinc containing hydroxyapatite in rabbits. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2013;24(6):1455-1463. [35] LYTKINA D, GUTSALOVA A, FEDORISHIN D, et al. Synthesis and Properties of Zinc-Modified Hydroxyapatite. J Funct Biomater. 2020; 11(1):10. [36] BHATTACHARJEE P, BEGAM H, CHANDA A, et al. Animal trial on zinc doped hydroxyapatite: A case study.J Asian Ceram Soc. 2014;2(1): 44-51. [37] DITTLER ML, UNALAN I, GRüNEWALD A, et al. Bioactive glass (45S5)-based 3D scaffolds coated with magnesium and zinc-loaded hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for tissue engineering applications. J Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019;182:110346. [38] BEGAM H, NANDI SK, CHANDA A, et al. Effect of bone morphogenetic protein on Zn-HAp and Zn-HAp/collagen composite: A systematic in vivo study. J Res Vet Sci. 2017;115:1-9. [39] GNANESHWAR PV, SUDAKARAN SV, ABISEGAPRIYAN S, et al. Ramification of zinc oxide doped hydroxyapatite biocomposites for the mineralization of osteoblasts. J Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;96:337-346. [40] TURLYBEKULY A, POGREBNJAK AD, SUKHODUB LF, et al. Synthesis, characterization, in vitro biocompatibility and antibacterial properties study of nanocomposite materials based on hydroxyapatite-biphasic ZnO micro- and nanoparticles embedded in Alginate matrix. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;104:109965. [41] ZHOU G, LI Y, XIAO W, et al. Synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activities of a novel nanohydroxyapatite/zinc oxide complex. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008;85(4):929-937. [42] STANNIC V, DIMITRIJEVIC S, ANTIC-STANKOVIC J, et al. Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of copper and zinc-doped hydroxyapatite nanopowders. Appl Surf Sci. 2010;256(20):6083-6089. [43] SWETHA M, SAHITHI K, MOORTHI A, et al. Synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial activity of nano-hydroxyapatite-zinc for bone tissue engineering applications. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2012;12(1):167-172. [44] ANWAR A, AKBAR S, SADIQA A, et al. Novel continuous flow synthesis, characterization and antibacterial studies of nanoscale zinc substituted hydroxyapatite bioceramics. J Inorganica Chimica Acta. 2016;453:16-22. [45] SERGI R, BELLUCCI D, CANDIDATO RT, et al. Bioactive Zn-doped hydroxyapatite coatings and their antibacterial efficacy against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Surf Coat Technol. 2018; 352:84-91. [46] GRAZA A, CIOBANU CS, POPA CL, et al. Structural Properties and Antifungal Activity against Candida albicans Biofilm of Different Composite Layers Based on Ag/Zn Doped Hydroxyapatite-Polydimethylsiloxanes. J Polymers (Basel). 2016;8(4):131. [47] ALIOUI H, BOURAS O, BOLLINGER JC. Toward an efficient antibacterial agent: Zn- and Mg-doped hydroxyapatite nanopowders. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2019;54(4):315-327. [50] CANDIDATO RT JR, THOUZELLIER C, PAWłOWSKI L. Evaluation of the in-vitro behavior of nanostructured hydroxyapatite and zinc doped hydroxyapatite coatings obtained using solution precursor plasma spraying. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2018;106(6):2101-2108. [51] OHTSU N, KAKUCHI Y, OHTSUKI T. Antibacterial effect of zinc oxide/hydroxyapatite coatings prepared by chemical solution deposition. J Appl Surf Sci. 2018;445:596-600. [52] SHANG S, ZHAO Q, ZHANG D, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation of the adsorption behavior of two different drugs on hydroxyapatite and Zn-doped hydroxyapatite. J Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;105:110017. [53] DEVANAND VENKATASUBBU G, RAMASAMY S, RAMAKRISHNAN V, et al. Nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite and zinc-doped hydroxyapatite as carrier material for controlled delivery of ciprofloxacin.3 Biotech. 2011;1(3):173-186. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Jiang Huanchang, Zhang Zhaofei, Liang De, Jiang Xiaobing, Yang Xiaodong, Liu Zhixiang. Comparison of advantages between unilateral multidirectional curved and straight vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1407-1411. |
| [3] | Xue Yadong, Zhou Xinshe, Pei Lijia, Meng Fanyu, Li Jian, Wang Jinzi . Reconstruction of Paprosky III type acetabular defect by autogenous iliac bone block combined with titanium plate: providing a strong initial fixation for the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1424-1428. |
| [4] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhou Qian, Zhang Qiang, Chen Qiu. Human salivary components and osteoporosis/osteopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [5] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [6] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [7] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [8] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [9] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [10] | Wu Bingshuang, Wang Zhi, Tang Yi, Tang Xiaoyu, Li Qi. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: from enthesis to tendon-to-bone healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1293-1298. |
| [11] | Li Wei, Zhu Hanmin, Wang Xin, Gao Xue, Cui Jing, Liu Yuxin, Huang Shuming. Effect of Zuogui Wan on bone morphogenetic protein 2 signaling pathway in ovariectomized osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1173-1179. |
| [12] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [13] | Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| [14] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [15] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||