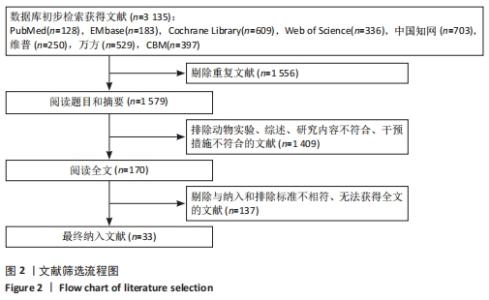
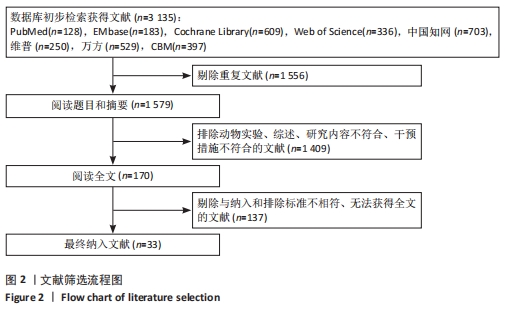
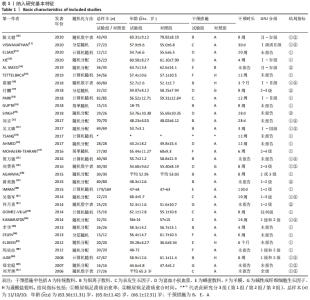
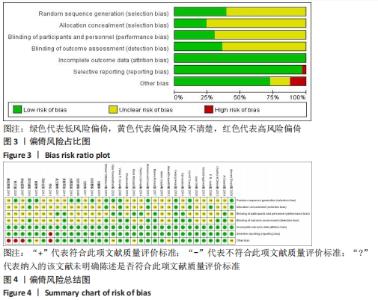
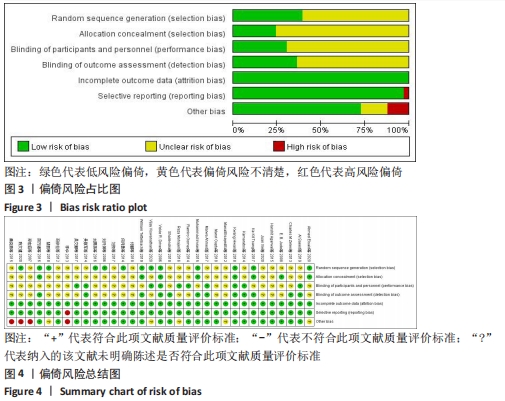
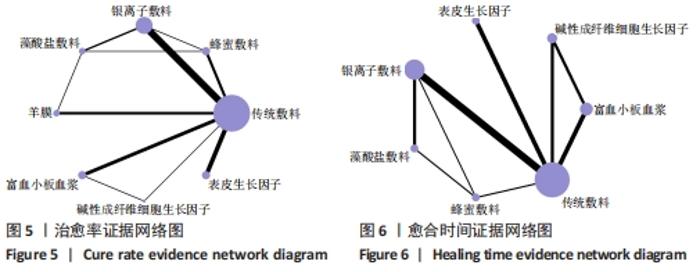
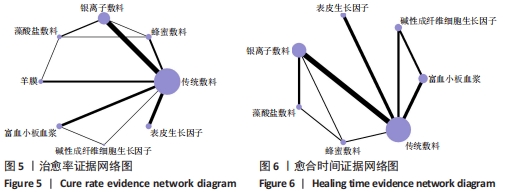
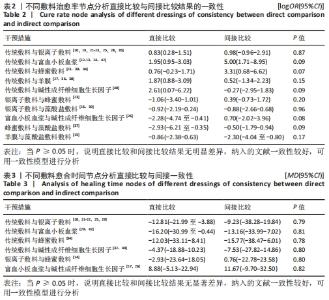
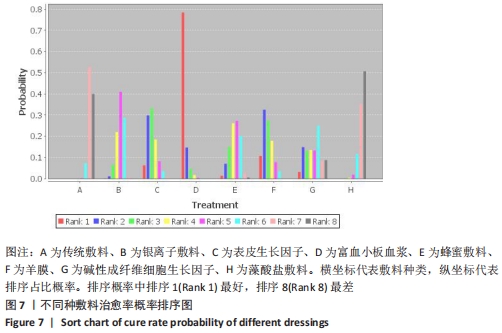
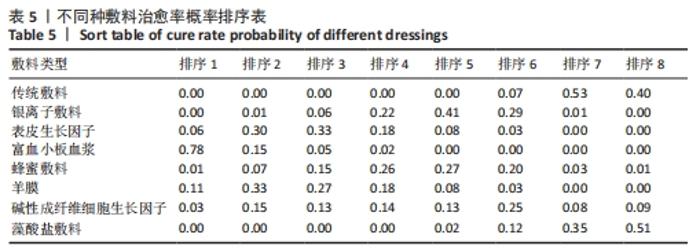
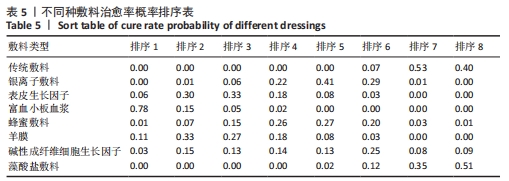
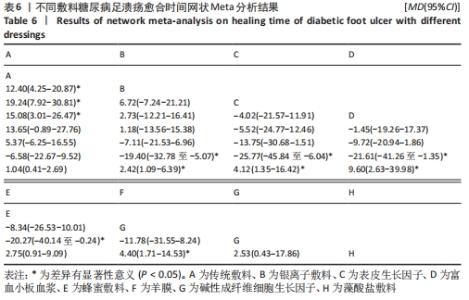
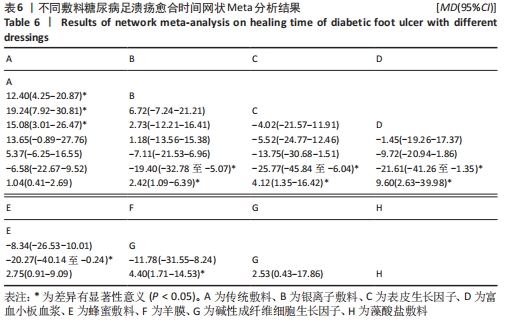
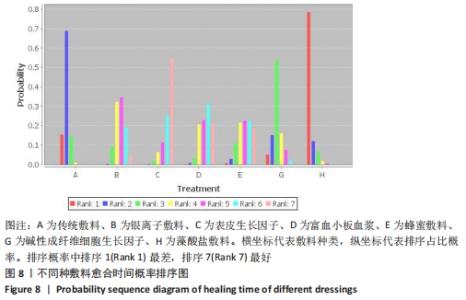
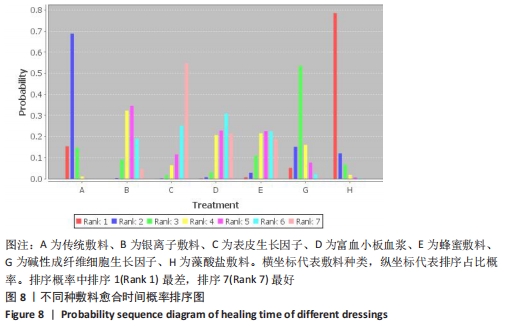
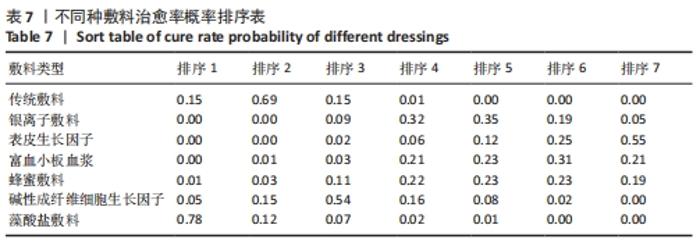
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (16): 2562-2569.doi: 10.12307/2022.258
Previous Articles Next Articles
A network meta-analysis of the efficacy of new medical dressings for diabetic foot ulcers
Zhou Junli1, Wang Xiaojun2, Wang Haijiao2, Li Chun1
- 1School of Nursing, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China; 2First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2020-12-13Revised:2020-12-15Accepted:2021-01-23Online:2022-06-08Published:2021-12-23 -
Contact:Li Chun, Associate professor, School of Nursing, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Zhou Junli, Master candidate, School of Nursing, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Characteristic Innovation Project of Guangdong Provincial Department of Education, No. 2020KTSCX025 (to LC); the Guangdong Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. 20181083 (to WHJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Junli, Wang Xiaojun, Wang Haijiao, Li Chun. A network meta-analysis of the efficacy of new medical dressings for diabetic foot ulcers[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2562-2569.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
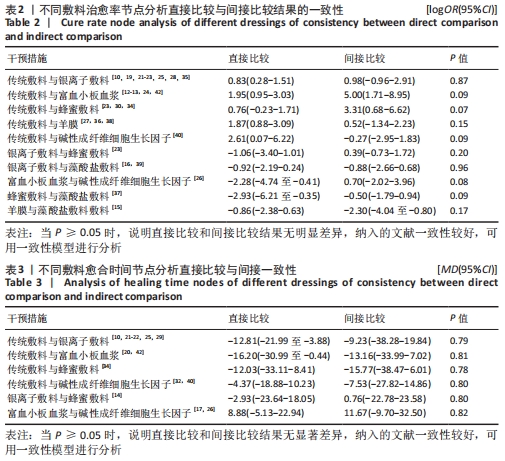
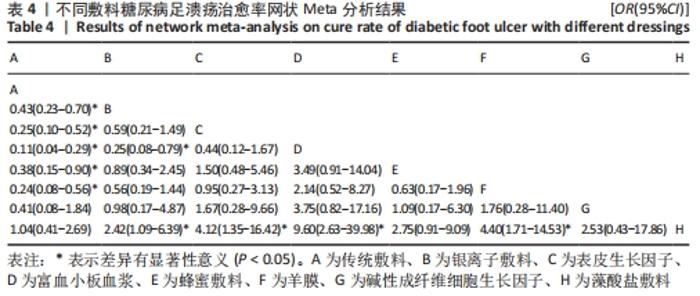
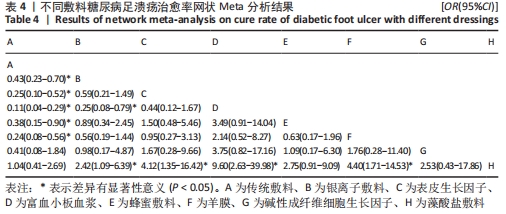
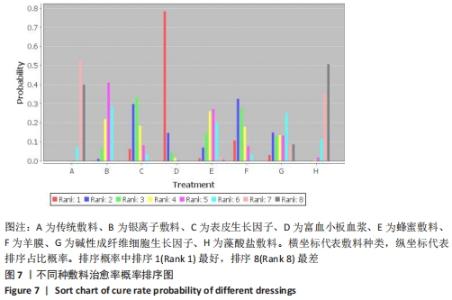
| [1] 谷涌泉.中国糖尿病足诊治指南[J].中国临床医生杂志,2020,48(1):19-27. [2] 薛耀明,邹梦晨.中国糖尿病足防治指南(2019版)解读[J].中华糖尿病杂志, 2019,11(2):88-91. [3] SINGH N, ARMSTRONG DG, LIPSKY BA. Preventing foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. JAMA. 2005;293(2):217-228. [4] ARMSTRONG DG, BOULTON AJM, BUS SA. Diabetic foot ulcers and their recurrence.N Engl J Med. 2017;376(24):2367-2375. [5] NDOSI M, WRIGHT-HUGHES A, BROWN S, et al. Prognosis of the infected diabetic foot ulcer: a 12-month prospective observational study. Diabet Med. 2018;35(1):78-88. [6] AMERICAN DIABETES ASSOCIATION. Economic costs of diabetes in the U.S. in 2012. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(4):1033-1046. [7] 田金徽,李伦,赵晔,等.网状Meta分析的撰写与报告[J].中国药物评价,2013, 30(6):321-323,333. [8] 汪洋.Cochran偏倚风险评估工具简介[J].中国全科医学,2019,22(11):1322. [9] VAN VALKENHOEF G, TERVONEN T, ZWINKELS T, et al. ADDIS: a decision support system for evidence-based medicine. Decision Support Systems. 2013;55(2):459-475. [10] 陈文健,廖米荣.纳米银烧烫伤贴与常规凡士林纱布治疗糖尿病足的疗效比较[J].中国现代医生,2020,58(1):113-115. [11] VISWANATHAN V, JUTTADA U, BABU M. Efficacy of recombinant human epidermal growth factor (Regen-D150) in healing diabetic foot ulcers: a hospital-based randomized controlled trial. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2020;19(2):158-164. [12] ELSAID A, EL-SAID M, EMILE S, et al. Randomized Controlled Trial on Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Saline Dressing in Treatment of Non-healing Diabetic Foot Ulcers.World J Surg. 2020;44(4):1294-1301. [13] XIE J, FANG Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Autologous Platelet-Rich Gel for the Treatment of Diabetic Sinus Tract Wounds: a Clinical Study. J Surg Res. 2020;247:271-279. [14] AL SAEED M. Prospective randomized comparison of controlled release ionic silver hydrophilic dressings and medicated honey-impregnated dressings in treating neuropathic diabetic foot ulcer. Saudi J Health Sci. 2019;8(1):25-30. [15] TETTELBACH W, CAZZELL S, REYZELMAN AM, et al. A confirmatory study on the efficacy of dehydrated human amnion/chorion membrane dHACM allograft in the management of diabetic foot ulcers: a prospective, multicentre, randomised, controlled study of 110 patients from 14 wound clinics. Int Wound J. 2019;16(1):19-29. [16] 裴丽,刘晓萱,陈春妹.银离子藻酸盐敷料治疗糖尿病足溃疡疗效观察[J].中华现代护理杂志,2018,24(27):3303 [17] 付鹏,冯佳丽,苗婷,等.自体富血小板凝胶治疗对糖尿病足溃疡患者修复效果及生活质量的影响[J].解放军预防医学杂志,2018,36(7):858-861. [18] PARK KH, HAN SH, HONG JP, et al. Topical epidermal growth factor spray for the treatment of chronic diabetic foot ulcers: a phase III multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018;142:335-344. [19] GUPTA V, KAKKAR G, GILL AS, et al. Comparative study of nanocrystalline silver iondressings with normal saline dressings in diabetic foot ulcers. J Clin Diagn Res. 2018;12(6):C1-C4. [20] SINGH SP, KUMAR V, PANDEY A, et al. Role of platelet-rich plasma in healing diabetic foot ulcers:a prospective study. J Wound Care.2018;27(9):550-556. [21] 刘京,徐曌,张庚良,等.不同敷料对糖尿病足感染患者创面闭合指数及临床疗效的影响研究[J].中华医院感染学杂志, 2017,27(21):4880-4883. [22] 吴文娜,陈庚,方亿琼.探究银离子抗菌敷料在糖尿病足溃疡创面护理中的应用疗效[J].中国卫生标准管理,2017, 8(24):191-192. [23] TSANG KK, KWONG EW, TO TS, et al. A pilot randomized, controlled study of nanocrystalline silver, manuka honey, and conventional dressing in healing diabetic foot ulcer. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:5294890. [24] AHMED M, REFFAT SA, Hassan A, et al. Platelet-rich plasma for the treatment ofclean diabetic foot ulcers. Ann Vasc Surg. 2017;38:206-211. [25] 贺万强,罗伟华,李磊,等.银离子敷料治疗糖尿病足溃疡的疗效观察[J].中国循证医学杂志,2016,16(5):510-512. [26] 刘贯英,邓晓龙,孙玥,等.自体富血小板凝胶用于糖尿病足溃疡的治疗效果[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2016, 37(2):264-267. [27] MOHAJERI-TEHRANI MR, VARIJI Z, MOHSENI S, et al. Comparison of a bioimplant dressing with a wet dressing for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers: a randomized, controlled clinical trial. Wounds. 2016;28(7):248-254. [28] AGARWAL H, GUPTA AK, GUPTA N, et al. Comparison of results of silver-impregnated dressing with povidone iodine based-dressing in patients with diabetic foot.Hellenic J Surg. 2015;87:465-467. [29] 黄奕燕,林少娜,陈清华.纳米银抗菌敷料应用对糖尿病足患者感染控制的研究[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2015,25(15): 3492-3494. [30] IMRAN M, HUSSAIN MB, BAIG M. A randomized, controlled clinical trial of honey-impregnated dressing for treating diabetic foot ulcer. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2015;25(10):721-725. [31] 吴敬军,张红侠.小剂量重组人表皮生长因子对糖尿病足溃疡愈合情况的影响[J].中医学报,2014(B12):499-500. [32] 何月勇,张蓓,王姣姣,等.碱性成纤维细胞生长因子在2型糖尿病难治性慢性溃疡患者中的临床应用[J].中国医师进修杂志,2014,37(10):66-68. [33] GOMEZ-VILLA R, AGUILAR-REBOLLEDO F, LOZANO-PLATONOFF A, et al. Efficacy of intralesional recombinant human epidermal growth factor in diabetic foot ulcers in Mexican patients: a randomized double‐blinded controlled trial. Wound Repair Regen. 2014;22(4):497-503. [34] KAMARATOS AV, TZIROGIANNIS KN, IRAKLIANOU SA, et al. Manuka honey-impregnateddressings in the treatment of neuropathic diabetic foot ulcers. Int Wound J. 2014;11(3):259-263. [35] 李华.纳米银医用抗菌敷料在糖尿病足护理中的应用[J].中华医院感染学杂志, 2013,23(5):1162. [36] ZELEN CM, SERENA TE, DENOZIERE G, et al. A prospective randomised comparativeparallel study of amniotic membrane wound graft in the management of diabetic foot ulcers. Int Wound J. 2013;10(5):502-507. [37] ELDEEN M, FATHEY R, HASABALLAH A, et al. Topical honey versus alginate as dressing for management of wagner type 2 diabetic foot ulcer. J Am Sci. 2012. doi:10.7537/marsjas080912.64. [38] 玛依拉,张柏芳,吕江丽.人胎羊膜贴敷治疗糖尿病足的疗效观察与护理体会[J].中国药业,2012,21(A01):119-120. [39] JUDE EB, APELQVIST J, SPRAUL M, et al. Prospective randomized controlled study ofHydrofiber® dressing containing ionic silver or calcium alginate dressings innon‐ischaemic diabetic foot ulcers. Diabet Med. 2007;24(3):280-288. [40] 郑宏庭,方芳,陈卫,等.贝复济在糖尿病下肢血管病变治疗中的应用研究[J].局解手术学杂志,2007,16(6):385-386. [41] 刘开渊,张芳芳,黄昭穗.重组人表皮生长因子治疗糖尿病足疗效观察:附53例报告[J].中国医师杂志,2006,8(8): 1135-1136. [42] DRIVER VR, HANFT J, FYLLING CP, et al. A prospective, randomized,controlled trial of autologous platelet-rich plasma gel for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. Ostomy Wound Manage. 2006;52(6):68-70. [43] 王轩宇,阙华发.糖尿病足溃疡的中西医治疗研究进展[J].江西中医药大学学报,2020,32(2):122-124. [44] 许飞,许志俊,廖文强,等.慢性难愈性创面的治疗研究进展[J].江西医药, 2020,55(3):354-358. [45] SHAO S, PAN R, CHEN Y. Autologous platelet-rich plasma for diabetic foot ulcer. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2020;31(12): 885-890. |
| [1] | Jing Jinpeng, Zhang Yue, Liu Xiaomin, Liu Yi. Traditional Chinese medicine injection for promoting blood circulation in prevention of deep vein thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1467-1476. |
| [2] | Wang Nan, Qian Yuzhang, Xie Lin. Network Meta-analysis of different acupuncture methods for the treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 813-820. |
| [3] | Yang Feng, Zhao Qian, Zhang Shixuan, Zhao Tienan, Feng Bo. Effectiveness and safety of rapamycin combined with CD133 antibody stent in preventing vascular restenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 579-584. |
| [4] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [5] | Liu Xiaolin, Liu Shutai, Han Xiaoqian, Mu Xinyue. Topical simvastatin administration in the treatment of periodontitis: effect of loading on sustained drug release system or biomaterial scaffold system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2596-2601. |
| [6] | Gao Lei, Qin Xinyuan, Li Tianbo, Wang Shuo, Yu Zeyang, Wang Jiangning. Co-transplantation of acellular allogeneic dermis and autologous split-thickness skin for repairing diabetic foot wound [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2138-2143. |
| [7] | Li Shijie, Ma Liqiong, Xiong Xianmei, Zhang Yan, Chen Zijie, Feng Junming, Gao Yijia, Zeng Zhanpeng. Effect of panax notoginseng saponins on platelet-rich plasma promoting bone defect healing in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2155-2160. |
| [8] | Zhao Zixi, Xu Jun, Ding Min, Li Xiwen, Zhang Jinghang, Wang Penghua. Changes of type I and III collagen and matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9 on the wound of diabetic foot ulcer with external application of medical collagen dressing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1544-1550. |
| [9] | Wen Ke, Lu Yanqing, Hou Nan, Ma Ruina, Cui Pengcheng, Lü Die, Xu Xiaoli. Application of biomaterial and tissue engineering in reconstruction of tympanic membrane defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1620-1624. |
| [10] | Jiang Hongying, Zhu Liang, Yu Xi, Huang Jing, Xiang Xiaona, Lan Zhengyan, He Hongchen. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on pressure ulcers after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1149-1153. |
| [11] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [12] | Li Li, Ma Li. Immobilization of lactase on magnetic chitosan microspheres and its effect on enzymatic properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 576-581. |
| [13] | Xiong Chen, He Guiping, Zhang Kun, He Xiao, Yang Jiarui, He Changjun, Wang Xiaolong, Wang Chen, Shi Zhengwei, Zhu Yangjun, Heng Lisong. Conservative treatment, open reduction, percutaneous minimally invasive plate internal fixation and intramedullary nail fixation in the treatment of humeral shaft fractures: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(36): 5878-5887. |
| [14] | Fang Xin, Guo Jinming, Liu Pinduan. Different concentrations of platelet rich plasma in the repair of cartilage defects in rabbits with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(35): 5588-5593. |
| [15] | Li Chenkai, Qin Wen, Liu Chun, Chen Wenyang, Zhao Hongbin. Three-dimensional electrohydrodynamic printing of attapulgite/polycaprolactone scaffolds and osteogenic differentiation ability in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(34): 5459-5464. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||