[1] WOODS AJ, ANTAL A, BIKSON M, et al. A technical guide to tDCS, and related non-invasive brain stimulation tools. Clin Neurophysiol. 2016;127(2):1031-1048.
[2] YAVARI F, JAMIL A, MOSAYEBI SAMANI M, et al. Basic and functional effects of transcranial Electrical Stimulation (tES)-An introduction. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018;85:81-92.
[3] LIEW SL, SANTARNECCHI E, BUCH ER, et al. Non-invasive brain stimulation in neurorehabilitation: local and distant effects for motor recovery. Front Hum Neurosci. 2014;8:378.
[4] MATSUMOTO H, UGAWA Y. Adverse events of tDCS and tACS: A review. Clin Neurophysiol Pract. 2017;2:19-25.
[5] ANTAL A, ALEKSEICHUK I, BIKSON M, et al. Low intensity transcranial electric stimulation: Safety, ethical, legal regulatory and application guidelines. Clin Neurophysiol. 2017;128(9):1774-1809.
[6] KEKIC M, BOYSEN E, CAMPBELL IC, et al. A systematic review of the clinical efficacy of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in psychiatric disorders. J Psychiatr Res. 2016;74:70-86.
[7] FLOEL A. tDCS-enhanced motor and cognitive function in neurological diseases. Neuroimage. 2014;85 Pt 3:934-947.
[8] PISONI A, MATTAVELLI G, PAPAGNO C, et al. Cognitive Enhancement Induced by Anodal tDCS Drives Circuit-Specific Cortical Plasticity. Cereb Cortex. 2018;28(4):1132-1140.
[9] LEFAUCHEUR JP. Boosting physical exercise with cortical stimulation or brain doping using tDCS: Fact or myth? Neurophysiol Clin. 2019;49(2):95-98.
[10] REARDON S. Performance boost paves way for ‘brain doping’ - Electrical stimulation seems to boost endurance in preliminary studies. Nature. 2016;531:283-284.
[11] 王开元,刘宇. “神经启动”技术增强运动表现[J].体育科学,2018,38(1):96-97.
[12] 卞秀玲,王雅娜,王开元,等.经颅直流电刺激技术及其在提升运动表现中的应用[J].体育科学,2018,38(5):66-72.
[13] HUANG L, DENG Y, ZHENG X, et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation with halo sport enhances repeated sprint cycling and cognitive performance. Front Physiol. 2019;10:118.
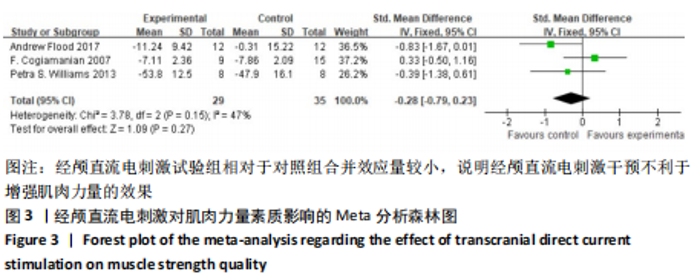
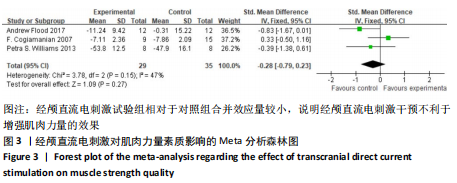
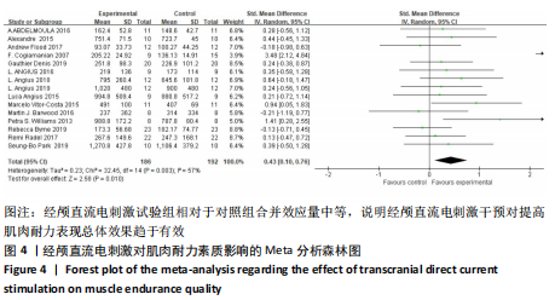
[14] COGIAMANIAN F, MARCEGLIA S, ARDOLINO G, et al. Improved isometric force endurance after transcranial direct current stimulation over the human motor cortical areas. Eur J Neurosci. 2007;26(1):242-249.
[15] BARWOOD MJ, BUTTERWORTH J, GOODALL S, et al. The effects of direct current stimulation on exercise performance, pacing and perception in temperate and hot environments. Brain Stimul. 2016;9(6): 842-849.
[16] OKANO AH, FONTES EB, MONTENEGRO RA, et al. Brain stimulation modulates the autonomic nervous system, rating of perceived exertion and performance during maximal exercise. Br J Sports Med. 2015; 49(18):1213-1218.
[17] ABDELMOULA A, BAUDRY S, DUCHATEAU J. Anodal transcranial direct current stimulation enhances time to task failure of a submaximal contraction of elbow flexors without changing corticospinal excitability. Neuroscience. 2016;322:94-103.
[18] ANGIUS L, MAUGER AR, HOPKER J, et al. Bilateral extracephalic transcranial direct current stimulation improves endurance performance in healthy individuals. Brain Stimul. 2018;11(1):108-117.
[19] WILLIAMS PS, HOFFMAN RL, CLARK BC. Preliminary evidence that anodal transcranial direct current stimulation enhances time to task failure of a sustained submaximal contraction. PLoS One. 2013; 8(12):e81418.
[20] VITOR-COSTA M, OKUNO NM, BORTOLOTTI H, et al. Improving cycling performance: transcranial direct current stimulation increases time to exhaustion in cycling. PLoS One. 2015;10(12):e0144916.
[21] PARK SB, SUNG DJ, KIM B, et al. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation of motor cortex enhances running performance. PLoS One. 2019;14(2):e0211902.
[22] RADEL R, TEMPEST G, DENIS G, et al. Extending the limits of force endurance: Stimulation of the motor or the frontal cortex? Cortex. 2017;97:96-108.
[23] DENIS G, ZORY R, RADEL R. Testing the role of cognitive inhibition in physical endurance using high-definition transcranial direct current stimulation over the prefrontal cortex. Hum Mov Sci. 2019;67:102507.
[24] BYRNE R, FLOOD A. The influence of transcranial direct current stimulation on pain affect and endurance exercise. Psychol Sport Exerc. 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.psychsport. 2019.101554
[25] ANGIUS L, HOPKER JG, MARCORA SM, et al. The effect of transcranial direct current stimulation of the motor cortex on exercise-induced pain. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2015;115(11):2311-2319.
[26] ANGIUS L, PAGEAUX B, HOPKER J, et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation improves isometric time to exhaustion of the knee extensors. Neuroscience. 2016; 339:363-375.
[27] ANGIUS L, SANTARNECCHI E, PASCUAL-LEONE A, et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation over the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex improves inhibitory control and endurance performance in healthy individuals. Neuroscience. 2019;419:34-45.
[28] FLOOD A, WADDINGTON G, KEEGAN RJ, et al. The effects of elevated pain inhibition on endurance exercise performance. Peer J. 2017;5:e3028.
[29] 国家体育总局科技司.现代教练员科学训练理论与实践[M].北京:人民体育出版社,2018:48-56.
[30] SUCHOMEL TJ, NIMPHIUS S, BELLON CR, et al. The importance of muscular strength: training considerations. Sports Med. 2018;48(4):765-785.
[31] KAMEN G. Neural issues in the control of muscular strength. Res Q Exerc Sport. 2004;75(1):3-8.
[32] MAUGER AR. Factors affecting the regulation of pacing: current perspectives. Open Access J Sports Med. 2014;5:209-214.
[33] FLOOD A, WADDINGTON G, CATHCART S. Examining the relationship between endogenous pain modulation capacity and endurance exercise performance. Res Sports Med. 2017;25(3):300-312.
(责任编辑:GD,ZN,SX)
|