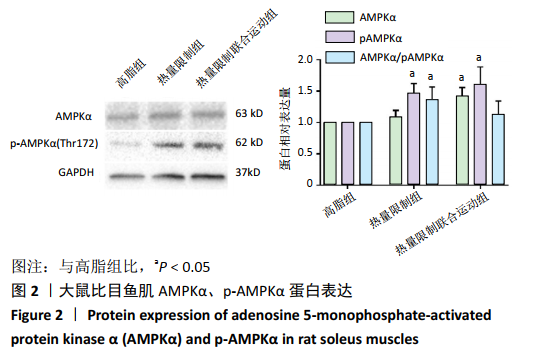
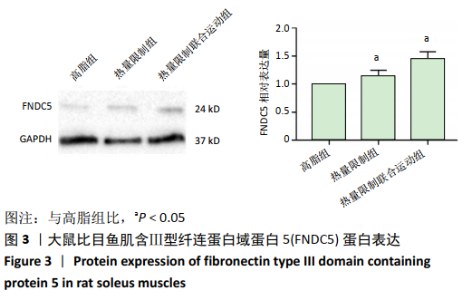
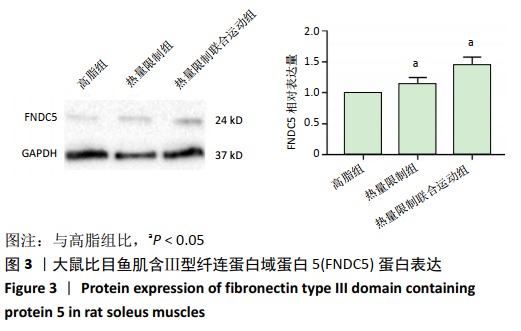
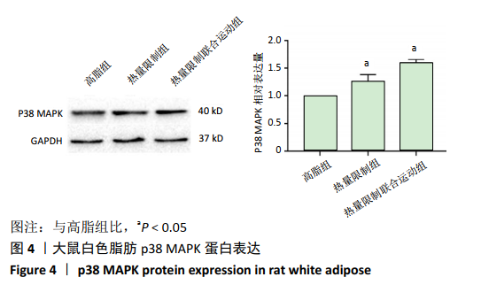
[1] REZA A, MARIANNE Y, LUCY P, et al. Altered Left Ventricular Ion Channel Transcriptome in a High-Fat-Fed Rat Model of Obesity: Insight into Obesity-Induced Arrhythmogenesis. J Obes. 2016;90(5):1244-1251.
[2] JOHN EH, JUSSARA MC, ALEXANDRE AS, et al. Obesity-induced hypertension: interaction of neurohumoral and renal mechanisms. Circ Res. 2015;116(6):991-1006.
[3] EMMA HA, STEPHEN DH. Obesity and cancer: mechanistic insights from transdisciplinary studies. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2015;22(6):365-386.
[4] JOHN W, SONS L. Irisin–a myokine potentially bridg/kiuing muscle and fat tissue in cachexia. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2015;6(4): 396-397.
[5] ZHANG Y, LI R, MENG Y, et al. Irisin stimulates browning of white adipocytes through mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 MAP kinase and ERK MAP kinase signaling. Diabetes. 2014;63(2):514-525.
[6] SHAN T, LIANG X, BI P, et al. Myostatin knockout drives browning of white adipose tissue through activating the AMPK-PGC1alpha-Fndc5 pathway in muscle. FASEB J. 2013;27:1981-1989.
[7] KAYSER B, VERGES S. Hypoxia, energy balance and obesity: from pathophysiological mechanisms to new treatment strategies. Obes Rev. 2013;14:579-592.
[8] WEISS EP, RACETTE SB, VILLAREAL DT, et al. Improvements in glucose tolerance and insulin action induced by increasing energy expenditure or decreasing energy intake: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006;84(5):1033-1042.
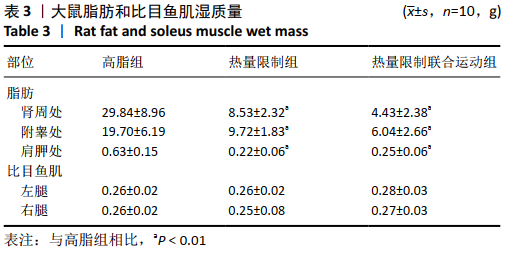
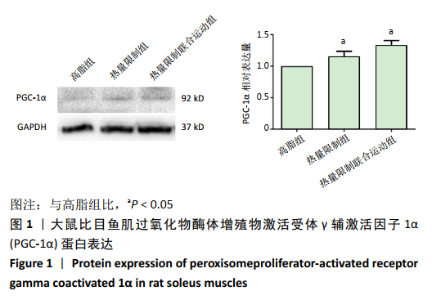
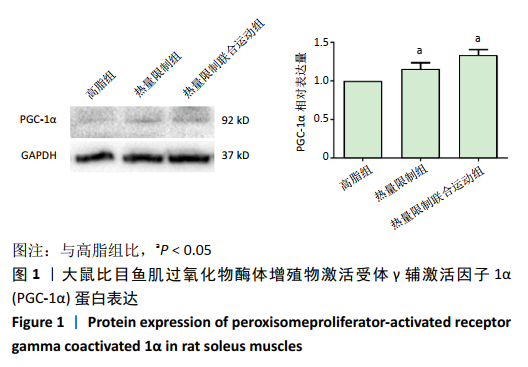
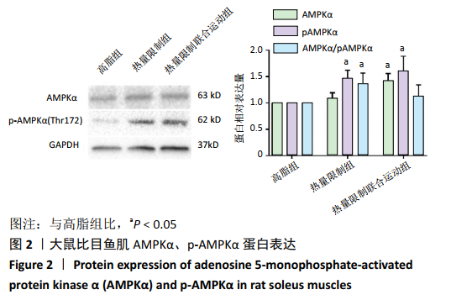
[9] 史霄雨,冯子洋,刘子铭,等.高强度间歇训练肥胖大鼠减脂效果及鸢尾素的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(14):2137-2141.
[10] 王祯,于亮,史霄雨.4 周间歇性禁食对大鼠骨骼肌质量及自噬的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2017,36(8):680-686.
[11] 王祯,于亮,付悦.间歇性禁食与运动对骨骼肌自噬的激活及减脂效果的比较[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2020,36(4):289-295.
[12] BROWNELL KD, GREENWOOD MR, STELLAR E, et al. The effects of repeated cycles of weight loss and regain in rats. Physiol Behav. 1986;38:459-464.
[13] Rodríguez A, Becerril S, Valentí V, et al. Short-term effects of sleeve gastrectomy and caloric restriction on blood pressure in diet-induced obese rats. Obes Surg.2012;22:1481-1490.
[14] Oh M, Kim S, An KY, et al. Effects of alternate day calorie restriction and exercise on cardiometabolic risk factors in overweight and obese adults: an exploratory randomized controlled study. BMC Public Health. 2018;18(1):1124.
[15] 刘文倩,张建刚,谢岚,等.运动和限食减肥对肥胖大鼠血浆和胃组织ghrelin表达的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2010,29(2):184-188.
[16] PARDO M, CRUJEIRAS AB, AMIL M, et al. Association of Irisin with fat mass, resting energy expenditure, and daily acticity in conditions of extreme body mass index. Int J Endocrinol. 2014;2014:857270.
[17] 苏坤霞.不同强度耐力运动影响高脂诱导肥胖模型小鼠血清Irisin含量、骨骼肌PGC-1α、NFDC5、PPARδ蛋白的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(3):427-434.
[18] BOSTROM P, WU J, CHOWSKI MP, et al. A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like deveopment of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature. 2012;481(7382):463-468.
[19] KIM HJ, SO B, CHOI M, et al. Resistance exercise training increases the expression of irisin concomitant with improvement of muscle function in aging mice and humans. Exp Gerontol. 2015;70:11-17.
[20] JEDRYCHOWSKI MP, WRANN CD, PAULO JA, et al. Detection and Quantitation of Circulating Human Irisin by Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Cell Metab. 2015;22(4):734-740.
[21] LALLY JS, FORD RJ, JOHAR J, et al. Skeletal muscle AMPK is essential for the maintenance of FNDC5 expression. Physiol Rep. 2015;3(5):e12343.
[22] O’NEILL HM, MAARBJERG SJ, CRANE JD, et al. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) beta1beta2 muscle null mice reveal an essential role for AMPK in maintaining mitochondrial content and glucose uptake during exercise. Natl Acad. 2011;108:16092-16097.
[23] MOHAMMAD JF, TIMOTHY M, KAMRAN G, et al. Does PGC1α/FNDC5/BDNF Elicit the Beneficial Effects of Exercise on Neurodegenerative Disorders? . Neuromolecular Med. 2016;18(1):1-15.
[24] COUSIN B, CINTI S, MORRONI M, et al. Occurrence of brown adipocytes in rat white adipose tissue: molecular and morphological characterization. J Cell Sci. 1992;103:931-942.
[25] PETROVIC N, WALDEN TB, SHABALINA IG, et al. Chronic Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor c (PPARc) Activation of Epididymally Derived White Adipocyte Cultures Reveals a Population of Thermogenically Competent, UCP1-containing Adipocytes Molecularly Distinct from Classic Brown Adipocytes. J of Biol Chem. 2010;285: 7153-7164.
[26] PUIGSERVER P, WU Z, PARK CW, et al. A ColdInducible Coactivator of Nuclear Receptors Linked to Adaptive Thermogenesis. Cell. 1998;92: 829-839. |