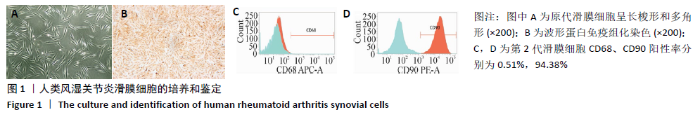
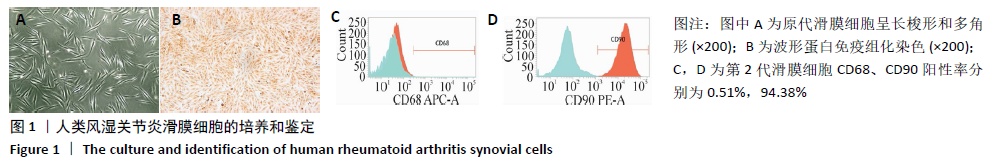
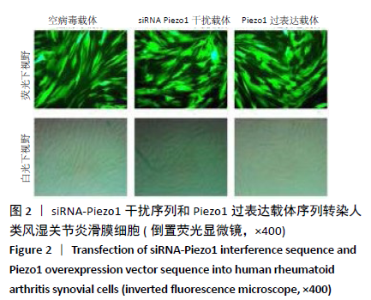
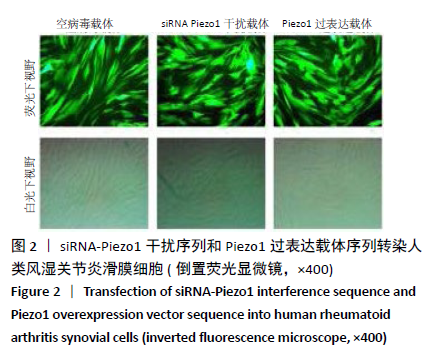
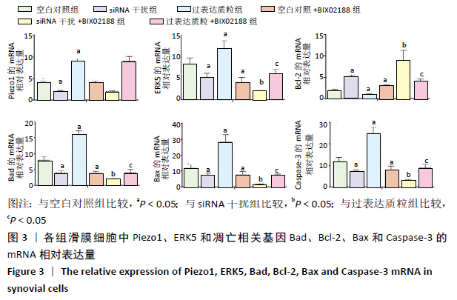
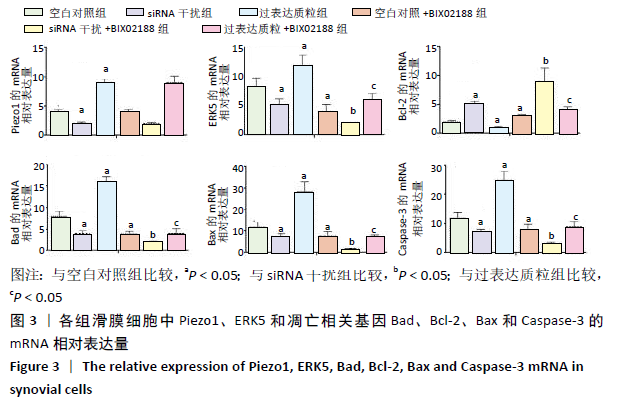
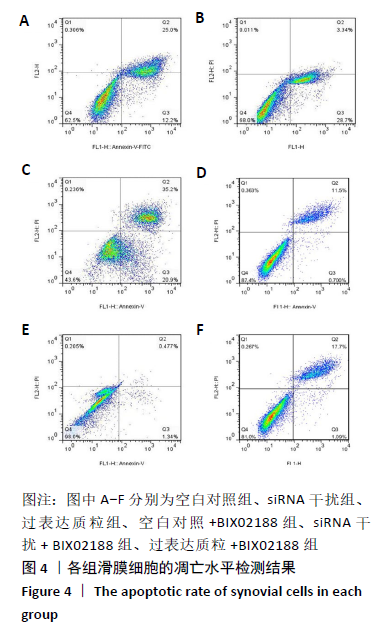
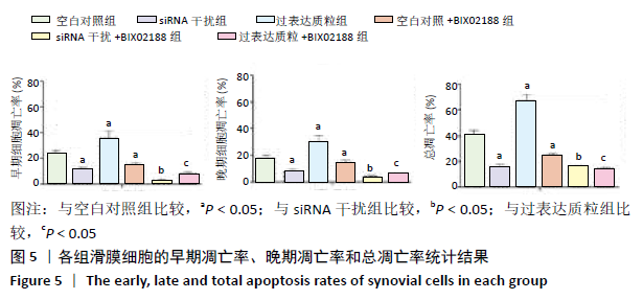
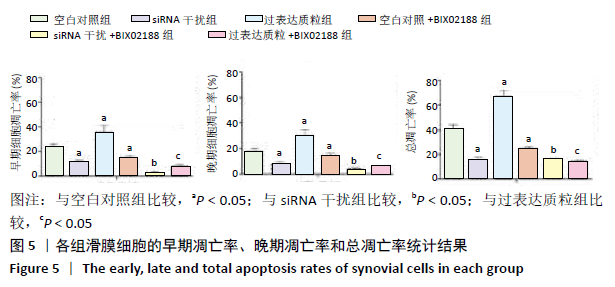
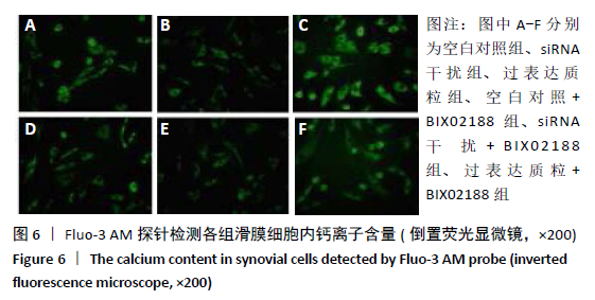
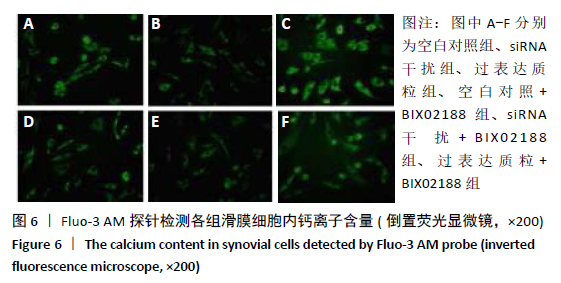
[1] 周祺,高益,魏康,等.全膝关节置换治疗类风湿关节炎:关节功能及相关生化指标的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,11(9): 1337-1341.
[2] MCINNES IB, SCHETT G. Pathogenetic insights from the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2017;389(10086):2328-2337.
[3] RAO DA, GURISH MF, MARSHALL JL, et al. Pathologically expanded peripheral T helper cell subset drives B cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2017;542(7639):110-114.
[4] 陈东旭,薄占东,张翼.间充质干细胞治疗类风湿性关节炎的研究与应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2011,15(49):9267-9270.
[5] 周薇,吕永钢, Singh GK,等.周期性机械拉伸对类风湿关节炎和骨关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞BMP-2表达的影响[J].医用生物力学, 2011,26(2):121-127.
[6] LIN YC, GUO YR, MIYAGI A, et al. Force-induced conformational changes in PIEZO1. Nature. 2019;573(7773):230-234.
[7] KANG H, HONG Z, ZHONG M, et al. Piezo1 mediates angiogenesis through activation of MT1-MMP signaling. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019;316(1):C92-C103.
[8] ROMAC JM, SHAHID RA, SWAIN SM, et al. Piezo1 is a mechanically activated ion channel and mediates pressure induced pancreatitis. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1715.
[9] GUDIPATY SA, LINDBLOM J, LOFTUS PD, et al. Mechanical stretch triggers rapid epithelial cell division through Piezo1. Nature. 2017;543 (7643):118-121.
[10] 杨骐宁,曹杨,周勇伟,等. Piezo1蛋白在人退变软骨细胞应力模型中的表达特点[J].中国骨伤,2018,31(6):550-555.
[11] MCINNES IB, SCHETT G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(23):2205-2219.
[12] PISETSKY DS. Advances in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Costs and Challenges. N C Med J. 2017;78(5):337-340.
[13] MOLLARD E, MICHAUD K. Mobile Apps for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Opportunities and Challenges. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2019;45(2): 197-209.
[14] NARAZAKI M, TANAKA T, KISHIMOTO T. The role and therapeutic targeting of IL-6 in rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2017;13(6):535-551.
[15] GIBOFSKY A. Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis: A Synopsis. Am J Manag Care. 2014;20(7 Suppl): S128-135.
[16] NAKAMURA T, SHIRAISHI N, MORIKAMI Y, et al. Systemic AA amyloidosis secondary to rheumatoid arthritis may be treatable but is still difficult to manage in daily clinical practice. Amyloid. 2019;26(sup1):123-124.
[17] 孙晓雷,赵斌,马信龙,等.循环牵张应力对人骨关节炎软骨细胞增殖的影响[J].天津医药,2013,41(11):1073-1075.
[18] COX CD, BAVI N, MARTINAC B. Cytoskeleton-Associated Proteins Modulate the Tension Sensitivity of Piezo1. Biophysical Journal. 2018; 114(3):111-127.
[19] LI XF, ZHANG Z, CHEN ZK, et al. Piezo1 protein induces the apoptosis of human osteoarthritis-derived chondrocytes by activating caspase-12, the signaling marker of ER stress. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40(3):845-853.
[20] FU H, HU D, ZHANG L, et al. Role of extracellular vesicles in rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Immunol. 2018;93:125-132.
[21] MIZOGUCHI F, SLOWIKOWSKI K, WEI K, et al. Functionally distinct disease-associated fibroblast subsets in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):789.
[22] YAN Y, SINGH GK, ZHANG F, et al. Comparative study of normal and rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes proliferation under cyclic mechanical stretch: role of prostaglandin E2. Connect Tissue Res. 2012;53(3):246-254.
[23] WINKLMAYR M, GAISBERGER M, KITTL M, et al. Dose-Dependent Cannabidiol-Induced Elevation of Intracellular Calcium and Apoptosis in Human Articular Chondrocytes. J Orthop Res. 2019;37(12):2540-2549.
[24] KIM SH, KIM KY, YU SN, et al. Monensin Induces PC-3 Prostate Cancer Cell Apoptosis via ROS Production and Ca2+ Homeostasis Disruption. Anticancer Res. 2016;36(11):5835-5843.
|