| [1] van Must AB. Femoral neck non-unions: How do I do it? Injury. 2007;38 Suppl 2: S51-S54. [2] Kaplan T, Akesen B, Demira? B,et al. Comparative results of percutaneous cannulated screws, dynamic compression type plate and screw for the treatment of femoral neck fractures. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2012;18(1):65-70. [3] Enocson A, Lapidus LJ. The vertical hip fracture -- a treatment challenge. a cohort study with an up to 9 year follow-up of 137 consecutive hips treated with sliding hip screw and antirotation screw. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012;13(1): 171. [4] Liporace F, Gaines R, Collinge C, et al. Results of internal fixation of Pauwels type-3 vertical femoral neck fractures. J Bone Joint Surg (Am). 2008;90(8): 1654-1659. [5] Lecerf G, Fessy MH, Philippot R, et al. Femoral offset: anatomical concept, definition, assessment, implications for preoperative templating and hip arthroplasty. Rev Chir Orthop Traumatol. 2009;95:210-219. [6] Boraiah S, Paul O, Hammoud S, et al. Predictable Healing of Femoral Neck Fractures Treated With Intraoperative Compression and Length-Stable Implants. J Trauma. 2010; 69(1): 142-147. [7] Zlowodzki M, Jönsson A, Paulke R. Shortening after femoral neck fracture fixation: is there a solution? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;(461):213-218. [8] Zlowodzki M, Brink O, Switzer J, et al. The effect of shortening and varus collapse of the femoral neck on function after fixation of intracapsular fracture of the hip: a multi-centre cohort study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90(11):1487-1494. [9] Caviglia HA, Osorio PQ, Comando D.Classification and diagnosis of intracapsular fractures of the proximal femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(399):17-27. [10] Mahomed NN, Arndt DC, McGrory BJ, et al. The Harris hip score: comparison of patient self - report with surgeon assessment. J Arthoplasty. 2001;16(5):575.[11] Bes C, Güven M, Akman B, et al. Can bone quality be predicted accurately by Singh index in patients with rheumatoid arthritis? Clin Rheumatol. 2012;31(1):85-89. [12] Van Embden D, Rhemrev SJ, Genelin F, et al. The reliability of a simplified Garden classification for intracapsular hip fractures. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012;98(4):405-408. [13] van Embden D, Roukema GR, Rhemrev SJ, et al.The Pauwels classification for intracapsular hip fractures: is it reliable? Injury. 2011;42(11):1238-1240. [14] Mei H, Chen W, Jiang F, et al. Longitudinal replication studies of GWAS risk SNPs influencing body mass index over the courseof childhood andadulthood. PLoS One. 2012;7(2): e31470. [15] Karanicolas PJ, Bhandari M, Walter SD, et al. Interobserver Reliability of Classification Systems to Rate the Quality of Femoral Neck Fracture Reduction. J Orthop Trauma. 2009; 23(6):408-412.[16] Mayman D, Vasarhelyi EM, Long W, et al. Computer-assisted guidewire insertion for hip fracture fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 2005;19:610-615.[17] Steines D, Liew SW, Arnaud C, et al.Radiographic Trabecular 2D and 3D Parameters of Proximal Femoral Bone Cores Correlate with Each Other and with Yield Stress. Osteoporos Int. 2009;20(11):1929-1938. [18] Razik F, Alexopoulos AS, El-Osta B, et al. Time to internal fixation of femoral neck fractures in patients under sixty years-does this matter in the development of osteonecrosis of femoral head? Int Orthop. 2012;36(10):2127-2132. [19] Weil YA, Khoury A, Zuaiter I, et al. Femoral neck shortening and varus collapse after navigated fixation of intracapsular femoral neck fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2012;26(1):19-23. [20] Boraiah S, Paul O, Gardner MJ, et al. Outcomes of length-stable fixation of femoral neck fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010;130(12):1523-1531.[21] Bhandari M, Tornetta P 3rd, Hanson B, et al. Optimal internal fixation for femoral neck fractures: multiple screws or sliding hip screws? J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23:403-407. [22] Berkes MB, Little MT, Lazaro LE,et al. Catastrophic failure after open reduction internal fixation of femoral neck fractures with a novel locking plate implant. J Orthop Trauma. 2012; 26(10):e170-176.[23] Kiyama L, Naito M, Shinoda L, et al. Hip abductor strengths after total hip arthroplasty via the lateral and posterolateral approaches. J Arthroplasty. 2010;25(1): 76-80.[24] Little NJ,Busch CA,Gallagher JA,et al. Acetabular polyethylene wear and acetabular inclination and femoral offset. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:2895-2900. [25] Lugade V, Wu A, Jewett B, et al. Gait asymmetry following an anterior and anterolateral approach to total hip arthroplasty. Clin Biomech. 2010;25(7):675-680. [26] Hossain S, Paton RW. The management of intracapsular fractures of the proximal femur. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001; 83:618.[27] Lee CE, Browell LM, Jones DL. Measuring health in patients with cervical and lumbosacral spinal disorders: is the 12-Item Short-Form Health Survey a valid alternative for the 36-Item Short-Form Health Survey? Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008; 89:829-833.[28] Liebergall M, Ben-David D,Weil Y, et al. Computerized navigation for the internal fixation of femoral neck fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88:1748-1754. [29] Gurusamy K, Parker MJ, Rowlands TK. The complications of displaced intracapsular fractures of the hip: the effect of screw positioning and angulation on fracture healing. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87: 632-634. [30] Charles MN, Bourne RB, Davey JR, et al. Soft-tissue balancing of the hip:the role of femoral offset restoration. Instr Course Lect. 2005;54:131-141. |
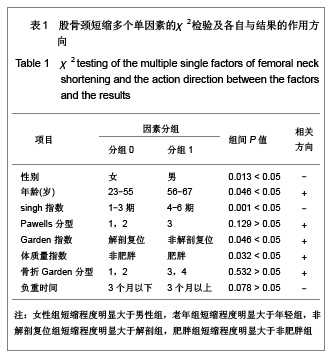
.jpg)