中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (4): 750-754.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.04.028
• 骨与关节循证医学 evidence-based medicine of the bone and joint • 上一篇 下一篇
关节内注射可乐定对比吗啡对膝关节镜后镇痛作用的Meta分析
孙 绕1,田宏亮1,2,李 伦1,2,杨克虎1,张泽倩1,3,李秀霞1
- 1兰州大学循证医学中心,兰州大学基础医学院 甘肃省兰州市 730000
2兰州大学第一临床医学院,甘肃省兰州市 730000
3兰州大学公共卫生学院,甘肃省兰州市 730000
Intraarticular clonidine versus morphine for analgesia after arthroscopic knee surgery: A Meta-analysis
Sun Rao1, Tian Hong-liang1, 2, Li Lun1, 2, Yang Ke-hu1, Zhang Ze-qian1, 3, Li Xiu-xia1
- 1 Evidence-Based Medicine Center of Lanzhou University, School of Basic Medical Science, Lanzhou Unversity, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China
2 The First Clinical Medical College of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China
3 School of Public Health, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China
摘要:
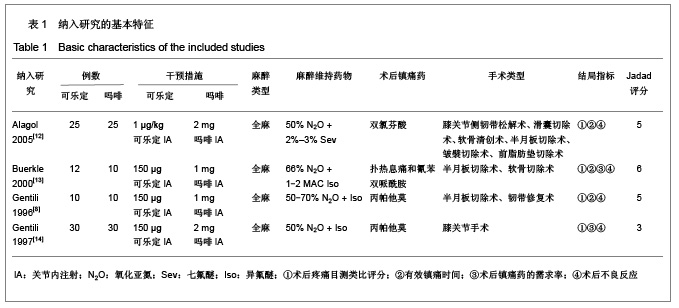
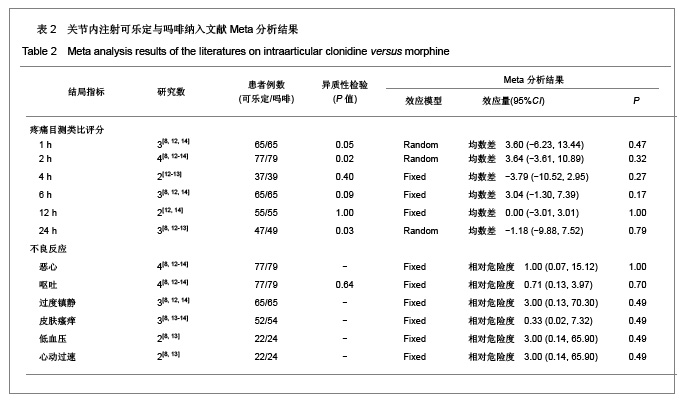
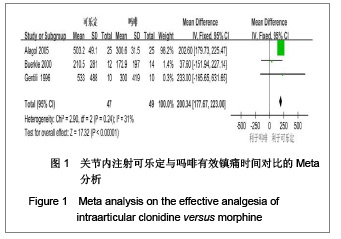
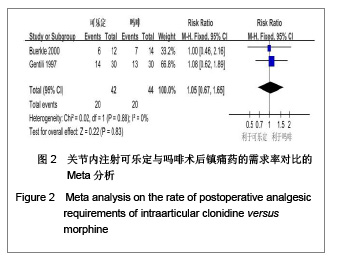
背景:关节内注射可乐定或吗啡均能产生镇痛作用,但二者的有效性和安全性存在争议。 目的:系统评价关节内注射可乐定对比吗啡治疗膝关节镜术后疼痛的有效性和安全性。 方法:计算机检索PubMed、EMBASE、Cochrane Library、ISI Web of knowledge、中国生物医学文献数据库(CBM)、中文科技期刊全文数据库(VIP)、中国期刊全文数据库(CNKI)及万方数据库中关节内注射可乐定对比吗啡治疗膝关节镜术后疼痛的随机对照试验(RCT),检索时间均从建库至2012年1月。两位研究者按照纳入标准筛选文献、提取资料,按照改良Jadad评分表评价纳入研究质量,采用RevMan5.1进行Meta分析。 结果与结论:纳入4个RCT,合计156例患者。Meta分析结果:①疼痛目测类比评分:二者在术后1,2,4,6,12,24 h无差异。②有效镇痛时间:可乐定与吗啡相比能延长术后有效镇痛时间[MD= 200.34,95%CI(177.67,223.00),P < 0.01]。③术后镇痛药的需求率:二者差异无显著性意义[RR=1.05,95%CI(0.67,1.65),P=0.83]。④不良反应:二者在术后恶心、呕吐、过度镇静、皮肤瘙痒、低血压和心动过速等不良反应的发生方面的作用无差别。现有证据表明,关节内注射可乐定与吗啡对膝关节镜术后疼痛的缓解程度相同,术后镇痛药的需求率也无明显差异,但可乐定能产生更长的镇痛作用,二者不良反应发生率无差异,结果尚需开展更多研究来证实。
中图分类号: