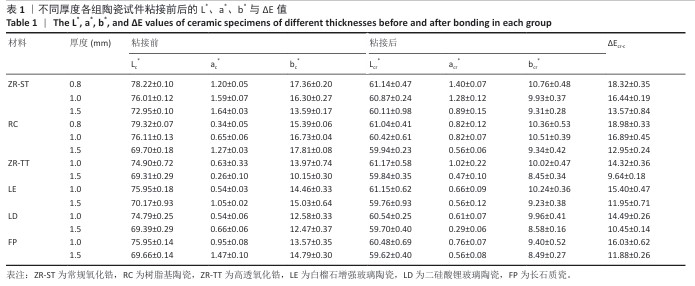
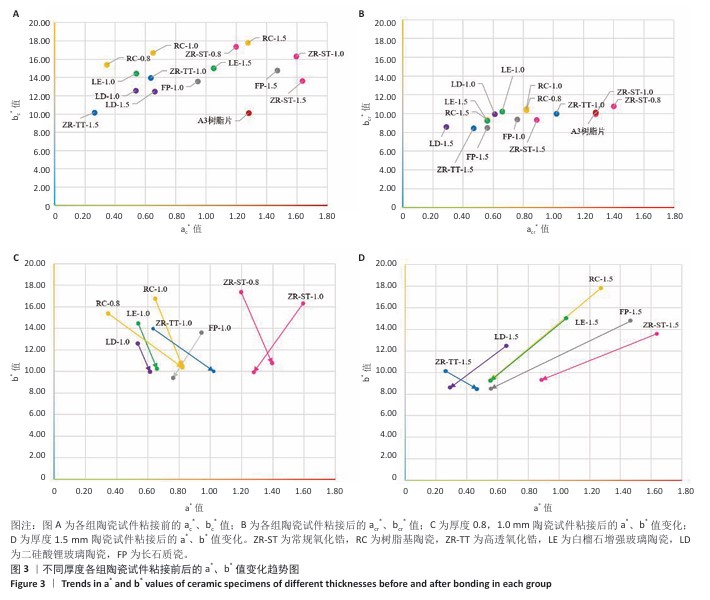
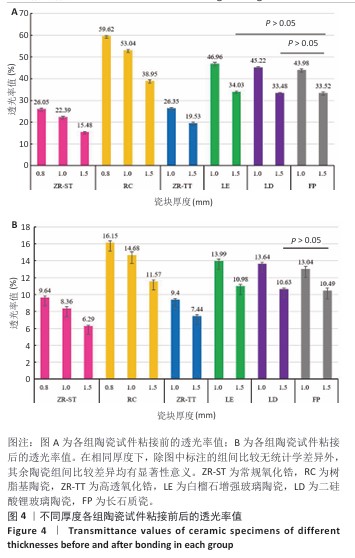
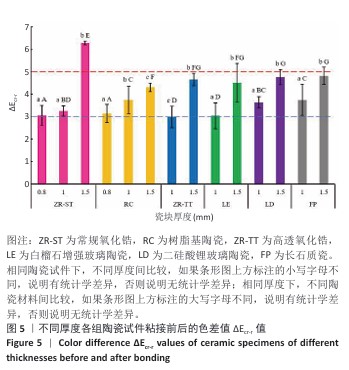
[1] 中华口腔医学会口腔美学专业委员会,中华口腔医学会口腔材料专业委员会.全瓷美学修复材料临床应用专家共识[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2019,54(12):825-828.
[2] BACCHI A, CESAR PF. Advances in ceramics for dental applications. Dent Clin North Am. 2022;66(4):591-602.
[3] 金诗韵,曹轶婷,孙健.高透、超透氧化锆陶瓷半透明度和弯曲强度的比较[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2020,29(1):3-8.
[4] BAYINDIR F, KOSEOGLU M. The effect of restoration thickness and resin cement shade on the color and translucency of a high translucency monolithic zirconia. J Prosthet Dent. 2020;123(1):149-154.
[5] BACCHI A, BOCCARDI S, ALESSANDRETTI R, et al. Substrate masking ability of bilayer and monolithic ceramics used for complete crowns and the effect of association with an opaque resin-based luting agent. J Prosthodont Res. 2019;63(3):321-326.
[6] BASEGIO MM, PECHO OE, GHINEA R, et al. Masking ability of indirect restorative systems on tooth-colored resin substrates. Dent Mater. 2019’35(6):e122-e130.
[7] 钱慧芬,林佳儒,林云红,等.核饰瓷厚度和基底颜色对铸瓷贴面修复四环素牙光学性能的影响[J]. 上海口腔医学,2020,29(2): 133-137.
[8] BOSCATO N, HAUSCHILD FG, KAIZER MDA R, et al. Effectiveness of combination of dentin and enamel layers on the masking ability of porcelain. Braz Dent J. 2015;26(6):654-659.
[9] AL HAMAD KQ, OBAIDAT II, BABA NZ. The effect of ceramic type and background color on shade reproducibility of all-ceramic restorations. J Prosthodont. 2020;29(6):511-517.
[10] ALAYAD AS, ALQHATANI A, ALKATHEERI MS, et al. Effects of CAD/CAM ceramics and thicknesses on translucency and color masking of substrates. Saudi Dent J. 2021;33(7):761-768.
[11] BARATH VS, FABER FJ, WESTLAND S, et al. Spectrophotometric analysis of all-ceramic materials and their interaction with luting agents and different backgrounds. Adv Dent Res. 2003;17:55-60.
[12] SANCAKTAR O, KOSEOGLU M, BAYINDIR F. Influence of ceramic thickness, background and cement shade on the translucency of zirconia reinforced lithium silicate and lithium disilicate ceramics. J Clin Exp Dent. 2023;15(9):e720-e725.
[13] TABATABAIAN F, KHALEDI Z, NAMDARI M. Effect of ceramic thickness and cement type on the color match of high-translucency monolithic zirconia restorations. Int J Prosthodont. 2021;34(3):334-340.
[14] AL-HAJ HUSAIN N, WALTHER L, ÖZCAN M, et al. Effect of thickness and shade of resin and ceramic- based hybrid materials on color masking abilities and optical performance of CAD/CAM materials. Eur J Prosthodont Restor Dent. 2021;29(1):14-21.
[15] WISNIEWSKA K, PICHOR W, KLOSEK-WAWRZYN E. Influence of firing temperature on phase composition and color properties of ceramic tile bodies. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(21):6380.
[16] KURTULMUS-YILMAZ S, CENGIZ E, ONGUN S, et al. The effect of surface treatments on the mechanical and optical behaviors of CAD/CAM restorative materials. J Prosthodont. 2019;28(2):e496-e503.
[17] SAHIN V, GULGEZEN AH, AKYEL A, et al. The effect of repetitive firings on the color of an alumina ceramic system with varying ceramic shade and thickness. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2019;31(5):471-477.
[18] ALFOUZAN AF, ALNAFAIY SM, ALSALEH LS, et al. Effects of background color and thickness on the optical properties of CAD-CAM resin-matrix ceramics. J Prosthet Dent. 2022;128(3):491-497.
[19] YILDIRIM B, RECEN D, TEKELI SA. Effect of cement color and tooth-shaded background on the final color of lithium disilicate and zirconia-reinforced lithium silicate ceramics: An in vitro study. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2021;33(2):380-386.
[20] SONZA QN, DELLA BA, PECHO OE, et al. Effect of substrate and cement on the final color of zirconia-based all-ceramic crowns. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2021;33(6):891-898.
[21] SIRAWUTTIPONG C, PALANUWECH M. Effect of Zirconia Thickness, Cement Color, and Titanium Implant Abutment Surface Treatment Type on the Esthetic Outcomes of High-Translucency Monolithic Zirconia. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2024;39(5):765-775.
[22] SHONO NN, AL NH. Contrast ratio and masking ability of three ceramic veneering materials. Oper Dent. 2012;37(4):406-416.
[23] HEFFERNAN MJ, AQUILINO SA, DIAZ-ARNOLD AM, et al. Relative translucency of six all-ceramic systems. Part I: core materials. J Prosthet Dent. 2002;88(1):4-9.
[24] 骆小平,钱冬冬,袁宇,等.前牙全瓷美学修复中值得注意的事项[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2013,31(2):113-117.
[25] ILLE CE, JIVĂNESCU A, POP D, et al. Exploring the properties and indications of chairside CAD/CAM materials in restorative dentistry. J Funct Biomater. 2025;16(2):46.
[26] 钱慧芬,李星星.瓷贴面光学性能影响因素的研究进展[J].医学综述,2018,24(7):1388-1392.
[27] BONA DA, NOGUEIRA DA, PECHO EO. Optical properties of CAD–CAM ceramic systems. J Dent. 2014;42(9):1202-1209.
[28] KÜRKLÜ D, AZER SS, YILMAZ B, et al. Porcelain thickness and cement shade effects on the colour and translucency of porcelain veneering materials. J Dent. 2013;41(11):1043-1050.
[29] VALIZADEH S, MAHMOUDI NA, DARYADAR M, et al. The effect of ceramic thickness on opalescence. Clin Exp Dent Res. 2020; 6(6):693-699.
[30] PERRONI AP, BARBON FJ, CHAVES ET, et al. Exploring the influence of tooth, ceramic, and resin luting agent variations on laminate veneer optical characteristics: a prospective clinical investigation. Clin Oral Investig. 2024;28(12):639.
[31] ELLAKANY P, MADI M, ALY NM, et al. Effect of CAD/CAM ceramic thickness on shade masking ability of discolored teeth: in vitro study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(24):13359-13359.
[32] VICHI A, FERRARI M, DAVIDSON CL. Influence of ceramic and cement thickness on the masking of various types of opaque posts. J Prosthet Dent. 2000;83(4):412-417.
[33] KIM JH, BYEON SM, BAE TS, et al. Impact of liner treatment on the translucency of CAD/CAM multi-colored lithium disilicate and multi-layered zirconia implant-supported crowns, and evaluation of fracture strength of ceramic crowns. Odontology. 2025;113(2):645-654.
[34] 蓝熙,廖健,刘琴,等.玻璃陶瓷全瓷冠与高透氧化锆全瓷冠在前牙美学修复中的应用比较[J].中国美容医学,2023,32(9):148-151.
[35] 陈瑾,夏绮,张玲玲,等.陶瓷材料对瓷贴面修复四环素牙光学性能的影响[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2021,39(3):341-346.
[36] 李思诺,张璐瑶,梁珊珊,等.瓷材料种类及厚度对椅旁可切削全瓷冠遮色能力的影响[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2024,42(1):56-61.
[37] JUNTAVEE N, JUNTAVEE A, PHETPANOMPOND S. Masking ability of different ceramics upon various underlying structures. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2022;34(2):430-439.
[38] DOTTO L, SOARES MP, SLONGO S, et al. Layering of discolored substrates with high-value opaque composites for CAD-CAM monolithic ceramics. J Prosthet Dent. 2021;126(1):121-128.
[39] LI Z, CHEN Y, FU W, et al. Effects of porcelain layer thickness and luting resin cement on the opalescence properties of porcelain veneers. BMC Oral Health. 2024;24(1):1243.
[40] GRACIS S, THOMPSON VP, FERENCZ JL, et al. A new classification system for all-ceramic and ceramic-like restorative materials. Int J Prosthodont. 2015;28(3):227-235.
[41] FRADEANI M, BACHERINI L, TURRINI R, et al. Minimally invasive prosthetic procedure (MIPP): up to 12-year survival of full-mouth rehabilitations in patients with severely worn dentition (managed with lithium disilicate ceramic restorations). Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2021;41(6):799-808.
[42] FRADEANI M, BARDUCCI G, BACHERINI L. Esthetic rehabilitation of a worn dentition with a minimally invasive prosthetic procedure (MIPP). Int J Esthet Dent. 2016;11(1):16-35.
[43] WU Z, TIAN J, WEI D, et al. Effects of thickness and polishing treatment on the translucency and opalescence of six dental CAD-CAM monolithic restorative materials: an in vitro study. BMC Oral Health. 2023;23(1):579.
[44] CHO Y, LIM Y, HAN J, et al. Effect of yttria content on the translucency and masking ability of yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal. Materials (Basel). 2020;13(21):4726.
[45] VANINI L. Light and color in anterior composite restorations. Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent. 1996;8(7):673-682,684.
[46] THILAGAR P, SAMPATHKUMAR J, KRISHNAN CS, et al. Comparative evaluation of the masking ability of lithium disilicate ceramic with different core thickness on the shade match of indirect restorations over metallic substrate: an in vitro study. Contemp Clin Dent. 2019; 10(1):56-63.
[47] GITI R, HOJATI SA. Effect of varying thickness and number of coloring liquid applications on the color of anatomic contour monolithic zirconia ceramics. J Dent (Shiraz). 2018;19(4):311-319.
[48] ANSARIFARD E, TAGHVA M, MOSADDAD SA, et al. The impact of various substrates, ceramic shades, and brands on the ultimate color and masking capacity of highly translucent monolithic zirconia: an in vitro study. Odontology. 2025;113(2):607-618.
[49] SON HJ, KIM WC, JUN SH, et al. Influence of dentin porcelain thickness on layered all-ceramic restoration color. J Dent. 2010;38 Suppl 2: e71-e77.
[50] DOUGLAS RD, PRZYBYLSKA M. Predicting porcelain thickness required for dental shade matches. J Prosthet Dent. 1999;82(2):143-149.
[51] BREWER JD, AKERS CK, GARLAPO DA, et al. Spectrometric analysis of the influence of metal substrates on the color of metal-ceramic restorations. J Dent Res. 1985;64(1):74-77.
[52] NOGUEIRA AD, DELLA BA. The effect of a coupling medium on color and translucency of CAD-CAM ceramics. J Dent. 2013;41 Suppl 3:e18-e23.
[53] IGIEL C, WEYHRAUCH M, MAYER B, et al. Effects of ceramic layer thickness, cement color, and abutment tooth color on color reproduction of feldspathic veneers. Int J Esthet Dent. 2018;13(1): 110-119.
[54] JORGENSON MW, GOODKIND RJ. Spectrophotometric study of five porcelain shades relative to the dimensions of color, porcelain thickness, and repeated firings. J Prosthet Dent. 1979;42(1):96-105.
[55] 曹静,何惠明,王忠义.不同厚度In-Ceram全瓷修复体的色差分析[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2004,20(12):742-744.
[56] ALGHAZALI N, BURNSIDE G, MOALLEM M, et al. Assessment of perceptibility and acceptability of color difference of denture teeth. J Dent. 2012;40 Suppl 1:e10-e17.
[57] 苏亚丽,王少海.天然牙与全瓷修复体光物理学特性及透光率[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2014,15(4):236-239.
[58] HASEGAWA A, IKEDA I, KAWAGUCHI S. Color and translucency of in vivo natural central incisors. J Prosthet Dent. 2000;83(4):418-423.
[59] OH S, SHIN SM, KIM HJ, et al. Influence of glass-based dental ceramic type and thickness with identical shade on the light transmittance and the degree of conversion of resin cement. Int J Oral Sci. 2018;10(1):5.
[60] SHEIBANI P, AHMADIZENOUS G, ESMAEILI B, et al. Effect of computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing bleach shade ceramic thickness on its light transmittance and microhardness of light-cured resin cement. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2024;21:44.
[61] RASETTO FH, DRISCOLL CF, PRESTIPINO V, et al. Light transmission through all-ceramic dental materials: a pilot study. J Prosthet Dent. 2004;91(5):441-446.
[62] 高飞, 骆小平, 李宁. 临床常用四种全瓷贴面材料光学性能的比较[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2015,50(1):43-46.
[63] 杨代洁,刘敏.桩核材料对2种全瓷修复体颜色的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2011,27(6):757-760.
[64] 王宣儒,姚佳景,黄慧.粘接剂与基牙颜色对三种CAD/CAM全瓷贴面颜色的影响[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2013,22(4):172-176.
[65] YEH CL, MIYAGAWA Y, POWERS JM. Optical properties of composites of selected shades. J Dent Res. 1982;61(6):791-801.
[66] 夏春明,施长溪,陈吉华,等.相同色号九种光固化复合树脂的无限光学厚度研究[J].上海口腔医学,2002,11(3):219-221 |