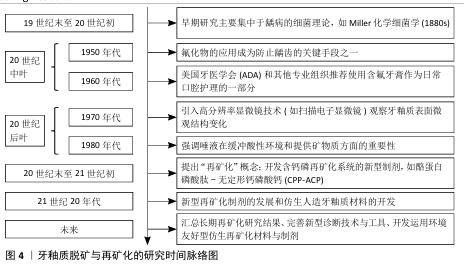
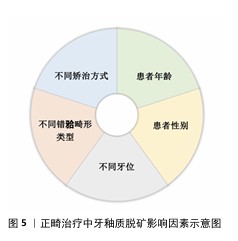
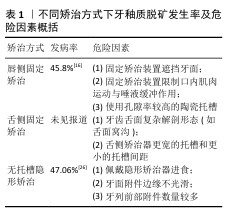
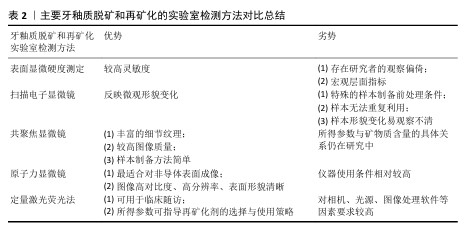
[1] 于世凤.口腔组织病理学[M].5版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2004.
[2] ZHAO H, LIU S, WEI Y, et al. Multiscale engineered artificial tooth enamel. Science. 2022;375(6580):551-556.
[3] FLYNN LN, JULIEN K, NOURELDIN A, et al. The efficacy of fluoride varnish vs a filled resin sealant for preventing white spot lesions during orthodontic treatment. Angle Orthod. 2022;92(2):204-212.
[4] MALCANGI G, PATANO A, MOROLLA R, et al. Analysis of Dental Enamel Remineralization: A Systematic Review of Technique Comparisons. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023; 10(4):472.
[5] WANG N, YU J, YAN J, et al. Recent advances in antibacterial coatings for orthodontic appliances. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023; 11:1093926.
[6] GORELICK L, GEIGER AM, GWINNETT AJ. Incidence of white spot formation after bonding and banding. Am J Orthod. 1982;81(2):93-98.
[7] 张婧琦,杨一,高嫣子,等.隐形与固定矫治器正畸后白垩斑发病率的比较[J].口腔医学研究,2024,40(2):152-155.
[8] RICHTER AE, ARRUDA AO, PETERS MC, et al. Incidence of caries lesions among patients treated with comprehensive orthodontics. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2011; 139(5):657-664.
[9] LIU Q, SONG Z. Incidence, severity, and risk factors for white spot lesions in adolescent patients treated with clear aligners. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2024; 27(5):704-713.
[10] ABBATE GM, CARIA MP, MONTANARI P, et al. Periodontal health in teenagers treated with removable aligners and fixed orthodontic appliances. J Orofac Orthop. 2015;76(3):240-250.
[11] SAGARIKA N, SUCHINDRAN S, LOGANATHAN S, et al. Prevalence of white spot lesion in a section of Indian population undergoing fixed orthodontic treatment: An in vivo assessment using the visual International Caries Detection and Assessment System II criteria. J Conserv Dent. 2012;15(2):104-108.
[12] JULIEN KC, BUSCHANG PH, CAMPBELL PM. Prevalence of white spot lesion formation during orthodontic treatment. Angle Orthod. 2013;83(4): 641-647.
[13] BUSCHANG PH, CHASTAIN D, KEYLOR CL, et al. Incidence of white spot lesions among patients treated with clear aligners and traditional braces. Angle Orthod. 2019; 89(3):359-364.
[14] KHALAF K. Factors Affecting the Formation, Severity and Location of White Spot Lesions during Orthodontic Treatment with Fixed Appliances. J Oral Maxillofac Res. 2014;5(1):e4.
[15] ALEXANDER SA. The effect of fixed and functional appliances on enamel decalcifications in early Class II treatment. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1993; 103(1):45-47.
[16] SUNDARARAJ D, VENKATACHALAPATHY S, TANDON A, et al. Critical evaluation of incidence and prevalence of white spot lesions during fixed orthodontic appliance treatment: A meta-analysis. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2015;5(6):433-439.
[17] O’REILLY MM, FEATHERSTONE JD. Demineralization and remineralization around orthodontic appliances: an in vivo study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1987;92(1):33-40.
[18] LAZAR L, VLASA A, BERESESCU L, et al. White Spot Lesions (WSLs)-Post-Orthodontic Occurrence, Management and Treatment Alternatives: A Narrative Review. J Clin Med. 2023;12(5):1908.
[19] CHHIBBER A, AGARWAL S, YADAV S, et al. Which orthodontic appliance is best for oral hygiene? A randomized clinical trial. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2018; 153(2):175-183.
[20] PELLEGRINI P, SAUERWEIN R, FINLAYSON T, et al. Plaque retention by self-ligating vs elastomeric orthodontic brackets: quantitative comparison of oral bacteria and detection with adenosine triphosphate-driven bioluminescence. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009;135(4): 426.e1-9.
[21] POLAT Ö, GÖKÇELIK A, ARMAN A, et al. A comparison of white spot lesion formation between a self-ligating bracket and a conventional preadjusted straight wire bracket. World J Orthod. 2008;9(2):e46-50.
[22] TOZ ERTOP M, CICEK O, ERENER H, et al. Evaluation of the Demineralization Development around Different Types of Orthodontic Brackets. Materials (Basel). 2023;16(3):984.
[23] ALMOSA NA, SIBAI BS, REJJAL OA, et al. Enamel demineralization around metal and ceramic brackets: an in vitro study. Clin Cosmet Investig Dent. 2019;11:37-43.
[24] KNÖSEL M, KLANG E, HELMS HJ, et al. Occurrence and severity of enamel decalcification adjacent to bracket bases and sub-bracket lesions during orthodontic treatment with two different lingual appliances. Eur J Orthod. 2016; 38(5):485-492.
[25] LOMBARDO L, ORTAN YÖ, GORGUN Ö, et al. Changes in the oral environment after placement of lingual and labial orthodontic appliances. Prog Orthod. 2013;14:28.
[26] 胡丹艳,陈慧芬,吴峻青,等.无托槽隐形矫治中牙釉质脱矿情况的临床调查[J].口腔医学,2024,44(10):742-746.
[27] AZEEM M, UL HAMID W. Incidence of white spot lesions during orthodontic clear aligner therapy. J World Fed Orthod. 2017;6(3): 127-130.
[28] ALBHAISI Z, AL-KHATEEB SN, ABU ALHAIJA ES. Enamel demineralization during clear aligner orthodontic treatment compared with fixed appliance therapy, evaluated with quantitative light-induced fluorescence: A randomized clinical trial. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2020;157(5):594-601.
[29] LOW B, LEE W, SENEVIRATNE CJ, et al. Ultrastructure and morphology of biofilms on thermoplastic orthodontic appliances in ‘fast’ and ‘slow’ plaque formers. Eur J Orthod. 2011;33(5):577-583.
[30] PITTS NB, ZERO DT, MARSH PD, et al. Dental caries. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017; 3:17030.
[31] SANTONOCITO S, POLIZZI A. Oral Microbiota Changes during Orthodontic Treatment. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2022; 14(3):19.
[32] LUCCHESE A, BONDEMARK L, MARCOLINA M, et al. Changes in oral microbiota due to orthodontic appliances: a systematic review. J Oral Microbiol. 2018; 10(1):1476645.
[33] MUMMOLO S, NOTA A, ALBANI F, et al. Salivary levels of Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacilli and other salivary indices in patients wearing clear aligners versus fixed orthodontic appliances: An observational study. PLoS One. 2020; 15(4):e0228798.
[34] SANDIĆ MZ, POPOVIĆ B, CARKIĆ J, et al. Changes in subgingival microflora after placement and removal of fixed orthodontic appliances. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2014; 142(5-6):301-305.
[35] SHOKEEN B, VILORIA E, DUONG E, et al. The impact of fixed orthodontic appliances and clear aligners on the oral microbiome and the association with clinical parameters: A longitudinal comparative study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2022;161(5): e475-e485.
[36] ERIKSSON L, LIF HOLGERSON P, JOHANSSON I. Saliva and tooth biofilm bacterial microbiota in adolescents in a low caries community. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):5861.
[37] ROUZI M, JIANG Q, ZHANG H, et al. Characteristics of oral microbiota and oral health in the patients treated with clear aligners: a prospective study. Clin Oral Investig. 2023;27(11):6725-6734.
[38] WANG Q, MA JB, WANG B, et al. Alterations of the oral microbiome in patients treated with the Invisalign system or with fixed appliances. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2019;156(5):633-640.
[39] ZHOU XD. Dental Caries: Principles and Management. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2016.
[40] 周学东.龋病学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2011.
[41] 崔晶.多乐氟、护牙素及含氟牙膏促进釉质再矿化的实验研究[D].西安:第四军医大学,2016.
[42] PHILIP N. State of the Art Enamel Remineralization Systems: The Next Frontier in Caries Management. Caries Res. 2019;53(3):284-295.
[43] 蔺孝慧,杨梦源,李春年.仿生再矿化治疗在牙釉质早期脱矿的作用及机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(4):856-865.
[44] BUCZKO P, ZALEWSKA A, SZARMACH I. Saliva and oxidative stress in oral cavity and in some systemic disorders. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015;66(1):3-9.
[45] BETTERIDGE DJ. What is oxidative stress? Metabolism. 2000;49(2 Suppl 1):3-8.
[46] RAHMAN MT, HOSSAIN A, PIN CH, et al. Zinc and Metallothionein in the Development and Progression of Dental Caries. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019;187(1):51-58.
[47] SKUTNIK-RADZISZEWSKA A, ZALEWSKA A. Salivary Redox Biomarkers in the Course of Caries and Periodontal Disease. Appl Sci. 2020;10(18):6240.
[48] ARAUJO HC, NAKAMUNE ACMS, GARCIA WG, et al. Carious Lesion Severity Induces Higher Antioxidant System Activity and Consequently Reduces Oxidative Damage in Children’s Saliva. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:3695683.
[49] CHENG X, XU X, ZHOU X, et al. Oxidative stress response: a critical factor affecting the ecological competitiveness of Streptococcus mutans. J Oral Microbiol. 2023;16(1):2292539.
[50] YU S, MA Q, LI Y, et al. Molecular and regulatory mechanisms of oxidative stress adaptation in Streptococcus mutans. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2023;38(1):1-8.
[51] BUCZKO P, KNAŚ M, GRYCZ M, et al. Orthodontic treatment modifies the oxidant-antioxidant balance in saliva of clinically healthy subjects. Adv Med Sci. 2017;62(1):129-135.
[52] ATUĞ ÖZCAN SS, CEYLAN I, OZCAN E, et al. Evaluation of oxidative stress biomarkers in patients with fixed orthodontic appliances. Dis Markers. 2014;2014:597892.
[53] 胡轶,苏丽萍,王胜朝.国际龋病检测与评估系统(ICDAS)的介绍[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2016,26(9):554-558.
[54] OLIVEIRA PRA, BARBOZA CM, BARRETO LSDC, et al. Effect of CPP-ACP on remineralization of artificial caries-like lesion: an in situ study. Braz Oral Res. 2020;34:e061.
[55] GANGWAR A, JHA KK, THAKUR J, et al. In Vitro evaluation of remineralization potential of novamin on artificially induced carious lesions in primary teeth using scanning electron microscope and vickers hardness. Indian J Dent Res. 2019;30(4):590-594.
[56] 郝丽英,刘宇峰,文莺惠,等.原子力显微镜对牙釉质脱矿再矿化的分析[J].实验室研究与探索,2024,43(1):27-31+49.
[57] RISNES S, SAEED M, SEHIC A. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Methods for Dental Enamel. Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1922:293-308.
[58] CHOKSHI K, CHOKSHI A, KONDE S, et al. An in vitro Comparative Evaluation of Three Remineralizing Agents using Confocal Microscopy. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016;10(6):ZC39-42.
[59] FARINA M, SCHEMMEL A, WEISSMÜLLER G, et al. Atomic force microscopy study of tooth surfaces. J Struct Biol. 1999;125(1):39-49.
[60] SUBRAMANI K, KWOK C, NAPOLES JA, et al. Enamel remineralization potential of bioactive glass air abrasion studied via elemental and surface morphology analysis. J Clin Exp Dent. 2023;15(10):e835-e841.
[61] PARK SW, KANG SM, LEE HS, et al. Lesion activity assessment of early caries using dye-enhanced quantitative light-induced fluorescence. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):
11848.
[62] DING L, HE D, ZHENG S, et al. In-vitro and in-vivo comparative studies of treatment effects on enamel demineralization during orthodontic therapy: implications for clinical early-intervention strategy. Clin Oral Investig. 2024;28(10):545.
[63] YAN J, CAO L, LUO T, et al. In vitro evaluation of a novel fluoride-coated clear aligner with antibacterial and enamel remineralization abilities. Clin Oral Investig. 2023;27(10):6027-6042.
[64] ABUFARWA M, NOURELDIN A, DZIAK R, et al. Efficacy of CPP-ACP fluoride varnish applied with and without acid etching in preventing enamel demineralization compared to light-curable fluoride varnish. Angle Orthod. 2022;92(2):213-219.
[65] HU H, FENG C, JIANG Z, et al. Effectiveness of remineralizing agents in the prevention and reversal of orthodontically induced white spot lesions: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Clin Oral Investig. 2020;24(12):4153-4167.
[66] MARGOLIS HC, MORENO EC, MURPHY BJ. Effect of low levels of fluoride in solution on enamel demineralization in vitro. J Dent Res. 1986;65(1):23-29.
[67] EL-WASSEFY NA. Remineralizing effect of cold plasma and/or bioglass on demineralized enamel. Dent Mater J. 2017;36(2):157-167.
[68] ZHONG JP, GREENSPAN DC, FENG JW. A microstructural examination of apatite induced by Bioglass in vitro. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2002;13(3):321-326.
[69] HAGHGOO R, AHMADVAND M, MOSHAVERINIA S. Remineralizing Effect of Topical NovaMin and Nano-hydroxyapatite on caries-like Lesions in Primary teeth. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2016;17(8):645-649.
[70] SHIHABI S, ALNESSER S, COMISI JC. Comparative Remineralization Efficacy of Topical NovaMin and Fluoride on Incipient Enamel Lesions in Primary Teeth: Scanning Electron Microscope and Vickers Microhardness Evaluation. Eur J Dent. 2021;15(3):420-424.
[71] FERNANDO D, ATTIK N, PRADELLE-PLASSE N, et al. Bioactive glass for dentin remineralization: A systematic review. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;76:1369-1377.
[72] MÜLLER WEG, NEUFURTH M, ACKERMANN M, et al. Bifunctional dentifrice: Amorphous polyphosphate a regeneratively active sealant with potent anti-Streptococcus mutans activity. Dent Mater. 2017;33(7): 753-764.
[73] GILMORE ND. The effect on dental caries-activity of supplementing diets with phosphates; a review. J Public Health Dent. 1969;29(3):188-207.
[74] COCHRANE NJ, CAI F, HUQ NL, et al. New approaches to enhanced remineralization of tooth enamel. J Dent Res. 2010;89(11): 1187-1197.
[75] CROSS KJ, HUQ NL, STANTON DP, et al. NMR studies of a novel calcium, phosphate and fluoride delivery vehicle-alpha(S1)-casein(59-79) by stabilized amorphous calcium fluoride phosphate nanocomplexes. Biomaterials. 2004;25(20):5061-5069.
[76] BAKRY AS, ABBASSY MA. Increasing the efficiency of CPP-ACP to remineralize enamel white spot lesions. J Dent. 2018; 76:52-57.
[77] DASHPER SG, SHEN P, SIM CPC, et al. CPP-ACP Promotes SnF2 Efficacy in a Polymicrobial Caries Model. J Dent Res. 2019;98(2):218-224.
[78] HANI TB, O’CONNELL AC, DUANE B. Casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate products in caries prevention. Evid Based Dent. 2016;17(2):46-47.
[79] HUA F, YAN J, ZHAO S, et al. In vitro remineralization of enamel white spot lesions with a carrier-based amorphous calcium phosphate delivery system. Clin Oral Investig. 2020;24(6):2079-2089.
[80] GUPTA R, PRAKASH V. CPP-ACP complex as a new adjunctive agent for remineralisation: a review. Oral Health Prev Dent. 2011;9(2): 151-165.
[81] HOSSEINPOUR-NADER A, KARIMI N, GHAFARI HA. Ex-vivo effects of propolis quantum dots-nisin-nanoquercetin-mediated photodynamic therapy on Streptococcus mutans biofilms and white spot lesions. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2023;41:103255.
[82] OLEK M, MACHOROWSKA-PIENIĄŻEK A, STÓS W, et al. Photodynamic Therapy in Orthodontics: A Literature Review. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(5):720.
[83] ALQERBAN A. Effectiveness of Riboflavin and Rose Bengal Photosensitizer Modified Adhesive Resin for Orthodontic Bonding. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021; 14(1):48.
[84] HUANG Y, LIU Y, PANDEY NK, et al. Iron oxide nanozymes stabilize stannous fluoride for targeted biofilm killing and synergistic oral disease prevention. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):6087.
[85] 许颖华,刘婧,尤权,等.掺钕钇铝钙钛晶体激光结合两种再矿化制剂与早期釉质龋的再矿化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2024,28(3):360-365.
[86] PAN G, WANG H, LI Z, et al. Photodynamic therapy based on bismuth oxyiodide nanoparticles for nondestructive tooth whitening. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2024;243:114133.
[87] TORRES C, MOECKE SE, MAFETANO A, et al. Influence of Viscosity and Thickener on the Effects of Bleaching Gels. Oper Dent. 2022;47(3):E119-E130.
[88] LUO T, YAN J, CAO L, et al. Novel orthodontic adhesives with antibacterial, mineralization and fluorescence properties for enamel demineralization prevention. Chem Eng J. 2024;500:156737.
[89] RAJENDRAN R, HUSSAIN MS, SANDHYA R, et al. Effect of Remineralization Agents on White Spot Lesions: A Systematic Review. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2022;14(Suppl 1): S7-S12. |