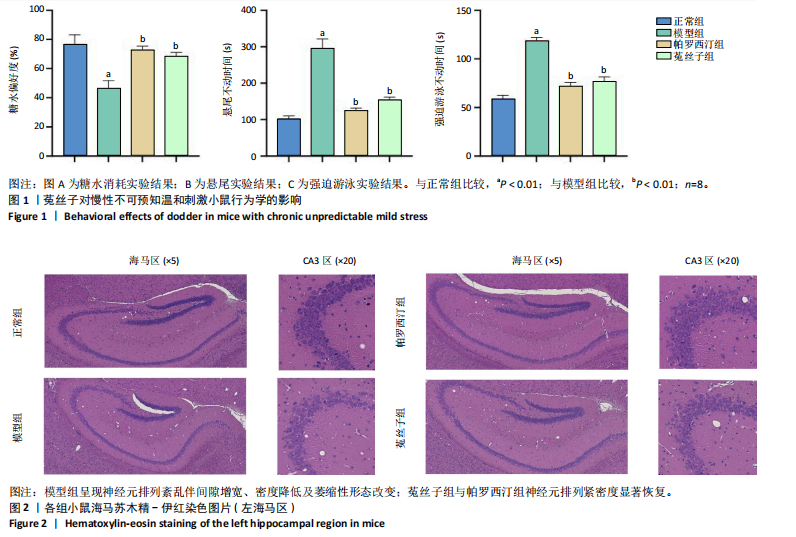
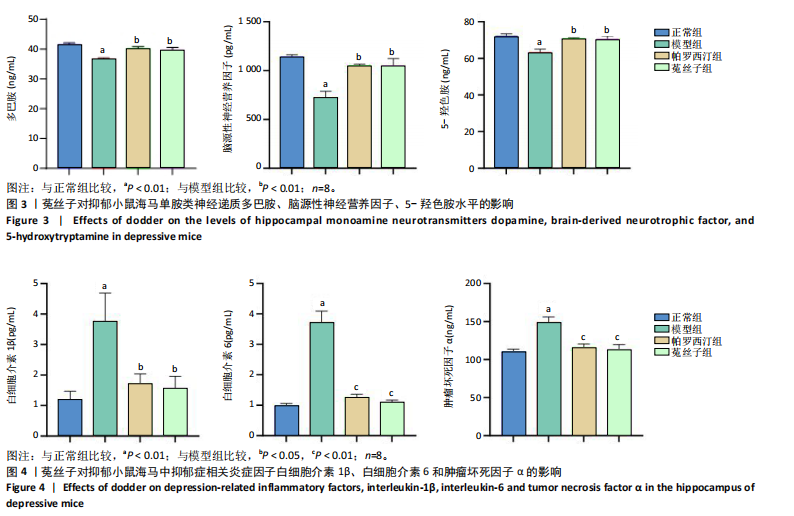
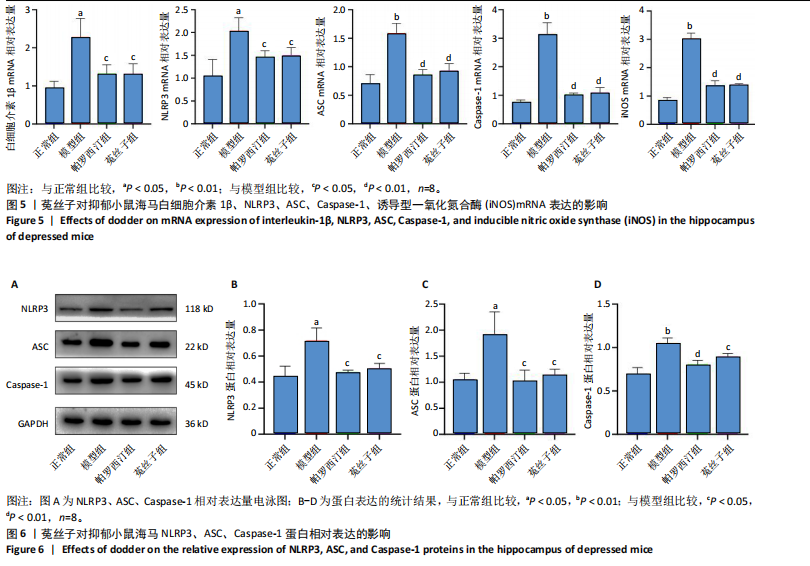
[1] PENNINX WB, LAMERS F, JANSEN R, et al.Immuno-metabolic depression: from concept to implementation.Lancet Reg Health Eur. 2024;48:101166.
[2] 王怡瑾,张雁绚,齐丽,等.基于CiteSpace分析有氧运动干预抑郁的研究现状与发展趋势[J].循证护理,2024,10(17):3174-3180.
[3] 杨婷,汪敬轩,谢志豪,等.中国老年居民抑郁症状现状及其影响因素分析[J].现代预防医学,2021,48(19):3461-3465+3599.
[4] 宋太医局. 太平惠民和剂局方[M]. 北京: 中国中医药出版社,2020.
[5] 林大栋. 扶阳之祖:大宋窦材与《扁鹊心书》[M]. 北京: 中国中医药出版社,2021.
[6] 姚广大.菟丝子中抗抑郁有效成分发现及其作用机制研究[D].银川:宁夏医科大学,2022.
[7] 王莹,张婧如,田伟,等.菟丝子及其提取物药理机制研究进展[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2023,29(11):1961-1964.
[8] ZHOU L, YANG C, LIU Z, et al. Neuroprotective effect of the traditional decoction Tian-Si-Yin against Alzheimer’s disease via suppression of neuroinflammation. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024;321:117569.
[9] HARSANYI S, KUPCOVA I, DANISOVIC L, et al. Selected Biomarkers of Depression: What Are the Effects of Cytokines and Inflammation? Int J Mol Sci. 2022;24(1):578.
[10] KOUBA BR, DE ARAUJO BORBA L, BORGES DE SOUZA P, et al. Role of Inflammatory Mechanisms in Major Depressive Disorder: From Etiology to Potential Pharmacological Targets. Cells. 2024;13(5):423.
[11] WU A, ZHANG J.Neuroinflammation, memory, and depression: new approaches to hippocampal neurogenesis. J Neuroinflammation. 2023;20(1):283.
[12] MA X, SHIN JW, CHO JH, et al. IL-6 expression-suppressing Lactobacillus reuteri strains alleviate gut microbiota-induced anxiety and depression in mice. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2024;77(1):ovad144.
[13] YE T, TAO WY, CHEN XY, et al. Mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and the development of peptide inhibitors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2023;74:1-13.
[14] DU L, FAN X, YANG Y, et al. Quercetin Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment in Depression by Targeting HSP90 to Inhibit NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Mol Neurobiol. 2024;61(9):6628-6641.
[15] CHEN H, MA Y, CHEN M, et al. Safflower extract improves depression in mice by inhibiting the TLR4-NLRP3 inflammation signaling pathway. Ann Palliat Med. 2021;10(7):8015-8023.
[16] XIA J, CHEN M, SHAO H, et al. Inflammation and Late-Life Depression: Unraveling the Complex Relationship and Potential Therapeutic Strategies. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023;28(12):356.
[17] FU J, WU H. Structural Mechanisms of NLRP3 Inflammasome Assembly and Activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2023;41:301-316.
[18] XIA CY, GUO YX, LIAN WW, et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome in depression: Potential mechanisms and therapies. Pharmacol Res. 2023;187:106625.
[19] RAMALINGAM V. NLRP3 inhibitors: Unleashing their therapeutic potential against inflammatory diseases. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023; 218:115915.
[20] ZHANG WJ, CHEN SJ, ZHOU SC, et al. Inflammasomes and Fibrosis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:643149.
[21] ZHOU JY, SARKAR MK, OKAMURA K, et al. Activation of the NLRP1 inflammasome in human keratinocytes by the dsDNA mimetic poly(dA:dT). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023;120(5):e2213777120.
[22] LOPES FB, SARANDY MM, NOVAES RD, et al. OxInflammatory Responses in the Wound Healing Process: A Systematic Review. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024;13(7):823.
[23] 徐小平,李兴民.实验方剂药理学[M]. 北京:军事医学科学出版社,2020.
[24] RATAJCZAK P, MARTYŃSKI J, ZIĘBA JK, et al. Comparative Efficacy of Animal Depression Models and Antidepressant Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceutics. 2024;16(9):1144.
[25] ZHOU Z, WANG Y, SUN S, et al. Paeonia lactiflora Pall. Polysaccharide alleviates depression in CUMS mice by inhibiting the NLRP3/ASC/Caspase-1 signaling pathway and affecting the composition of their intestinal flora. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;316:116716.
[26] ZHANG W, YU M, ZHANG Q, et al. DFO treatment protects against depression-like behaviors and cognitive impairment in CUMS mice. Brain Res Bull. 2022;187:75-84.
[27] TROUBAT R, BARONE P, LEMAN S, et al. Neuroinflammation and depression: A review. Eur J Neurosci. 2021;53(1):151-171.
[28] GUO B, ZHANG M, HAO W, et al. Neuroinflammation mechanisms of neuromodulation therapies for anxiety and depression. Transl Psychiatry. 2023;13(1):5.
[29] 熊庭旺,张珏,石京山.中药抗抑郁作用机制研究进展[J].中医药通报,2024,23(2):65-69.
[30] CHEN CY, WANG YF, LEI L, et al. MicroRNA-specific targets for neuronal plasticity, neurotransmitters, neurotrophic factors, and gut microbes in the pathogenesis and therapeutics of depression.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2025;136:111186.
[31] (唐)王冰撰注;鲁兆麟主校.黃帝內經素問[M].沈阳:辽宁科学技术出版社,1997.
[32] 梁喆盈,雷英菊,金玲.张景岳论治郁证浅析[J].时珍国医国药, 2008,19(2):493-494.
[33] 叶橙,孙文军,唐启盛,等. 益肾调气法治疗肾虚肝郁型抑郁障碍远期复发率的多中心前瞻性队列研究[J]. 世界中医药,2024,19(15): 2308-2313.
[34] 楼炎灵,李振龙. 定经汤加味联合针灸治疗肾虚肝郁型更年期综合征抑郁症状的临床研究[J]. 中国医药科学,2023,13(5):20-24,32.
[35] 罗玉君,肖晓岚,梁敏莉. 肾虚肝郁型绝经综合征患者抑郁与躯体症状的调研[J]. 实用医学杂志,2013,29(11):1861-1863.
[36] 宋•唐慎微.宋•寇宗奭衍義,金•張存惠重修.重修政和经史证类备用本草[M].北京:人民卫生出版,1957.
[37] 武晓冬. 菟丝子性味功效及临床应用探析[J]. 中国中医基础医学杂志,2023,29(2):280-284.
[38] 苏丹,王晓丽,贾孟辉,等.回药阿夫忒蒙丸对失眠大鼠下丘脑5-HT和5-HIAA含量的影响[J].中国民族医药杂志,2016,22(7):54-55.
[39] 焦阳,李方,贾孟辉,等.回药阿夫忒蒙丸对80例顽固性失眠患者血浆5-羟色胺水平表达的影响[J].中国民族医药杂志,2015,21(7):5-6.
[40] MA J, WANG R, CHEN Y, et al. 5-HT attenuates chronic stress-induced cognitive impairment in mice through intestinal flora disruption. J Neuroinflammation. 2023;20(1):23.
[41] GASNIER M, ELLUL P, PLAZE M, et al. A New Look on an Old Issue: Comprehensive Review of Neurotransmitter Studies in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Schizophrenia and Antipsychotic Effect on Monoamine’s Metabolism. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2021;19(3): 395-410.
[42] SPENCER NJ, KEATING DJ. Role of 5-HT in the enteric nervous system and enteroendocrine cells. Br J Pharmacol. 2025;182(3):471-483.
[43] Tian Y. The Role of Dopamine Neurotransmitters in Neurological Diseases: New Sight. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(14):7529.
[44] ZELADA MI, GARRIDO V, LIBERONA A, et al. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) as a Predictor of Treatment Response in Major Depressive Disorder (MDD): A Systematic Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2023; 24(19):14810.
[45] STEFFEN J, FOCKEN N, ÇALıŞKAN G. Recognizing depression as an inflammatory disease: the search for endotypes. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024;327(1):C205-C212.
[46] DE OLIVEIRA J, KUCHARSKA E, GARCEZ ML, et al. Inflammatory Cascade in Alzheimer’s Disease Pathogenesis: A Review of Experimental Findings. Cells. 2021;10(10):2581.
[47] COOMBS JR, ZAMOSHNIKOVA A, HOLLEY CL, et al. NLRP12 interacts with NLRP3 to block the activation of the human NLRP3 inflammasome. Sci Signal. 2024;17(820):eabg8145.
[48] GUO ML, ROODSARI SK, CHENG Y, et al. Microglia NLRP3 Inflammasome and Neuroimmune Signaling in Substance Use Disorders. Biomolecules. 2023;13(6):922.
[49] ZHANG D, ZHANG Y, PAN J, et al. Degradation of NLRP3 by p62-dependent-autophagy improves cognitive function in Alzheimer’s disease by maintaining the phagocytic function of microglia. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023;29(10):2826-2842.
[50] LI S, FANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al.Microglial NLRP3 inflammasome activates neurotoxic astrocytes in depression-like mice. Cell Rep. 2022;41(4): 111532.
[51] LIU X, WANG Y, ZENG Y, et al.Microglia-neuron interactions promote chronic itch via the NLRP3-IL-1β-GRPR axis. Allergy. 2023;78(6):1570-1584.
[52] ZHU J, ZHOU F, ZHOU Q, et al.NLRP3 activation in microglia contributes to learning and memory impairment induced by chronic lead exposure in mice. Toxicol Sci. 2023;191(1):179-191. |