中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (1): 184-193.doi: 10.12307/2025.573
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
外泌体分泌调控机制及在生物医学中的应用前景
吕茹月,顾路路,刘 茜,周思仪,李贝贝,薛乐天,孙 鹏
- 华中科技大学同济医学院附属协和医院急诊科,湖北省武汉市 430022
-
收稿日期:2024-11-30接受日期:2025-01-24出版日期:2026-01-08发布日期:2025-07-02 -
通讯作者:孙鹏,博士,主任医师,华中科技大学同济医学院附属协和医院急诊科,湖北省武汉市 430022 -
作者简介:吕茹月,女,1993年生,河南省开封市人,汉族,华中科技大学同济医学院在读硕士,医师,主要从事心肺复苏后脑损伤研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金面上项目(82072137),项目负责人:孙鹏
Regulatory mechanisms of exosome secretion and its application prospects in biomedicine
Lyu Ruyue, Gu Lulu, Liu Qian, Zhou Siyi, Li Beibei, Xue Letian, Sun Peng
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2024-11-30Accepted:2025-01-24Online:2026-01-08Published:2025-07-02 -
Contact:Sun Peng, PhD, Chief physician, Department of Emergency Medicine, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Lyu Ruyue, Master candidate, Physician, Department of Emergency Medicine, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82072137 (to SP)
摘要:
文题释义:
外泌体:是由细胞分泌到细胞外的膜性结构,具有脂质双分子层包裹,包含来自原始细胞的复杂内容物,如细胞因子、蛋白质、RNA、miRNA和脂质等生物活性分子,通常直径在30-150 nm之间,是最小的细胞外囊泡类型。外泌体在多种生物体液和组织中广泛存在,包括血液、尿液、唾液、乳汁、羊水、滑液和脑脊液等。TAT-5:是一种特定的P4-ATP酶家族成员,P4-ATP酶指的是一类具有ATP水解酶活性的膜蛋白。TAT-5具有磷脂翻转酶活性,主要负责将磷脂酰乙醇胺从细胞膜的外侧转运到内侧,以维持磷脂酰乙醇胺在细胞膜上的不对称分布。当TAT-5的功能受到抑制或缺失时,磷脂酰乙醇胺会暴露在细胞膜的外侧,这可能会触发一系列生物学反应,如细胞外囊泡的出芽和形成等过程。因此,TAT-5在细胞膜磷脂的翻转和细胞外囊泡的调控中发挥着关键作用。
摘要
背景:外泌体作为细胞外囊泡的一种,以纳米级尺寸和富含多种生物活性物质而成为细胞间通讯的关键媒介。外泌体分泌调控研究不仅具有重要的科学价值,而且在临床具有广泛的应用前景,对于推动医学进步和改善人类健康具有重要意义。
目的:综述外泌体的生物特性、生物学功能、生物发生过程以及分泌的生化调控机制,并探讨外泌体在疾病诊断、治疗和疫苗开发等领域的应用前景,为外泌体的基础研究和临床转化提供理论依据和参考。
方法:第一作者于2024年10月检索PubMed及中国知网数据库2010年1月至2024年10月发表的相关文献,以“exosomes,biological functions,biogenesis,secretion or release,regulatory mechanisms,application prospects”等为英文检索词,以“外泌体,生物学功能,生发过程,分泌释放,调控机制,应用前景”等为中文检索词,最终纳入92篇文献进行分析。
结果与结论:外泌体的分泌水平可以通过物理或生化手段进行调控。外泌体在疾病诊断、治疗以及疫苗开发等领域展现出广泛的应用前景,特别是在心脑血管疾病和癌症治疗中可能发挥关键作用。此综述为外泌体的临床转化和应用研究提供了有价值的信息,有助于推动未来在外泌体研究和应用方面的进展。
中图分类号:
引用本文
吕茹月, 顾路路, 刘 茜, 周思仪, 李贝贝, 薛乐天, 孙 鹏. 外泌体分泌调控机制及在生物医学中的应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(1): 184-193.
Lyu Ruyue, Gu Lulu, Liu Qian, Zhou Siyi, Li Beibei, Xue Letian, Sun Peng. Regulatory mechanisms of exosome secretion and its application prospects in biomedicine[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 184-193.
外泌体的内容物丰富多样,包含来自原始细胞的复杂成分,如细胞因子、蛋白质、RNA、miRNA和脂质等生物活性分子,这些成分赋予外泌体强大的生物学功能,能够参与细胞间的信息传递和调节[1-6]。例如,外泌体可以通过转运蛋白质和核酸等物质,调节受体细胞的基因表达和蛋白质合成,从而影响细胞的生理功能和状态[1-6]。此外,外泌体还能够重塑细胞外环境,通过释放生物活性物质,促进细胞间的通讯和协调[5]。
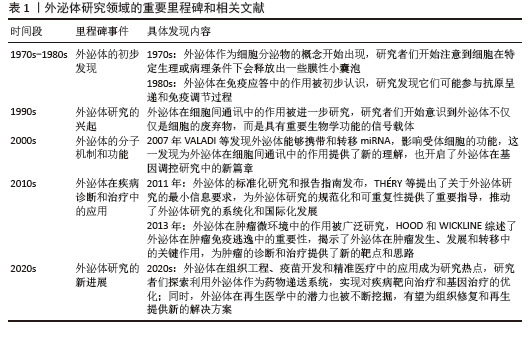
外泌体在多种生理和病理过程中发挥关键作用。例如,在免疫应答过程中,外泌体能够携带抗原和免疫调节分子,激活或抑制免疫细胞的功能,调节免疫反应的强度和方向[17-18]。在组织修复和再生过程中,外泌体通过促进细胞增殖、分化和血管新生,加速受损组织的愈合[19-21]。在癌症发生和发展中,肿瘤细胞分泌的外泌体能够携带致癌因子和促转移分子,促进肿瘤的生长、侵袭和转移[22-23]。因此,外泌体不仅在基础研究中具有重要的科学价值,而且在临床应用及生物医学领域中展现出广阔的前景,特别是在疾病诊断、治疗和药物递送等领域。关于外泌体发展的研究见表1。
2.2 外泌体的生物学功能 外泌体在生物学和医学领域中扮演着重要的角色,其功能和作用机制有以下几个方面:①细胞代谢的调节:外泌体可以作为信号信使和载体,将信号传递给相应的靶细胞,从而改变生理功能和状态。外泌体含有脂质、蛋白质、DNA和RNA等多种生物活性分子,这些分子可以调节细胞代谢[5-6]。②炎症的控制:外泌体与各种炎症性疾病的发生发展密切相关[24-27]。在炎症状态下,外泌体释放增多,可以促使外泌体与受体细胞结合,进而使外泌体内含物的结构及生物性能发生改变,从而对受体细胞产生影响[28]。③促进血管新生:外泌体可以促进血管生成,例如在肿瘤组织内乏氧状态下释放的外泌体,刺激周围血管形成,促进肿瘤的生长及转移[29],间充质干细胞来源外泌体通过细胞因子促进血管生成,如miR-21可以通过PTEN/Akt途径促进血管生成[30-31]。④促进组织修复:外泌体可以通过携带多种生长因子和细胞因子,调节细胞外基质的合成和重塑,促进血管生成和神经再生,此外,外泌体能够携带多种生物活性分子,如蛋白质、脂质、核酸等,通过调节细胞信号传导、细胞增殖、迁移和分化等过程,促进软组织的修复和再生[20-21]。⑤免疫调节:外泌体通过携带多种生物活性分子,调节免疫细胞的激活与抑制、炎症反应的强度、免疫耐受的诱导以及免疫记忆的形成,从而在免疫调节中发挥重要作用[32-33],如NK细胞分泌的外泌体中还含有多种免疫成分,可通过旁分泌途径或通过循环系统靶向免疫系统来发挥免疫调节作用[34]。⑥癌症发生与发展:肿瘤细胞的外泌体与正常细胞的外泌体之间存在差异,研究发现肿瘤细胞会释放携带致癌因子与细胞凋亡因子的外泌体,使受体细胞癌变,而且携带特定的生物活性分子可改变受体细胞的基因表达和功能,从而促进肿瘤的生长和转移[35-36]。⑦抗原呈递:外泌体可以作为抗原呈递细胞的载体,将抗原信息传递给免疫细胞,从而激活免疫反应,树突状细胞是专业的抗原呈递细胞,其分泌的外泌体含有MHC分子和抗原肽复合物,能够有效地呈递抗原并激活T细胞,外泌体因能够携带抗原并激活免疫系统特性,被研究用于疫苗设计中,以增强免疫反应[37-39]。
此外,干细胞来源外泌体作为一种“无细胞治疗”策略,近年来在多种疾病的治疗中展现出显著的疗效,例如具有免疫调节、抗炎、抗纤维化、抑制氧化应激、增强血管生成等疗效[40]。研究发现,间充质干细胞来源外泌体能够通过携带免疫调节分子,调节T细胞和B细胞的功能,抑制过度的免疫反应,从而在自身免疫性疾病中发挥治疗作用[41];间充质干细胞来源外泌体通过诱导结肠巨噬细胞向免疫抑制的M2表型极化,减少炎症细胞因子和趋化因子的产生,增加抗炎细胞因子的浓度,从而有效缓解结肠炎症[42];在肝纤维化的治疗中,人骨髓间充质干细胞衍生外泌体通过 Wnt/β-catenin 通路缓解肝纤维化,从而减缓肝纤维化的进展[43];脂肪来源干细胞外泌体通过携带抗氧化分子,调节细胞内的氧化应激反应,从而保护心肌细胞免受氧化损伤[44];在缺血性疾病的治疗中,干细胞外泌体携带的血管生成因子,如血管内皮生长因子,能够促进血管内皮细胞的增殖和迁移,加速新生血管的形成,改善组织的血液供应[45]。这些研究表明,干细胞来源外泌体通过调节免疫反应、减轻炎症、抑制纤维化、清除氧化应激和促进血管生成等多种机制,在多种疾病的治疗中具有广泛的应用潜力,为临床治疗提供了新的思路和方法。
2.3 外泌体的生物发生过程 外泌体的形成过程可以分为几个关键步骤:①内吞作用:外泌体的形成始于细胞膜的内吞作用,细胞膜内陷形成早期内吞体,这些早期内吞体可以与其他细胞器融合,进一步成熟为晚期内吞体[5-6,46]。②多囊泡体(multivesicular bodies,MVBs)的形成:晚期内吞体内膜通过内向出芽作用形成多个腔内囊泡(intraluminal vesicles,ILVs),这些囊泡就是外泌体的前体,最终形成多囊泡体[5-6,46]。③外泌体的释放:大多数多囊泡体会与溶酶体融合,导致内容物的降解,而少数多囊泡体则通过与细胞膜融合,将腔内囊泡释放到细胞外,形成外泌体[5-6,46]。外泌体的具体生发过程示意图见图3。此过程涉及特定的膜蛋白如CD63和溶酶体跨膜蛋白(如LAMP1、LAMP2),这些蛋白在多囊泡体的膜表面发挥重要作用[5]。
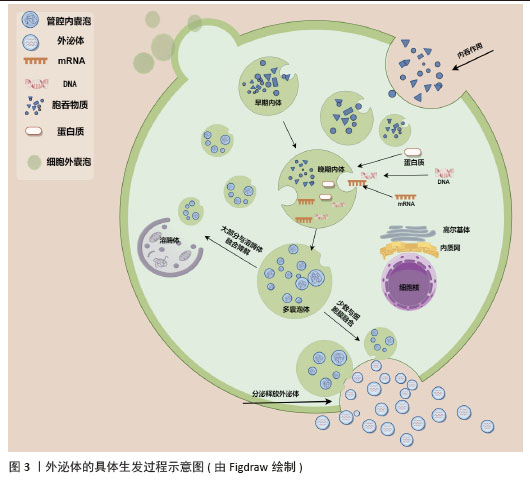
多囊泡体和腔内囊泡的形成主要依赖内吞体分选复合物(endosomal sorting complex required for transport,ESCRT)机制和非依赖内吞体分选复合物两种机制[5-6,46-48]。ESCRT复合物在调控多囊泡体的形成中发挥关键作用,包含ESCRT-0、ESCRT-I、ESCRT-II、ESCRT-III和相关的ATP酶VPS4复合物。ESCRT复合物通过在内吞体膜上时序性招募组装,介导泛素化的膜受体蛋白分选至腔内囊泡中,进而送至溶酶体被降解[46,48]。具体来说,ESCRT-0识别和分隔泛素化标记的内吞体膜跨膜蛋白;ESCRT-I与ESCRT-II协同作用,使内吞体膜通过内向生芽作用包裹特异的内容物;ESCRT-III将形成的囊泡剪开。ESCRT的解离和再循环需要ATP酶VPS4的辅助作用。除了ESCRT依赖的途径,多囊泡体也可以不依赖ESCRT途径而由特定脂质分子介导形成。参与调控多囊泡体形成的脂类主要包括神经酰胺、磷脂酸、鞘氨醇-1-磷酸等,这些脂类可能通过促进内吞体膜上富含鞘磷脂的“脂筏”微结构域的形成和进一步扩张,或诱发自发的负性曲度促进腔内囊泡的形成。细胞内生成多囊泡体后,降解型多囊泡体的主要功能是将内含物运送至溶酶体进行降解,在这一过程中,多囊泡体与溶酶体膜融合,使得多囊泡体内部的内含物(包括蛋白质、脂质和核酸等)被释放到溶酶体内;分泌型多囊泡体与细胞膜(质膜)融合,使得多囊泡体内部的内含物被释放到细胞外环境中。这一过程涉及到多种膜运输和融合蛋白,如RAB家族GTP酶和SNARE蛋白,它们协同作用促进多囊泡体与细胞膜的融合[5,46]。RAB家族蛋白主要在细胞囊泡运输过程中发挥功能,通过GTP和GDP结合形式的转换,起到分子开关的作用,调控囊泡的出芽、形成、转运、锚着和融合,SNARE家族蛋白则在囊泡融合过程中起关键作用,通过形成紧密的复合体,聚集脂膜,促进囊泡与质膜的融合[49]。
2.4 外泌体释放的生化调控机制
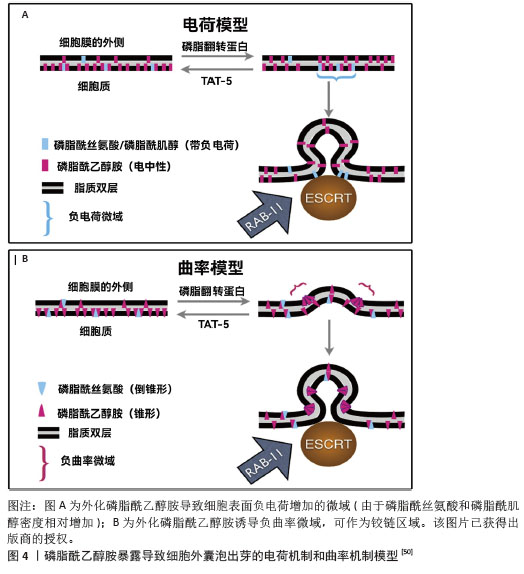
2.4.1 TAT-5抑制细胞外囊泡出芽 TAT-5具有磷脂反转酶活性,负责将磷脂分子从细胞膜的外侧转运到内侧,可维持磷脂酰乙醇胺在细胞膜上的不对称定位,防止磷脂酰乙醇胺暴露。若TAT-5缺失,磷脂酰乙醇胺暴露,会导致细胞外囊泡出芽。在秀丽隐杆线虫中,TAT-5是防止磷脂酰乙醇胺暴露所必需的,其缺失会导致磷脂酰乙醇胺暴露,进而引发细胞外囊泡出芽。TAT-5通常内化磷脂酰乙醇胺,而用一种磷脂翻转蛋白酶将磷脂酰乙醇胺外化,可能导致ESCRT复合体在细胞膜上募集或稳定,促使ESCRT复合体在细胞膜上出芽形成外泌体。RAB-11是一种与循环内体相关的GTP酶,可以将出芽所需的蛋白质传递到质膜上,也可以在出芽过程中发挥更直接的作用。综上所述,TAT-5的缺失导致磷脂酰乙醇胺外化,在细胞膜上形成负电荷微域和负曲率微域,这可能促进ESCRT复合体的募集和外泌体的形成。同时,RAB-11在这一过程中也发挥着重要作用,通过GTP酶活性影响蛋白质的运输和外泌体的出芽。这些机制共同参与了外泌体的生物合成和释放过程[50],见图4。
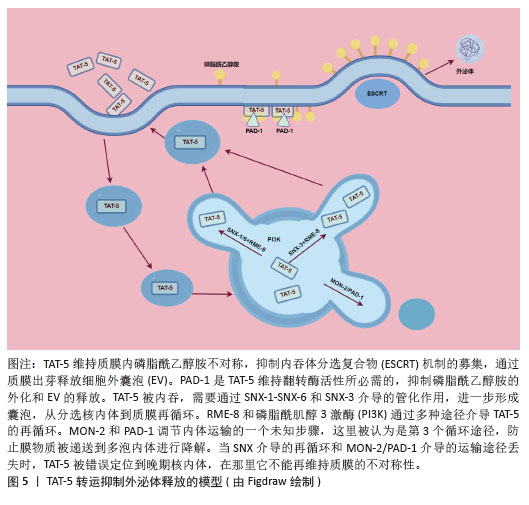
TAT-5在细胞内的定位受到细胞内冗余因子的调节[51],见图5。以下是一些关键的逆转运蛋白和相关因子,它们在调节TAT-5的定位和功能中起作用:①逆转运蛋白RME-8(DNAJC13):RME-8是人类DNAJC13的同源蛋白,它在内体蛋白运输中起作用,并与retromer和WASH复合体相关联,这两个复合体都与自噬有关。RME-8/DNAJC13在细胞蛋白稳态网络中作为一个正向调节因子,影响自噬过程[52]。
②磷脂酰肌醇3激酶(phosphoinositide 3 kinase,PI3K):PI3K是一类具有丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶活性的酶,它们在细胞内信号传导中起着关键作用,尤其是在自噬过程中。③PAD-1:PAD-1是一种Dopey结构域蛋白,它在植物中的功能与生长素稳态相关,但在动物细胞中,PAD-1可能与TAT-5的回收和定位有关[53]。④Beclin1同源蛋白BEC-1:Beclin1是自噬过程中的关键调节蛋白,它与Ⅲ类PI3K形成复合体来调节ATG蛋白在自噬前体结构中的定位,从而调节自噬活性。⑤Ⅲ类PI3Kinase VPS-34:VPS-34是自噬过程中的一个关键蛋白,它在细胞内除了诱导自噬之外,还能够通过激活p62,促进肿瘤的发生和发展;⑥Dna J结构域蛋白RME-8:RME-8/DNAJC13在细胞蛋白稳态网络中起作用,影响ATG9A的运输和自噬。RME-8、PI3K、PAD-1已被证实可抑制细胞微囊泡释放,Beclin1同源蛋白BEC-1、Ⅲ类PI3Kinase VPS-34、Dopey结构域蛋白PAD-1、Dna J结构域蛋白RME-8这4个基因的破坏可增加外泌体的释放,进一步研究证实TAT-5被这些逆转运相关蛋白通过不同的分子信号途径从胞质回收到质膜上[51]。
2.4.2 中性鞘磷脂酶抑制剂途径调控外泌体的分泌 鞘磷脂酶将膜脂质鞘磷脂水解为磷酰胆碱和神经酰胺,不同的鞘磷脂酶具有酸性、碱性或中性的最佳pH值,可以将丰富的膜脂质鞘磷脂水解为磷酰胆碱和神经酰胺,SMPD3是研究最多的中性鞘磷脂酶,由磷脂酰丝氨酸和磷脂酸等阴离子磷脂激活,SMPD2在体外和体内都具有中性鞘磷脂酶活性,并且定位于高尔基体和内质网[54]。神经酰胺是一种具有生物活性的鞘脂,参与许多生物学功能,如增殖、凋亡、分化和炎症,在外泌体的形成和分泌过程中起着至关重要的作用。用中性鞘磷脂酶抑制剂GW4869处理细胞后,外泌体的释放量可显著减少。近期有研究使用GW4869阻断蜱成虫唾液腺的外泌体分泌,从而达到了降低病毒传播率的效果[55]。微囊泡和外泌体是细胞外囊泡的两种形式,外泌体大小50-150 nm,微囊泡大小100-500 nm,微囊泡直接从质膜出芽,而外泌体从早期内体和多囊泡体中通过出芽形成腔内囊泡,并通过与质膜融合释放[56],中性鞘磷脂酶的抑制对两者的调节作用是不同的,用GW4869或RNAi对SMPD2/3抑制后,会减少外泌体的分泌,但也会增加质膜中微囊泡的分泌[56]。
2.5 目前已知调控外泌体释放的研究 目前已有报道称通过物理、生化手段可以提高外泌体分泌水平,其中一些新的方法可以使外泌体的产量提高约100倍,外泌体产量研究的进步使得外泌体的临床应用转化更易实现[57]。
2.5.1 关于提高外泌体分泌的物理方法及对外泌体的影响
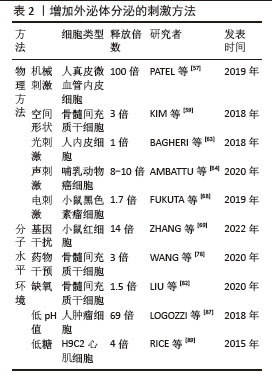
(1)机械刺激:机械刺激可以影响外泌体的产生,有研究表明在特定的机械剪切力作用下,可以显著增加细胞外泌体的分泌量。具体来说,当低剪切率(1.5 mN/cm2)应用于3D柱阵列支架上培养的人真皮微血管内皮细胞时,与静水压力对照组相比,外泌体的分泌量可以显著增加,至少增加100倍[57],这表明适当的机械剪切力可以显著促进外泌体的分泌。而机械敏感性YAP抑制剂的加入导致外泌体分泌量急剧减少,再次证明了外泌体是由机械敏感性介导的分泌过程[58];循环张力负荷是细胞在各种组织中所受的另一种机械刺激,例如骨骼肌和心肌,与静态控制相比,当原代人骨骼肌细胞暴露于循环拉伸时,可将外泌体分泌量增加一个数量级[58];这些研究结果表明,机械刺激对外泌体的产生具有显著影响,并且这种影响可能通过特定的机械敏感性途径介导。这些发现对于理解外泌体的生物合成和分泌机制,以及开发新的外泌体生产技术具有重要意义。
(2)空间形状:有研究者发现培养细胞的空间几何形状会影响外泌体分泌的量[58-59],将细胞培养方案从传统的2D培养瓶换成具有3D几何结构的培养条件,可以增加外泌体分泌的量,例如有研究者比较了常规2D单层细胞培养与甲基丙烯酸羟乙酯涂布法形成的3D悬滴球体培养的骨髓间充质干细胞的外泌体分泌量,发现3D培养的方法使外泌体量分泌增加了3倍[59]。研究还探讨了3D培养提高外泌体产量的可能机制,包括球体尺寸增大导致的细胞数量减少以及缺氧、高细胞密度和非贴壁细胞形态等因素,结果表明非贴壁的圆形细胞本身可能是影响外泌体分泌的一个重要因素[59]。另一项研究中,通过3D培养的人脐带间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体(3D-hUMSCs-Exos)在治疗白癜风方面展现出更为显著的效果,这表明3D培养的外泌体在临床应用中具有潜力[60]。还有研究探讨了不同维度支架培养细胞产生的外泌体对减少β淀粉样蛋白沉积的影响,发现3D外泌体与2D外泌体中产生的miRNAs和蛋白质明显不同,3D外泌体能够在体内、体外上调ADAM10的表达,下调BACE1的表达,降低脑内β淀粉样蛋白的沉积[61]。综上所述,3D培养条件能够显著增加外泌体的分泌量,并且可能通过不同的机制影响外泌体的生物合成和分泌。这些发现对于优化外泌体的生产和应用具有重要意义。
(3)光刺激:高功率低水平激光照射是一种非侵入性的治疗方式,它使用特定波长的光来刺激细胞活动,促进组织修复和再生。Wnt信号通路是细胞内一个关键的信号传导系统,它在多种生物学过程中发挥作用,包括细胞分化、增殖和存活[62]。有研究显示高功率低水平激光照射通过Wnt信号通路可以增加人内皮细胞外泌体的分泌[63]。这一发现表明低水平激光照射可能成为一种新的治疗手段,通过调节外泌体的分泌来治疗与血管功能障碍相关的疾病。
(4)声刺激:有研究发现通过使用高频(4 W,10 MHz)超声刺激细胞可以使外泌体分泌量提高8-10倍,刺激模式为超声刺激10 min,细胞孵育30 min后再重复1次[64]。低强度脉冲超声是一种无创治疗方法,有研究发现,低强度(0.6-2.1 W/cm2或0.6-3.4 W/cm2)脉冲超声促进外泌体分泌,而较高强度(3.4-5.0 W/cm2或5.0 W/cm2)脉冲超声抑制外泌体分泌,这种现象可能与自噬有关[65],结果表明超声刺激是一种有效的手段,可以显著增加外泌体的分泌量,这对于外泌体的基础研究和临床应用具有重要意义[66-67]。
(5)电刺激:有研究者测试了低水平电刺激处理对细胞分泌外泌体的影响,在小鼠黑色素瘤和小鼠成纤维细胞上施加0.34 mA/cm2 电场持续60 min,可以引起外泌体分泌增加1.7倍[68]。这些研究结果证实了低水平电刺激可以作为一种有效的方法来增加细胞外泌体的分泌,这对于外泌体的基础研究和潜在的临床应用可能会提供一定思路。
2.5.2 通过干扰分子机制促进外泌体释放的方法
(1)基因水平干扰影响外泌体释放:敲除Rab4基因在促进外泌体生物发生方面具有较高的功效,且没有明显的细胞毒性,Rab4敲低和红细胞膜颗粒补充剂的组合将外泌体产量提高了14倍,且不影响外泌体对物质的装载效率[69];此外,在培养基中补充红细胞膜颗粒进一步促进了外泌体的产生[69]。ISG15修饰(ISG化,是一种蛋白质翻译后修饰过程)通过促进溶酶体对多囊泡体蛋白的降解来控制外泌体的分泌[70],敲低5种Rab蛋白(Rab2b、Rab9a、Rab5a、Rab27a和Rab27b)可以抑制外泌体的分泌,这些Rab蛋白在调节外泌体的生成中起着关键作用,不同的Rab蛋白负责特定细胞类型中外泌体的分选或分泌[71]。KIBRA被识别为稳定Rab27a的衔接蛋白样蛋白,而Rab27a则在体外和体内都控制着外泌体的分泌。KIBRA敲除时,Rab27a的表达在蛋白质水平显著下调,但mRNA水平无变化。Rab27a的蛋白质降解可以通过蛋白酶体抑制剂lactacystine(Lac)恢复,但不能通过溶酶体抑制剂bafilomycin A1(Baf)恢复。KIBRA与Rab27a相互作用,通过泛素蛋白-蛋白酶体途径阻止Rab27a的泛素化和降解,从而控制外泌体的分泌[72],TRX2可以和Rab35相互作用,诱导Rab35降解,导致外泌体分泌受损[73],也有研究者探索了Rab35及GTP酶激活蛋白TBC1D10A–C对外泌体分泌的调节机制[74]。还有研究者通过抑制内体成熟以及减少溶酶体功能来探索是否会影响外泌体的释放,他们通过使用RNA干扰技术,靶向内体运输过程中的两个已知参与蛋白NDRG1和Rab7,结果发现NDRG1表达减少导致外泌体的释放增加了2倍[75]。这些研究结果提供了关于不同蛋白和修饰对外泌体分泌影响的证据,表明通过调节这些蛋白和修饰,可以有效控制外泌体的生物合成和分泌,这对于外泌体释放调控的基础研究具有重要意义。
(2)药物干预影响外泌体释放:研究发现速效救心丸通过上调GTP酶(包括Rab27a和Rab27b)促进外泌体从间充质干细胞分泌,证实了速效救心丸调节心脏平衡的一种新的机制[76]。有研究通过高通量筛选发现了多种药物能够调节外泌体的生物合成和分泌,这些药物包括抑制剂如替法尼布和尼替康唑,以及激活剂如西他沙星和福斯可林,为癌症治疗提供了新的药物再利用策略。研究还揭示了这些药物通过影响ESCRT依赖和非依赖途径以及Ras/ERK信号通路来调节外泌体的生成和释放,为理解外泌体在肿瘤进展中的作用机制提供了重要见解[77]。有研究者选择了4种FDA批准的药物(非诺特罗、去甲肾上腺素、N-甲基多巴胺和甲苯甘醚)以及另一种营养补充剂(毛喉素)来观察对外泌体分泌的影响,结果发现用N-甲基多巴胺和去甲肾上腺素组合处理骨髓间充质干细胞可以通过增强与ESCRT非依赖性通路相关基因(如中性鞘磷脂酶2)的表达,导致外泌体的分泌量增加3倍[78]。有研究者使用碘乙酸钠(糖酵解抑制剂)和2,4-二硝基苯酚氧化磷酸化抑制剂处理细胞,可以导致细胞内的能量消耗,表现为ATP水平降低和AMP水平升高,这种能量消耗状态刺激细胞释放腺苷,进而激活A2B受体系统,最终导致外泌体产生量增加3-16倍[79]。这些研究结果提供了关于不同药物和化合物对外泌体分泌影响的证据,通过调节这些药物和化合物,可以有效控制外泌体的生物合成和分泌,这对于外泌体的潜在临床应用可能具有重要意义。
2.5.3 环境因素对外泌体分泌的影响
(1)缺氧环境:有大量研究发现缺氧环境刺激可以增加细胞外泌体的释放[80-83],可能与缺氧诱导因子信号通路的激活有关[81],另外有学者在没有缺氧刺激的条件下通过对缺氧诱导因子过表达,发现对外泌体分泌量的影响有类似的效果[84]。
(2)低pH值环境:已知酸性环境下外泌体分泌会增加[85-86],与正常pH条件相比,HEK293T细胞在高pH值(11.0)下分泌的外泌体少5倍,在低pH值(4.0)下分泌的外泌体多6倍。pH值从7.4逐渐适度降低到6.5导致肿瘤细胞释放的外泌体增加高达69倍[87]。
(3)低糖环境:在葡萄糖剥夺情况下,永生化的H9C2心肌细胞外泌体分泌增加约4倍[88],在一项关于氧和葡萄糖调控胎盘细胞外泌体生物活性的研究中发现,中度缺氧和低血糖的结合可以导致滋养层细胞外泌体的产生增加三四倍[89]。这些研究结果提供了关于不同环境因素对外泌体分泌影响的证据,通过调节这些环境因素,可以有效控制外泌体的生物合成和分泌,见表2。
2.6 外泌体产品部分临床试验结果 外泌体作为一种新兴的生物医学工具,在多个领域的临床试验中展现出显著的潜力和效果。在抗衰老领域,间充质干细胞外泌体能够有效修复受氧化损伤的衰老细胞,降低β-半乳糖苷酶活性和γ-H2AX水平,减少DNA损伤,使衰老细胞恢复活力[90]。在老年小鼠模型中,外泌体治疗还显著降低了心肌细胞中的哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白活性和P21表达,恢复至年轻小鼠水平[90]。在神经退行性疾病领域,外泌体在阿尔茨海默病治疗中也取得了积极进展。一项Ⅰ/Ⅱ期临床试验通过间充质干细胞来源外泌体喷鼻治疗,结果显示中等剂量组患者的ADAS-cog评分在第12周下降2.33分,MoCA-B评分增加2.38分,认知功能得到改善,并且在第36周ADAS-cog评分持续下降3.98分,未报告不良事件[91]。在免疫调节领域,外泌体同样表现出色。在移植物抗宿主病的病例报告中,间充质干细胞来源外泌体治疗后,临床移植物抗宿主病症状显著改善,皮肤和黏膜移植物抗宿主病在2周内表现出明显抑制,4个月后仍稳定。肿瘤细胞衍生外泌体也被用于引发抗肿瘤免疫反应,在一些小规模临床试验中用于免疫疗法是安全和可行的 [92]。在糖尿病领域,脐血间充质干细胞衍生外泌体在1型糖尿病患者的临床试验中,能够改善炎症、增加局部胰腺细胞数量并增加循环表皮生长因子,从而降低血糖并增加胰岛素分泌[92]。外泌体在其他领域如COVID-19和骨关节炎的治疗中也显示出潜力[92]。在COVID-19的前瞻性非随机开放标签队列研究中,使用骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体治疗,患者存活率为83%,约71%的患者痊愈。在骨关节炎的试点研究中,外泌体治疗使患者的平均病情在6个月的随访中有所改善[92]。
2.7 外泌体释放调控研究的应用前景 目前关于外泌体调控的很多机制已被研究,但各种调控机制作为外泌体生产调节的应用研究仍较少。外泌体在精准医疗中的应用前景十分广阔,它们不仅可以用于疾病的早期筛查、实时监控、治疗反应监控和预后判断,还可以作为药物递送系统,为基因治疗、靶向药物治疗等提供新的可能性。随着技术的不断进步和研究的深入,外泌体有望在未来的生物医药领域发挥更加重要的作用。通过设计的载体对基因进行组织或细胞特异性递送,可以实现具有低毒性或风险的基因治疗。外泌体分泌调控的研究不仅加深了对外泌体在心脑血管疾病和癌症等疾病中作用的理解,而且为开发新的诊断方法和治疗策略提供了可能。随着对外泌体认识的不断深入,这些研究有望在未来实现并造福于患者。
| [1] GURUNATHAN S, KANG MH, KIM JH. A Comprehensive Review on Factors Influences Biogenesis, Functions, Therapeutic and Clinical Implications of Exosomes. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021;16:1281-1312. [2] HAN QF, LI WJ, HU KS, et al. Exosome biogenesis: machinery, regulation, and therapeutic implications in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2022;21(1):207. [3] RÄDLER J, GUPTA D, ZICKLER A, et al. Exploiting the biogenesis of extracellular vesicles for bioengineering and therapeutic cargo loading. Mol Ther. 2023;31(5):1231-1250. [4] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478): eaau6977. [5] GURUNG S, PEROCHEAU D, TOURAMANIDOU L, et al. The exosome journey: from biogenesis to uptake and intracellular signalling. Cell Commun Signal. 2021;19(1):47. [6] ARYA SB, COLLIE SP, PARENT CA. The ins-and-outs of exosome biogenesis, secretion, and internalization. Trends Cell Biol. 2024;34(2): 90-108. [7] CECCHIN R, TROYER Z, WITWER K, et al. Extracellular vesicles: The next generation in gene therapy delivery. Mol Ther. 2023;31(5): 1225-1230. [8] ZHAO Z, QU L, SHUANG T, et al. Low-intensity ultrasound radiation increases exosome yield for efficient drug delivery. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2020;57:101713. [9] YAN L, WU X. Exosomes produced from 3D cultures of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in a hollow-fiber bioreactor show improved osteochondral regeneration activity. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2020;36(2):165-178. [10] KINK JA, BELLIO MA, FORSBERG MH, et al. Large-scale bioreactor production of extracellular vesicles from mesenchymal stromal cells for treatment of acute radiation syndrome. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024;15(1):72. [11] CAO Z, LI P, LI Y, et al. Encapsulation of Nano-Bortezomib in Apoptotic Stem Cell-Derived Vesicles for the Treatment of Multiple Myeloma. Small. 2023;19(40):e2301748. [12] JIAO Y, TANG Y, LI Y, et al. Tumor cell-derived extracellular vesicles for breast cancer specific delivery of therapeutic P53. J Control Release. 2022;349:606-616. [13] YANG F, XUE J, WANG G, et al. Nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:999404. [14] GORSHKOV A, PURVINSH L, BRODSKAIA A, et al. Exosomes as Natural Nanocarriers for RNA-Based Therapy and Prophylaxis. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022;12(3):524. [15] LAI JJ, CHAU ZL, CHEN SY, et al. Exosome Processing and Characterization Approaches for Research and Technology Development. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(15):e2103222. [16] LAN F, QING Q, PAN Q, et al. Serum exosomal miR-301a as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for human glioma. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2018;41(1):25-33. [17] KALLURI R. The biology and function of extracellular vesicles in immune response and immunity. Immunity. 2024;57(8):1752-1768. [18] LV M, YAO T, ZHANG Y, et al. Exosomes loading Tapasin enhance T cell immune response by autophagy to inhibit HBV replication. J Med Virol. 2023;95(4):e28746. [19] ZOU J, YANG W, CUI W, et al. Therapeutic potential and mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as bioactive materials in tendon-bone healing. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):14. [20] GUILLAMAT-PRATS R. The Role of MSC in Wound Healing, Scarring and Regeneration. Cells. 2021;10(7):1729. [21] WAN R, HUSSAIN A, BEHFAR A, et al. The Therapeutic Potential of Exosomes in Soft Tissue Repair and Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(7):3869. [22] LIANG Y, YE F, LUO D, et al. Exosomal circSIPA1L3-mediated intercellular communication contributes to glucose metabolic reprogramming and progression of triple negative breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 2024;23(1):125. [23] HAN Q, XIE QR, LI F, et al. Targeted inhibition of SIRT6 via engineered exosomes impairs tumorigenesis and metastasis in prostate cancer. Theranostics. 2021;11(13):6526-6541. [24] LIU C, XIAO K, XIE L. Advances in the use of exosomes for the treatment of ALI/ARDS. Front Immunol. 2022;13:971189. [25] OZANSOY M, MIKATI H, VELIOGLU HA, et al. Exosomes: A missing link between chronic systemic inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease? Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;159:114161. [26] SHEN K, WANG X, WANG Y, et al. miR-125b-5p in adipose derived stem cells exosome alleviates pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells ferroptosis via Keap1/Nrf2/GPX4 in sepsis lung injury. Redox Biol. 2023;62:102655. [27] KONAKA H, KATO Y, HIRANO T, et al. Secretion of mitochondrial DNA via exosomes promotes inflammation in Behçet’s syndrome. EMBO J. 2023;42(20):e112573. [28] BUZAS EI. The roles of extracellular vesicles in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2023;23(4):236-250. [29] KUMAR A, DEEP G. Exosomes in hypoxia-induced remodeling of the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Lett. 2020;488:1-8. [30] 马元,庄雪莹,陈旭.间充质干细胞外泌体调控血管生成机制的研究进展[J].中国医科大学学报,2021,50(10):944-947. [31] 郑玉军,姜巍,陈东妍,等.外泌体在恶性肿瘤中的研究进展[J].中国肺癌杂志,2020, 23(8):689-694. [32] ZOU J, PENG H, LIU Y. The Roles of Exosomes in Immunoregulation and Autoimmune Thyroid Diseases. Front Immunol. 2021;12:757674. [33] ESSOLA JM, ZHANG M, YANG H, et al. Exosome regulation of immune response mechanism: Pros and cons in immunotherapy. Bioact Mater. 2023;32:124-146. [34] FEDERICI C, SHAHAJ E, CECCHETTI S, et al. Natural-Killer-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Immune Sensors and Interactors. Front Immunol. 2020;11:262. [35] PANDA SS, SAHOO RK, PATRA SK, et al. Molecular insights to therapeutic in cancer: role of exosomes in tumor microenvironment, metastatic progression and drug resistance. Drug Discov Today. 2024;29(8):104061. [36] TAI YL, CHEN KC, HSIEH JT, et al. Exosomes in cancer development and clinical applications. Cancer Sci. 2018;109(8):2364-2374. [37] SHENODA BB, AJIT SK. Modulation of Immune Responses by Exosomes Derived from Antigen-Presenting Cells. Clin Med Insights Pathol. 2016;9(Suppl 1):1-8. [38] EL SAFADI D, MOKHTARI A, KREJBICH M, et al. Exosome-Mediated Antigen Delivery: Unveiling Novel Strategies in Viral Infection Control and Vaccine Design. Vaccines (Basel). 2024;12(3):280. [39] HONG S, RUAN S, GREENBERG Z, et al. Development of surface engineered antigenic exosomes as vaccines for respiratory syncytial virus. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):21358. [40] 张怡璇,陆有群,洪晶,等.干细胞衍生外泌体:再生医学的治疗新策略[J].临床医学进展,2022,12(12):11329-11337. [41] LIU M, WANG J, LIU M, et al. Study of immunomodulatory function of exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015;95(32):2630-2633. [42] CAO L, XU H, WANG G, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells attenuate dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis by promoting M2 macrophage polarization. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;72:264-274. [43] RONG X, LIU J, YAO X, et al. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviate liver fibrosis through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):98. [44] LIU Z, XU Y, WAN Y, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent cardiomyocyte apoptosis induced by oxidative stress. Cell Death Discov. 2019;5:79. [45] MOEINABADI-BIDGOLI K, REZAEE M, HOSSEIN-KHANNAZER N, et al. Exosomes for angiogenesis induction in ischemic disorders. J Cell Mol Med. 2023;27(6):763-787. [46] KRYLOVA SV, FENG D. The Machinery of Exosomes: Biogenesis, Release, and Uptake. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(2):1337. [47] VIETRI M, RADULOVIC M, STENMARK H. The many functions of ESCRTs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(1):25-42. [48] CHRIST L, RAIBORG C, WENZEL EM, et al. Cellular Functions and Molecular Mechanisms of the ESCRT Membrane-Scission Machinery. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017;42(1):42-56. [49] WEI H, CHEN Q, LIN L, et al. Regulation of exosome production and cargo sorting. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(1):163-177. [50] WEHMAN AM, POGGIOLI C, SCHWEINSBERG P, et al. The P4-ATPase TAT-5 inhibits the budding of extracellular vesicles in C. elegans embryos. Curr Biol. 2011;21(23):1951-1959. [51] BEER KB, RIVAS-CASTILLO J, KUHN K, et al. Extracellular vesicle budding is inhibited by redundant regulators of TAT-5 flippase localization and phospholipid asymmetry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018; 115(6):E1127-E1136. [52] BESEMER AS, MAUS J, AX MDA, et al. Receptor-mediated endocytosis 8 (RME-8)/DNAJC13 is a novel positive modulator of autophagy and stabilizes cellular protein homeostasis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021;78(2):645-660. [53] MATSUO S, MIYATAKE K, ENDO M, et al. Loss of function of the Pad-1 aminotransferase gene, which is involved in auxin homeostasis, induces parthenocarpy in Solanaceae plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(23):12784-12790. [54] XIANG H, JIN S, TAN F, et al. Physiological functions and therapeutic applications of neutral sphingomyelinase and acid sphingomyelinase. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;139:111610. [55] SULTANA H, AHMED W, NEELAKANTA G. GW4869 inhibitor affects vector competence and tick-borne flavivirus acquisition and transmission by blocking exosome secretion. iScience. 2024;27(8):110391. [56] GUO BB, BELLINGHAM SA, HILL AF. The neutral sphingomyelinase pathway regulates packaging of the prion protein into exosomes. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(6):3455-3467. [57] PATEL DB, LUTHERS CR, LERMAN MJ, et al. Enhanced extracellular vesicle production and ethanol-mediated vascularization bioactivity via a 3D-printed scaffold-perfusion bioreactor system. Acta Biomater. 2019;95:236-244. [58] GUO S, DEBBI L, ZOHAR B, et al. Stimulating Extracellular Vesicles Production from Engineered Tissues by Mechanical Forces. Nano Lett. 2021;21(6):2497-2504. [59] KIM M, YUN HW, PARK DY, et al. Three-Dimensional Spheroid Culture Increases Exosome Secretion from Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;15(4): 427-436. [60] WANG Q, GUO W, NIU L, et al. 3D-hUMSCs Exosomes Ameliorate Vitiligo by Simultaneously Potentiating Treg Cells-Mediated Immunosuppression and Suppressing Oxidative Stress-Induced Melanocyte Damage. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(31):e2404064. [61] YANG L, ZHAI Y, HAO Y, et al. The Regulatory Functionality of Exosomes Derived from hUMSCs in 3D Culture for Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy. Small. 2020;16(3):e1906273. [62] ZHANG RF, WANG Q, ZHANG AA, et al. Low-level laser irradiation promotes the differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells into osteoblasts through the APN/Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(9):2860-2868. [63] BAGHERI HS, MOUSAVI M, REZABAKHSH A, et al. Low-level laser irradiation at a high power intensity increased human endothelial cell exosome secretion via Wnt signaling. Lasers Med Sci. 2018;33(5):1131-1145. [64] AMBATTU LA, RAMESAN S, DEKIWADIA C, et al. High frequency acoustic cell stimulation promotes exosome generation regulated by a calcium-dependent mechanism. Commun Biol. 2020;3(1):553. [65] ZENG Q, HONG S, WANG X, et al. Regulation of exosomes secretion by low-intensity pulsed ultrasound in lung cancer cells. Exp Cell Res. 2019;383(1):111448. [66] DENG Z, WANG J, XIAO Y, et al. Ultrasound-mediated augmented exosome release from astrocytes alleviates amyloid-β-induced neurotoxicity. Theranostics. 2021;11(9): 4351-4362. [67] LIAO Q, LI BJ, LI Y, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes osteoarthritic cartilage regeneration by BMSC-derived exosomes via modulating the NF-κB signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;97:107824. [68] FUKUTA T, NISHIKAWA A, KOGURE K. Low level electricity increases the secretion of extracellular vesicles from cultured cells. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2019;21:100713. [69] ZHANG R, BU T, CAO R, et al. An optimized exosome production strategy for enhanced yield while without sacrificing cargo loading efficiency. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1): 463. [70] VILLARROYA-BELTRI C, BAIXAULI F, MITTELBRUNN M, et al. ISGylation controls exosome secretion by promoting lysosomal degradation of MVB proteins. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13588. [71] OSTROWSKI M, CARMO NB, KRUMEICH S, et al. Rab27a and Rab27b control different steps of the exosome secretion pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12(1):19-30. [72] SONG L, TANG S, HAN X, et al. KIBRA controls exosome secretion via inhibiting the proteasomal degradation of Rab27a. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1639. [73] ZHANG T, ZHAO L, HAN L, et al. TRX2/Rab35 Interaction Impairs Exosome Secretion by Inducing Rab35 Degradation. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(12):6557. [74] HSU C, MOROHASHI Y, YOSHIMURA S, et al. Regulation of exosome secretion by Rab35 and its GTPase-activating proteins TBC1D10A-C. J Cell Biol. 2010;189(2):223-232. [75] ORTEGA FG, ROEFS MT, DE MIGUEL PEREZ D, et al. Interfering with endolysosomal trafficking enhances release of bioactive exosomes. Nanomedicine. 2019;20: 102014. [76] RUAN XF, JU CW, SHEN Y, et al. Suxiao Jiuxin pill promotes exosome secretion from mouse cardiac mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018;39(4):569-578. [77] DATTA A, KIM H, MCGEE L, et al. High-throughput screening identified selective inhibitors of exosome biogenesis and secretion: A drug repurposing strategy for advanced cancer. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):8161. [78] WANG J, BONACQUISTI EE, BROWN AD, et al. Boosting the Biogenesis and Secretion of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes. Cells. 2020;9(3):660. [79] LUDWIG N, YERNENI SS, MENSHIKOVA EV, et al. Simultaneous Inhibition of Glycolysis and Oxidative Phosphorylation Triggers a Multi-Fold Increase in Secretion of Exosomes: Possible Role of 2’3’-cAMP. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):6948. [80] BISTER N, PISTONO C, HUREMAGIC B, et al. Hypoxia and extracellular vesicles: A review on methods, vesicular cargo and functions. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020;10(1):e12002. [81] ZENG Z, ZHAO Y, CHEN Q, et al. Hypoxic exosomal HIF-1α-stabilizing circZNF91 promotes chemoresistance of normoxic pancreatic cancer cells via enhancing glycolysis. Oncogene. 2021;40(36):5505-5517. [82] LIU W, LI L, RONG Y, et al. Hypoxic mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote bone fracture healing by the transfer of miR-126. Acta Biomater. 2020;103:196-212. [83] TSE SW, TAN CF, PARK JE, et al. Microenvironmental Hypoxia Induces Dynamic Changes in Lung Cancer Synthesis and Secretion of Extracellular Vesicles. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(10):2917. [84] GONZALEZ-KING H, GARCÍA NA, ONTORIA-OVIEDO I, et al. Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α Potentiates Jagged 1-Mediated Angiogenesis by Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes. Stem Cells. 2017;35(7):1747-1759. [85] LOGOZZI M, SPUGNINI E, MIZZONI D, et al. Extracellular acidity and increased exosome release as key phenotypes of malignant tumors. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019;38(1-2): 93-101. [86] LOGOZZI M, ANGELINI DF, IESSI E, et al. Increased PSA expression on prostate cancer exosomes in in vitro condition and in cancer patients. Cancer Lett. 2017;403:318-329. [87] LOGOZZI M, MIZZONI D, ANGELINI DF, et al. Microenvironmental pH and Exosome Levels Interplay in Human Cancer Cell Lines of Different Histotypes. Cancers (Basel). 2018; 10(10):370. [88] GARCIA NA, ONTORIA-OVIEDO I, GONZÁLEZ-KING H, et al. Glucose Starvation in Cardiomyocytes Enhances Exosome Secretion and Promotes Angiogenesis in Endothelial Cells. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0138849. [89] RICE GE, SCHOLZ-ROMERO K, SWEENEY E, et al. The Effect of Glucose on the Release and Bioactivity of Exosomes From First Trimester Trophoblast Cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(10):E1280-1288. [90] SHI HZ, ZENG JC, SHI SH, et al. Extracellular Vesicles of GMSCs Alleviate Aging-Related Cell Senescence. J Dent Res. 2021;100(3): 283-292. [91] XIE X, SONG Q, DAI C, et al. Clinical safety and efficacy of allogenic human adipose mesenchymal stromal cells-derived exosomes in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease: a phase I/II clinical trial. Gen Psychiatr. 2023;36(5):e101143. [92] LOTFY A, ABOQUELLA NM, WANG H. Mesenchymal stromal/stem cell (MSC)-derived exosomes in clinical trials. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):66. |
| [1] | 左 娜, 唐 琪, 于 猛, 陶 凯. 脂肪干细胞源性外泌体中miR-196b-5p对大鼠烧伤创面愈合的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(1): 43-49. |
| [2] | 袁为远, 雷秦袆, 李秀琪, 卢铁柱, 傅子文, 梁志丽, 季韶洋, 李一佳, 任 宇. 脂肪来源间充质干细胞及外泌体对地塞米松诱导肌肉减少症小鼠的治疗作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(1): 58-67. |
| [3] | 张婷婷, 李亚龙, 岳浩迪, 李颜君, 耿熙炆, 张玉薇, 刘小转. 不同鼠龄骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体保护放射性肺损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(1): 1-9. |
| [4] | 于漫亚, 崔 兴. 骨髓微环境中不同细胞对多发性骨髓瘤骨病外泌体环状RNA的贡献及相互作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(1): 101-110. |
| [5] | 张钊伟, 陈欧子乐, 白明茹, 汪成林. 牙源性间充质干细胞分泌生物活性物质用于骨修复的治疗潜力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(1): 163-174. |
| [6] | 刘 念, 董昕玥, 王菘芃, 徐英江, 张晓明. 干细胞外泌体和生物材料辅助外泌体修复骨缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(1): 175-183. |
| [7] | 刘 宇, 龚森怡, 杨丽华, 李伟风, 胡玉雯, 闫钦彪, 郭美锦. 间充质干细胞来源外泌体分离、鉴定技术及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(1): 194-203. |
| [8] | 罗文彬, 李若云, 潘超凡, 罗长江. 工程化外泌体修复组织损伤:应用潜力及优异的生物稳定性和靶向特异性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(1): 204-217. |
| [9] | 赖鹏宇, 梁 冉, 沈 山. 组织工程技术修复颞下颌关节:问题与挑战[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [10] | 李加根, 陈跃平, 黄柯琪, 陈尚桐, 黄川洪. 线粒体自噬视域下的类风湿关节炎:多机器学习算法构建预测模型及验证并免疫调控分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(在线): 1-15. |
| [11] | 金 凯, 唐 婷, 李美乐, 谢裕安. 人脐带间充质干细胞条件培养基及外泌体对肝癌细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭和凋亡的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [12] | 艾克帕尔·艾尔肯, 陈晓涛, 吾凡别克·巴合提. 成骨诱导人牙周膜干细胞来源外泌体促进炎症微环境下人牙周膜干细胞成骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [13] | 吕丽婷, 于 霞, 张金梅, 高巧婧, 刘仁凡, 李 梦, 王 璐. 脑衰老与外泌体研究进程及现状的文献计量学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1457-1465. |
| [14] | 李佳林, 张耀东, 娄艳茹, 于 洋, 杨 蕊. 间充质干细胞分泌组发挥作用的分子机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1512-1522. |
| [15] | 郑伊桐, 汪永新, 刘 文, 阿木吉特, 秦 虎. 神经内镜下人脐带间充质干细胞外泌体鞘内移植修复脊髓损伤的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(36): 7743-7751. |
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者于2024年10月应用计算机进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 2010年1月至2024年10月,重点检索近5年发表的英文文献。
1.1.3 检索数据库 英文数据库:PubMed数据库;中文数据库:中国知网。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“外泌体,生物学功能,生发过程,分泌释放,调控机制”,英文检索词为“exosomes,biological functions,biogenesis,secretion and release,regulatory mechanisms”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 综述、研究原著及著作。
1.1.6 检索策略 以PubMed数据库为例,检索策略见图1。
1.1.7 检索文献量 初步检索到文献346篇,包括英文文献326篇、中文文献20篇。
1.2 纳入标准 ①已正式发表的期刊文献,文献内容与“关键词”内容密切相关;②文献内容及观点具有创新性,论证科学严谨;③体现该领域最新研究进展的文献。
1.3 排除标准 ①发表时间过早的文献;②观点陈旧及重复的文献;③与研究内容和目的无关的文献。
1.4 资料整合 在数据库对文献进行初步检索,排除重复文献及研究内容相关性差的文献,根据入选标准筛选文献并进行质量评估,最终得到文献92篇(中文文献3篇,英文文献89篇),见图2。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
3.2 此综述区别于他人他篇的特点 此综述系统总结了外泌体的生物特性、功能、生成过程及调控机制,涵盖了生化和物理调控方法,提供了较为全面的研究视角。此综述结合生物学、医学和工程学等多个学科的研究进展,从跨学科视角探讨了外泌体在不同领域的应用潜力和研究热点,强调了跨学科合作的重要性,且重点分析了近年来外泌体研究的新进展,如新型调控机制的发现、外泌体在新兴领域的应用等,具有较强的时效性和前沿性。
3.3 综述的局限性 由于外泌体的研究领域广泛且复杂,此综述可能无法对每一个具体的研究方向进行深入探讨,部分细节和机制可能未能详尽阐述。不同研究的实验条件和方法差异较大,导致数据整合和比较存在一定困难,可能影响对某些结论的准确性和普适性的判断。虽然此综述总结了当前的研究进展和趋势,但对未来研究方向的预测可能存在一定的局限性,需要后续研究的不断验证和完善。
3.4 综述的重要意义 为研究人员提供了一个系统了解外泌体研究现状和进展的平台,有助于促进学术交流和合作,推动该领域的进一步发展。总结了当前研究中存在的问题和挑战,为未来的研究提供了方向和思路,有助于研究者在相关领域开展更深入和有针对性的研究。此综述强调了外泌体在疾病诊断和治疗中的应用前景,为临床转化研究提供了理论基础和参考依据,有助于加速外泌体从基础研究到临床应用的转化进程。
3.5 对未来的建议
3.5.1 基础研究方向 ①深入探究调控机制:加强对外泌体生成和分泌调控机制的研究,尤其是对ESCRT非依赖途径、特定脂质分子作用机制以及物理刺激影响的深入探讨,揭示不同调控机制之间的相互作用和协同效应,为精准调控外泌体分泌提供理论依据。②解析功能机制的多样性:针对不同来源和组成的外泌体,在不同生理和病理状态下的具体作用机制进行深入研究,明确外泌体在细胞间通讯、免疫调节、组织修复、癌症发展等过程中的具体功能和分子机制。③跨学科研究的加强:促进生物学、医学、工程学等多学科的交叉融合,利用纳米技术、生物信息学、系统生物学等新兴技术手段,开展外泌体的高通量筛选、功能鉴定和调控网络研究,推动对外泌体复杂系统的全面理解。
3.5.2 技术开发与应用方向 ①优化分离与纯化技术:开发更为高效、特异且可重复的外泌体分离和纯化方法,建立统一的标准化流程,提高外泌体的纯度和产量,为后续研究和临床应用奠定基础。同时,探索适用于大规模生产的外泌体提取技术,降低生产成本。②提升检测与分析能力:发展高灵敏度、高特异性的外泌体检测技术,实现对外泌体数量、大小、形态、成分等的精准分析和定量检测。利用先进的成像技术和质谱分析等手段,深入研究外泌体的动态变化和相互作用,为揭示外泌体功能和调控机制提供有力支持。③构建有效的递送系统:研究和构建高效、稳定且具有靶向性的外泌体递送系统,提高药物在体内的传递效率和靶向性,减少不良反应。探索外泌体与其他递送载体的联合应用,发挥协同作用,提升治疗效果。
3.5.3 临床研究与转化方向 ①加强临床前研究:在临床应用前,深入开展外泌体的临床前研究,包括动物实验和体外实验,系统评估外泌体的安全性、有效性和稳定性。研究外泌体在不同疾病模型中的作用机制和治疗效果,为临床试验提供充分的科学依据和数据支持。②推进临床试验与转化:积极推动外泌体相关临床试验的开展,探索外泌体在疾病诊断、治疗和预后评估中的应用价值。加强与医疗机构的合作,建立临床研究平台,促进外泌体研究成果的转化应用,推动外泌体在临床实践中的广泛应用,造福患者。③关注伦理与监管问题:在开展外泌体临床研究和应用过程中,注重伦理和监管问题,确保研究的合规性和患者的权益。加强对外泌体临床应用的监管,制定相应的规范和标准,促进外泌体研究的健康发展和临床应用的规范化。
文题释义:
外泌体:是由细胞分泌到细胞外的膜性结构,具有脂质双分子层包裹,包含来自原始细胞的复杂内容物,如细胞因子、蛋白质、RNA、miRNA和脂质等生物活性分子,通常直径在30-150 nm之间,是最小的细胞外囊泡类型。外泌体在多种生物体液和组织中广泛存在,包括血液、尿液、唾液、乳汁、羊水、滑液和脑脊液等。
TAT-5:是一种特定的P4-ATP酶家族成员,P4-ATP酶指的是一类具有ATP水解酶活性的膜蛋白。TAT-5具有磷脂翻转酶活性,主要负责将磷脂酰乙醇胺从细胞膜的外侧转运到内侧,以维持磷脂酰乙醇胺在细胞膜上的不对称分布。当TAT-5的功能受到抑制或缺失时,磷脂酰乙醇胺会暴露在细胞膜的外侧,这可能会触发一系列生物学反应,如细胞外囊泡的出芽和形成等过程。因此,TAT-5在细胞膜磷脂的翻转和细胞外囊泡的调控中发挥着关键作用。
#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
研究者们正在积极探索外泌体生物合成和分泌的分子机制,特别是ESCRT依赖和非依赖途径,以及脂质分子如神经酰胺在外泌体形成中的作用,物理刺激(如机械力、光、声、电刺激)和化学手段(如药物干预)对外泌体分泌的影响是当前研究的热点,旨在发现新的调控策略以提高外泌体的产量和功能性。随着对外泌体生产和纯化技术的改进,规模化生产和质量控制将成为实现外泌体临床应用的关键。外泌体的基础研究成果将加速向临床应用的转化,特别是在液体活检和无细胞疗法中。随着纳米技术、生物信息学和系统生物学的发展,跨学科研究将推动对外泌体复杂调控网络的深入理解。
#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||