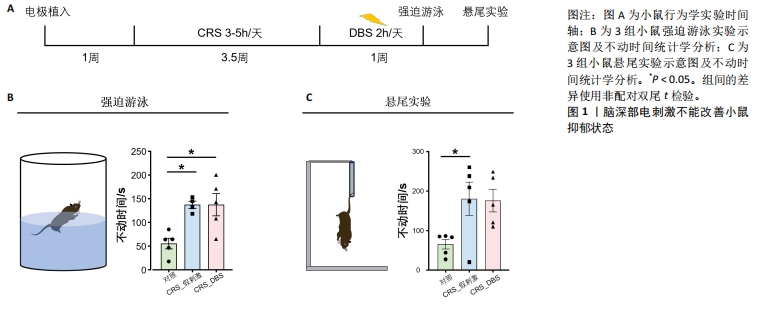
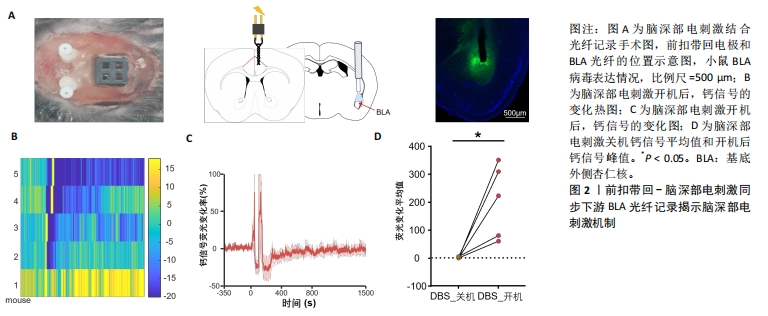
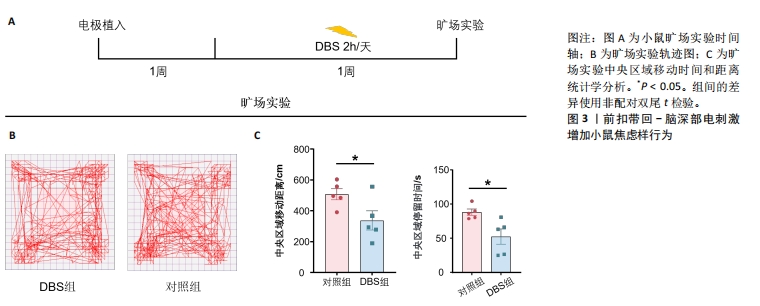
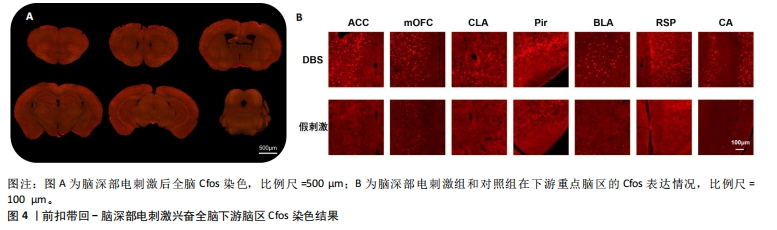
[1] BROMET E, ANDRADE L H, HWANG I, et al. Cross-national epidemiology of DSM-IV major depressive episode. BMC medicine.2011; 9: 90.
[2] Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet (London, England).2018; 392(10159): 1789-858.
[3] WALKER ER, MCGEE RE, DRUSS BG. Mortality in mental disorders and global disease burden implications: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA psychiatry.2015;72(4): 334-41.
[4] ROE-SEPOWITZ D. Adolescent female murderers: characteristics and treatment implications. The American journal of orthopsychiatry.2007;77(3): 489-96.
[5] GAYNES BN, LUX L, GARTLEHNER G, et al. Defining treatment-resistant depression. Depression and anxiety.2020; 37(2): 134-45.
[6] MONCRIEFF J, COOPER R E, STOCKMANN T, et al. The serotonin theory of depression: a systematic umbrella review of the evidence. Molecular psychiatry.2023;28(8): 3243-56.
[7] SANDOVAL-PISTORIUS SS, HACKER ML, WATERS AC, et al. Advances in Deep Brain Stimulation: From Mechanisms to Applications. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience.2023;43(45): 7575-86.
[8] GILBERT Z, MASON X, SEBASTIAN R, et al. A review of neurophysiological effects and efficiency of waveform parameters in deep brain stimulation. Clinical neurophysiology : official journal of the International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology.2023;152: 93-111.
[9] JOHNSON K A, OKUN M S, SCANGOS K W, et al. Deep brain stimulation for refractory major depressive disorder: a comprehensive review. Molecular psychiatry.2024; 29(4): 1075-87.
[10] MAYBERG HS, LOZANO AM, VOON V, et al. Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Neuron.2005; 45(5): 651-60.
[11] HOLTZHEIMER PE, HUSAIN M M, LISANBY SH, et al. Subcallosal cingulate deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: a multisite, randomised, sham-controlled trial]. The lancet Psychiatry.2017;4(11): 839-849.
[12] RAMASUBBU R, ANDERSON S, HAFFENDEN A, et al. Double-blind optimization of subcallosal cingulate deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: a pilot study. Journal of psychiatry & neuroscience : JPN.2013;38(5): 325-332.
[13] UDUPA K, CHEN R. The mechanisms of action of deep brain stimulation and ideas for the future development. Progress in neurobiology.2015;133: 27-49.
[14] KRAUSS J K, LIPSMAN N, AZIZ T, et al. Technology of deep brain stimulation: current status and future directions [J]. Nature reviews Neurology.2021;17(2): 75-87.
[15] CHIKEN S, NAMBU A. Mechanism of Deep Brain Stimulation: Inhibition, Excitation, or Disruption?. The Neuroscientist : a review journal bringing neurobiology, neurology and psychiatry.2016; 22(3): 313-22.
[16] SHARIM J, POURATIAN N. Anterior Cingulotomy for the Treatment of Chronic Intractable Pain: A Systematic Review. Pain physician.2016;19(8): 537-50.
[17] BARTHAS F, HUMO M, GILSBACH R, et al. Cingulate Overexpression of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Phosphatase-1 as a Key Factor for Depression. Biological psychiatry.2017; 82(5): 370-9.
[18] KIM K S, HAN P L. Optimization of chronic stress paradigms using anxiety- and depression-like behavioral parameters. Journal of neuroscience research.2006; 83(3): 497-507.
[19] LI Y, ZHONG W, WANG D, et al. Serotonin neurons in the dorsal raphe nucleus encode reward signals. Nature communications, 2016, 7: 10503.
[20] HAMANI C, MAYBERG H, STONE S, et al. The subcallosal cingulate gyrus in the context of major depression. Biological psychiatry. 2011; 69(4): 301-8.
[21] CAI X, PADOA-SCHIOPPA C. Neuronal encoding of subjective value in dorsal and ventral anterior cingulate cortex. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience.2012;32(11): 3791-808.
[22] PALOMERO-GALLAGHER N, HOFFSTAEDTER F, MOHLBERG H, et al. Human Pregenual Anterior Cingulate Cortex: Structural, Functional, and Connectional Heterogeneity. Cerebral cortex (New York, NY : 1991).2019; 29(6): 2552-74.
[23] YUAN Z, QI Z, WANG R, et al. A corticoamygdalar pathway controls reward devaluation and depression using dynamic inhibition code [J]. Neuron, 2023, 111(23): 3837-53.e5.
[24] GAO Y, GAO D, ZHANG H, et al. BLA DBS improves anxiety and fear by correcting weakened synaptic transmission from BLA to adBNST and CeL in a mouse model of foot shock. Cell reports.2024;43(2): 113766.
[25] LOWET E, KONDABOLU K, ZHOU S, et al. Deep brain stimulation creates informational lesion through membrane depolarization in mouse hippocampus. Nature communications.2022;13(1): 7709.
[26] PUIGDEMONT D, PéREZ-EGEA R, PORTELLA M J, et al. Deep brain stimulation of the subcallosal cingulate gyrus: further evidence in treatment-resistant major depression. The international journal of neuropsychopharmacology.2012;15(1): 121-133.
[27] LIN Z J, GU X, GONG W K, et al. Stimulation of an entorhinal-hippocampal extinction circuit facilitates fear extinction in a post-traumatic stress disorder model. The Journal of clinical investigation.2024;134(22).
[28] SONG N, LIU Z, GAO Y, et al. NAc-DBS corrects depression-like behaviors in CUMS mouse model via disinhibition of DA neurons in the VTA . Molecular psychiatry.2024; 29(5): 1550-66.
[29] ASHKAN K, ROGERS P, BERGMAN H, et al. Insights into the mechanisms of deep brain stimulation. Nature reviews Neurology.2017;13(9): 548-54.
[30] PIALLAT B, CHABARDèS S, DEVERGNAS A, et al. Monophasic but not biphasic pulses induce brain tissue damage during monopolar high-frequency deep brain stimulation. Neurosurgery.2009; 64(1): 156-62; discussion 62-63.
[31] BüHNING F, MIGUEL TELEGA L, TONG Y, et al. Electrophysiological and molecular effects of bilateral deep brain stimulation of the medial forebrain bundle in a rodent model of depression. Experimental neurology.2022; 355: 114122.
[32] DOURNES C, BEESKé S, BELZUNG C, et al. Deep brain stimulation in treatment-resistant depression in mice: comparison with the CRF1 antagonist, SSR125543. Progress in neuro-psychopharmacology & biological psychiatry.2013; 40: 213-20.
[33] ZHANG Y, MA L, ZHANG X, et al. Deep brain stimulation in the lateral habenula reverses local neuronal hyperactivity and ameliorates depression-like behaviors in rats. Neurobiology of disease. 2023; 180: 106069.
[34] SCHOR JS, GONZALEZ MONTALVO I, SPRATT P WE, et al. Therapeutic deep brain stimulation disrupts movement-related subthalamic nucleus activity in parkinsonian mice. eLife. 2022; 11.
[35] VAN DEN BOOM B J G, ELHAZAZ-FERNANDEZ A, RASMUSSEN P A, et al. Unraveling the mechanisms of deep-brain stimulation of the internal capsule in a mouse model . Nature communications. 2023; 14(1): 5385.
[36] GONG W K, LI X, WANG L, et al. Prefrontal FGF1 Signaling is Required for Accumbal Deep Brain Stimulation Treatment of Addiction. Advanced science (Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany). 2025; 12(16): e2413370.
[37] SPIX T A, NANIVADEKAR S, TOONG N, et al. Population-specific neuromodulation prolongs therapeutic benefits of deep brain stimulation. Science (New York, NY). 2021, 374(6564): 201-6.
[38] MIGUEL TELEGA L, ASHOURI VAJARI D, STIEGLITZ T, et al. New Insights into In Vivo Dopamine Physiology and Neurostimulation: A Fiber Photometry Study Highlighting the Impact of Medial Forebrain Bundle Deep Brain Stimulation on the Nucleus Accumbens. Brain sciences. 2022; 12(8).
[39] SCHOR J S, NELSON A B. Multiple stimulation parameters influence efficacy of deep brain stimulation in parkinsonian mice. The Journal of clinical investigation.2019; 129(9): 3833-8.
[40] PAULK A C, ZELMANN R, CROCKER B, et al. Local and distant cortical responses to single pulse intracranial stimulation in the human brain are differentially modulated by specific stimulation parameters. Brain stimulation.2022; 15(2): 491-508.
[41] MURPHY KR, FARRELL JS, BENDIG J, et al. Optimized ultrasound neuromodulation for non-invasive control of behavior and physiology . Neuron. 2024; 112(19): 3252-66.e5.
[42] VALVERDE S, VANDECASTEELE M, PIETTE C, et al. Deep brain stimulation-guided optogenetic rescue of parkinsonian symptoms [J]. Nature communications, 2020, 11(1): 2388.
[43] ALEXANDER L, JELEN L A, MEHTA M A, et al. The anterior cingulate cortex as a key locus of ketamine’s antidepressant action. Neuroscience and biobehavioral reviews.2021; 127: 531-54.
[44] DIENER C, KUEHNER C, BRUSNIAK W, et al. A meta-analysis of neurofunctional imaging studies of emotion and cognition in major depression. NeuroImage. 2012; 61(3): 677-685.
[45] HOLMES S E, HINZ R, CONEN S, et al. Elevated Translocator Protein in Anterior Cingulate in Major Depression and a Role for Inflammation in Suicidal Thinking: A Positron Emission Tomography Study. Biological psychiatry.2018; 83(1): 61-9.
[46] SELLMEIJER J, MATHIS V, HUGEL S, et al. Hyperactivity of Anterior Cingulate Cortex Areas 24a/24b Drives Chronic Pain-Induced Anxiodepressive-like Consequences. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience. 2018; 38(12): 3102-15.
[47] MAYBERG H S, LIOTTI M, BRANNAN S K, et al. Reciprocal limbic-cortical function and negative mood: converging PET findings in depression and normal sadness. The American journal of psychiatry.1999; 156(5): 675-82.
[48] PALOMERO-GALLAGHER N, EICKHOFF S B, HOFFSTAEDTER F, et al. Functional organization of human subgenual cortical areas: Relationship between architectonical segregation and connectional heterogeneity. NeuroImage. 2015; 115: 177-90.
[49] KISELY S, LI A, WARREN N, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of deep brain stimulation for depression. Depression and anxiety. 2018; 35(5): 468-80.
[50] MAYBERG H S. Targeted electrode-based modulation of neural circuits for depression. The Journal of clinical investigation. 2009; 119(4): 717-25.
[51] CROWELL A L, RIVA-POSSE P, HOLTZHEIMER P E, et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Subcallosal Cingulate Deep Brain Stimulation for Treatment-Resistant Depression. The American journal of psychiatry. 2019; 176(11): 949-56. |