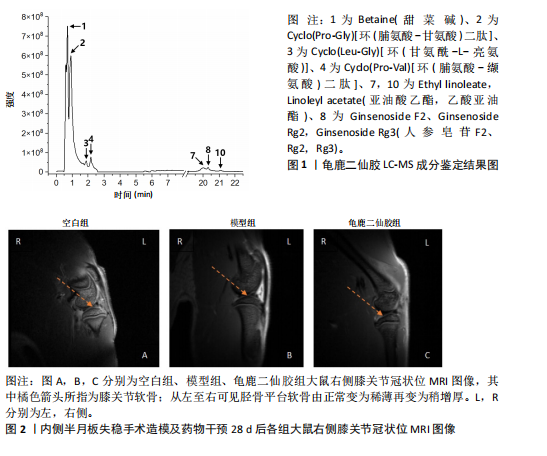
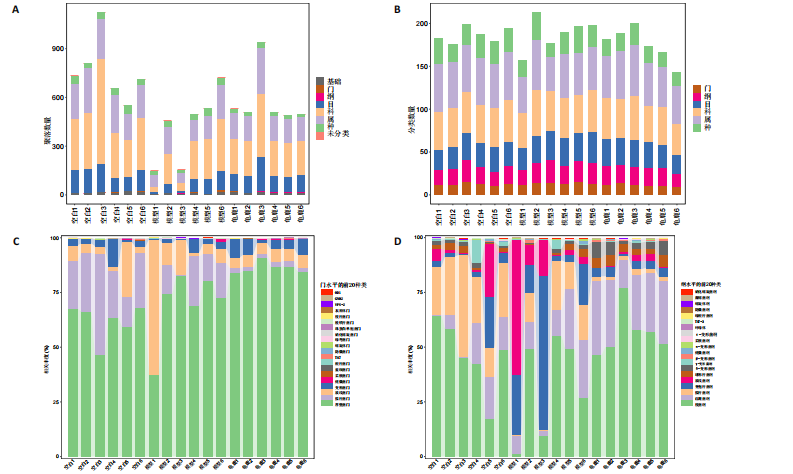
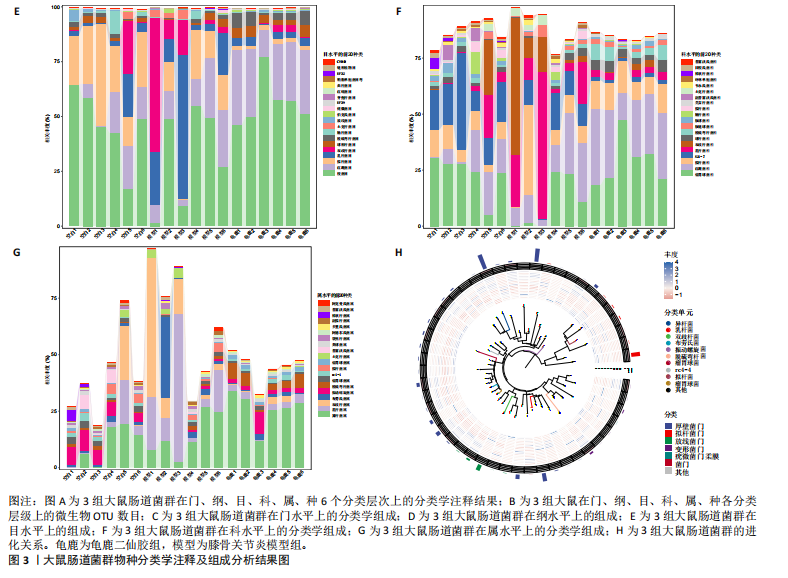
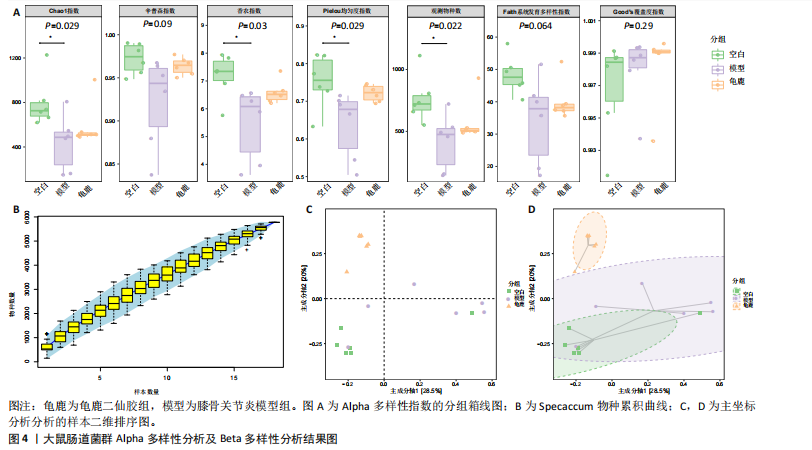
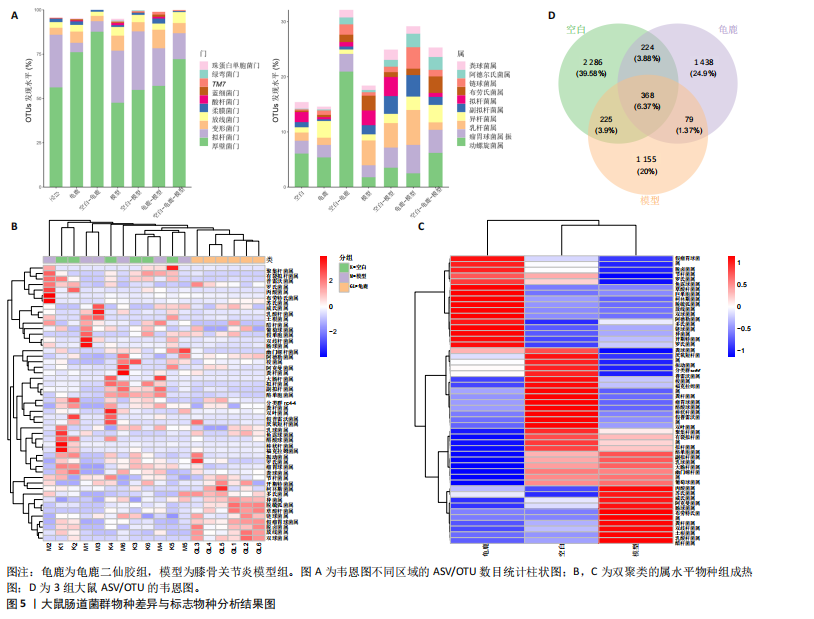
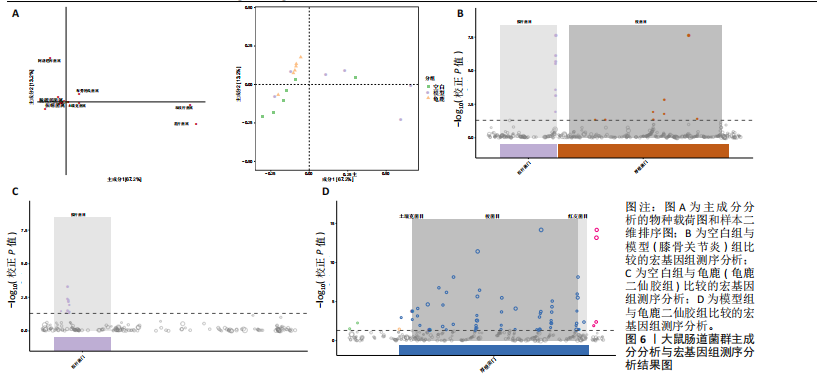
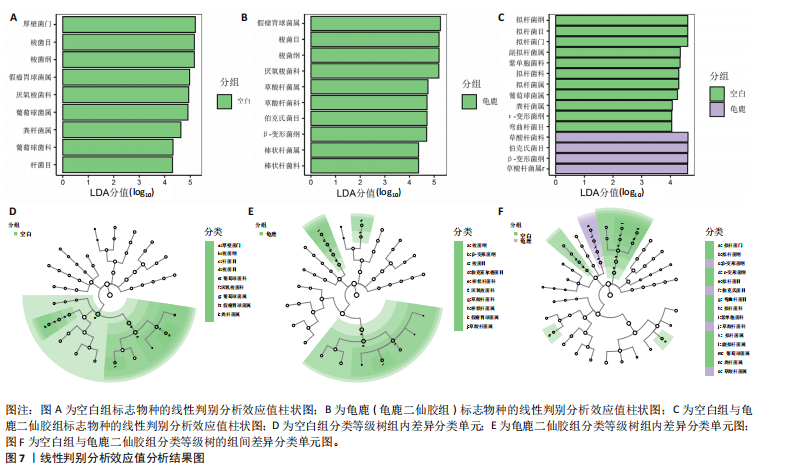
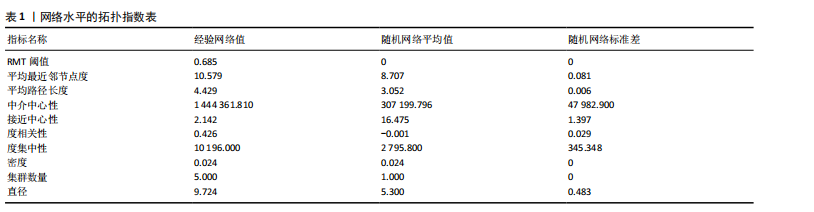
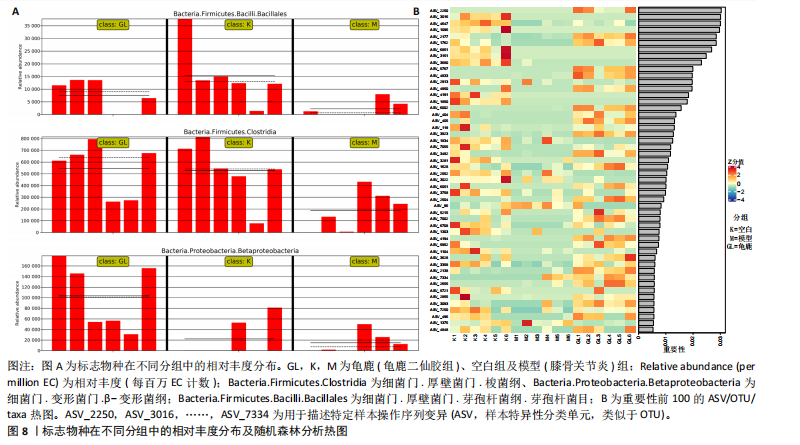
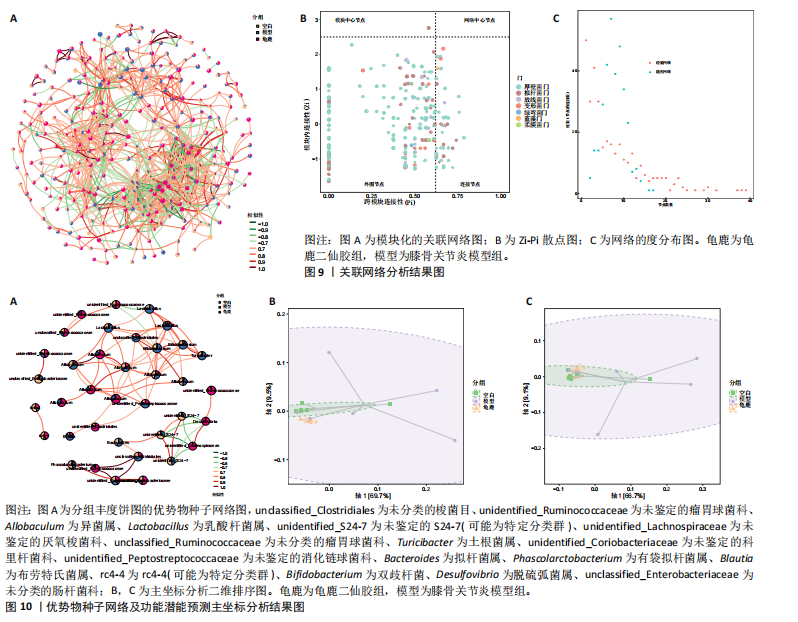
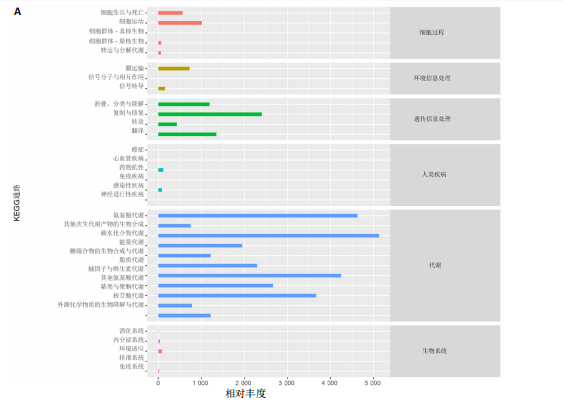
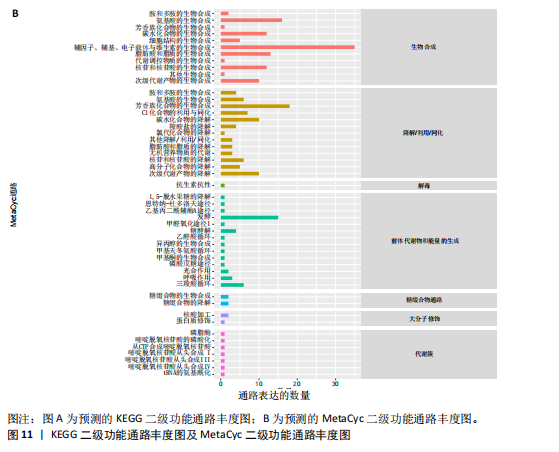
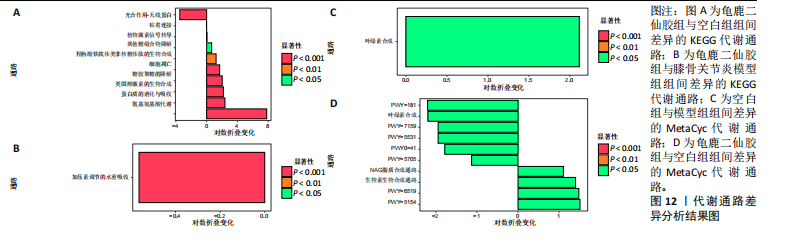
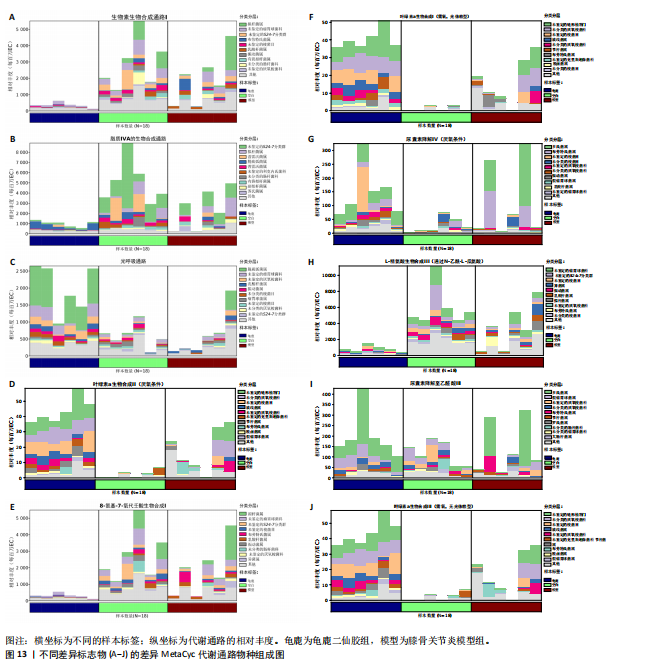
[1] 肖剑伟.骨关节炎中西医结合诊疗指南[J].风湿病与关节炎,2023,12(6):70-80.
[2] 周荣, 廖文洁.软骨下骨在骨关节炎中的病理改变及其机制研究[J].系统医学,2021,6(24):190-193.
[3] 李崇,缪季峰,林秋宁,等.外泌体非编码RNA在骨关节炎软骨损伤修复中的研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志,2021,41(3):186-194.
[4] GRASSEL S, ASZODI A. Osteoarthritis and cartilage regeneration: focus on pathophysiology and molecular mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(24): 6156.
[5] JANG S, LEE K, JU JH. Recent updates of diagnosis, pathophysiology, and treatment on osteoarthritis of the knee. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2619.
[6] BELK JW, KRAEUTLER MJ, HOUCK DA, et al. Platelet-rich plasma versus hyaluronic acid for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Sport Med. 2021;49(1):249-260.
[7] ZEITER S, KOSCHITZKI K, ALINI M, et al. Evaluation of preclinical models for the testing of bone tissue-engineered constructs. Tissue Eng Part C-Methods. 2020;26(2):107-117.
[8] 李文顺,李楠,余丹丹,等.龟鹿二仙胶汤治疗膝骨关节炎的临床研究[J].福建中医学院学报, 2005,15(6):30-32.
[9] 李楠,雒焕生,赵诣,等.龟鹿二仙胶汤及其拆方对大鼠软骨细胞凋亡基因表达的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2011,19(7):1-3.
[10] 李楠,杜江,黄远鹏,等.龟鹿二仙胶及其拆方对SD大鼠膝骨关节炎的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2013,28(6):1677-1680.
[11] 耿秋东,葛海雅,王和鸣,等.基于网络药理学探讨龟鹿二仙胶治疗骨关节炎的作用及机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(8):1229-1236.
[12] SENGPRASERT P, WAITAYANGKONN P, KAMENKIT O, et al. Catabolic mediators from TLR2-mediated proteoglycan aggrecan peptide-stimulated chondrocytes are reduced by Lactobacillus-conditioned media. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):18043.
[13] STEVENS C, NORRIS S, ARBEEVA L, et al. Gut microbiome and osteoarthritis: insights from the naturally occurring canine model of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024;76(12):1758-1763.
[14] WANG Y, MA M, DAI W, et al. Bacteroides salyersiae is a potent chondroitin sulfate-degrading species in the human gut microbiota. Microbiome. 2024;12(1):41.
[15] LUO S, CHEN Z, DENG L, et al. Causal link between gut microbiota, neurophysiological states, and bone diseases: a comprehensive mendelian randomization study. Nutrients. 2023;15(18):3934.
[16] LIU L, TIAN F, LI G, et al. The effects and significance of gut microbiota and its metabolites on the regulation of osteoarthritis: close coordination of gut-bone axis. Front Nutr. 2022;9: 1012087.
[17] HAO X, SHANG X, LIU J, et al. The gut microbiota in osteoarthritis: where do we stand and what can we do? Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):42.
[18] ARORA V, SINGH G, O-SULLIVAN I, et al. Gut-microbiota modulation: the impact of thegut-microbiotaon osteoarthritis. Gene. 2021;785: 145619.
[19] ELSAWY NA, IBRAHIEM AH, YOUNIS GA, et al. Microbiome and femoral cartilage thickness in knee osteoarthritis: is there a link? Cartilage. 2024. doi: 10.1177/19476035241276852.
[20] CHEN LC, LIN YY, TSAI YS, et al. Live and dead clostridium butyricum gkb7 diminish osteoarthritis pain and progression in preclinical animal model. Environ Toxicol. 2024;39(11):4927-4935.
[21] 易南星,米倚林,许晓彤,等.加味独活寄生合剂缓解小鼠膝骨关节炎过程中肠道菌群的参与机制[J].中国药理学通报,2022,38(4):625-632.
[22] BIAN M, ZHU C, NIE A, et al. Guizhi Shaoyao Zhimu Decoction ameliorates gouty arthritis in rats via altering gut microbiota and improving metabolic profile. Phytomedicine. 2024;131:155800.
[23] CUEVAS-SIERRA A, RAMOS-LOPEZ O, RIEZU-BOJ JI, et al. Diet, gut microbiota, and obesity: links with host genetics and epigenetics and potential applications. Adv Nutr. 2019;10(suppl_1):S17-S30.
[24] KARIM A. Unveiling the potential of probiotics in osteoarthritis management. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2024;27(1):2.
[25] 刘晓辰,付维力.骨关节炎动物模型的选择[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(11):1769-1776.
[26] 李仪奎.中药药理实验方法学[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,2006.
[27] LIU Q, HAO H, LI J, et al. Oral administration of bovine milk-derived extracellular vesicles attenuates cartilage degeneration via modulating gut microbiota in dmm-induced mice. Nutrients. 2023;15(3):747.
[28] NAKAHATA A, ITO A, NAKAHARA R, et al. Meniscus injury induces patellofemoral osteoarthritis development mediated by synovitis and gait kinematics: a preclinical study. Cartilage. 2024. doi: 10.1177/19476035241299769.
[29] MILLER KA, BAIER MANWELL LM, BARTELS CM, et al. Implementing an osteoarthritis management program to deliver guideline-driven care for knee and hip osteoarthritis in a U.S. academic health system. Osteoarthr Cartilage. 2024;6(2):100452.
[30] PAN H, GUO R, JU Y, et al. A single bacterium restores the microbiome dysbiosis to protect bones from destruction in a rat model of rheumatoid arthritis. Microbiome. 2019;7(1):107.
[31] LYU J, WANG T, CHEN Y, et al. Oral intake of streptococcus thermophilus improves knee osteoarthritis degeneration: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study. Heliyon. 2020;6(4):e3757.
[32] TAYE I, BRADBURY J, GRACE S, et al. Probiotics for pain of osteoarthritis; An N-of-1 trial of individual effects. Complement Ther Med. 2020;54:102548.
[33] BIVER E, BERENBAUM F, VALDES AM, et al. Gut microbiota and osteoarthritis management: An expert consensus of the European society for clinical and economic aspects of osteoporosis, osteoarthritis and musculoskeletal diseases (ESCEO). Ageing Res Rev. 2019;55:100946.
[34] BONANZINGA T, CONTE P, ANZILLOTTI G, et al. Native intra-articular knee microbiome is a matter of facts: a systematic review of clinical evidence. EFORT Open Rev. 2024;9(10):969-979.
[35] 叶敏兰,唐晓颇,高阳鹭,等.基于16S rDNA测序技术的膝骨关节炎湿热痹阻证、寒湿痹阻证患者肠道菌群差异性研究[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2024,31(1):152-158.
[36] 吴霜,袁立霞,廖晴,等.基于16S rDNA测序研究当归拈痛汤对膝骨关节炎小鼠肠道菌群的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2024,30(11):9-17.
[37] HUANG Z, CHEN J, LI B, et al. Faecal microbiota transplantation from metabolically compromised human donors accelerates osteoarthritis in mice. ARD. 2020;79(5):646-656.
[38] YUAN X, CHEN R, ZHANG Y, et al. Gut microbiota: effect of pubertal status. BMC Microbiol. 2020; 20(1):334.
[39] FAVAZZO LJ, HENDESI H, VILLANI DA, et al. The gut microbiome-joint connection: implications in osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2020; 32(1):92-101.
[40] LI J, LIANG J, LIU Y, et al. Corrigendum: Basal metabolic rate mediates the causal relationship between gut microbiota and osteoarthritis: a two-step bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Front Microbiol. 2024;15:1510272.
[41] ZHU D, WANG X, XI Z, et al. Diet influences knee osteoarthritis osteophyte formation via gut microbiota and serum metabolites. iScience. 2024;27(6):110111.
[42] WANG J, WANG Y, CHEN Z, et al. Study on the mechanism of Shugan Lidan Xiaoshi granule in preventing acute pancreatitis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. Heliyon. 2024;10(5):e27365.
[43] ZHANG X, KHAKISAHNEH S, HAN S, et al. Ginseng extracts improve circadian clock gene expression and reduce inflammation directly and indirectly through gut microbiota and PI3K signaling pathway. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2024;10(1):24.
[44] ZHOU X, LI W, ZHUANG C, et al. Lei’s formula attenuates osteoarthritis mediated by suppression of chondrocyte senescence via the mTOR axis: in vitro and in vivo experiments. Aging. 2024;16(5):4250.
[45] FAN Y, BIAN X, MENG X, et al. Unveiling inflammatory and prehypertrophic cell populations as key contributors to knee cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis using multi-omics data integration. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024;83(7):926-944.
[46] 陈景涛,陈有,李玉静,等.黄芪多糖抑制Toll样受体4/核因子κB p65通路治疗大鼠膝骨关节炎[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(31):5002-5008.
[47] 韩铁玲.益生菌辅助治疗膝关节骨关节炎的临床研究[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古医科大学,2023.
[48] LEE YC, CHANG YT, CHENGY H, et al. Pterostilbene protects against osteoarthritis through NLRP3 inflammasome inactivation and improves gut microbiota as evidenced by in vivo and in vitro studies. J Agric Food Chem. 2024;72(16):9150-9163.
[49] ZHENG YZ, CHEN QR, YANG HM, et al. Modulation of gut microbiota by crude mulberry polysaccharide attenuates knee osteoarthritis progression in rats. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024; 262(Pt 2):129936.
[50] LIU M, MATUSZEK G, AZCARATE-PERIL MA, et al.
An exploratory case-control study on the associations of bacterially-derived vitamin K forms with the intestinal microbiome and obesity-related osteoarthritis. Curr Dev Nutr. 2023;7(3):100049.
[51] SONG X, LIU Y, CHEN S, et al. Knee osteoarthritis: a review of animal models and intervention of traditional Chinese medicine. Amem. 2024;7(2):114-126.
[52] Delfino DV, Hu W, Hung Y, et al. Editorial: herbal medicines in pain management, volume II. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15:1364073.
[53] BOER CG, RADJABZADEH D, MEDINA-GOMEZ C, et al. Intestinal microbiome composition and its relation to joint pain and inflammation. Nat Common. 2019;10(1):4881.
[54] OLIPHANT K, ALLEN-VERCOE E. Macronutrient metabolism by the human gut microbiome: major fermentation by-products and their impact on host health. Microbiome. 2019;7(1):91.
[55] LIU Y, DING W, WANG HL, et al. Gut microbiota and obesity-associated osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(9):1257-1265.
[56] WU X, WANG Y, XIAO Y, et al. Extracellular vesicles: potential role in osteoarthritis regenerative medicine. J Orthop Translat. 2020;21:73-80.
[57] ASGHAR S, LITHERLAND GJ, LOCKHART JC, et al. Exosomes in intercellular communication and implications for osteoarthritis. Rheumatology. 2020;59(1):57-68.
[58] DENG Z, YANG C, XIANG T, et al. Gold nanoparticles exhibit anti-osteoarthritic effects via modulating interaction of the “microbiota-gut-joint” axis. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024;22(1):157.
[59] YANG F, XIONG W, LI C, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells mediate extracellular matrix remodeling in osteoarthritis through the transport of microRNA-29a. World J Stem Cells. 2024;16(2):191-206.
[60] HRIDAYANKA K, DUTTAROY AK, BASAK S. Bioactive compounds and their chondroprotective effects for osteoarthritis amelioration: a focus on nanotherapeutic strategies, epigenetic modifications, and gut microbiota. Nutrients. 2024;16(21):3587.
[61] MA K, PHAM T, WANG J, et al. Nanoparticle-based inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors alleviates osteoarthritis pain and cartilage damage. Sci Adv. 2024;10(7):i5501.
[62] ABUGHAZALEH N, SMITH H, SEERATTAN RA, et al. Development of shoulder osteoarthritis and bone lesions in female and male rats subjected to a high fat/sucrose diet. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):25871. |