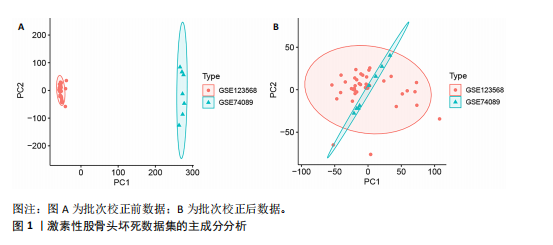
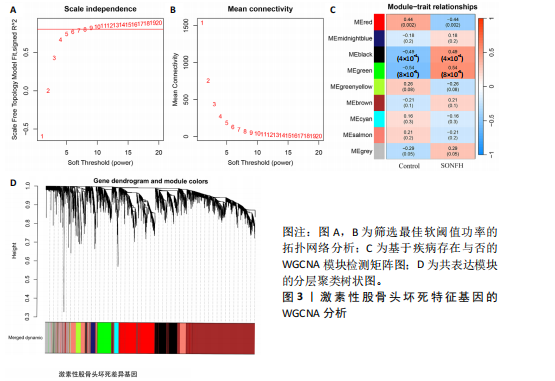
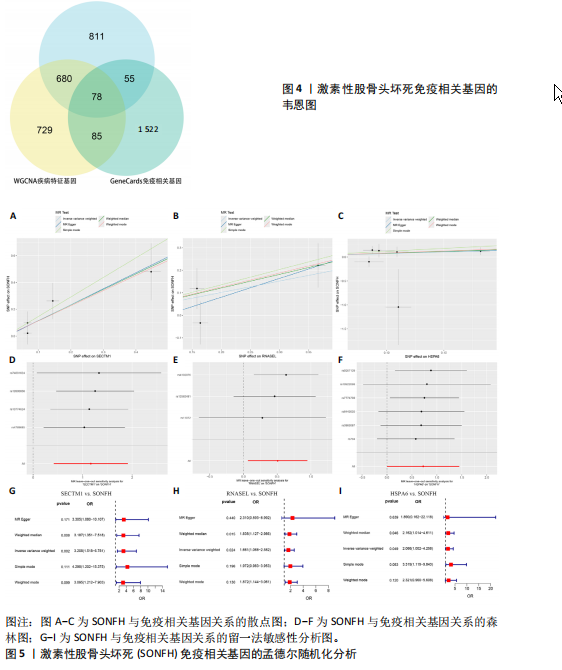
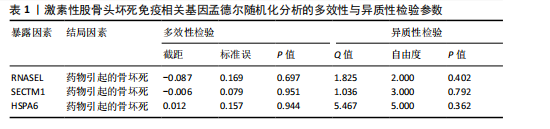
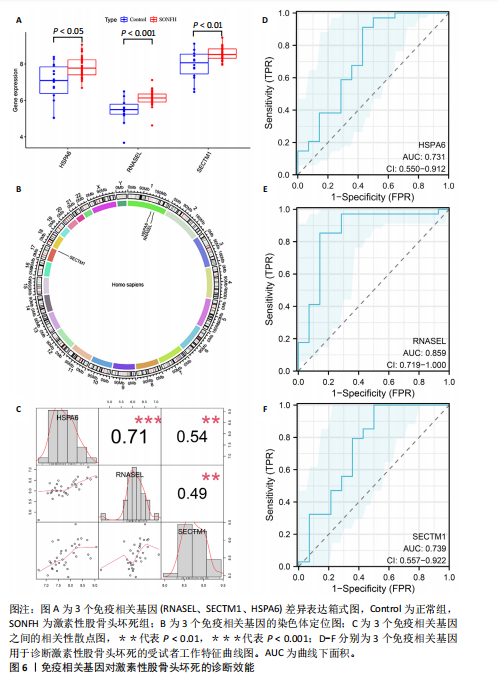
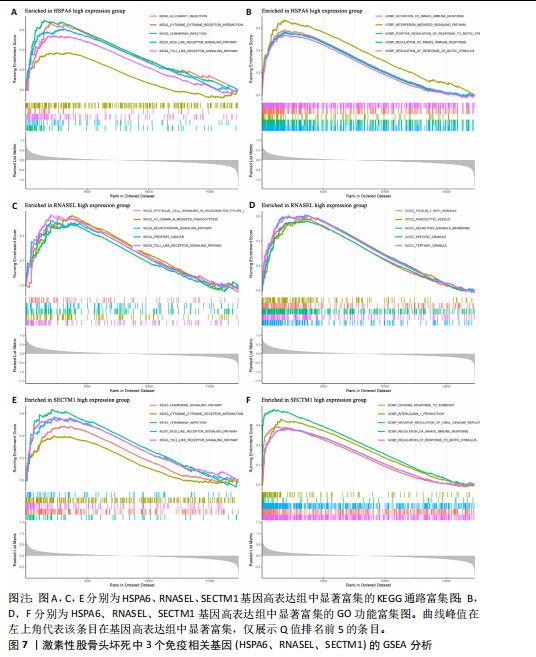
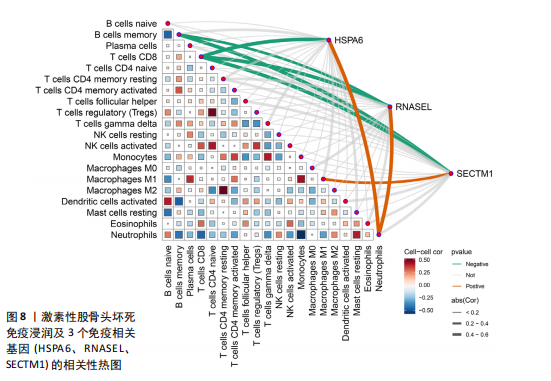
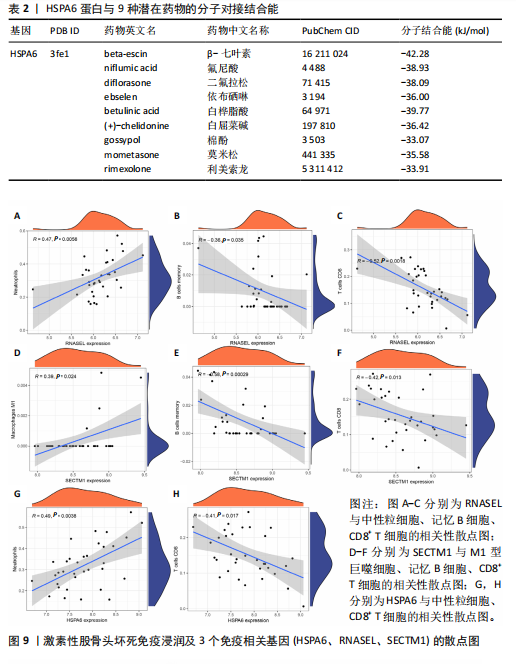
[1] ZHAO DW, YU M, HU K, et al. Prevalence of Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head and its Associated Risk Factors in the Chinese Population: Results from a Nationally Representative Survey. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015;128(21):2843-2850.
[2] 孙伟,高福强,李子荣.股骨头坏死临床诊疗技术专家共识(2022年)[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2022,36(11):1319-1326.
[3] ZHAO D, ZHANG F, WANG B, et al. Guidelines for clinical diagnosis and treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in adults (2019 version). J Orthop Translat. 2020; 21:100-110.
[4] MUSTAFA SS. Steroid-induced secondary immune deficiency. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2023;130(6):713-717.
[5] POWELL C, CHANG C, GERSHWIN ME. Current concepts on the pathogenesis and natural history of steroid-induced osteonecrosis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011;41(1):102-113.
[6] KWON H M, HAN M, LEE TS, et al. Effect of Corticosteroid Use on the Occurrence and Progression of Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: A Nationwide Nested Case-Control Study. J Arthroplasty. 2024;39(10):2496-2505.
[7] WU T, SHI W, ZHOU Y, et al. Identification and validation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-related genes in patients with steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):21634.
[8] YANG S, ZHAO Y, TAN Y, et al. Identification of microtubule-associated biomarker using machine learning methods in osteonecrosis of the femoral head and osteosarcoma. Heliyon. 2024;10(11):e31853.
[9] ZHU Y, WANG X, LIU R. Bioinformatics proved the existence of potential hub genes activating autophagy to participate in cartilage degeneration in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Mol Histol. 2024; 55(4):539-554.
[10] AN W, YANG Y, HE W, et al. Three-dimensional mapping of necrotic lesions for early-stage osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024;19(1):577.
[11] 李岩,王兴河.基于生物信息学分析三阴性乳腺癌的差异表达基因和药物靶点挖掘[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2024,40(2): 269-272.
[12] SEKULA P, DEL GMF, PATTARO C, et al. Mendelian Randomization as an Approach to Assess Causality Using Observational Data. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;27(11):3253-3265.
[13] 林苗远,杨继滨,闫文强,等.组织工程技术促进股骨头坏死骨组织再血管化的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2021,35(11):1479-1485.
[14] JIA Y, ZHANG Y, LI S, et al. Identification and assessment of novel dynamic biomarkers for monitoring non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head staging. Clin Transl Med. 2023;13(6): 1295.
[15] LU X, WANG X, WANG P, et al. Identification of candidate genes and chemicals associated with osteonecrosis of femoral head by multiomics studies and chemical-gene interaction analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024;15:1419742.
[16] GONG N, TUO Y, LIU P. Identification and Mendelian randomization validation of pathogenic gene biomarkers in obstructive sleep apnea. Front Neurol. 2024;15:1442835.
[17] GHARIB SA, HURLEY AL, ROSEN MJ, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea and CPAP therapy alter distinct transcriptional programs in subcutaneous fat tissue. Sleep. 2020;43(6): zsz314.
[18] LANGFELDER P, HORVATH S. WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008;9:559.
[19] WANG Q, SU Z, ZHANG J, et al. Unraveling the copper-death connection: Decoding COVID-19’s immune landscape through advanced bioinformatics and machine learning approaches. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024;20(1):2310359.
[20] JI L, WANG Y, LU T, et al. Assessing the causal relationship between blood metabolites and low back pain: a Mendelian randomization study. Am J Transl Res. 2024;16(4):1366-1374.
[21] KURKI MI, KARJALAINEN J, PALTA P, et al. FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population. Nature. 2023;613(7944):508-518.
[22] BURGESS S, DUDBRIDGE F, THOMPSON SG. Combining information on multiple instrumental variables in Mendelian randomization: comparison of allele score and summarized data methods. Stat Med. 2016;35(11):1880-1906.
[23] HEMANI G, BOWDEN J, DAVEY SG. Evaluating the potential role of pleiotropy in Mendelian randomization studies. Hum Mol Genet. 2018;27(R2):R195-R208.
[24] SUN Q, BAI L, ZHU S, et al. Analysis of Lymphoma-Related Genes with Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes Enrichment. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022:8503511.
[25] LV Y, JI L, DAI H, et al. Identification of key regulatory genes involved in myelination after spinal cord injury by GSEA analysis. Exp Neurol. 2024;382:114966.
[26] GENTLES AJ, NEWMAN AM, LIU CL, et al. The prognostic landscape of genes and infiltrating immune cells across human cancers. Nat Med. 2015;21(8):938-945.
[27] WARDE-FARLEY D, DONALDSON SL, COMES O, et al. The GeneMANIA prediction server: biological network integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38(Web Server issue):W214-W220.
[28] YOO M, SHIN J, KIM J, et al. DSigDB: drug signatures database for gene set analysis. Bioinformatics. 2015;31(18):3069-3071.
[29] TROTT O, OLSON AJ. AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem. 2010;31(2):455-461.
[30] 李洵珣,金晨,陈康,等.基于网络药理学和分子对接分析丰城鸡血藤治疗乳腺癌的分子靶点和机制[J]. 中国药理学通报,2022,38(5):767-775.
[31] LI XH, PANG WW, ZHANG Y, et al. A Mendelian randomization study for drug repurposing reveals bezafibrate and fenofibric acid as potential osteoporosis treatments. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14: 1211302.
[32] HUANG X, ZHANG T, GUO P, et al. Association of antihypertensive drugs with fracture and bone mineral density: A comprehensive drug-target Mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1164387.
[33] GU Y, JIN Q, HU J, et al. Causality of genetically determined metabolites and metabolic pathways on osteoarthritis: a two-sample mendelian randomization study. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1): 357.
[34] BORGELT L, HAACKE N, LAMPE P, et al. Small-molecule screening of ribonuclease L binders for RNA degradation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;154:113589.
[35] FERRANDI C, RICHARD F, TAVANO P, et al. Characterization of immune cell subsets during the active phase of multiple sclerosis reveals disease and c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway biomarkers. Mult Scler. 2011;17(1):43-56.
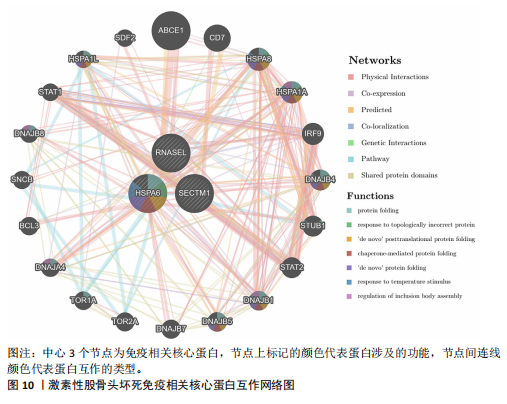
[36] WANG T, HUANG C, LOPEZ-CORAL A, et al. K12/SECTM1, an interferon-γ regulated molecule, synergizes with CD28 to costimulate human T cell proliferation. J Leukoc Biol. 2012;91(3):449-459.
[37] WANG T, GE Y, XIAO M, et al. SECTM1 produced by tumor cells attracts human monocytes via CD7-mediated activation of the PI3K pathway. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134(4):1108-1118.
[38] SONG B, SHEN S, FU S, et al. HSPA6 and its role in cancers and other diseases. Mol Biol Rep. 2022;49(11):10565-10577.
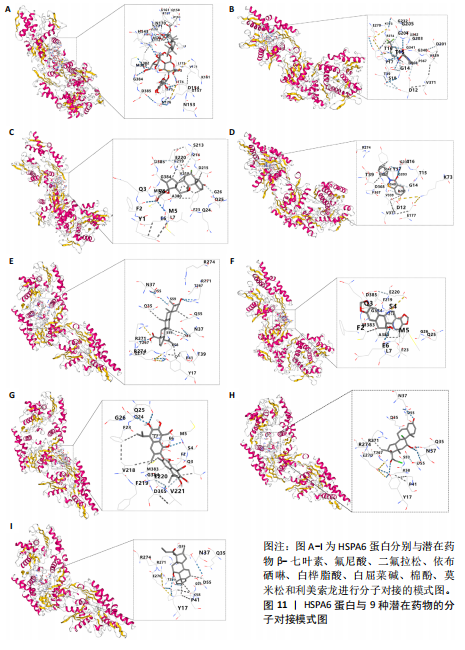
[39] JIANG J, LIU X, LAI B, et al. Correlational analysis between neutrophil granulocyte levels and osteonecrosis of the femoral head. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):393.
[40] NONOKAWA M, SHIMIZU T, YOSHINARI M, et al. Association of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps with the Development of Idiopathic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Am J Pathol. 2020;190(11):2282-2289.
[41] LUO D, GAO X, ZHU X, et al. Identification of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head biomarkers based on immunization and animal experiments. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024;25(1):596.
[42] CHEN B, LIU Y, CHENG L. IL-21 Enhances the Degradation of Cartilage Through the JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway During Osteonecrosis of Femoral Head Cartilage. Inflammation. 2018;41(2):595-605.
[43] GENG W, ZHANG W, MA J. IL-9 exhibits elevated expression in osteonecrosis of femoral head patients and promotes cartilage degradation through activation of JAK-STAT signaling in vitro. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;60:228-234.
[44] KOSUKEGAWA I, OKAZAKI S, YAMAMOTO M, et al. The proton pump inhibitor, lansoprazole, prevents the development of non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head: an experimental and prospective clinical trial. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2020;30(4):713-721.
[45] ADAPALA NS, YAMAGUCHI R, PHIPPS M, et al. Necrotic Bone Stimulates Proinflammatory Responses in Macrophages through the Activation of Toll-Like Receptor 4. Am J Pathol. 2016;186(11): 2987-2999.
[46] YU R, MA C, LI G, et al. Inhibition of Toll-Like Receptor 4 Signaling Pathway Accelerates the Repair of Avascular Necrosis of Femoral Epiphysis through Regulating Macrophage Polarization in Perthes Disease. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023;20(3):489-501.
[47] HE Z, HU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Asiaticoside exerts neuroprotection through targeting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Phytomedicine. 2024;127:155494.
[48] BARROW F, KHAN S, FREDRICKSON G, et al. Microbiota-Driven Activation of Intrahepatic B Cells Aggravates NASH Through Innate and Adaptive Signaling. Hepatology. 2021; 74(2):704-722.
[49] CEGIEŁA U, PYTLIK M, JANIEC W, et al. Effects of alpha-Escin on mechanical features of the femoral bone in rats with experimental post-steroid osteopenia. Acta Pol Pharm. 2000;57(4):317-320. |