中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (35): 7601-7610.doi: 10.12307/2025.988
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
牙周炎的病理过程、炎症反应及相关生物标志物:多组学分析
张艺璇,李东娜,刘春艳
- 河北医科大学口腔医(学)院正畸科;河北省口腔医学重点实验室;河北省口腔健康技术创新中心,河北省石家庄市 050017
-
收稿日期:2024-11-11接受日期:2024-12-31出版日期:2025-12-18发布日期:2025-05-07 -
通讯作者:刘春艳,博士,主任医师,教授,河北医科大学口腔医(学)院正畸科,河北省口腔医学重点实验室,河北省口腔健康技术创新中心,河北省石家庄市 050017 -
作者简介:张艺璇,女,2000年生,福建省宁化县人,汉族,河北医科大学在读硕士,主要从事牙周组织再生方面的研究。 -
基金资助:2023年中央引导地方科技发展资金项目(236Z7740G),项目负责人:刘春艳
Pathological processes, inflammatory responses, and related biomarkers of periodontitis: a multi-omics analysis
Zhang Yixuan, Li Dongna, Liu Chunyan
- Department of Orthodontics, School and Hospital of Stomatology, Hebei Medical University; Hebei Key Laboratory of Stomatology; Hebei Oral Health Technology Innovation Center, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2024-11-11Accepted:2024-12-31Online:2025-12-18Published:2025-05-07 -
Contact:Liu Chunyan, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Orthodontics, School and Hospital of Stomatology, Hebei Medical University; Hebei Key Laboratory of Stomatology; Hebei Oral Health Technology Innovation Center, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Zhang Yixuan, Master candidate, Department of Orthodontics, School and Hospital of Stomatology, Hebei Medical University; Hebei Key Laboratory of Stomatology; Hebei Oral Health Technology Innovation Center, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:2023 Centralized Guided Local Science and Technology Development Funding Project, No. 236Z7740G (to LCY)
摘要:
文题释义:
组学分析:是一种综合性的生物学研究方法,通过对生物体内不同层次的生物分子进行系统性分析,以揭示生物系统的复杂性和动态变化。组学技术涵盖多个领域,主要包括基因组学、转录组学、蛋白质组学、代谢组学等,通过结合上述各类组学数据,能够提供对生物体在健康和疾病状态下的全面理解。
牙周炎:是一种常见的慢性炎症性疾病,主要影响牙齿周围的支持组织,包括牙龈、牙槽骨和牙周韧带,牙周炎发病通常与牙菌斑的积累密切相关。牙周炎不仅会影响口腔健康,还与全身多种疾病存在相关性,如心血管疾病、糖尿病等。因此,早期诊断和有效治疗对于预防牙周炎的进展和相关并发症至关重要。
背景:近年来,随着组学技术的迅猛发展,口腔医学研究迈入了一个崭新的阶段。组学技术的广泛应用不仅能系统地揭示生物体内的复杂性和动态变化,还为包括牙周炎在内的多种疾病的研究提供了更全面的视角。
目的:综述组学技术在牙周炎研究中的应用进展,并探讨了当前存在的问题,旨在为牙周炎预防和治疗及在临床其他领域的应用拓展思路。
方法:检索PubMed数据库、中国知网1993年6月至2024年8月收录的相关文献。英文检索词为“omics,periodontitis,transcriptomics and periodontitis,proteomics and periodontitis,genomics and periodontitis,metabolomics and periodontitis,multi-omics and periodontitis”,中文检索词为“组学,牙周炎,转录组学和牙周炎,蛋白质组学和牙周炎,基因组学和牙周炎,代谢组学和牙周炎,多组学联合分析和牙周炎”,最终纳入72篇文献进行归纳总结。
结果与结论:①通过基因组学、转录组学、蛋白质组学和代谢组学等技术,研究人员能够从多维度深入分析牙周炎的病理过程、炎症反应及相关生物标志物;②近年来的研究表明,组学技术可以识别与牙周炎相关的关键基因和代谢物等,促进对疾病的精准理解与干预。随着技术的不断进步,组学分析在牙周炎的研究中将更加广泛应用,推动更有效的预防和治疗策略的发展,从而提高患者的生活质量。
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-8696-7170(张艺璇)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
张艺璇, 李东娜, 刘春艳. 牙周炎的病理过程、炎症反应及相关生物标志物:多组学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(35): 7601-7610.
Zhang Yixuan, Li Dongna, Liu Chunyan. Pathological processes, inflammatory responses, and related biomarkers of periodontitis: a multi-omics analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7601-7610.
2.1 转录组学在牙周炎研究中的应用 转录组学(transcriptomics)作为一门专注于探索转录组复杂性的学科,其核心任务在于精准测定某一特定时期内,生物体在给定环境或生理条件下的基因表达谱,这一过程涉及对细胞内RNA分子的深入鉴定与定量分析。转录组所展现的基因表达谱可直接反映细胞功能活动情况,深刻映射了生物体当前的生理状态及对外界刺激的响应机制。牙周炎作为一种慢性破坏性炎症性疾病,转录组学也在牙周炎发病机制的研究中广泛应用。
2.1.1 转录组学分析技术在牙周炎诊断中的应用 转录组学分析技术通过对细胞和组织中所有转录本的全面测定,能够揭示基因表达谱在牙周炎不同阶段的变化。在牙周炎的早期诊断中,转录组学分析技术不仅提供了精准的诊断标志物,见表1,还有助于深入理解牙周组织的病理生理机制,推动个性化治疗的实现。
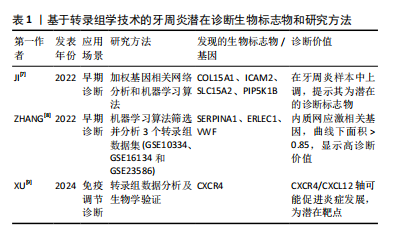
有研究指出,基于加权基因相关网络分析和机器算法分析牙周炎和正常样本的转录组数据和样本信息,发现COL15A1、ICAM2、SLC15A2和 PIP5K1B 在牙周炎样本中均上调,提示为牙周炎的潜在诊断生物标志物[7]。也有学者通过两种机器学习算法在3个牙周炎转录组学数据集(GSE10334、GES16134和GES23586)中筛选并分析牙周炎和健康牙周组织之间的内质网应激相关差异表达基因的基因本体(gene ontology,GO)、京都基因与基因组百科全书(Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes,KEGG)和疾病本体(disease ontology,DO)富集,该研究筛选出了 11个关键差异表达基因,并发现SERPINA1、ERLEC1和VWF 3个内质网应激相关基因显示出较高的诊断价值(曲线下面积> 0.85)和牙周炎生物标志物潜力,为未来牙周炎早期诊断和治疗研究提供了靶点基础[8]。尤其值得关注的是,XU等[9]通过转录组数据分析证明牙周炎与免疫调节密切相关,炎症进展与CXCR4表达呈正相关。除了生物信息学验证外,这项研究还收集了临床和细胞样本,并构建了小鼠牙周炎模型,通过实验证实了CXCR4在牙周炎中的重要作用,该研究发现CXCR4/CXCL12轴向信号可能通过介导中性粒细胞动力学促进牙周炎的发展,表明CXCR4可能是一个潜在的靶点,有助于促进牙周炎临床诊断新策略的开发。这些研究表明,转录组学分析技术在牙周炎的诊断中展现出巨大的应用潜力,为探索疾病的分子机制及开发创新诊断方法提供了重要的理论依据。
2.1.2 转录组学分析技术在牙周炎发病机制中的应用 在牙周炎的发病机制和易感基因方面,Caetano等[10]全面评估了全基因组关联研究(genome-wide association studies,GWAS)鉴定的26个牙周炎易感基因在牙龈黏膜内的表达,发现巨噬细胞表达最多的分析基因,表明巨噬细胞可能在牙周炎的发病机制和遗传性中发挥重要作用。值得注意的是,AGRAFIOTI等[11]同样通过单细胞RNA测序(single-cell RNA sequencing,scRNA-seq)来分析健康与牙周炎牙龈组织中驻留巨噬细胞的异质性,发现巨噬细胞的异质性和过度炎症激活可能与牙周炎的发病机制和结果有关,并且在2型糖尿病患者中可能会进一步增强。有研究报道,应用空间增强分辨率组学测序(SpaTial Enhanced REsolution Omics-sequencing,Stereo-seq)技术来获得健康个体和牙周炎患者牙龈的空间转录组图谱,观察到与健康个体相比,牙周炎患者牙龈内皮细胞中炎症相关信号通路如JAK-STAT和NF-κB信号通路显著上调。此外,该研究还表征了牙龈中牙周炎风险基因的空间分布,发现IFI16 在炎性牙龈内皮细胞中的表达显著增加[12]。另有研究利用牙龈卟啉单胞菌Δpg1007∷ ermF 突变体进行RNA测序,发现突变体中59个基因的表达水平显著改变,其中AOP、ABC转运蛋白和一些膜蛋白的基因表达上调,表明牙龈卟啉单胞菌pg1007是一种调节多种ABC转运蛋白表达的GntR家族转录因子,并证明了牙龈卟啉单胞菌参与成人慢性牙周炎病因的重要毒力特征,深化了对牙龈卟啉单胞菌生长和蛋白酶活性调控的理解[13]。除此之外,牙周袋及龈下菌斑中一些其他的致病微生物也引起了众多研究者的广泛注意。已有研究通过元转录组学分析健康、牙龈炎和牙周炎状态的细菌特征,发现健康部位和牙周炎部位之间的细菌组成和功能特征存在明显差异,表明健康向牙周炎微生物组的转变伴随着细菌网络结构和复杂性的改变[14]。
2.1.3 转录组学分析技术在牙周炎治疗中的应用 菌斑是牙周炎发生的始动因子,许多研究证实,在牙周袋及龈下菌斑这一特定的微生态环境中,存在着一类被统称为“红色复合体”的微生物群落,该复合体主要由牙龈卟啉单胞菌、福赛坦氏菌以及齿垢密螺旋体等病原菌构成,这些微生物在牙周袋内的相对丰度变化,被广泛认为与牙周炎的发病进程及疾病严重程度之间存在着密切的关联性。已有研究报道,用RNA-seq测定暴露于无细胞齿垢密螺旋体条件培养基的牙龈卟啉单胞菌转录组,发现牙龈卟啉单胞菌和齿垢密螺旋体之间存在代谢协同性[15],二者共同感染可使细菌毒力增强[16]。应当指出的是,阻止“红色复合体”对牙槽骨丢失的影响是防治牙周炎的重要方法之一,在这其中也不乏转录组学的参与。ZHANG等[17]借助16S核糖体RNA测序发现白细胞介素17-TRAF3IP2-中性粒细胞轴在保护牙龈免疫屏障免受牙龈卟啉单胞菌侵袭方面具有重要作用,这提示靶向调节免疫反应可能是干预牙周炎进程的有效策略。同时,通过对菌群与宿主细胞的相互作用进行转录组学测序分析,揭示了细菌毒力因子对宿主炎症信号通路的调控机制。已有研究报道,用具核梭杆菌和嗜黏蛋白阿克曼菌处理牙龈上皮细胞后,对培养基上清液进行转录组测序和ELISA检测,嗜黏蛋白阿克曼菌通过抑制TLR/MyD88/NF-κB通路和炎症因子的分泌来抑制具核梭杆菌对牙龈上皮细胞的炎症作用,动物实验表明,嗜黏蛋白阿克曼菌可以抑制具核梭杆菌诱导的BALB/c小鼠牙周炎[18],这不仅加深了对炎症调控机制的理解,也为开发以抑制关键信号通路为核心的靶向治疗方案提供了理论支持。
2.1.4 转录组学视角下牙周炎与全身疾病的关联研究 牙周炎转录组学的另一个研究热点在于牙周炎和其他疾病之间的串扰基因和免疫关系。研究表明,牙周炎和许多疾病都有着潜在的关联[19–21]。有研究报道,使用单样本基因集富集分析(single-sample gene set enrichment Analysis,ssGSEA)、加权基因共表达网络分析(weighted gene co-expression network analysis,WGCNA)、GO富集分析、最小绝对收缩与选择算子(least absolute shrinkage and selection operator,LASSO)分析等多种转录组学分析方法发现牙周炎与多发性硬化症之间的相关性,FAM46C、SLC7A7、LY96等多个基因是牙周炎和多发性硬化症之间最重要的串扰基因;进一步研究发现,CFI、DDIT4L和FAM46C是牙周炎和多发性硬化症的潜在生物标志物[22]。
也有研究者从基因表达综合数据库(gene expression omnibus,GEO)下载了牙周炎和IgA肾病(IgAN)数据进行转录组学分析,发现SPAG4、CCDC69、KRT10、CXCL12、HPGD、CLDN20 和 CCL187 基因是牙周炎与IgA肾病之间最重要的串扰基因;T细胞和B细胞驱动的免疫反应可能在牙周炎和IgA肾病之间的关联中发挥重要作用[23]。此外,XIONG等[24]也使用了来自GEO的数据研究炎症性肠病和牙周炎之间的潜在关联,通过转录组学分析结合体内和体外实验将IGKC和COL4A1基因确定为这两种疾病的特征基因和新的干预靶点,并发现英夫利昔单抗可用于治疗或预防炎症性肠病和牙周炎。由此可见,转录组学在牙周炎与多种全身性疾病的关联研究中也起到重要作用。
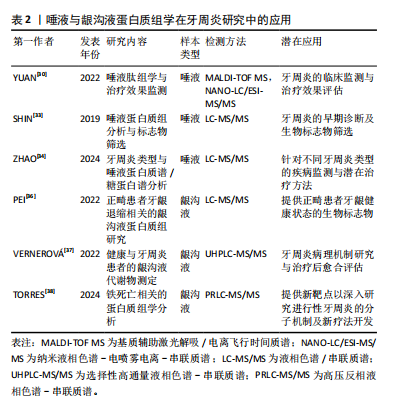
2.2 蛋白质组学在牙周炎研究中的应用 蛋白质组学(Proteomics)是一门将探索的焦点汇聚于蛋白质组,致力于解析细胞、组织乃至整个生物体内部蛋白质组成及变化规律的科学[25]。这一领域始于WILKINS等[26]于1996年创造性地将“蛋白质”与“基因组”这两个词汇熔铸成“蛋白质组”(Proteome)这一概念,揭示了基因组全面编码并表达出的全套蛋白质的研究范畴。蛋白质组学通过从宏观尺度上剖析蛋白质的特征,包括表达丰度变化、翻译后修饰以及相互作用等,由此得以在蛋白质层面上构建出关于疾病发病机制、细胞代谢等生命活动深层次规律的全面且连贯的认知蓝图。近年来,唾液和龈沟液以便于收集且可以提供口腔重要信息的优点在蛋白质组学中的研究受到越来越多学者的关注,在临床应用方面有重要的诊断价值[27]。在牙周炎领域,蛋白质组学被广泛应用于生物标记物的研究中[28-29],通过比较牙周炎患者与健康人唾液、龈沟液中的蛋白质表达谱,能够发现与牙周炎相关的特异性蛋白质标志物。
2.2.1 唾液蛋白质组学与牙周炎 有研究报道,在基线(T0)、超声龈上刮治后1周(T1)和龈下刮治和根面平整后8周(T2)收集17 例患者的唾液样本进行基质辅助激光解吸/电离飞行时间质谱(matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry,MALDI-TOF MS)检测肽组学谱的变化,同时进行纳米液相色谱-电喷雾电离-串联质谱(nano liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry,NANO-LC/ESI-MS/MS)鉴定潜在的肽生物标志物,发现从治疗前的时间点到治疗后的时间点,患者唾液中的大多数肽呈下降趋势,揭示了唾液肽组反映Ⅰ/Ⅱ期全身性牙周炎的能力,证明了唾液在临床和社区牙周病监测中的应用前景[30]。为了对唾液进行全面的蛋白质组学表征,许多实验研究试图利用多种蛋白质/肽分离技术结合大规模液相色谱串联质谱法(liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry,LC-MS/MS),最大限度地提高蛋白质组覆盖率和唾液蛋白[31-32]。例如SHIN等[33]使用了基于二维液相色谱-串联质谱技术的鸟枪法蛋白质组学策略对207名受试者的唾液样本进行分析,发现牙周炎患者唾液S100A8和S100A9水平高于无牙周炎者,表明唾液S100A8和S100A9是牙周炎的候选生物标志物。另外,ZHAO等[34]学者分析了轻度-中度、重度、侵袭性牙周炎和牙周炎伴2型糖尿病者以及接受抗糖尿病药物治疗者的唾液蛋白质组和完整N-糖肽,揭示了唾液蛋白和糖蛋白在不同类型牙周炎中的特异性变化,发现N-糖基化模式的变化与疾病的严重程度密切相关,尤其是富含岩藻糖和唾液酸的N-糖肽的表达在所有牙周炎组中都有增加,并且在2型糖尿病相关牙周炎中,抗糖尿病药物治疗逆转了在唾液蛋白质组和完整N-糖肽中观察到的许多变化。这些发现为牙周炎的发病机制提供了新的见解,并强调了唾液生物标志物在诊断、预后以及监测疾病进展和治疗反应方面的潜力。
2.2.2 龈沟液蛋白质组学与牙周炎 龈沟液作为来源于龈沟或牙周袋并富含蛋白质的渗出液,其含量与成分的动态变化与牙周组织的健康状态紧密相关。在牙周病发作期间,龈沟液中显著富集了炎症因子及各类特异性生物标志物,在牙周病的诊断乃至治疗过程中发挥着不可替代的关键作用[35]。一项研究报道,通过基于数据独立获取的液相色谱串联质谱法,比较未接受正畸治疗的健康牙龈、接受正畸治疗的健康牙龈和接受正畸治疗的退缩牙龈的龈沟液的蛋白质组,能够确定正畸患者牙龈退缩诊断相关的生物标志物[36]。此外,选择性高通量液相色谱-串联质谱(ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry,UHPLC-MS/MS)和荧光检测(fluorescence detector,FLD)方法也被用于测定健康人和牙周炎患者龈沟液中的新蝶呤、肌酐、犬尿氨酸和色氨酸水平,在探讨牙周发病机制和评估治疗愈后结果方面具有良好的潜力[37]。值得关注的是,TORRES等[38]收集了16例牙周炎患者的龈沟液,结合临床指标、蛋白质组学数据、计算机模拟方法和生物信息学工具进行分析,使用高压反相液相色谱-串联质谱联用(pressure reversed-phase liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry,PRLC-MS/MS)分析以确定与牙周炎进展相关的蛋白质谱,并探索它们与铁死亡的潜在联系。该研究发现一组枢纽蛋白,包括 SNCA、CA1、HBB、SLC4A1和ANK1与牙周炎的临床进展状态密切相关,并发现了与铁死亡相关的特定蛋白质驱动或抑制因子(SNCA、FTH1、HSPB1、CD44和GCLC),揭示了这种特定的调控性细胞死亡类型在牙周炎临床进展过程中的共同发生现象。TORRES等[38]首次揭示了牙周病患者与铁死亡相关的蛋白质和过程,这为进行性牙周病的分子机制研究提供了新的见解。
唾液与龈沟液样本的采集优势为研究者提供了一个实时洞察牙周组织动态变化的窗口,见表2,这一特性能够为牙周疾病的分期与分级诊断提供新颖且有价值的参考框架。同时,已有研究表明唾液与龈沟液样本与多种组学技术(如基因组学、蛋白质组学、代谢组学等)的交叉融合有助于深化对牙周病发生发展机制的理解并提高预防、诊断与治疗水平[39]。
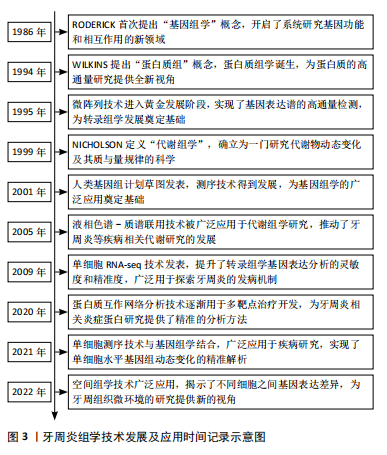
2.3 基因组学在牙周炎研究中的应用 基因组学(genomics)是研究生物体全部基因功能及相互作用的学科,1986年由美国遗传学家Roderick首次提出,旨在系统解析基因、调控序列、非编码RNA等元素及网络[40-41]。随着测序技术的不断进步,基因组学已经广泛应用于多个领域,并在牙周炎研究中发挥重要作用,帮助揭示疾病的发病机制和潜在的遗传因素,见图4。
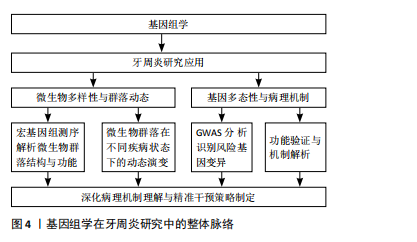
2.3.1 基因组学揭示牙周炎微生物多样性与群落动态 基因组学作为揭示微生物群落功能与多样性的重要工具,已在微生物生态学研究中占据关键地位。该方法通过对环境样本中微生物群体基因组的直接测序与分析,构建宏基因组文库,结合先进的基因组学策略,能够深入解析微生物的基因组成及其潜在的功能机制[42-43]。
近年来,随着测序技术的迅速发展,宏基因组鸟枪法测序逐渐成为研究复杂生物群落微生物的首选方法[42],尤其在包括牙周致病微生物在内的病原微生物群落的分类与功能研究中展现出强大的优势[44]。例如,FARINA等[45]通过全基因组鸟枪测序分析比较不同牙周状况下糖尿病患者和非糖尿病患者的龈下微生物群,发现糖尿病与牙周炎的共存通常会导致龈下微生物群的多样性和丰富度下降,并在患有牙周炎的糖尿病患者中发现了厌氧绳菌属的细菌显著增加。ZHANG等[46]则讨论了牙周炎的发病机制,强调了高通量测序技术在揭示牙周病相关细菌多样性和群落动态中的应用,提出牙周病是由菌群失调引起,而非某些特定病原体的直接作用。另有研究探讨了健康、牙龈炎和牙周炎3种状态下的微生物特征,通过16S核糖体基因组学分析发现,在健康状态下,常见的微生物是罗氏菌和链球菌,而牙龈炎和牙周炎则逐渐表现出以革兰阴性厌氧菌为主的病原菌群,揭示了炎症反应中核心菌种的存在及其相互作用是牙周病进展的重要因素[47]。
2.3.2 基因组学分析牙周炎相关基因多态性及病理机制 牙周炎是一种多基因作用的复杂性疾病,因此也不乏关于牙周炎相关基因多态性的研究[48]。有研究人员通过GWAS寻找与牙周炎相关的遗传变异,探讨了两种主要牙周炎表型——侵袭性牙周炎和慢性牙周炎的共同基因风险位点,识别出SIGLEC5和 DEFA1A3基因区域的核苷酸变异与牙周炎存在显著关联,并且在混合样本中与牙周炎全基因组显著性水平相关,提出了这两个基因位点是牙周炎的风险位点[49]。此外,作为白细胞介素6信号下调的替代指标,NOLDE等[50]选择了52个与GWAS中较低的循环C-反应蛋白水平相关的位于编码白细胞介素6受体基因附近的遗传变异,用逆方差加权孟德尔随机化测试了与牙周炎的相关性,发现通过基因表征的白细胞介素6信号下调与较低的牙周炎发生概率相关,且循环C-反应蛋白可能是白细胞介素6对牙周炎影响的因果靶点。不可忽视的是,还有学者使用了GWAS中的遗传代理,结合多种孟德尔随机化方法,探讨了免疫细胞与牙周炎的因果关系,转录组关联研究和共定位分析确定了与中性粒细胞介导的牙周炎相关的潜在基因S100A9和S100A12 [51]。通过识别与牙周炎症过程相关的关键基因,这些发现有助于开发更精确的生物标志物,用于预测和预防牙周炎的进展,为理解牙周炎的病理机制以及为患者制定定制化干预方案提供了有价值的科学依据。
2.4 代谢组学在牙周炎研究中的应用 代谢组学由英国伦敦帝国理工大学的Jeremy Nicholson教授创立并迅速发展,在1999年正式被定义为一门对体液和组织中的内源性代谢物质进行定量研究的学科,揭示生物体在内外因变化下所产生的代谢应答的动态变化及质与量规律的科学[52]。作为基因组学、转录组学和蛋白质组学的继承和发展,代谢组学被视为组学研究的“终点”。代谢组学作为组学研究中的重要组成部分,通过揭示代谢物与生理病理变化的直接关联,为医学研究,尤其是牙周炎的早期诊断、发病机制探讨以及治疗干预提供了全新的视角,对于牙周炎的代谢组学研究,常用的样本有唾液、龈沟液、血清等[53-55]。
2.4.1 代谢组学分析技术在牙周炎诊断中的应用 牙周炎的传统诊断方法主要依赖于临床和放射学检查[56-57],但在牙周炎的早期诊断和预测方面,这些技术存在一定局限性。因此,许多潜在的生物标志物作为牙周病诊断的候选指标,以期提高诊断准确性和早期检测能力,见表3。早在2011年,BARNES等[58]就通过非靶向代谢组学分析的方法,使用了针对碱性和酸性物质优化的UHPLC-MS/MS和气相色谱/质谱法(gas chromatography-mass spectrometry,GC-MS)比较了健康人与牙周病患者的唾液,发现牙周病患者唾液中多种代谢物显著变化,包括二肽、氨基酸、碳水化合物、脂质和核苷酸等。这些变化与牙周病患者中蛋白质、三酰基甘油、甘油磷脂、多糖和核苷酸等大分子降解的增加高度相关,证明了代谢组学技术在区分健康与牙周病状态中的诊断潜力。有研究报道,使用质子核磁共振波谱对92名健康对照和129名牙周炎患者的唾液样本进行代谢组学分析,发现并验证了乙醇、牛磺酸、异戊酸盐、丁酸盐和葡萄糖5种牙周炎的代谢物生物标志物[59]。ROMANO等[60]同样通过核磁共振(nuclear magnetic resonance,NMR)代谢组学谱分析发现,与健康者相比,慢性牙周炎和全身性侵袭性牙周炎患者的丙酮酸、 N-乙酰基和乳酸水平显著降低,脯氨酸、苯丙氨酸和酪氨酸水平较高。这些生物标志物能够有效地将牙周炎患者与健康者区分开。
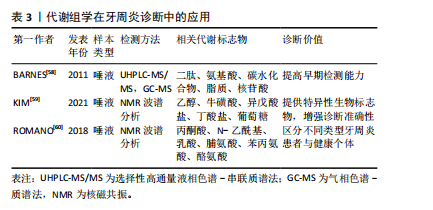
2.4.2 代谢组学分析技术在牙周炎发病机制中的应用 在牙周炎的发病机制研究方面,DONG等[61]研究了牙龈卟啉单胞菌诱导的代谢紊乱对血清代谢组的影响,通过非靶向代谢组学分析发现牙龈卟啉单胞菌处理小鼠体内的代谢物发生了显著变化,主要涉及色氨酸代谢和胆碱代谢等途径,这表明牙周炎期间牙周致病菌的定植会引发口腔内的代谢改变。另有研究通过气相色谱-质谱法进行代谢组学分析,发现全身性侵袭性牙周炎患者和健康对照患者的血清和龈沟液代谢组均存在显著差异,这些代谢谱在诊断全身性侵袭性牙周炎和帮助理解潜在机制具有重大意义[62]。此外,也有学者分析了牙龈炎患者、牙周炎患者和健康对照者唾液标本的代谢组学,探讨了代谢特征迁移与牙周病进展之间的相关性,发现牙龈炎和牙周炎患者的唾液代谢物谱与健康对照者显著不同,表明唾液代谢谱随牙周病的进展而变化,牙周组织和牙周病原微生物的异常代谢是牙周炎发病、发展和预后的机制之一[63]。值得注意的是,CHEN等[64]表征了高脂饮食诱导的患有/不患有牙周炎的肥胖小鼠的牙龈代谢组学特征,发现与瘦对照组相比,高脂饮食小鼠牙周炎的代谢组学影响通常更大;K-medoids 聚类分析显示,高脂饮食放大了牙周炎对牙龈代谢组强度和广泛性的影响,表明摄入过量高脂饮食的肥胖人群对牙周炎的代谢反应放大,表现出对牙周破坏加剧的代谢易感性。
2.4.3 代谢组学分析技术在牙周炎治疗中的应用 随着牙周炎研究的不断深入,代谢组学作为研究生物体代谢变化的技术,已在牙周炎治疗监测中展现出重要价值。通过对体液中代谢物的分析,研究者能够更加精准地评估疾病进展及治疗效果。例如,KUBONIWA等[65]探索了利用唾液代谢物反映牙周炎症严重程度的可能性,确定了包括准确性较高的尸胺、5-氧脯氨酸和组氨酸在内的8种代谢物作为潜在的牙周炎症指示物,这些标志物有望用于评估牙周炎症的严重程度,并为监测牙周炎患者的疾病活动提供依据。DEDE等[66]则评估了初始牙周治疗对慢性牙周炎患者龈沟液中8-羟基脱氧鸟苷水平的影响,发现与健康者相比,慢性牙周炎患者龈沟液中的8-羟基脱氧鸟苷水平升高并在初始牙周治疗后显著降低,表明8-羟基脱氧鸟苷可用于评估牙周病的严重程度和牙周治疗的效果。如降低8-羟基脱氧鸟苷的合成水平,有望缓解牙周炎症并减轻组织破坏。
以上研究显示,代谢组学技术在牙周炎研究领域展现了巨大的潜力。现阶段,关于牙周炎的病因、诊断和治疗的研究都已经从代谢组学中取得了一定进展。此外,代谢组学技术已用于监测治疗前后的代谢物水平变化,为评估治疗效果提供了新型生物标志物。通过揭示代谢物与生理病理变化的直接联系,代谢组学有望成为促进基础研究向临床应用转化的关键工具。未来,通过靶向代谢通路的药物研发,可望改善牙周炎的治疗效果。
2.5 多组学联合分析在牙周炎研究中的应用 随着组学技术的更新及相关研究的推进,多组学联合分析已成为组学研究中的前沿技术,通过综合基因组学、转录组学、蛋白质组学和代谢组学等多层次数据,提供了全面解析生物系统复杂性的新手段。该方法依托于高通量组学技术的快速发展以及先进生物信息学工具的支持,能够将不同层面的组学信息有机结合,揭示生物体内多维分子网络的全貌及动态变化[67]。近年来,多组学联合分析在牙周炎研究中也得到了广泛关注,通过整合不同组学数据的优势,为深入探索牙周炎的分子机制、诊断标志物及治疗靶点提供了全新的研究视角。
2.5.1 多组学联合分析阐释牙周炎微生物组与代谢特征 有学者运用16S核糖体RNA测序和高通量靶向代谢组学技术对中国人群中牙周炎患者和健康个体的唾液微生物组与代谢组进行了联合分析,揭示了牙周炎患者微生物组构成和代谢功能的显著变化。研究发现,牙周炎患者唾液中的93种微生物分类单元和103种代谢产物发生了显著变化,功能富集分析表明牙周炎患者的铁死亡、色氨酸代谢、谷胱甘肽代谢和碳代谢途径显著上调,这一多组学联合分析为牙周炎的诊断和发病机制研究提供了重要线索,并展现了唾液微生物与代谢物联合分析在疾病诊断和预后评估中的潜力[68]。另有研究结合了16S核糖体RNA测序、非靶向代谢组学和临床特征数据,分析了31例牙周炎患者和23例健康对照的龈下菌斑、唾液、血清及粪便样本,发现牙周炎显著影响肠道微生物组与代谢特征,还发现牙周炎可通过口腔-肠道轴影响妊娠早期的肠道微生物与代谢物变化,强调将牙周健康纳入产科管理的重要性,并为改善母体健康提供了潜在方向[69]。
2.5.2 基于多组学联合分析的牙周炎发病机制与炎症调控探索 已有研究结合了3 189名参与者的美国国家健康与营养检查调查数据库(National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey,NHANES)和GWAS的统计数据以及单细胞测序数据,通过基于横断面数据的多元回归分析、孟德尔随机化和多组学整合分析探讨了生物衰老与牙周炎风险之间的因果关联及潜在分子机制。研究发现较高的生物年龄与牙周炎风险增加之间存在关联,并有一些证据表明二者之间存在因果关系,表明生物衰老通过多种机制增加了牙周炎的风险,并强调了改善相关风险因素在衰老及牙周炎防治中的重要性,从因果关系、潜在机制和预防措施的角度为生物衰老和牙周炎的预防和治疗提供了新的见解[70]。
LAFLEUR等[71]则运用多组学联合分析研究了高糖环境对牙周炎患者和健康炎症反应及转录组的影响,该研究通过微阵列分析探讨了差异基因表达,同时结合16S核糖体RNA测序分析龈下微生物组,发现基因krt76、krt27、pnma5、mansc4、rab41、thoc6、tm6sf2和znf506以及促炎细胞因子白细胞介素1β、粒细胞巨噬细胞集落刺激因子、成纤维细胞生长因子2、白细胞介素10、基质金属蛋白酶3和基质金属蛋白酶8在高糖环境中与牙周炎相关炎症反应密切相关。此外,对应扩增子序列变体105(Amplicon Sequence Variant,ASV 105)、ASV 211、ASV 299序列的细菌以及普雷沃氏菌、弯曲杆菌和弗雷蒂氏菌的细菌属被鉴定为高糖环境中牙周炎症的关键微生物关联因素,该研究通过多组学整合分析揭示了高糖环境中牙周炎症调控的复杂互作网络,同时提出基于天然分子(如多酚、益生菌)的辅助治疗策略是潜在的牙周炎疗法研究方向,可减少细菌负荷并控制由口腔病原体诱导的炎症。
这些研究系统地揭示了牙周炎发病过程中多层次的分子机制,涵盖了关键基因、代谢物及微生物的复杂关联,同时展现了组学技术在疾病诊断标志物筛选、治疗策略优化及机制解析中的独特优势。这些发现不仅为牙周炎的深层次研究提供了重要依据,也为未来基于多组学整合的深入研究指明了方向。

| [1] DARVEAU RP, TANNER A, PAGE RC. The microbial challenge in periodontitis. Periodontol 2000. 1997;14:12-32. [2] KINANE DF. Causation and pathogenesis of periodontal disease. Periodontol 2000. 2001;25:8-20. [3] SCHWARTZ Z, GOULTSCHIN J, DEAN DD, et al. Mechanisms of alveolar bone destruction in periodontitis. Periodontol 2000. 1997;14:158-172. [4] NARAD P, KIRTHANASHRI SV. Introduction to Omics//ARIVARADARAJAN P, MISRA G. Omics Approaches, Technologies And Applications: Integrative Approaches For Understanding OMICS Data. Singapore: Springer, 2018: 1-10. [5] JUN L, YUANYUAN L, ZHIQIANG W, et al. Multi-omics study of key genes, metabolites, and pathways of periodontitis. Arch Oral Biol. 2023;153:105720. [6] CHAN HH, RAHIM ZHA, JESSIE K, et al. Salivary proteins associated with periodontitis in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(4):4642-4654. [7] JI J, LI X, ZHU Y, et al. Screening of periodontitis-related diagnostic biomarkers based on weighted gene correlation network analysis and machine algorithms. Technol Health Care. 2022;30(5):1209-1221. [8] ZHANG Q, JIAO Y, MA N, et al. Identification of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Related Biomarkers of Periodontitis Based on Machine Learning: A Bioinformatics Analysis. Dis Markers. 2022;2022:8611755. [9] XU X, LI T, TANG J, et al. CXCR4-mediated neutrophil dynamics in periodontitis. Cell Signal. 2024;120:111212. [10] CAETANO AJ, D’AGOSTINO EM, SHARPE P, et al. Expression of periodontitis susceptibility genes in human gingiva using single-cell RNA sequencing. J Periodontal Res. 2022;57(6):1210-1218. [11] AGRAFIOTI P, MORIN-BAXTER J, TANAGALA KKK, et al. Decoding the role of macrophages in periodontitis and type 2 diabetes using single-cell RNA-sequencing. FASEB J. 2022;36(2):e22136. [12] SHEN Z, ZHANG R, HUANG Y, et al. The spatial transcriptomic landscape of human gingiva in health and periodontitis. Sci China Life Sci. 2024; 67(4):720-732. [13] QIU Y, TAN X, LEI Z, et al. A GntR family transcription factor in Porphyromonas gingivalis regulates bacterial growth, acylpeptidyl oligopeptidase, and gingipains activity. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2023; 38(1):48-57. [14] NEMOTO T, SHIBA T, KOMATSU K, et al. Discrimination of Bacterial Community Structures among Healthy, Gingivitis, and Periodontitis Statuses through Integrated Metatranscriptomic and Network Analyses. mSystems. 2021;6(6):e0088621. [15] KIN LX, BUTLER CA, SLAKESKI N, et al. Metabolic cooperativity between Porphyromonas gingivalis and Treponema denticola. J Oral Microbiol. 2020;12(1):1808750. [16] TAN KH, SEERS CA, DASHPER SG, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis and Treponema denticola exhibit metabolic symbioses. PLoS Pathog. 2014; 10(3):e1003955. [17] ZHANG J, SUN L, WITHANAGE MHH, et al. TRAF3IP2-IL-17 Axis Strengthens the Gingival Defense against Pathogens. J Dent Res. 2023; 102(1):103-115. [18] SONG B, XIAN W, SUN Y, et al. Akkermansia muciniphila inhibited the periodontitis caused by Fusobacterium nucleatum. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2023;9(1):49. [19] LOPEZ-OLIVA I, MALCOLM J, CULSHAW S. Periodontitis and rheumatoid arthritis-Global efforts to untangle two complex diseases. Periodontol 2000. 2024. doi: 10.1111/prd.12530. [20] LI W, PENG J, SHANG Q, et al. Periodontitis and the risk of all-cause and cause-specific mortality among US adults with diabetes: A population-based cohort study. J Clin Periodontol. 2024;51(3):288-298. [21] LI X, KIPROWSKA M, KANSARA T, et al. Neuroinflammation: A Distal Consequence of Periodontitis. J Dent Res. 2022;101(12):1441-1449. [22] WU E, CHENG M, ZHANG X, et al. Exploration of potential shared gene signatures between periodontitis and multiple sclerosis. BMC Oral Health. 2024;24(1):75. [23] GAO X, GUO Z, WANG P, et al. Transcriptomic analysis reveals the potential crosstalk genes and immune relationship between IgA nephropathy and periodontitis. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1062590. [24] XIONG Z, FANG Y, LU S, et al. Identification and Validation of Signature Genes and Potential Therapy Targets of Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Periodontitis. J Inflamm Res. 2023;16:4317-4330. [25] GÖRG A, WEISS W, DUNN MJ. Current two-dimensional electrophoresis technology for proteomics. Proteomics. 2004;4(12):3665-3685. [26] WILKINS MR, SANCHEZ JC, GOOLEY AA, et al. Progress with proteome projects: why all proteins expressed by a genome should be identified and how to do it. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 1996;13:19-50. [27] NONAKA T, WONG DTW. Saliva Diagnostics. Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif). 2022;15(1):107-121. [28] BELLEI E, BERTOLDI C, MONARI E, et al. Proteomics Disclose the Potential of Gingival Crevicular Fluid (GCF) as a Source of Biomarkers for Severe Periodontitis. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(6):2161. [29] BLANCO-PINTOS T, REGUEIRA-IGLESIAS A, SEIJO-PORTO I, et al. Accuracy of periodontitis diagnosis obtained using multiple molecular biomarkers in oral fluids: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Periodontol. 2023;50(11):1420-1443. [30] YUAN C, MA Z, TONG P, et al. Peptidomic changes of saliva after non-surgical treatment of stage I/II generalized periodontitis. Oral Dis. 2022;28(6):1640-1651. [31] BALCI N, KURGAN Ş, ÇEKICI A, et al. Free amino acid composition of saliva in patients with healthy periodontium and periodontitis. Clin Oral Investig. 2021;25(6):4175-4183. [32] ŞENGÜL V, GÜNEY Z, KURGAN Ş, et al. Evaluation of salivary and serum methylated arginine metabolites and nitric oxide synthase in advanced periodontitis patients. Clin Oral Investig. 2022;26(7):5061-5070. [33] SHIN MS, KIM YG, SHIN YJ, et al. Deep sequencing salivary proteins for periodontitis using proteomics. Clin Oral Investig. 2019;23(9):3571-3580. [34] ZHAO Z, SUN X, CAO L, et al. Salivary Proteome and Intact N-Glycopeptides Analysis Reveal Specific Signatures in Periodontitis. J Proteome Res. 2024;23(1):25-39. [35] QIU C, ZHOU W, SHEN H, et al. Profiles of subgingival microbiomes and gingival crevicular metabolic signatures in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024;16(1):41. [36] PEI F, WANG M, WANG Y, et al. Quantitative proteomic analysis of gingival crevicular fluids to identify novel biomarkers of gingival recession in orthodontic patients. J Proteomics. 2022;266:104647. [37] VERNEROVÁ A, KRČMOVÁ LK, HENEBERK O, et al. Liquid chromatography method with tandem mass spectrometry and fluorescence detection for determination of inflammatory biomarkers in gingival crevicular fluid as a tool for diagnosis of periodontal disease. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2022;212:114644.
[38] TORRES A, MICHEA MA, VÉGVÁRI Á, et al. A multi-platform analysis of human gingival crevicular fluid reveals ferroptosis as a relevant regulated cell death mechanism during the clinical progression of periodontitis. Int J Oral Sci. 2024;16(1):43. [39] PEI J, LI F, XIE Y, et al. Microbial and metabolomic analysis of gingival crevicular fluid in general chronic periodontitis patients: lessons for a predictive, preventive, and personalized medical approach. EPMA J. 2020;11(2):197-215. [40] HIETER P, BOGUSKI M. Functional genomics: it’s all how you read it. Science. 1997;278(5338):601-602. [41] OUDELAAR AM, HIGGS DR. The relationship between genome structure and function. Nat Rev Genet. 2021;22(3):154-168. [42] NEW FN, BRITO IL. What Is Metagenomics Teaching Us, and What Is Missed? Annu Rev Microbiol. 2020;74:117-135. [43] RINKE C, SCHWIENTEK P, SCZYRBA A, et al. Insights into the phylogeny and coding potential of microbial dark matter. Nature. 2013;499(7459): 431-437. [44] 林仁杰,戴安娜,汪淑华,等.糖尿病影响牙周炎患者口腔龈下菌群和唾液菌群组成的研究进展[J].口腔医学,2024,44(6):458-461+ 474. [45] FARINA R, SEVERI M, CARRIERI A, et al. Whole metagenomic shotgun sequencing of the subgingival microbiome of diabetics and non-diabetics with different periodontal conditions. Arch Oral Biol. 2019; 104:13-23. [46] ZHANG S, YU N, ARCE RM. Periodontal inflammation: Integrating genes and dysbiosis. Periodontol 2000. 2020;82(1):129-142. [47] ABUSLEME L, HOARE A, HONG BY, et al. Microbial signatures of health, gingivitis, and periodontitis. Periodontol 2000. 2021;86(1):57-78. [48] VAITHILINGAM RD, SAFII SH, BAHARUDDIN NA, et al. Moving into a new era of periodontal genetic studies: relevance of large case-control samples using severe phenotypes for genome-wide association studies. J Periodontal Res. 2014;49(6):683-695. [49] MUNZ M, WILLENBORG C, RICHTER GM, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies nucleotide variants at SIGLEC5 and DEFA1A3 as risk loci for periodontitis. Hum Mol Genet. 2017;26(13):2577-2588. [50] NOLDE M, ALAYASH Z, RECKELKAMM SL, et al. Downregulation of interleukin 6 signaling might reduce the risk of periodontitis: a drug target Mendelian randomization study. Front Immunol. 2023;14: 1160148. [51] YE X, BAI Y, LI M, et al. Genetic associations between circulating immune cells and periodontitis highlight the prospect of systemic immunoregulation in periodontal care. Elife. 2024;12:RP92895. [52] NICHOLSON JK, LINDON JC, HOLMES E. ‘Metabonomics’: understanding the metabolic responses of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli via multivariate statistical analysis of biological NMR spectroscopic data. Xenobiotica. 1999;29(11):1181-1189. [53] MIKKONEN JJ, SINGH SP, HERRALA M, et al. Salivary metabolomics in the diagnosis of oral cancer and periodontal diseases. J Periodontal Res. 2016;51(4):431-437. [54] BAIMA G, CORANA M, IADEROSA G, et al. Metabolomics of gingival crevicular fluid to identify biomarkers for periodontitis: A systematic review with meta-analysis. J Periodontal Res. 2021;56(4):633-645. [55] YUAN G, CHEN J, WANG X, et al. Serum metabolomics provides clues in understanding colitis exacerbating experimental periodontitis in female mice. Arch Oral Biol. 2023;145:105583. [56] BRÄGGER I. Radiographic diagnosis of periodontal disease progression. Curr Opin Periodontol. 1996;3:59-67. [57] WILLIAMS RC, HOWELL TH. New technologies for the diagnosis of periodontal disease. J Prosthet Dent. 1993;69(6):551-557. [58] BARNES VM, CIANCIO SG, SHIBLY O, et al. Metabolomics reveals elevated macromolecular degradation in periodontal disease. J Dent Res. 2011;90(11):1293-1297. [59] KIM S, KIM HJ, SONG Y, et al. Metabolic phenotyping of saliva to identify possible biomarkers of periodontitis using proton nuclear magnetic resonance. J Clin Periodontol. 2021;48(9):1240-1249. [60] ROMANO F, MEONI G, MANAVELLA V, et al. Analysis of salivary phenotypes of generalized aggressive and chronic periodontitis through nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics. J Periodontol. 2018;89(12):1452-1460. [61] DONG Z, LV W, ZHANG C, et al. Correlation Analysis of Gut Microbiota and Serum Metabolome With Porphyromonas gingivalis-Induced Metabolic Disorders. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022;12:858902. [62] CHEN HW, ZHOU W, LIAO Y, et al. Analysis of metabolic profiles of generalized aggressive periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. 2018;53(5): 894-901. [63] 陈娇,杜悦,周学东,等.牙周病患者唾液代谢轮廓分析[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2022,53(5):842-850. [64] CHEN ZY, XU TT, LIANG ZJ, et al. Untargeted and targeted gingival metabolome in rodents reveal metabolic links between high-fat diet-induced obesity and periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol. 2021;48(8):1137-1148. [65] KUBONIWA M, SAKANAKA A, HASHINO E, et al. Prediction of Periodontal Inflammation via Metabolic Profiling of Saliva. J Dent Res. 2016;95(12):1381-1386. [66] DEDE FÖ, OZDEN FO, AVCI B. 8-hydroxy-deoxyguanosine levels in gingival crevicular fluid and saliva in patients with chronic periodontitis after initial periodontal treatment. J Periodontol. 2013;84(6):821-828. [67] LIANG H, LUO H, SANG Z, et al. GREMI: An Explainable Multi-Omics Integration Framework for Enhanced Disease Prediction and Module Identification. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2024;28(11):6983-6996. [68] DING J, LI J, ZHANG C, et al. High-Throughput Combined Analysis of Saliva Microbiota and Metabolomic Profile in Chinese Periodontitis Patients: A Pilot Study. Inflammation. 2024;47(3):874-890. [69] CHENG T, WEN P, YU R, et al. Integrative microbiome and metabolome profiles reveal the impacts of periodontitis via oral-gut axis in first-trimester pregnant women. J Transl Med. 2024;22(1):819. [70] HUANG Z, PENG S, CEN T, et al. Association between biological ageing and periodontitis: Evidence from a cross-sectional survey and multi-omics Mendelian randomization analysis. J Clin Periodontol. 2024;51(10):1369-1383. [71] LAFLEUR S, BODEIN A, MBUYA MALAÏKA MUTOMBO J, et al. Multi-Omics Data Integration Reveals Key Variables Contributing to Subgingival Microbiome Dysbiosis-Induced Inflammatory Response in a Hyperglycemic Microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(10):8832. [72] SHOKEEN B, DINIS MDB, HAGHIGHI F, et al. Omics and interspecies interaction. Periodontol 2000. 2021;85(1):101-111. |
| [1] | 刘 琳, 刘世轩, 陆馨悦, 王 侃. 慢性肌筋膜触发点模型大鼠的尿液代谢组学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1585-1592. |
| [2] | 白 静, 张 雪, 任 燕, 李月辉, 田晓宇. lncRNA-TNFRSF13C调控miR-1246对牙周细胞低氧诱导因子1α的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(5): 928-935. |
| [3] | 赵增波, 李晨曦, 窦晨雷, 马 娜, 周冠军. 壳聚糖/甘油磷酸钠/海藻酸钠/益母草碱水凝胶的抗炎与促成骨作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(4): 678-685. |
| [4] | 王其飞, 杜兴彬, 孔健达. 中枢疲劳的神经生理基础及运动诱发机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(32): 6979-6988. |
| [5] | 柴金莲, 孙铁锋, 李 威, 张博淳, 李广政, 周忠起, 梁学振, 王 平. 鹿角胶对激素性股骨头坏死模型大鼠的治疗作用:粪便代谢组学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(29): 6187-6197. |
| [6] | 刘昊为, 田浩冬, 黄 丽, 余杭林, 彭 莉. 血流限制抗阻运动对肥胖青年男性血清代谢物的急性影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(29): 6249-6259. |
| [7] | 李泽铭, 张云涛, 王茂林, 侯玉东. 缺氧诱导因子1α调节骨稳态在口腔颌面部疾病治疗中的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(26): 5680-5687. |
| [8] | 刘 源, 渠 源, 万雅坤, 郭婧宇, 姜 萍. 基底膜相关基因在类风湿关节炎不同中医证型中的转录组学分析及药物预测[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(25): 5486-5500. |
| [9] | 王之枫, 杨 娇, 郗域江, 徐双凤, 施 婷, 蓝浚峯, 郝志慧, 和鹏芬, 杨爱明, 潘 攀, 王 健. 非靶向代谢组学分析影响轻中度脑卒中后认知功能障碍的生物标记物[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(24): 5116-5126. |
| [10] | 高红丽, 秦玉凤, 张玥晗, 舒佳玉, 陈河林. 铜代谢与口腔疾病的诊断及治疗[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(20): 4316-4324. |
| [11] | 梁 周, 张 驰, 潘成镇, 杨 博, 蒲张林, 刘 桦, 彭金辉, 文立春, 凌观汉, 陈 锋. 基于肠道菌群和广泛靶向代谢组学的山柰酚抗骨质疏松的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(20): 4190-4204. |
| [12] | 叶 丽, 田 川, 赵晓娟, 陈梦蝶, 叶倩倩, 李 强, 廖珠银, 李 晔, 朱向情, 阮光萍, 何志旭, 舒莉萍, 潘兴华. 高活性脐带间充质干细胞干预老年树鼩衰老脾脏的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(19): 4000-4010. |
| [13] | 阮 珍, 寇久社. 转录组测序与定量蛋白质组学分析医用臭氧治疗兔骨骼肌损伤的分子机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(18): 3767-3774. |
| [14] | 季明意, 季欣意, 徐俊峰. 褪黑素促进骨再生机制及在口腔种植中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(18): 3868-3876. |
| [15] | 何 丽, 任 潞, 江小茜, 刘旭倩, 黎春晖, . 1,8-桉叶油素干预大鼠实验性牙周炎模型的炎症反应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(17): 3605-3613. |
牙周炎的发病机制涉及多因素的复杂相互作用,包括宿主与病原菌之间的相互作用及其引发的炎症反应、免疫调控和组织破坏等过程。牙周致病菌不仅通过直接侵袭宿主组织来引发病变,还通过其毒力因子激活宿主的炎症信号通路,诱导免疫失调和骨吸收。与此同时,环境因素(如吸烟和糖尿病)和遗传易感性也是牙周炎发生与发展的关键因素。
组学分析作为现代生物学的重要分支,涵盖了基因组学、转录组学、表观遗传组学、蛋白质组学、代谢组学等多个领域,核心目标在于利用高通量、非靶向的手段来定性和定量研究生物体中的各类生物大分子(如DNA、RNA、蛋白质、代谢产物等)及相互作用,能够在给定时间同时分析响应环境刺激的多种分子成分,从而揭示生物体的基因组成、蛋白质功能、代谢途径等生物学信息[4]。
鉴于牙周炎发病机制的复杂性,组学分析技术为深入探究疾病的分子基础提供了前所未有的机遇。随着组学分析技术的飞速发展,针对牙周炎的探索正逐步迈向更深层次,涵盖了发病机制、诊断、治疗和疾病预测的多个方面。在这一过程中,组学分析这一前沿技术得到了广泛关注。例如,JUN等[5]通过整合转录组学和代谢组学来研究影响牙周炎发病机制的关键基因、代谢物和通路,探索出了PDGFD等3个牙周炎的潜在生物标志物,这些标志物不仅有助于理解疾病的发病机制,还为早期诊断提供了新的思路。也有学者通过凝胶蛋白质组学对患有牙周炎的糖尿病患者和非牙周炎患者的唾液样本进行二维凝胶电泳(two-dimensional gel electrophoresis,2-DE)分析,发现有7种蛋白质的表达存在显著差异,揭示了糖尿病患者局部宿主反应受到干扰从而较健康者更易患牙周炎[6]。这些组学手段不仅开辟了对牙周炎病因的全新研究角度,还为疾病的诊断和治疗提供了潜在的靶点,进一步推动了牙周病学的发展。
通过组学技术,研究人员能够深入理解牙周炎的分子机制,并识别出具有诊断、治疗及预防潜力的生物标志物。文章就组学分析,特别是转录组学、蛋白质组学、基因组学、代谢组学和多组学联合分析在牙周炎发病机制、诊断、治疗等方面的应用作简要综述,为增强宿主防御、开发个性化治疗方案、预防牙周炎提供科学参考。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
1.1 资料来源
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者于2024年8月应用计算机进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 检索时限重点为1993年6月至2024年8月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed数据库和中国知网。
1.1.4 检索途径 采用主题词、关键词和摘要检索。
1.1.5 检索词 英文检索词包括“omics,periodontitis,transcriptomics and periodontitis,proteomics and periodontitis,genomics and periodontitis,metabolomics and periodontitis,multi-omics and periodontitis”,中文检索词包括“组学,牙周炎,转录组学和牙周炎,蛋白质组学和牙周炎,基因组学和牙周炎,代谢组学和牙周炎,多组学联合分析和牙周炎”。
1.1.6 检索文献类型 综述性论文及研究性论文。
1.1.7 手工检索情况 无。
1.1.8 检索策略 以PubMed数据库检索策略为例,见图1。
1.2 纳入与排除标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 组学分析与牙周炎相关研究。
1.2.2 排除标准 研究目的及内容偏离主题范畴的文献;重复性研究。
1.3 文献质量评估及数据提取 共检索到文献5 391篇,排除与研究目的关联度低及重复的文献5 319篇,纳入72篇符合标准的文献进行综述,包含中国知网2篇,PubMed 数据库70篇,文献检索流程如图2所示。
3.1 既往他人在该领域研究的贡献和存在的问题 牙周炎作为一种常见的慢性炎症性疾病,其严重性正受到越来越多的重视。同时,近年来组学分析技术也取得了快速发展并在牙周炎研究中广泛应用[72]。由于组学技术可以对牙周炎机体的各类变化进行系统分析,从而为疾病的早期诊断和治疗策略提供理论依据,所以许多学者将研究重点放在组学分析技术和牙周炎症的关系上,从而靶向各类生物标记物探讨新的防治措施。值得注意的是,由于2010年以前组学技术尚处于起步阶段,研究手段和技术应用尚未成熟,牙周炎的研究主要依赖于传统技术(如PCR和ELISA)进行单一指标分析,这些方法虽为牙周炎研究提供了基础数据,但在分辨率和系统性上存在一定局限性。近年来,随着高通量测序、RNA-Seq、质谱分析以及非靶向代谢组学等技术的快速发展,研究不再局限于单一生物标志物的分析,而是通过多组学联合分析全面揭示牙周炎的复杂病理机制,见图5。这些技术进步不仅提升了研究的精准度,还为多维度探讨牙周炎的发病机制、诊断和治疗提供了更为广阔的视角。
3.3 综述的局限性 尽管此综述对组学分析技术在牙周炎研究中的应用进行了较为全面的总结,但仍存在一定的局限性。目前,一些新兴的组学技术如互作组学和单细胞组学正逐渐显现出在疾病研究中的重要性,这些新技术的探索和在牙周炎中的应用尚未在此综述中得到充分讨论,未来需要进一步的研究和系统性总结以揭示其潜在价值。
3.4 综述的重要意义 组学分析能够全面解析生物体的复杂性和动态变化,为生物医学研究、药物开发和个性化医疗提供强大的支持。在生命科学的众多领域中,牙周炎研究正逐步成为组学技术应用的重要方向之一。此综述系统总结了组学技术在牙周炎研究中的应用与进展,从转录组学、蛋白质组学、基因组学、代谢组学到多组学联合分析,全面探讨了这些技术在牙周炎诊断、发病机制及治疗中的作用。转录组学揭示了牙周炎相关的基因表达变化,不仅为疾病早期诊断提供了潜在标志物,还深入探讨了与全身性疾病的关联。蛋白质组学重点研究唾液和龈沟液中的蛋白质变化,进一步丰富了疾病诊断与治疗的策略选择。基因组学通过分析微生物多样性和群落动态,以及牙周炎相关基因的多态性,阐明了疾病的遗传机制与病理基础。代谢组学从代谢物及代谢通路的变化入手,展示了牙周炎在不同病程阶段的病理特征及治疗潜力。多组学联合分析整合了转录组、代谢组和微生物组等多维数据,全面解析了疾病的复杂病理机制与炎症调控网络,为探索新的治疗策略提供了重要方向。通过基因组学、转录组学、蛋白质组学和代谢组学等组学技术的应用,研究人员能够从多个维度探讨牙周炎的发病机制、病理过程和复杂的炎症反应。这种系统化的分析不仅有助于揭示疾病的分子基础,还为早期诊断和个性化治疗方案的制定提供了坚实的理论依据。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 目前,对于牙周炎的发病机制及复杂的病理过程,尤其是各类组学技术在牙周炎中的作用机制,仍未完全明晰。尽管已有一些研究初步揭示了单一组学技术在牙周炎防治中的潜力,但不同组学技术间的协同作用及对牙周炎发病机制的综合影响尚处于探索阶段。未来需要进一步加强多组学的联合研究,以系统阐明在牙周炎研究中的潜在价值。通过整合基因组学、代谢组学、蛋白质组学等数据,多组学联合分析将更加全面地揭示牙周炎的复杂病理机制与炎症调控网络。此外,多组学技术的协同应用能够助力探索疾病的动态变化规律,并为个性化诊断和治疗提供多维度的科学依据。例如,基于多组学联合分析的生物标志物筛选可以优化早期诊断方法,而利用多组学数据构建疾病网络模型则有助于预测疾病进程并制定针对性的治疗策略。
同时,随着新兴组学技术的发展,如单细胞测序和空间组学,未来应考虑将这些前沿技术应用于不同病程阶段和个体特异性差异的研究中。通过更全面的组学分析,不仅有望丰富牙周炎的诊断和治疗方法,还将为实现个性化防治策略提供理论支持,为牙周炎的精准医疗提供更坚实的理论支持和临床指导。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||