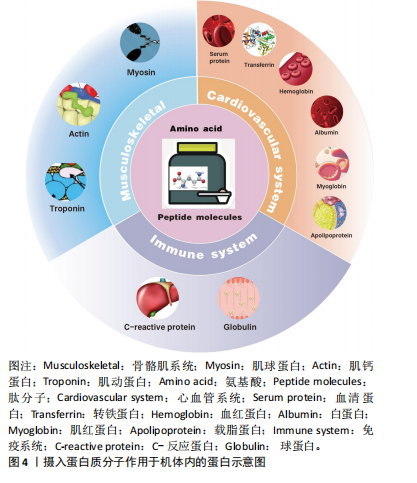
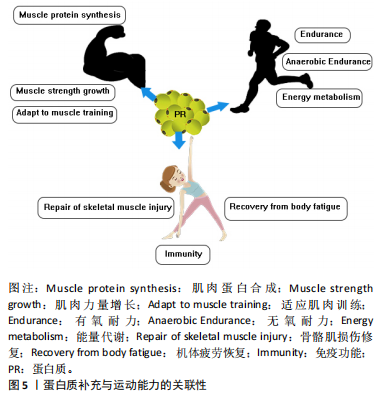
[1] DI MEO A, SOHAEI D, BATRUCH I, et al. Proteomic Profiling of the Human Tissue and Biological Fluid Proteome. J Proteome Res. 2021; 20(1):444-452.
[2] CAMERA DM. Evaluating the Effects of Increased Protein Intake on Muscle Strength, Hypertrophy and Power Adaptations with Concurrent Training: A Narrative Review. Sports Med. 2022;52(3):441-461.
[3] ZELENKOVA IE, ZOTKIN SV, KORNEEV PV, et al. Relationship between total hemoglobin mass and competitive performance in endurance athletes. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2019;59(3):352-356.
[4] MAUNDER E, ROTHSCHILD JA, FRITZEN AM, et al. Skeletal muscle proteins involved in fatty acid transport influence fatty acid oxidation rates observed during exercise. Pflugers Arch. 2023;475(9):1061-1072.
[5] LI C, LU Y, WANG J, et al. Immunoregulation of bovine lactoferrin together with osteopontin promotes immune system development and maturation. Food Funct. 2024;15(2):866-880.
[6] 李世成,杨则宜.活性肽及其在运动中的应用[J].中国运动医学杂志,2003,22(2):174-176,149.
[7] MASTER PBZ, MACEDO RCO. Effects of dietary supplementation in sport and exercise: a review of evidence on milk proteins and amino acids. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2021;61(7):1225-1239.
[8] MANORE MM, PATTON-LOPEZ MM, MENG Y, et al. Sport Nutrition Knowledge, Behaviors and Beliefs of High School Soccer Players. Nutrients. 2017;9(4):350.
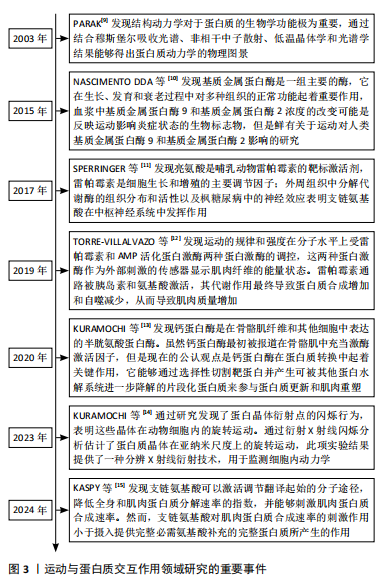
[9] PARAK FG. Proteins in action: the physics of structural fluctuations and conformational changes. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2003;13(5):552-557.
[10] NASCIMENTO DDA C, DURIGAN RDE C, TIBANA RA, et al. The response of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and -2 to exercise. Sports Med. 2015; 45(2):269-278.
[11] SPERRINGER JE, ADDINGTON A, HUTSON SM. Branched-Chain Amino Acids and Brain Metabolism. Neurochem Res. 2017;42(6):1697-1709.
[12] TORRE-VILLALVAZO I, ALEMAN-ESCONDRILLAS G, VALLE-RIOS R, et al. Protein intake and amino acid supplementation regulate exercise recovery and performance through the modulation of mTOR,AMPK,FGF21,and immunity. Nutr Res. 2019;72:1-17.
[13] KURAMOCHI M, HYATT HW, POWERS SK. The Role of Calpains in Skeletal Muscle Remodeling with Exercise and Inactivity-induced Atrophy. Int J Sports Med. 2020;41(14):994-1008.
[14] KURAMOCHI M, SUGAWARA I, SHINKAI Y, et al. Time-Resolved X-ray Observation of Intracellular Crystallized Protein in Living Animal. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(23):16914.
[15] KASPY MS, HANNAIAN SJ, BELL ZW, et al. The effects of branched-chain amino acids on muscle protein synthesis,muscle protein breakdown and associated molecular signalling responses in humans: an update. Nutr Res Rev. 2024;37(2):273-286.
[16] 田麦久,田烈,高玉花.运动训练理论核心概念的界定及认知的深化[J].天津体育学院学报,2020,35(5):497-505,512
[17] HERZOG W, SCHAPPACHER-TILP G. Molecular mechanisms of muscle contraction: A historical perspective. J Biomech. 2023;155:111659.
[18] 冯兰兰,窦燕,陈嘉威,等.高蛋白运动补剂对空手道运动员骨密度的影响[J].食品研究与开发,2023,44(23):234-236.
[19] 李良,苏浩.运动后联合补充糖与蛋白质对肌糖原合成效果的研究进展[J].体育科学,2015,35(9):84-89.
[20] PEARSON AG, HIND K, MACNAUGHTON LS. The impact of dietary protein supplementation on recovery from resistance exercise-induced muscle damage: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2023;77(8):767-783.
[21] DIRKS ML, GROEN BB, FRANSSEN R, et al. Neuromuscular electrical stimulation prior to presleep protein feeding stimulates the use of protein-derived amino acids for overnight muscle protein synthesis. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017;122(1):20-27.
[22] KOVACS MS, BAKER LB. Recovery interventions and strategies for improved tennis performance. Br J Sports Med. 2014;48 Suppl 1 (Suppl 1):i18-21.
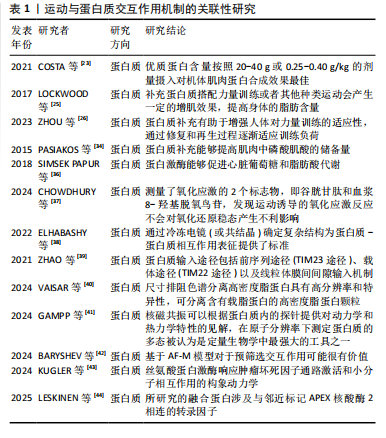
[23] COSTA JV, MICHEL JM, MADZIMA TA. The Acute Effects of a Relative Dose of Pre-Sleep Protein on Recovery Following Evening Resistance Exercise in Active Young Men. Sports (Basel). 2021;9(4):44.
[24] UR REHMAN H, AZAM N, YAO J, et al. A three-way approach for protein function classification. PLoS One. 2017;12(2):e0171702.
[25] LOCKWOOD CM, ROBERTS MD, DALBO VJ, et al. Effects of Hydrolyzed Whey versus Other Whey Protein Supplements on the Physiological Response to 8 Weeks of Resistance Exercise in College-Aged Males. J Am Coll Nutr. 2017;36(1):16-27.
[26] ZHOU HH, LIAO Y, ZHOU X, et al. Effects of Timing and Types of Protein Supplementation on Improving Muscle Mass,Strength,and Physical Performance in Adults Undergoing Resistance Training: A Network Meta-Analysis. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2023;34(1):54-64.
[27] MACKAY-PHILLIPS K, ORSSATTO LBR, POLMAN R, et al. Effects of α-lactalbumin on strength,fatigue and psychological parameters: a randomised double-blind cross-over study. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2023; 123(2):381-393.
[28] ARENT SM, CINTINEO HP, MCFADDEN BA, et al. Nutrient Timing: A Garage Door of Opportunity? Nutrients. 2020;12(7):1948.
[29] KRITIKOS S, PAPANIKOLAOU K, DRAGANIDIS D, et al. Effect of whey vs. soy protein supplementation on recovery kinetics following speed endurance training in competitive male soccer players: a randomized controlled trial. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2021;18(1):23.
[30] ZHAO C, GONG Y, ZHENG L, et al. Whey protein hydrolysate enhances exercise endurance, regulates energy metabolism, and attenuates muscle damage in exercise mice. Food Bioscience. 2023;52:102453.
[31] CAMERA DM, ONG JN, COFFEY VG, et al. Selective Modulation of MicroRNA Expression with Protein Ingestion Following Concurrent Resistance and Endurance Exercise in Human Skeletal Muscle. Front Physiol. 2016;7:87.
[32] TAN AY, HAMZAH SH, HUANG CY, et al. Pre-exercise Carbohydrate Drink Adding Protein Improves Post-exercise Fatigue Recovery. Front Physiol. 2021;12:765473.
[33] LI F, HSUEH YT, HSU YJ, et al. Effects of Isolated Soy Protein Supplementation Combined with Aerobic Exercise Training on Improving Body Composition,Anthropometric Characteristics and Cardiopulmonary Endurance in Women: A Pilot Study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(22):11798.
[34] PASIAKOS SM, MCLELLAN TM, LIEBERMAN HR. The effects of protein supplements on muscle mass,strength,and aerobic and anaerobic power in healthy adults: a systematic review. Sports Med. 2015;45(1): 111-131.
[35] CHEN Y, NIELSEN J. Energy metabolism controls phenotypes by protein efficiency and allocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(35): 17592-17597.
[36] SIMSEK PAPUR O, SUN A, GLATZ JFC, et al. Acute and Chronic Effects of Protein Kinase-D Signaling on Cardiac Energy Metabolism. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018;5:65.
[37] CHOWDHURY MMH, FONTAINE MN, LORD SE, et al. Impact of a tailored exercise regimen on physical capacity and plasma proteome profile in post-COVID-19 condition. Front Physiol. 2024;15:1416639.
[38] ELHABASHY H, MERINO F, ALVA V, et al. Exploring protein-protein interactions at the proteome level. Structure. 2022;30(4):462-475.
[39] ZHAO F, ZOU MH. Role of the Mitochondrial Protein Import Machinery and Protein Processing in Heart Disease. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021; 8:749756.
[40] VAISAR T, BABENKO I, HORVATH KV, et al. Relationships between HDL subpopulation proteome and HDL function in overweight/obese people with and without coronary heart disease. Atherosclerosis. 2024;397:118565.
[41] GAMPP O, KAGAVATH H,RIEK R. NMR tools to detect protein allostery. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2024;86:102792.
[42] BARYSHEV A, LA FLEUR A, GROVES B, et al. Massively parallel measurement of protein-protein interactions by sequencing using MP3-seq. Nat Chem Biol. 2024;20(11):1514-1523.
[43] KUGLER V, SCHWAIGHOFER S, FEICHTNER A, et al. Impact of protein and small molecule interactions on kinase conformations. Elife. 2024; 13:RP94755.
[44] LESKINEN HL, UDVADIA AJ. Development and Validation of a Proximity Labeling Fusion Protein Construct to Identify the Protein-Protein Interactions of Transcription Factors. Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2848: 269-297.
[45] MOON JY, CHAI JC, YU B, et al. Metabolomic Signatures of Sedentary Behavior and Cardiometabolic Traits in US Hispanics/Latinos: Results from HCHS/SOL. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2023;55(10):1781-1791.
[46] PINCKAERS PJM, KOUW IWK, HENDRIKS FK,et al. No differences in muscle protein synthesis rates following ingestion of wheat protein,milk protein,and their protein blend in healthy, young males. Br J Nutr. 2021;126(12):1832-1842.
[47] KRITIKOS S, PAPANIKOLAOU K, DRAGANIDIS D, et al. soy protein supplementation on recovery kinetics following speed endurance training in competitive male soccer players: a randomized controlled trial. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2021;18(1):23.
[48] HOLWERDA AM, TROMMELEN J, KOUW IWK, et al. Exercise Plus Presleep Protein Ingestion Increases Overnight Muscle Connective Tissue Protein Synthesis Rates in Healthy Older Men. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2021;31(3):217-226.
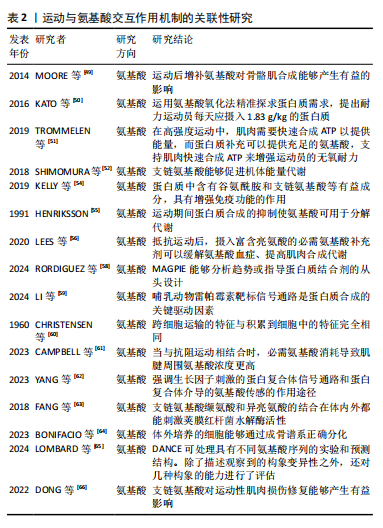
[49] MOORE DR, CAMERA DM, ARETA JL, et al. Beyond muscle hypertrophy: why dietary protein is important for endurance athletes. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2014;39(9):987-997.
[50] KATO H, SUZUKI K, BANNAI M, et al. Protein Requirements Are Elevated in Endurance Athletes after Exercise as Determined by the Indicator Amino Acid Oxidation Method. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0157406.
[51] TROMMELEN J, BETZ MW, VAN LOON LJC. The Muscle Protein Synthetic Response to Meal Ingestion Following Resistance-Type Exercise. Sports Med. 2019;49(2):185-197.
[52] SHIMOMURA Y, KITAURA Y. Physiological and pathological roles of branched-chain amino acids in the regulation of protein and energy metabolism and neurological functions. Pharmacol Res. 2018;133: 215-217.
[53] SAUNDERS B, ELLIOTT-SALE K, ARTIOLI GG, et al. β-alanine supplementation to improve exercise capacity and performance: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51(8): 658-669.
[54] KELLY B, PEARCE EL. Amino Assets: How Amino Acids Support Immunity. Cell Metab. 2020;32(2):154-175.
[55] HENRIKSSON J. Effect of exercise on amino acid concentrations in skeletal muscle and plasma. J Exp Biol. 1991;160:149-165.
[56] LEES MJ, WILSON OJ, WEBB EK, et al. Novel Essential Amino Acid Supplements Following Resistance Exercise Induce Aminoacidemia and Enhance Anabolic Signaling Irrespective of Age: A Proof-of-Concept Trial. Nutrients. 2020;12(7):2067.
[57] JÄGER R, KERKSICK CM, CAMPBELL BI, et al. International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: protein and exercise. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2017;14:20.
[58] RODRIGUEZ DCP, WEBER KC, SUNDBERG B, et al. MAGPIE: An interactive tool for visualizing and analyzing protein-ligand interactions. Protein Sci. 2024;33(8):e502.
[59] LI G, LI Z, LIU J. Amino acids regulating skeletal muscle metabolism: mechanisms of action,physical training dosage recommendations and adverse effects. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2024;21(1):41.
[60] CHRISTENSEN HN, OXENDER DL. Transport of amino acids into and across cells. Am J Clin Nutr. 1960;8:131-136.
[61] CAMPBELL NWC, PATEL SH, FERRANDI P, et al. Impact of essential amino acid intake,resistance exercise,and aging on the concentration of Achilles peritendinous amino acids and procollagen Iα1 in humans. Amino Acids. 2023;55(6):777-787.
[62] YANG Z, YU Z, XIAO B. Coordinated Regulation of Myelination by Growth Factor and Amino-acid Signaling Pathways. Neurosci Bull. 2023; 39(3):453-465.
[63] FANG M, BAUER CE. Regulation of stringent factor by branched-chain amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(25):6446-6451.
[64] BONIFACIO MA, CASSANO A, VINCENTI A, et al. In Vitro Evaluation of the Effects of Hyaluronic Acid and an Aminoacidic Pool on Human Osteoblasts. Biomedicines. 2023;11(3):751.
[65] LOMBARD V, GRUDININ S, LAINE E. Explaining Conformational Diversity in Protein Families through Molecular Motions. Sci Data. 2024;11(1): 752.
[66] DONG Y, ZHANG X, MIAO R, et al. Branched-chain amino acids promotes the repair of exercise-induced muscle damage via enhancing macrophage polarization. Front Physiol. 2022;13:1037090.
[67] KUMAR S, PANDEY G. Biofortification of pulses and legumes to enhance nutrition. Heliyon. 2020;6(3):e03682.
[68] TKACZEWSKA J, JAMROZ E, KULAWIK P, et al. Evaluation of the potential use of a carp (Cyprinus carpio) skin gelatine hydrolysate as an antioxidant component. Food Funct. 2019;10(2):1038-1048.
[69] ZHANG H, CHEN Y, GUO Y, et al. Label-free quantification proteomics reveals the active peptides from protein degradation during anaerobic fermentation of tea. LWT. 2021;(39):111950.
[70] HA S, KIM I, TAKATA T, et al. Identification of ᴅ-amino acid-containing peptides in human serum. PLoS One. 2017;12(12):e0189972.
[71] PRAET SFE, PURDAM CR, WELVAERT M, et al. Oral Supplementation of Specific Collagen Peptides Combined with Calf-Strengthening Exercises Enhances Function and Reduces Pain in Achilles Tendinopathy Patients. Nutrients. 2019;11(1):76.
[72] APOSTOLOPOULOS V, BOJARSKA J, CHAI TT, et al. A Global Review on Short Peptides: Frontiers and Perspectives. Molecules. 2021;26(2):430.
[73] YOO SH, LEE HS. Foldectures: 3D Molecular Architectures from Self-Assembly of Peptide Foldamers. Acc Chem Res. 2017;50(4):832-841.
|