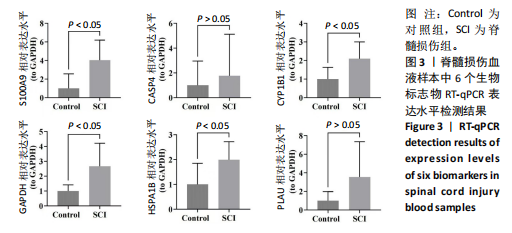
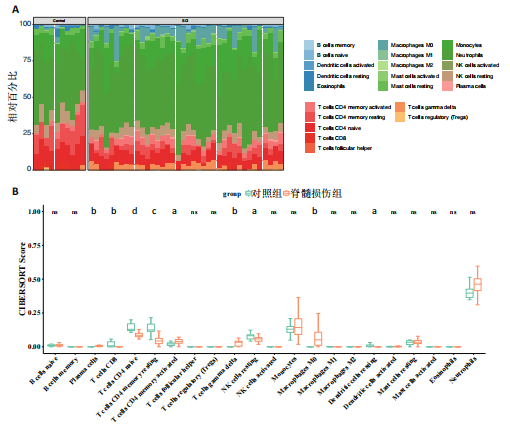
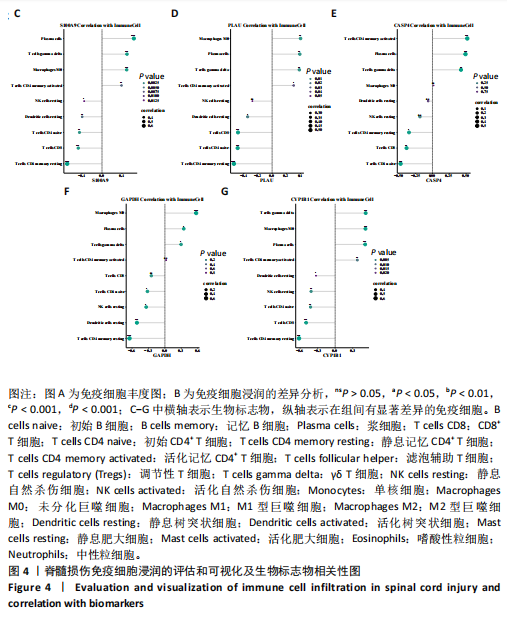
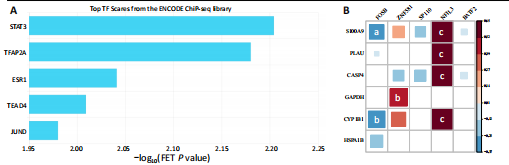
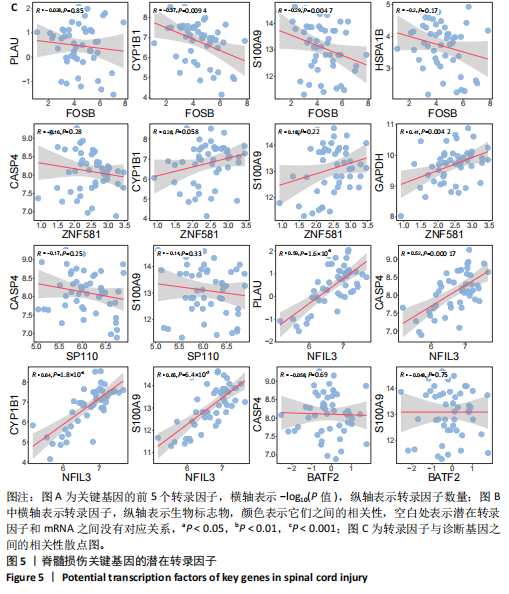
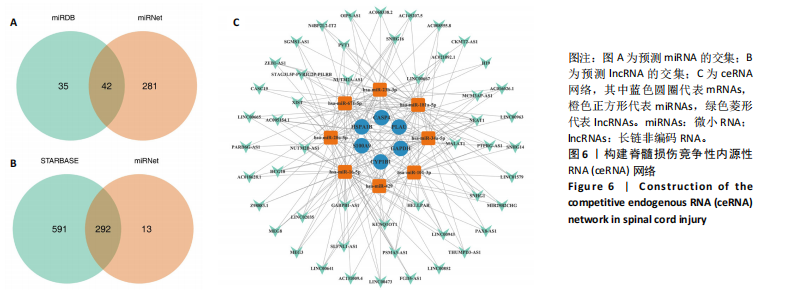
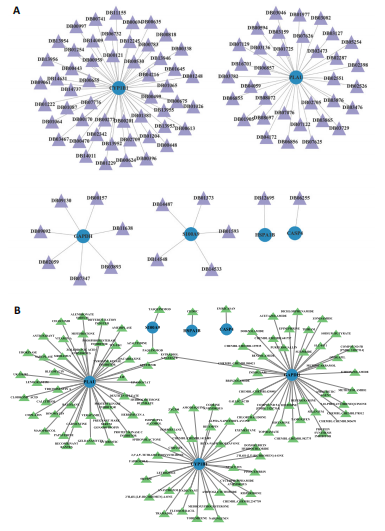
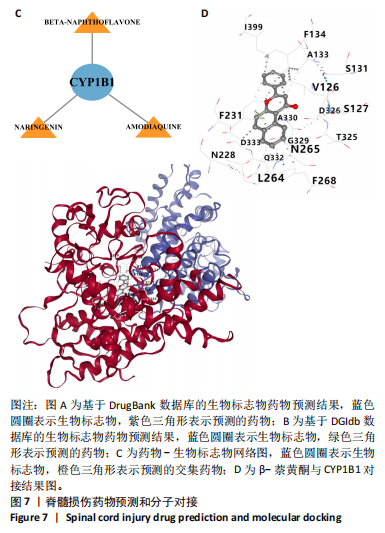
[1] STERNER RC, STERNER RM. Immune response following traumatic spinal cord injury: Pathophysiology and therapies. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1084101.
[2] AHUJA CS, WILSON JR, NORI S, et al. Traumatic spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17018.
[3] GUHA L, KUMAR H. Drug Repurposing for Spinal Cord Injury: Progress Towards Therapeutic Intervention for Primary Factors and Secondary Complications. Pharmaceut Med. 2023;37(6):463-490.
[4] ROPPER AE, ROPPER AH. Acute Spinal Cord Compression. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(14):1358-1369.
[5] GUHA L, KUMAR H. Drug Repurposing for Spinal Cord Injury: Progress Towards Therapeutic Intervention for Primary Factors and Secondary Complications. Pharmaceut Med. 2023;37(6):463-490.
[6] MA H, WANG C, HAN L, et al. Tofacitinib Promotes Functional Recovery after Spinal Cord Injury by Regulating Microglial Polarization via JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 2023;19(15):4865-4882.
[7] FREYERMUTH-TRUJILLO X, SEGURA-URIBE JJ, SALGADO-CEBALLOS H, et al. Inflammation: A Target for Treatment in Spinal Cord Injury. Cells. 2022;11(17):2692.
[8] LI SS, ZHANG BY, YIN SG, et al. A new peptide, VD11, promotes structural and functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(10):2260-2267.
[9] HAMANN K, SHI R. Acrolein scavenging: a potential novel mechanism of attenuating oxidative stress following spinal cord injury. J Neurochem. 2009;111(6):1348-1356.
[10] BRAUGHLER JM, HALL ED. Central nervous system trauma and stroke. I. Biochemical considerations for oxygen radical formation and lipid peroxidation. Free Radic Biol Med. 1989;6(3):289-301.
[11] PAPASTEFANAKI F, MATSAS R. From demyelination to remyelination: the road toward therapies for spinal cord injury. Glia. 2015;63(7): 1101-1125.
[12] YU Q, JIANG X, LIU X, et al. Glutathione-modified macrophage-derived cell membranes encapsulated metformin nanogels for the treatment of spinal cord injury. Biomater Adv. 2022;133:112668.
[13] ZHANG C, ZHAI T, ZHU J, et al. Research Progress of Antioxidants in Oxidative Stress Therapy after Spinal Cord Injury. Neurochem Res. 2023;48(12):3473-3484.
[14] FAKHRI S, ABBASZADEH F, MORADI SZ, et al. Effects of Polyphenols on Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Interconnected Pathways during Spinal Cord Injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022: 8100195.
[15] WANG B, HUANG M, SHANG D, et al. Mitochondrial Behavior in Axon Degeneration and Regeneration. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021;13: 650038.
[16] LI Q, GAO S, KANG Z, et al. Rapamycin Enhances Mitophagy and Attenuates Apoptosis After Spinal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Front Neurosci. 2018;12:865.
[17] GU C, LI L, HUANG Y, et al. Salidroside Ameliorates Mitochondria-Dependent Neuronal Apoptosis after Spinal Cord Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Partially through Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Promoting Mitophagy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:3549704.
[18] KYRITSIS N, TORRES-ESPIN A, SCHUPP PG, et al. Diagnostic blood RNA profiles for human acute spinal cord injury. J Exp Med. 2021; 218(3):e20201795.
[19] LIU S, WANG Z, ZHU R, et al. Three Differential Expression Analysis Methods for RNA Sequencing: limma, EdgeR, DESeq2. J Vis Exp. 2021; (175). doi: 10.3791/62528.
[20] WANG F, LIN H, SU Q, et al. Cuproptosis-related lncRNA predict prognosis and immune response of lung adenocarcinoma. World J Surg Oncol. 2022;20(1):275.
[21] XIE L, HUANG G, GAO M, et al. Identification of Atrial Fibrillation-Related lncRNA Based on Bioinformatic Analysis. Dis Markers. 2022; 2022:8307975.
[22] YU G, WANG LG, HAN Y, et al. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS. 2012;16(5): 284-287.
[23] ANJUM A, YAZID MD, FAUZI DM, et al. Spinal Cord Injury: Pathophysiology, Multimolecular Interactions, and Underlying Recovery Mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20). doi: 10.3390/ijms21207533.
[24] QUADRI S A, FAROOQUI M, IKRAM A, et al. Recent update on basic mechanisms of spinal cord injury. Neurosurg Rev. 2020;43(2):425-441.
[25] LIU G, DENG B, HUO L, et al. Temporal profiling and validation of oxidative stress-related genes in spinal cord injury. Brain Res Bull. 2023;205:110832.
[26] NAGAREDDY PR, MURPHY AJ, STIRZAKER RA, et al. Hyperglycemia promotes myelopoiesis and impairs the resolution of atherosclerosis. Cell Metab. 2013;17(5):695-708.
[27] COTOI OS, DUNER P, KO N, et al. Plasma S100A8/A9 correlates with blood neutrophil counts, traditional risk factors, and cardiovascular disease in middle-aged healthy individuals. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014;34(1):202-210.
[28] PEI H, QU J, CHEN J, et al. S100A9 as a Key Myocardial Injury Factor Interacting with ATP5 Exacerbates Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Sepsis-Induced Cardiomyopathy. J Inflamm Res. 2024;17:4483-4503.
[29] FAN S, ZHAO H, LIU Y, et al. Isoproterenol Triggers ROS/P53/S100-A9 Positive Feedback to Aggravate Myocardial Damage Associated with Complement Activation. Chem Res Toxicol. 2020;33(10):2675-2685.
[30] MCMAHON BJ, KWAAN HC. Components of the Plasminogen-Plasmin System as Biologic Markers for Cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;867: 145-156.
[31] MAHMOOD N, MIHALCIOIU C, RABBANI SA. Multifaceted Role of the Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator (uPA) and Its Receptor (uPAR): Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Applications. Front Oncol. 2018;8:24.
[32] STAN SD, HAHM ER, WARIN R, et al. Withaferin A causes FOXO3a- and Bim-dependent apoptosis and inhibits growth of human breast cancer cells in vivo. Cancer Res. 2008;68(18):7661-7669.
[33] QU B, JIA Y, LIU Y, et al. The detection and role of heat shock protein 70 in various nondisease conditions and disease conditions: a literature review. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2015;20(6): 885-892.
[34] ZININGA T, RAMATSUI L, SHONHAI A. Heat Shock Proteins as Immunomodulants. Molecules. 2018;23(11). doi: 10.3390/molecules 23112846.
[35] PISHESHA N, HARMAND TJ, PLOEGH HL. A guide to antigen processing and presentation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2022;22(12):751-764.
[36] CHAKRABORTY P, BJORK P, KALLBERG E, et al. Vesicular Location and Transport of S100A8 and S100A9 Proteins in Monocytoid Cells. PLoS One. 2015;10(12):e0145217.
[37] CATALA A, ZVARA A, PUSKAS LG, et al. Melatonin-induced gene expression changes and its preventive effects on adriamycin-induced lipid peroxidation in rat liver. J Pineal Res. 2007;42(1):43-49.
[38] LIDIN E, SKOLD MK, ANGERIA M, et al. Hippocampal Expression of Cytochrome P450 1B1 in Penetrating Traumatic Brain Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(2):722.
[39] SHIMADA T, NAGAYOSHI H, MURAYAMA N, et al. Oxidation of 3’-methoxyflavone, 4’-methoxyflavone, and 3’,4’-dimethoxyflavone and their derivatives having 5,7-dihydroxyl moieties by human cytochromes P450 1B1 and 2A13. Xenobiotica. 2022;52(2):134-145.
[40] Du F, DING Z, RONNOW CF, et al. S100A9 induces reactive oxygen species-dependent formation of neutrophil extracellular traps in abdominal sepsis. Exp Cell Res. 2022;421(2):113405.
[41] MIHAILA AC, CIORTAN L, MACARIE RD, et al. Transcriptional Profiling and Functional Analysis of N1/N2 Neutrophils Reveal an Immunomodulatory Effect of S100A9-Blockade on the Pro-Inflammatory N1 Subpopulation. Front Immunol. 2021;12:708770.
[42] HUANG S, ZHEN Y, YIN X, et al. KMT2C Induced by FABP5P3 Aggravates Keratinocyte Hyperproliferation and Psoriasiform Skin Inflammation by Upregulating the Transcription of PIK3R3. J Invest Dermatol. 2023; 143(1):37-47.
[43] LIU Q, FU H, SUN F, et al. miR-16 family induces cell cycle arrest by regulating multiple cell cycle genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36(16): 5391-5404.
[44] GONZALEZ-LOPEZ P, ALVAREZ-VILLARREAL M, RUIZ-SIMON R, et al. Role of miR-15a-5p and miR-199a-3p in the inflammatory pathway regulated by NF-kappaB in experimental and human atherosclerosis. Clin Transl Med. 2023;13(8):e1363.
[45] D’ANTONA S, PORRO D, GALLIVANONE F, et al. Characterization of cell cycle, inflammation, and oxidative stress signaling role in non-communicable diseases: Insights into genetic variants, microRNAs and pathways. Comput Biol Med. 2024;174:108346.
[46] ZHANG Y, YANG G, LUO Y. Long non-coding RNA PVT1 promotes glioma cell proliferation and invasion by targeting miR-200a. Exp Ther Med. 2019;17(2):1337-1345.
[47] ZHAO W, ZHANG Y, ZHANG M, et al. Effects of total glucosides of paeony on acute renal injury following ischemia-reperfusion via the lncRNA HCG18/miR-16-5p/Bcl-2 axis. Immunobiology. 2022;227(2): 152179.
[48] ZOTTA A, O’NEILL L, YIN M. Unlocking potential: the role of the electron transport chain in immunometabolism. Trends Immunol. 2024;45(4): 259-273.
[49] HANNAN MA, DASH R, SOHAG A, et al. Neuroprotection Against Oxidative Stress: Phytochemicals Targeting TrkB Signaling and the Nrf2-ARE Antioxidant System. Front Mol Neurosci. 2020;13:116.
[50] ZHENG M, LIU Y, ZHANG G, et al. The Applications and Mechanisms of Superoxide Dismutase in Medicine, Food, and Cosmetics. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023;12(9):1675.
[51] ANKENY DP, POPOVICH PG. Mechanisms and implications of adaptive immune responses after traumatic spinal cord injury. Neuroscience. 2009;158(3):1112-1121.
[52] GARCIA E, AGUILAR-CEVALLOS J, SILVA-GARCIA R, et al. Cytokine and Growth Factor Activation In Vivo and In Vitro after Spinal Cord Injury. Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:9476020.
[53] XU Y, LI Y, ZHANG Z, et al. [Expressions and implications of Th1/Th2 cytokines in injured rat brain and spinal cord]. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013;29(9):919-922,926.
[54] POPOVICH PG, TOVAR CA, WEI P, et al. A reassessment of a classic neuroprotective combination therapy for spinal cord injured rats: LPS/pregnenolone/indomethacin. Exp Neurol. 2012;233(2):677-685.
[55] PENG H, TIAN Z. Natural Killer Cell Memory: Progress and Implications. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1143.
[56] JUELKE K, KILLIG M, LUETKE-EVERSLOH M, et al. CD62L expression identifies a unique subset of polyfunctional CD56dim NK cells. Blood. 2010;116(8):1299-1307.
[57] XU L, ZHANG Y, ZHANG R, et al. Elevated plasma BDNF levels are correlated with NK cell activation in patients with traumatic spinal cord injury. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;74:105722.
[58] ZELTER M, MENSCH-DECHENE J, LOCKHART A. [Pulmonary blood volume. Definition, measurement, normal values]. Pathol Biol (Paris). 1975;23(4):323-332.
[59] FELTEN DL, FELTEN SY, CARLSON SL, et al. Noradrenergic and peptidergic innervation of lymphoid tissue. J Immunol. 1985; 135(2 Suppl):755s-765s.
[60] HERMAN P, STEIN A, GIBBS K, et al. Persons with Chronic Spinal Cord Injury Have Decreased Natural Killer Cell and Increased Toll-Like Receptor/Inflammatory Gene Expression. J Neurotrauma. 2018;35(15): 1819-1829.
[61] WANG Q, LIU L, CAO J, et al. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis reveals that CXCL10, IRF7, MX1, RSAD2, and STAT1 are related to the chronic stage of spinal cord injury. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(15): 1248.
[62] GE X, TANG P, RONG Y, et al. Exosomal miR-155 from M1-polarized macrophages promotes EndoMT and impairs mitochondrial function via activating NF-kappaB signaling pathway in vascular endothelial cells after traumatic spinal cord injury. Redox Biol. 2021;41:101932.
[63] VAN BROECKHOVEN J, SOMMER D, DOOLEY D, et al. Macrophage phagocytosis after spinal cord injury: when friends become foes. Brain. 2021;144(10):2933-2945.
[64] FAN H, TANG HB, SHAN LQ, et al. Quercetin prevents necroptosis of oligodendrocytes by inhibiting macrophages/microglia polarization to M1 phenotype after spinal cord injury in rats. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;16(1):206.
[65] WANG Y, LI W, WANG M, et al. Quercetin prevents the ferroptosis of OPCs by inhibiting the Id2/transferrin pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 2023,381:110556.
[66] ZHU K, ZHENG Z, ZHANG YY, et al. A comprehensive and systematic review of the potential neuroprotective effect of quercetin in rat models of spinal cord injury. Nutr Neurosci. 2024;27(8):857-869.
[67] WIKLUND L, SHARMA A, MURESANU DF, et al. TiO(2)-Nanowired Delivery of Chinese Extract of Ginkgo biloba EGb-761 and Bilobalide BN-52021 Enhanced Neuroprotective Effects of Cerebrolysin Following Spinal Cord Injury at Cold Environment. Adv Neurobiol. 2023;32: 353-384.
[68] LIU G, DENG B, HUO L, et al. Temporal profiling and validation of oxidative stress-related genes in spinal cord injury. Brain Res Bull. 2023;205:110832.
[69] HE Z, ZHANG C, LIANG JX, et al. Targeting Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress: Potential Neuroprotective Therapy for Spinal Cord Injury. J Integr Neurosci. 2023;22(6):153.
[70] SOHN HM, HWANG JY, RYU JH, et al. Simvastatin protects ischemic spinal cord injury from cell death and cytotoxicity through decreasing oxidative stress: in vitro primary cultured rat spinal cord model under oxygen and glucose deprivation-reoxygenation conditions. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):36.
[71] KAUR J, MOJUMDAR A. A mechanistic overview of spinal cord injury, oxidative DNA damage repair and neuroprotective therapies. Int J Neurosci. 2023;133(3):307-321.
[72] WU AG, ZHOU XG, QIAO G, et al. Targeting microglial autophagic degradation in NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;65:101202.
[73] ROCA FJ, WHITWORTH LJ, REDMOND S, et al. TNF Induces Pathogenic Programmed Macrophage Necrosis in Tuberculosis through a Mitochondrial-Lysosomal-Endoplasmic Reticulum Circuit. Cell. 2019; 178(6) 1344-1361.
[74] ZHANG S, ZHANG J, GUO D, et al. Biotoxic effects and gene expression regulation of urban PM(2.5) in southwestern China. Sci Total Environ. 2021;753:141774.
[75] WU YR, CHANG KH, CHAO CY, et al. Association of SOD2 p.V16A polymorphism with Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis in Han Chinese. J Formos Med Assoc. 2021;120(1 Pt 2):501-507.
[76] LIU W, ZHU J, WU Z, et al. Insight of novel biomarkers for papillary thyroid carcinoma through multiomics. Front Oncol. 2023;13:1269751.
|