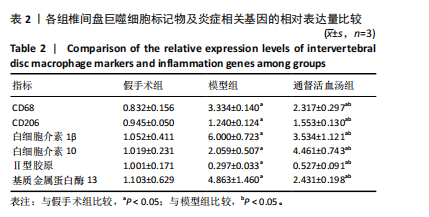
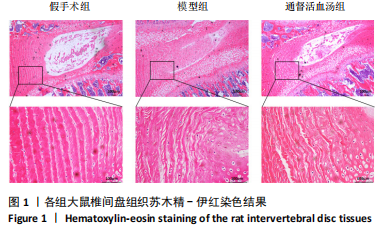
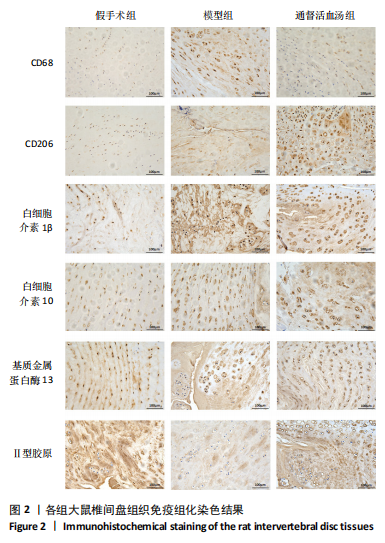
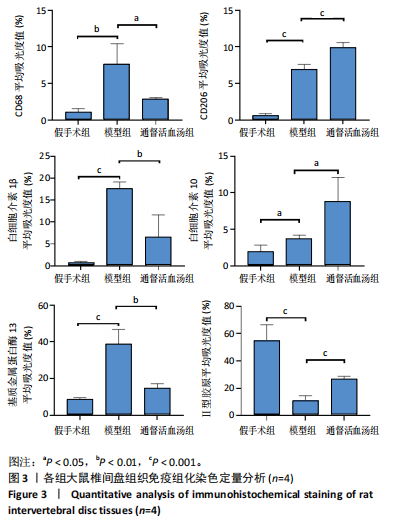
[1] WANG F, CAI F, SHI R, et al. Aging and age related stresses: a senescence mechanism of intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(3):398-408.
[2] SAMANTA A, LUFKIN T, KRAUS P. Intervertebral disc degeneration-Current therapeutic options and challenges. Front Public Health. 2023;11:1156749.
[3] MOHD II, TEOH SL, MOHD NN, et al. Discogenic Low Back Pain: Anatomy, Pathophysiology and Treatments of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;24(1):208.
[4] 郭炯炯, 杨惠林, 朱雪松, 等. 中国南方人群腰椎间盘退变的影像学和流行病学研究[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2014,34(5):546-552.
[5] OICHI T, TANIGUCHI Y, OSHIMA Y, et al. Pathomechanism of intervertebral disc degeneration. JOR Spine. 2020;3(1):e1076.
[6] KANG L, ZHANG H, JIA C, et al. Epigenetic modifications of inflammation in intervertebral disc degeneration. Ageing Res Rev. 2023;87:101902.
[7] HOU Y, SHI G, GUO Y, et al. Epigenetic modulation of macrophage polarization prevents lumbar disc degeneration. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(8):6558-6569.
[8] PARISI L, GINI E, BACI D, et al. Macrophage Polarization in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases: Killers or Builders? J Immunol Res. 2018;2018: 8917804.
[9] LI XC, LUO SJ, FAN W, et al. Macrophage polarization regulates intervertebral disc degeneration by modulating cell proliferation, inflammation mediator secretion, and extracellular matrix metabolism. Front Immunol. 2022;13:922173.
[10] JAMES G, SLUKA KA, BLOMSTER L, et al. Macrophage polarization contributes to local inflammation and structural change in the multifidus muscle after intervertebral disc injury. Eur Spine J. 2018; 27(8):1744-1756.
[11] 熊雨墨, 李梓宸, 李瑛, 等. 通督活血汤对腰椎间盘突出症急性期患者腰椎功能及血清炎症因子水平的影响[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2024,30(13):135-141.
[12] 吴子健, 胡昭端, 周晓红, 等. 通督活血汤含药血清可抑制椎间盘纤维环细胞的焦亡[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(14):2148-2154.
[13] 廖瑶, 涂婷, 曾惜羽, 等. 瑞芬太尼对椎间盘退变模型大鼠椎间盘的影响及机制[J]. 重庆医科大学学报,2023,48(7):760-764.
[14] 李强, 汤耿民. 通督活血汤治疗退行性腰椎管狭窄症[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,1990,6(3):19-21.
[15] 孙尚, 赵振达, 蒋嫒, 等. 力学刺激在椎体软骨终板退变中的作用及机制[J]. 医用生物力学,2021,36(4):652-657.
[16] VELNAR T, GRADISNIK L. Endplate role in the degenerative disc disease: A brief review. World J Clin Cases. 2023;11(1):17-29.
[17] VOELKER A, SCHROETER F, STEINKE H, et al. Degeneration of the lumbar spine and its relation to the expression of collagen and elastin in facet joint capsules and ligament flavum. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2022;56(3):210-216.
[18] NEWTON MD, MAREK AA, PLANALP M, et al. Longitudinal characterization of intervertebral disc remodeling following acute annular injury in a rat model of degenerative disc disease. Connect Tissue Res. 2020;61(6):568-576.
[19] HÖFLSAUER S, BONNAIRE FC, BAMBERGER CE, et al. Changes in stiffness of the extracellular and pericellular matrix in the anulus fibrosus of lumbar intervertebral discs over the course of degeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:1006615.
[20] RISBUD MV, SHAPIRO IM. Role of cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: pain and disc content. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10(1): 44-56.
[21] VERWOERD AJ, PEUL WC, WILLEMSEN SP, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of history taking to assess lumbosacral nerve root compression. Spine J. 2014;14(9):2028-2037.
[22] YU ZG, XU N, WANG WB, et al. Interleukin-1 inhibits Sox9 and collagen type II expression via nuclear factor-kappaB in the cultured human intervertebral disc cells. Chin Med J (Engl). 2009;122(20):2483-2488.
[23] WANG Y, CHE M, XIN J, et al. The role of IL-1β and TNF-α in intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131: 110660.
[24] SHI S, KANG XJ, ZHOU Z, et al. Excessive mechanical stress-induced intervertebral disc degeneration is related to Piezo1 overexpression triggering the imbalance of autophagy/apoptosis in human nucleus pulpous. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022;24(1):119.
[25] YUNNA C, MENGRU H, LEI W, et al. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;877:173090.
[26] 朱健, 孙凯强, 史建刚. 巨噬细胞与椎间盘退变的研究进展[J]. 第二军医大学学报,2019,40(12):1350-1355.
[27] YANG H, LIU B, LIU Y, et al. Secreted Factors from Intervertebral Disc Cells and Infiltrating Macrophages Promote Degenerated Intervertebral Disc Catabolism. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019;44(9):E520-E529.
[28] 张艺翊, 何伟. 基于数据挖掘探讨名老中医李同生治疗退变性腰椎管狭窄症的用药规律[J]. 湖北中医杂志,2022,44(2):59-63.
[29] 何伟, 李博宁. 李同生名老中医治疗腰椎管狭窄症经验总结[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2015,23(11):67-69.
[30] 鄢来军, 颜浪辉, 林庆宾, 等. 通督活血汤对大鼠脊髓损伤后内质网应激信号表达的影响[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2020,28(5):1-4.
[31] 颜浪辉, 鄢来军, 林庆宾, 等. 通督活血汤对大鼠急性脊髓损伤后炎症反应影响[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报,2020,22(4):51-54.
[32] HE S, ZHANG Y, ZHOU Z, et al. Similarity and difference between aging and puncture-induced intervertebral disc degeneration. J Orthop Res. 2022;40(11):2565-2575. |