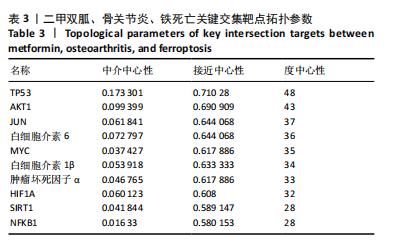
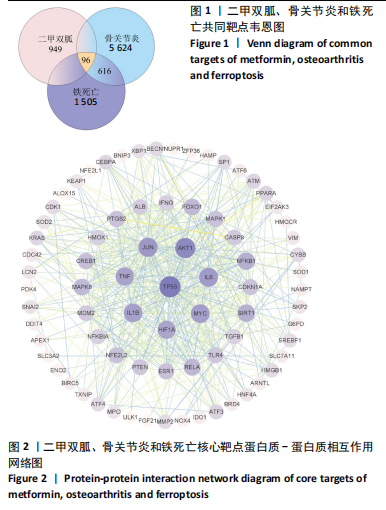
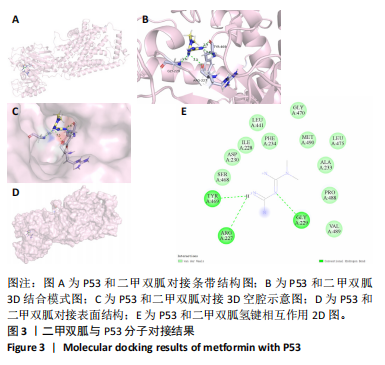
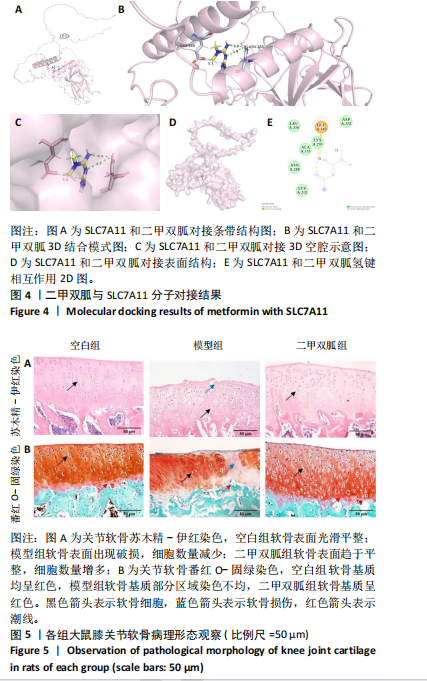
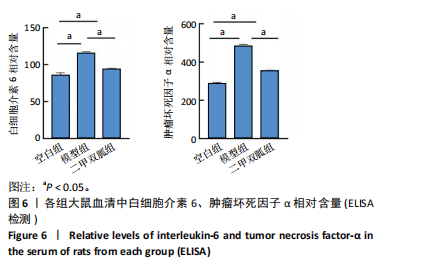
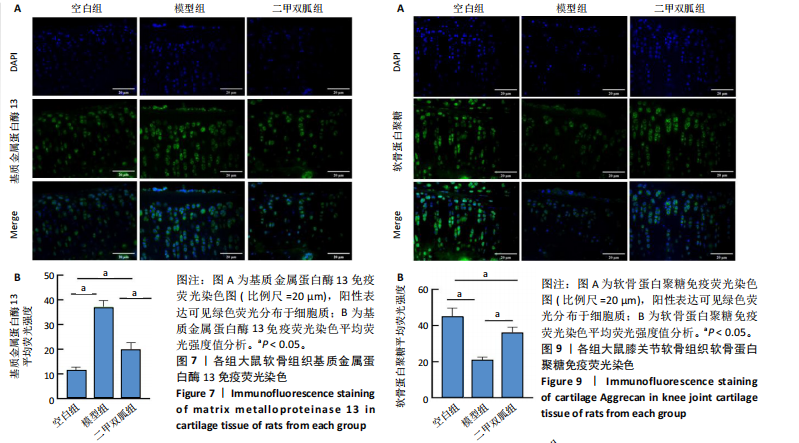
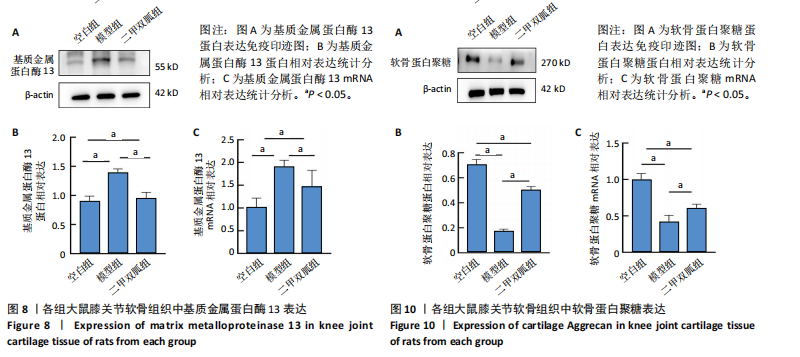
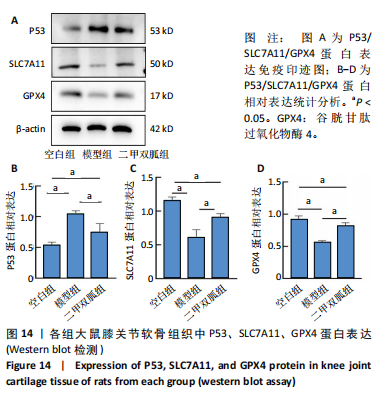
[1] TONG L, YU H, HUANG X, et al. Current understanding of osteoarthritis pathogenesis and relevant new approaches. Bone Res. 2022;10(1):60.
[2] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393(10182):1745-1759.
[3] WANG H, SU J, YU M, et al. PGC-1α in osteoarthritic chondrocytes: From mechanism to target of action. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1169019.
[4] KUSWANTO W, BAKER MC. Repurposing drugs for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2024;32(8):886-895.
[5] ARODA VR, KNOWLER WC, CRANDALL JP, et al. Metformin for diabetes prevention: insights gained from the Diabetes Prevention Program/Diabetes Prevention Program Outcomes Study. Diabetologia. 2017;60(9):1601-1611.
[6] WANG C, YANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Protective effects of metformin against osteoarthritis through upregulation of SIRT3-mediated PINK1/Parkin-dependent mitophagy in primary chondrocytes. Biosci Trends. 2019;12(6):605-612.
[7] TERKELTAUB R, YANG B, LOTZ M, et al. Chondrocyte AMP-activated protein kinase activity suppresses matrix degradation responses to proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor α. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(7):1928-1937.
[8] YAO X, SUN K, YU S, et al. Chondrocyte ferroptosis contribute to the progression of osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. 2020;27:33-43.
[9] XIE Y, HOU W, SONG X, et al. Ferroptosis: process and function. Cell Death Differ. 2016;23(3):369-379.
[10] ZOU Z, HU W, KANG F, et al. Interplay between lipid dysregulation and ferroptosis in chondrocytes and the targeted therapy effect of metformin on osteoarthritis. J Adv Res. 2024. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.04.012.
[11] YI Y, ZHANG W, YI J, et al. Role of p53 Family Proteins in Metformin Anti-Cancer Activities. J Cancer. 2019;10(11):2434-2442.
[12] LIU Y, GU W. p53 in ferroptosis regulation: the new weapon for the old guardian. Cell Death Differ. 2022;29(5):895-910.
[13] JIANG L, KON N, LI T, et al. Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated activity during tumour suppression. Nature. 2015;520(7545):57-62.
[14] KANG R, KROEMER G, TANG D. The tumor suppressor protein p53 and the ferroptosis network. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;133:162-168.
[15] YAN J, FENG G, MA L, et al. Metformin alleviates osteoarthritis in mice by inhibiting chondrocyte ferroptosis and improving subchondral osteosclerosis and angiogenesis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):333.
[16] LI J, ZHANG B, LIU WX, et al. Metformin limits osteoarthritis development and progression through activation of AMPK signalling. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(5):635-645.
[17] 罗臻,李宏栩,卢启贵,等.红姜提取物保护早期膝骨关节炎模型大鼠的关节软骨[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(32):5155-5161.
[18] 徐田杰,樊佳欣,郭小玲,等.二甲双胍抑制PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路保护骨关节炎模型大鼠关节软骨[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(5):1003-1012.
[19] GEZER HH, OSTOR A. What is new in pharmacological treatment for osteoarthritis? Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2023;37(2):101841.
[20] PERRUCCIO AV, YOUNG JJ, WILFONG JM, et al. Osteoarthritis year in review 2023: Epidemiology & therapy. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2024;32(2):159-165.
[21] FLORY J, LIPSKA K. Metformin in 2019. JAMA. 2019;321(19):1926-1927.
[22] TRIGGLE CR, MOHAMMED I, BSHESH K, et al. Metformin: Is it a drug for all reasons and diseases? Metabolism. 2022;133:155223.
[23] LV Z, GUO Y. Metformin and Its Benefits for Various Diseases. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11:191.
[24] LI D, RUAN G, ZHANG Y, et al. Metformin attenuates osteoarthritis by targeting chondrocytes, synovial macrophages and adipocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023;62(4):1652-1661.
[25] NA HS, KWON JY, LEE SY, et al. Metformin Attenuates Monosodium-Iodoacetate-Induced Osteoarthritis via Regulation of Pain Mediators and the Autophagy-Lysosomal Pathway. Cells. 2021;10(3):681.
[26] LAI FTT, YIP BHK, HUNTER DJ, et al. Metformin use and the risk of total knee replacement among diabetic patients: a propensity-score-matched retrospective cohort study. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):11571.
[27] FENG X, PAN J, LI J, et al. Metformin attenuates cartilage degeneration in an experimental osteoarthritis model by regulating AMPK/mTOR. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(2):1087-1103.
[28] FUJII Y, LIU L, YAGASAKI L, et al. Cartilage Homeostasis and Osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(11):6316.
[29] GAO Y, LIU S, HUANG J, et al. The ECM-cell interaction of cartilage extracellular matrix on chondrocytes. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:648459.
[30] HOLLANDER AP, DICKINSON SC, KAFIENAH W. Stem cells and cartilage development: complexities of a simple tissue. Stem Cells. 2010;28(11):1992-1996.
[31] KAPOOR M, MARTEL-PELLETIER J, LAJEUNESSE D, et al. Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011; 7(1):33-42.
[32] ZHENG W, ZHOU T, ZHANG Y, et al. Simplified α2-macroglobulin as a TNF-α inhibitor for inflammation alleviation in osteoarthritis and myocardial infarction therapy. Biomaterials. 2023;301:122247.
[33] YU Y, KIM SM, PARK K, et al. Therapeutic Nanodiamonds Containing Icariin Ameliorate the Progression of Osteoarthritis in Rats. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(21):15977.
[34] RAPP AE, ZAUCKE F. Cartilage extracellular matrix-derived matrikines in osteoarthritis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2023;324(2):C377-C394.
[35] ROUGHLEY PJ, MORT JS. The role of aggrecan in normal and osteoarthritic cartilage. J Exp Orthop. 2014;1(1):8.
[36] HU Q, ECKER M. Overview of MMP-13 as a Promising Target for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1742.
[37] JIANG X, STOCKWELL BR, CONRAD M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22(4):266-282.
[38] LIU MR, ZHU WT, PEI DS. System Xc-: a key regulatory target of ferroptosis in cancer. Invest New Drugs. 2021;39(4):1123-1131.
[39] WU X, LI Y, ZHANG S, et al. Ferroptosis as a novel therapeutic target for cardiovascular disease. Theranostics. 2021;11(7):3052-3059.
[40] LIU J, KANG R, TANG D. Signaling pathways and defense mechanisms of ferroptosis. FEBS J. 2022;289(22):7038-7050.
[41] LIANG D, MINIKES AM, JIANG X. Ferroptosis at the intersection of lipid metabolism and cellular signaling. Mol Cell. 2022;82(12):2215-2227.
[42] WANG S, LI W, ZHANG P, et al. Mechanical overloading induces GPX4-regulated chondrocyte ferroptosis in osteoarthritis via Piezo1 channel facilitated calcium influx. J Adv Res. 2022;41:63-75.
[43] MIAO Y, CHEN Y, XUE F, et al. Contribution of ferroptosis and GPX4’s dual functions to osteoarthritis progression. EBioMedicine. 2022;76:103847.
[44] ZHANG X, HOU L, GUO Z, et al. Lipid peroxidation in osteoarthritis: focusing on 4-hydroxynonenal, malondialdehyde, and ferroptosis. Cell Death Discov. 2023;9(1):320.
[45] XU R, WANG W, ZHANG W. Ferroptosis and the bidirectional regulatory factor p53. Cell Death Discov. 2023;9(1):197.
[46] KOPPULA P, ZHUANG L, GAN B. Cystine transporter SLC7A11/xCT in cancer: ferroptosis, nutrient dependency, and cancer therapy. Protein Cell. 2021;12(8):599-620.
[47] GONG Z, WANG Y, LI L, et al. Cardamonin alleviates chondrocytes inflammation and cartilage degradation of osteoarthritis by inhibiting ferroptosis via p53 pathway. Food Chem Toxicol. 2023;174:113644.
[48] FAN Z, WIRTH AK, CHEN D, et al. Nrf2-Keap1 pathway promotes cell proliferation and diminishes ferroptosis. Oncogenesis. 2017;6(8):e371.
[49] INGOLD I, BERNDT C, SCHMITT S, et al. Selenium Utilization by GPX4 Is Required to Prevent Hydroperoxide-Induced Ferroptosis. Cell. 2018;172(3):409-422.e21.
[50] LIM JKM, DELAIDELLI A, MINAKER SW, et al. Cystine/glutamate antiporter xCT (SLC7A11) facilitates oncogenic RAS transformation by preserving intracellular redox balance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(19):9433-9442.
[51] XIAO J, LUO C, LI A, et al. Icariin inhibits chondrocyte ferroptosis and alleviates osteoarthritis by enhancing the SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024;133:112010.
[52] ZENG C, LIN J, ZHANG K, et al. SHARPIN promotes cell proliferation of cholangiocarcinoma and inhibits ferroptosis via p53/SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling. Cancer Sci. 2022;113(11):3766-3775. |