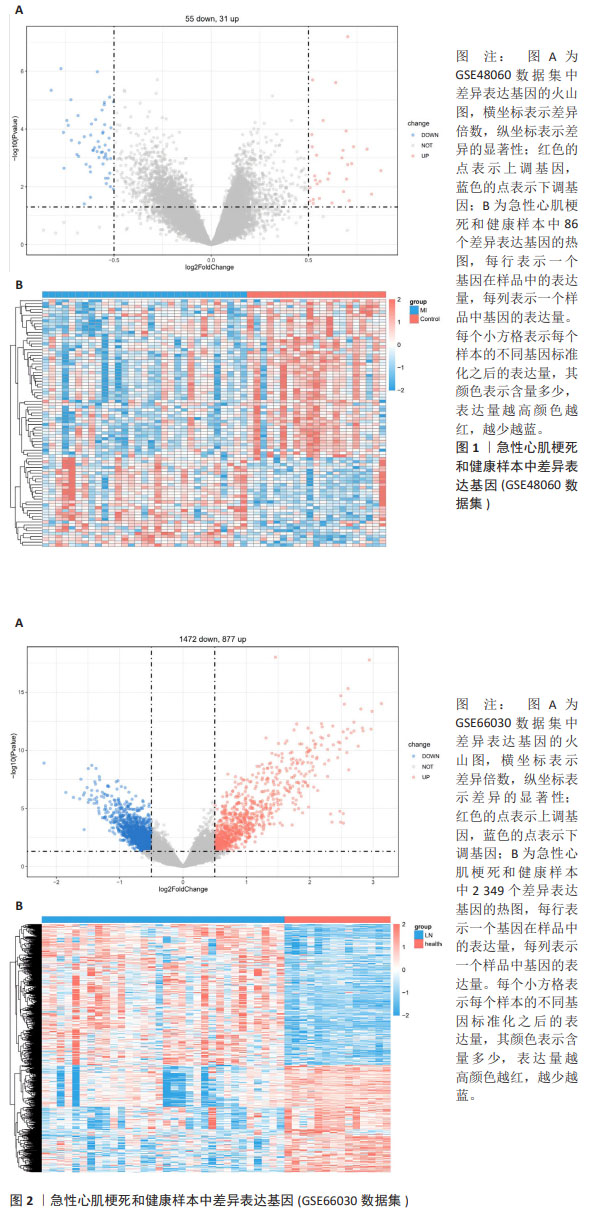
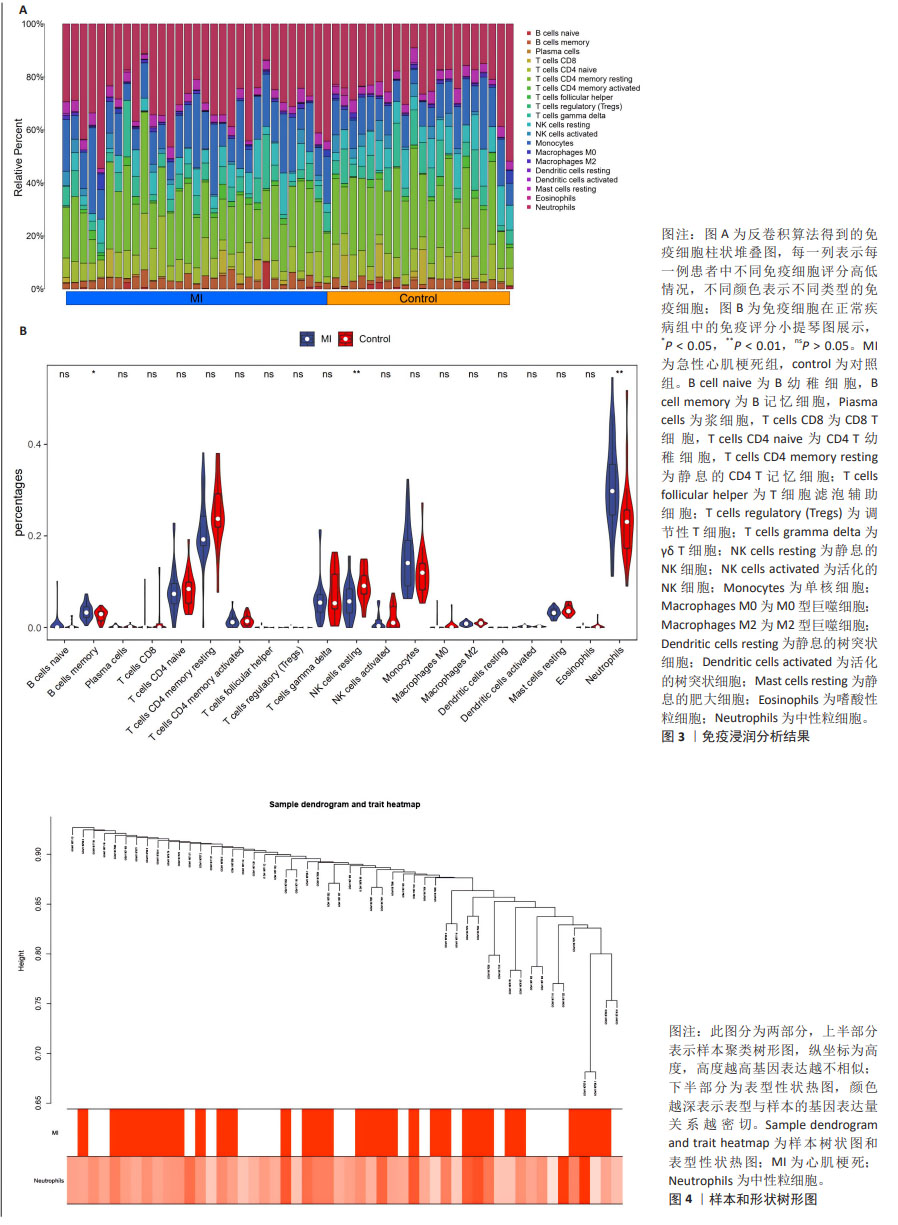
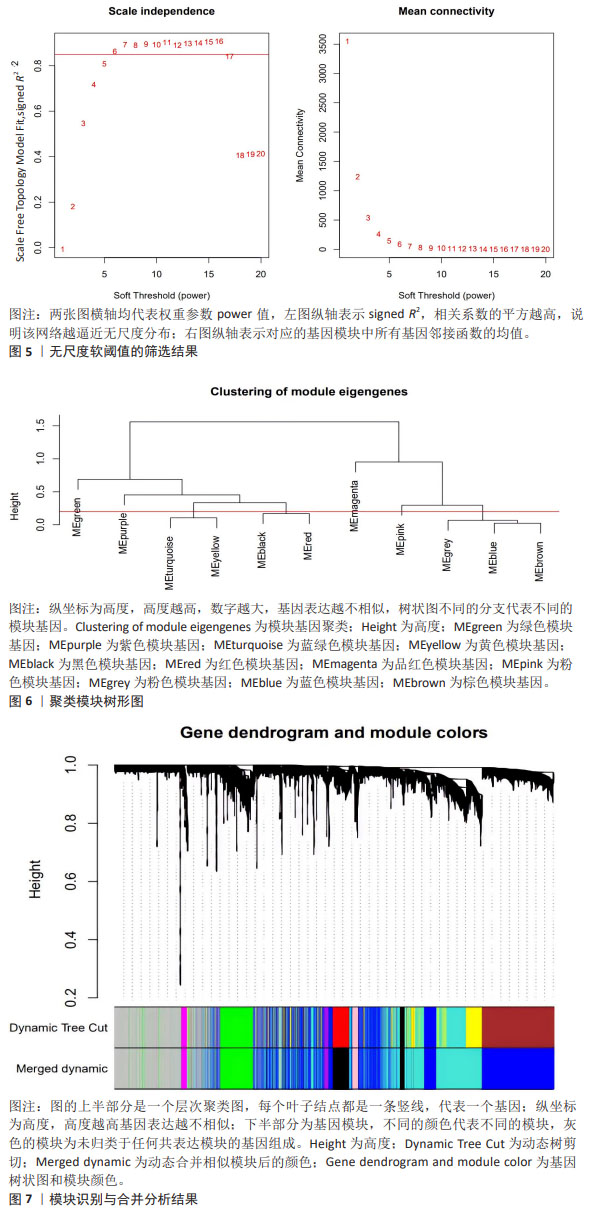
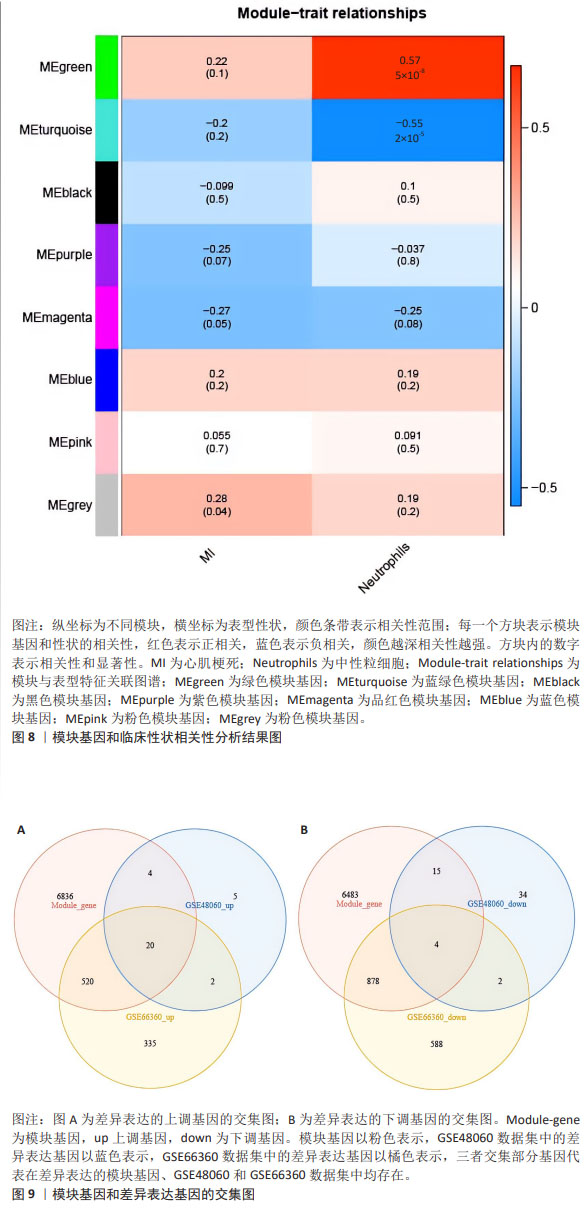
[1] MEHTA LS, BECKIE TM, DEVON HA, et al. Acute myocardial infarction in women: a scientific statement from the american heart association. Circulation. 2016;133(9):916-947.
[2] PAGIDIPATI NJ, GAZIANO TA. Estimating deaths from cardiovascular disease: a review of global methodologies of mortality measurement. Circulation. 2013; 127(6):749-756.
[3] ALAOUR B, LIEW F, KAIER TE. Cardiac Troponin -diagnostic problems and impact on cardiovascular disease. Ann Med. 2018; 50(8):655-665.
[4] THYGESEN K, ALPERT JS, JAFFE AS, et al. Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction (2018). Circulation. 2018;138(20):e618-e651.
[5] CLERICO A, ZANINOTTO M, PLEBANI M. Rapid rule-in and rule-out protocols of acute myocardial infarction using hs-cTnI and hs-cTnT methods. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2024;62(2):213-217.
[6] PRABHU SD, FRANGOGIANNIS NG. The biological basis for cardiac repair after myocardial infarction: from inflammation to fibrosis. Circ Res. 2016;119(1):91-112.
[7] EL KM, SHI H, VUONG S, et al. Nitroxides mitigate neutrophil-mediated damage to the myocardium after experimental myocardial infarction in rats. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7650.
[8] DELEON-PENNELL KY, TIAN Y, ZHANG B, et al. CD36 Is a Matrix metalloproteinase-9 substrate that stimulates neutrophil apoptosis and removal during cardiac remodeling. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2016; 9(1):14-25.
[9] HORCKMANS M, RING L, DUCHENE J, et al. Neutrophils orchestrate post-myocardial infarction healing by polarizing macrophages towards a reparative phenotype. Eur Heart J. 2017;38(3):187-197.
[10] CURAJ A, SCHUMACHER D, RUSU M, et al. Neutrophils modulate fibroblast function and promote healing and scar formation after murine myocardial infarction. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(10):3685.
[11] SREEJIT G, ABDEL-LATIF A, ATHMANATHAN B, et al. Neutrophil-derived s100a8/a9 amplify granulopoiesis after myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2020;141(13): 1080-1094.
[12] CHRISTIA P, BUJAK M, GONZALEZ-QUESADA C, et al. Systematic characterization of myocardial inflammation, repair, and remodeling in a mouse model of reperfused myocardial infarction. J Histochem Cytochem. 2013;61(8):555-570.
[13] SWIRSKI FK, NAHRENDORF M. Leukocyte behavior in atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, and heart failure. Science. 2013;339(6116):161-166.
[14] KOLOGRIVOVA I, SHTATOLKINA M, SUSLOVA T, et al. Cells of the immune system in cardiac remodeling: main players in resolution of inflammation and repair after myocardial infarction. Front Immunol. 2021;12:664457.
[15] ZHOU X, ZHANG C, WU X, et al. Dusp6 deficiency attenuates neutrophil-mediated cardiac damage in the acute inflammatory phase of myocardial infarction. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):6672.
[16] RIDKER PM, MACFADYEN JG, GLYNN RJ, et al. Inhibition of interleukin-1beta by canakinumab and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71(21):2405-2414.
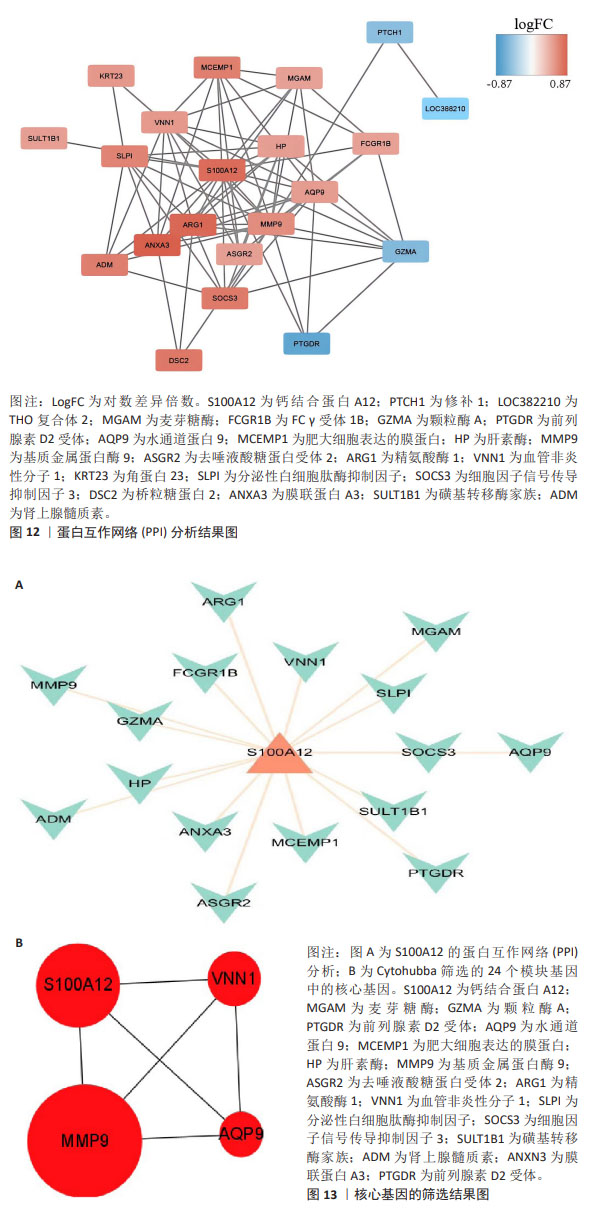
[17] ZHENG PF, ZOU QC, CHEN LZ, et al. Identifying patterns of immune related cells and genes in the peripheral blood of acute myocardial infarction patients using a small cohort. J Transl Med. 2022;20(1):321.
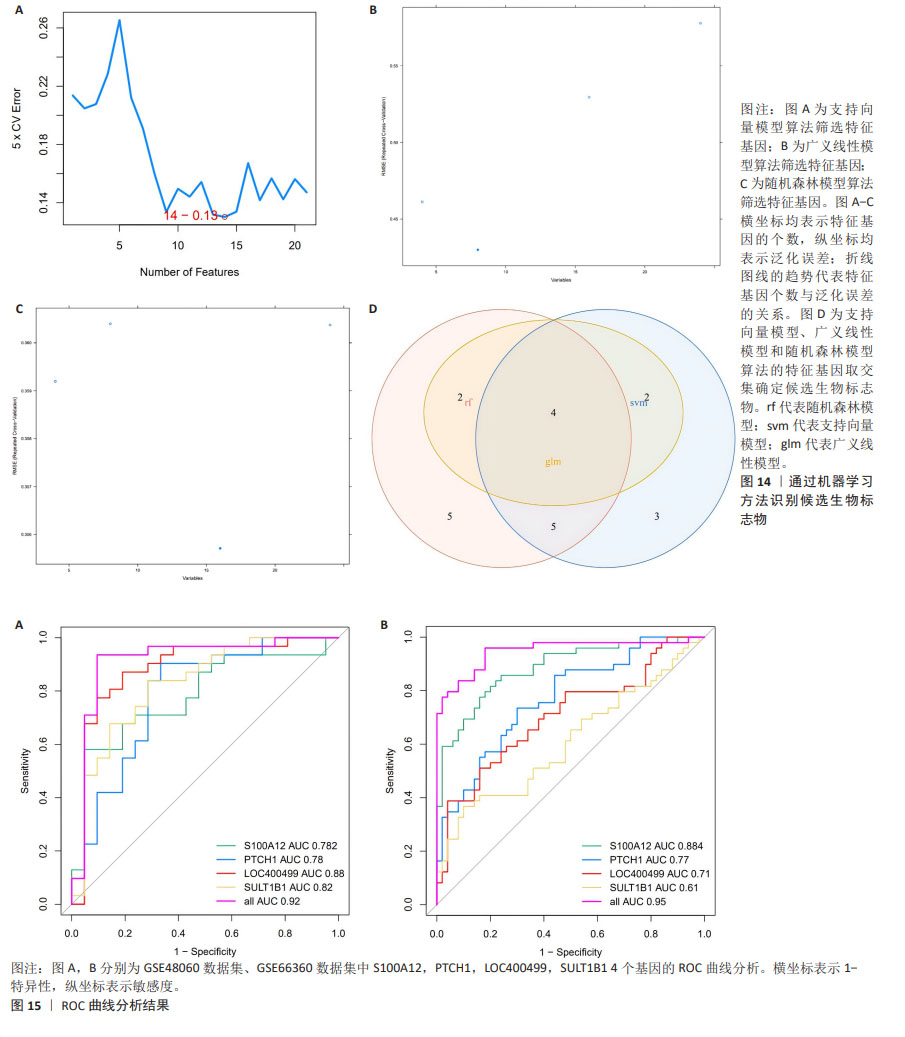
[18] TORUN FM, VIRREIRA WS, DOLL S, et al. Transparent exploration of machine learning for biomarker discovery from proteomics and omics data. J Proteome Res. 2023;22(2):359-367.
[19] MIAO M, CAO S, TIAN Y, et al. Potential diagnostic biomarkers: 6 cuproptosis- and ferroptosis-related genes linking immune infiltration in acute myocardial infarction. Genes Immun. 2023;24(4):159-170.
[20] ALGOET M, JANSSENS S, HIMMELREICH U, et al. Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and the influence of inflammation. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2023;33(6):357-366.
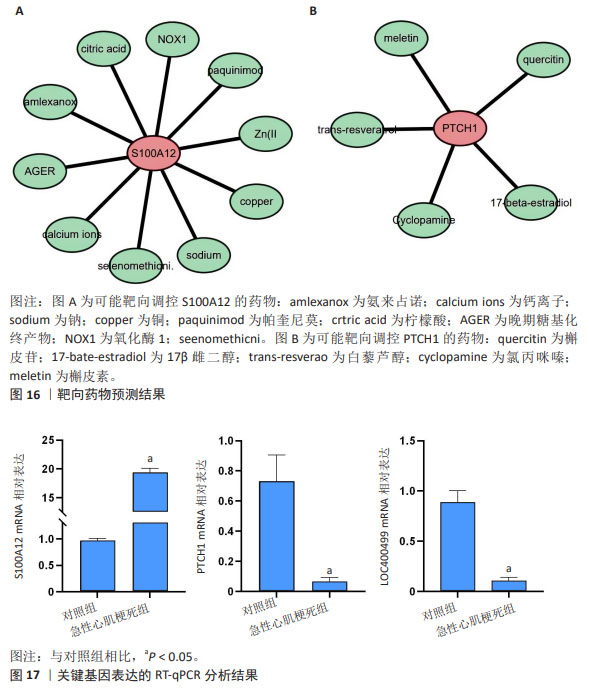
[21] CARVALHO A, LU J, FRANCIS JD, et al. S100A12 in digestive diseases and health: a scoping review. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2020;2020:2868373.
[22] ZHAI H, HUANG L, GONG Y, et al. Human plasma transcriptome implicates dysregulated s100a12 expression: a strong, early-stage prognostic factor in st-segment elevated myocardial infarction: bioinformatics analysis and experimental verification. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:874436.
[23] ZHANG X, CHENG M, GAO N, et al. Utility of S100A12 as an early biomarker in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:747511.
[24] ELLSWORTH DL, CROFT DJ, WEYANDT J, et al. Intensive cardiovascular risk reduction induces sustainable changes in expression of genes and pathways important to vascular function. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2014;7(2):151-160.
[25] LI Q, DENG G, GAO Y. S100 calcium-binding protein A12 knockdown ameliorates hypoxia-reoxygenation-induced inflammation and apoptosis in human cardiomyocytes by regulating caspase-4-mediated non-classical pyroptosis. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2022;41(4):287-297.
[26] HASANOVIC A, MUS-VETEAU I. Targeting the multidrug transporter ptch1 potentiates chemotherapy efficiency. Cells. 2018;7(8): 107.
[27] DOHENY D, MANORE SG, WONG GL, et al. Hedgehog signaling and truncated GLI1 in cancer. Cells. 2020;9(9):2114.
[28] POLA R, LING LE, SILVER M, et al. The morphogen Sonic hedgehog is an indirect angiogenic agent upregulating two families of angiogenic growth factors. Nat Med. 2001;7(6):706-711.
[29] LI SH, ZHANG YY, SUN YL, et al. Inhibition of microRNA-802-5p inhibits myocardial apoptosis after myocardial infarction via Sonic Hedgehog signaling pathway by targeting PTCH1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021;25(1):326-334.
[30] LAVINE KJ, KOVACS A, ORNITZ DM. Hedgehog signaling is critical for maintenance of the adult coronary vasculature in mice. J Clin Invest. 2008; 118(7):2404-2414.
[31] YAN L, BJORK P, BUTUC R, et al. Beneficial effects of quinoline-3-carboxamide (ABR-215757) on atherosclerotic plaque morphology in S100A12 transgenic ApoE null mice. Atherosclerosis. 2013;228(1): 69-79.
[32] ALBADRANI GM, BINMOWYNA MN, BIN-JUMAH MN, et al. Quercetin prevents myocardial infarction adverse remodeling in rats by attenuating TGF-beta1/Smad3 signaling: different mechanisms of action. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021;28(5):2772-2782.
[33] MO C, HAN H, TANG X, et al. Protein kinase TBK1/IKKepsilon inhibitor Amlexanox improves cardiac function after acute myocardial infarction in rats. Panminerva Med. 2023;65(3):343-350. |