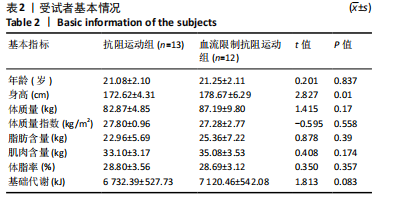
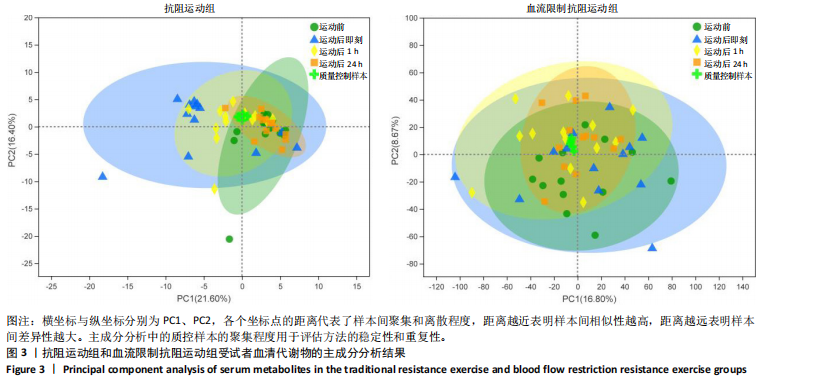
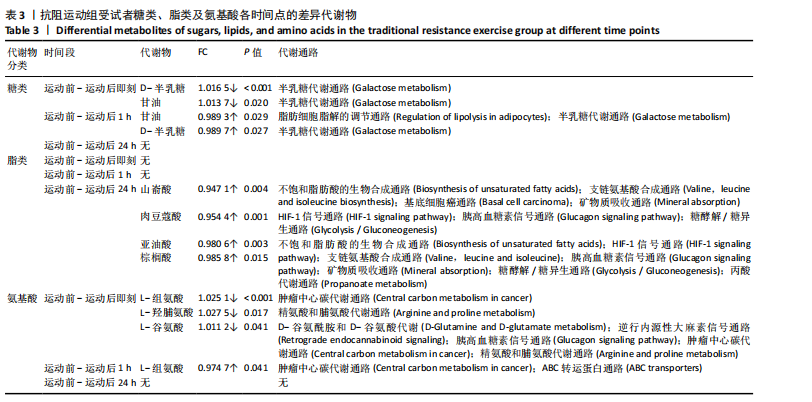
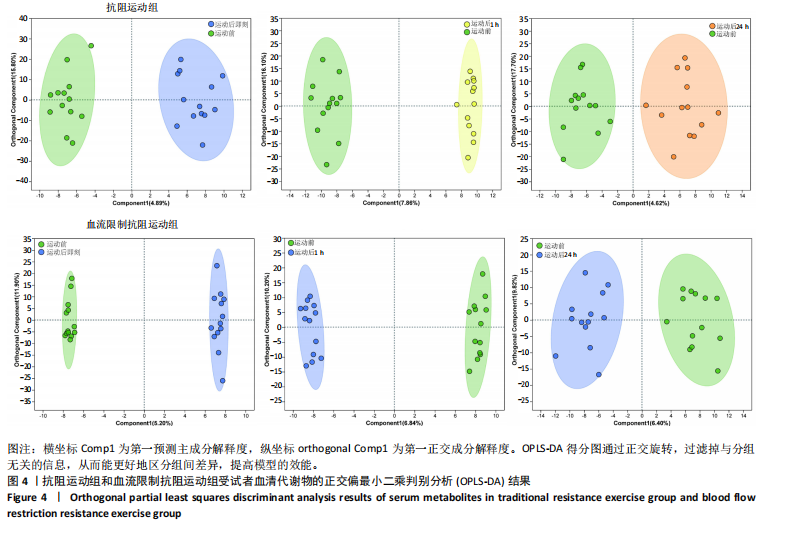
[1] 陈伟,江华.2016年中国超重/肥胖医学营养治疗专家共识解读[J].中国实用内科杂志,2017,37(5):430-433.
[2] LANDECHO MF, MARIN-OTO M, RECALDE-ZAMACONA B, et al. Obesity as an adipose tissue dysfunction disease and a risk factor for infections - Covid-19 as a case study. Eur J Intern Med. 2021;91:3-9.
[3] SAGHAFI-ASL M, ALIASGHARZADEH S, ASGHARI-JAFARABADI M. Factors influencing weight management behavior among college students: An application of the Health Belief Model. PLoS One. 2020;15(2):e0228058.
[4] 王祥全,姜勇,冯志钢,等.国外运动科学领域减肥研究的热点内容及发展趋向[J].武汉体育学院学报,2020,54(6):73-79.
[5] 孟怡秀.不同训练方法减脂效果的比较与机理分析[J].体育科技文献通报, 2021,29(6):174-176.
[6] MINNITI MC, STATKEVICH AP, KELLY RL, et al. The Safety of Blood Flow Restriction Training as a Therapeutic Intervention for Patients With Musculoskeletal Disorders: A Systematic Review. Am J Sports Med. 2020;48(7):1773-1785.
[7] SEGAL N, DAVIS MD, MIKESKY AE. Efficacy of Blood Flow-Restricted Low-Load Resistance Training For Quadriceps Strengthening in Men at Risk of Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2015;6(3):160-167.
[8] WANG HN, CHEN Y, CHENG L, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Blood Flow Restriction Training in Patients With Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2022;74(1): 89-98.
[9] 雷森林,张明辉,马春莲,等.加压抗阻训练的肌肉效应、量效关系及生理机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(26):4254-4264.
[10] LIXANDRÃO ME, UGRINOWITSCH C, BERTON R, et al. Magnitude of Muscle Strength and Mass Adaptations Between High-Load Resistance Training Versus Low-Load Resistance Training Associated with Blood-Flow Restriction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2018;48(2):361-378.
[11] SAATMANN N, ZAHARIA OP, LOENNEKE JP, et al. Effects of Blood Flow Restriction Exercise and Possible Applications in Type 2 Diabetes. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2021;32(2):106-117.
[12] SU Y, WANG F, WANG M, et al. Effects of blood flow restriction training on muscle fitness and cardiovascular risk of obese college students. Front Physiol. 2024;14:1252052.
[13] SAKAGUCHI CA, NIEMAN DC, SIGNINI EF, et al. Metabolomics-Based Studies Assessing Exercise-Induced Alterations of the Human Metabolome: A Systematic Review. Metabolites. 2019;9(8):164.
[14] FATOUROS IG, CHATZINIKOLAOU A, TOURNIS S, et al. Intensity of resistance exercise determines adipokine and resting energy expenditure responses in overweight elderly individuals. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(12):2161-2167.
[15] SMILIOS I, TSOUKOS P, ZAFEIRIDIS A, et al. Hormonal responses after resistance exercise performed with maximum and submaximum movement velocities. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2014;39(3):351-357.
[16] WISHART DS. Metabolomics for Investigating Physiological and Pathophysiological Processes. Physiol Rev. 2019;99(4):1819-1875.
[17] 郭新明,吴丽君,向欢.间歇性大强度运动前后人体血清代谢组学特征[J].中国运动医学杂志,2019,38(9):755-761.
[18] 李佳.急性大强度运动前后人体血液代谢组学特征的研究[D].太原:山西大学,2017.
[19] COHEN J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Cambrideg: Academic Press, 2013.
[20] AMRHEIN V, GREENLAND S, MCSHANE B. Scientists rise up against statistical significance. Nature. 2019;567(7748):305-307.
[21] BIAU DJ, KERNÉIS S, PORCHER R. Statistics in brief: the importance of sample size in the planning and interpretation of medical research. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(9):2282-2288.
[22] 中华医学会内分泌学分会,中华中医药学会糖尿病分会,中国医师协会外科医师分会肥胖和糖尿病外科医师委员会,等.基于临床的肥胖症多学科诊疗共识(2021年版)[J].中华消化外科杂志,2021,20(11):1137-1152.
[23] BULL FC, AL-ANSARI SS, BIDDLE S, et al. World Health Organization 2020 guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Br J Sports Med. 2020; 54(24):1451-1462.
[24] BORG G. Borg’s Perceived Exertion and Pain Scales. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics, 1998.
[25] AMERICAN COLLEGE OF SPORTS MEDICINE. ACSM’s exercise testing and prescription[M]. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams, 2023.
[26] (美)哈夫, (美)特里普利特.NSCA-CSCS美国国家体能协会体能教练认证指南[M]. 北京:人民邮电出版社,2021.
[27] 魏佳,李博,冯连世,等.血流限制训练的方法学因素及潜在安全性问题[J].中国体育科技,2019,55(3):3-12.
[28] MADARAME H, NEYA M, OCHI E, et al. Cross-transfer effects of resistance training with blood flow restriction. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2008;40(2):258-263.
[29] LOENNEKE JP, FAHS CA, ROSSOW LM, et al. Effects of cuff width on arterial occlusion: implications for blood flow restricted exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2012;112(8):2903-2912.
[30] REN Y, YU G, SHI C, et al. Majorbio Cloud: A one-stop, comprehensive bioinformatic platform for multiomics analyses. Imeta. 2022;1(2):e12.
[31] MORVILLE T, SAHL RE, MORITZ T, et al. Plasma Metabolome Profiling of Resistance Exercise and Endurance Exercise in Humans. Cell Rep. 2020;33(13):108554.
[32] KNUIMAN P, HOPMAN MT, MENSINK M. Glycogen availability and skeletal muscle adaptations with endurance and resistance exercise. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2015;12:59.
[33] 崔益玮,王利敏,戴志远,等.脂质组学在食品科学领域的研究现状与展望[J].中国食品学报,2019,19(1):262-270.
[34] 倪致雅,唐苗苗,夏瑢.基于色谱质谱联用技术的中医痰湿体质的代谢组学研究[J].中华中医药学刊,2017,35(4):918-923.
[35] MILLER JM, COYLE EF, SHERMAN WM, et al. Effect of glycerol feeding on endurance and metabolism during prolonged exercise in man. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1983;15(3):237-242.
[36] VAN ROSENDAL SP, OSBORNE MA, FASSETT RG, et al. Physiological and performance effects of glycerol hyperhydration and rehydration. Nutr Rev. 2009; 67(12):690-705.
[37] YOON SY, AHN D, JI YH, et al. Linoleic acid exerts antidiabetic effects by inhibiting protein tyrosine phosphatases associated with insulin resistance. J Funct Foods. 2021;83:104532.
[38] MARANGONI F, AGOSTONI C, BORGHI C, et al. Dietary linoleic acid and human health: Focus on cardiovascular and cardiometabolic effects. Atherosclerosis. 2020;292:90-98.
[39] YANG L, GUAN G, LEI L, et al. Palmitic acid induces human osteoblast-like Saos-2 cell apoptosis via endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2018;23(6):1283-1294.
[40] AMINE H, BENOMAR Y, TAOUIS M. Palmitic acid promotes resistin-induced insulin resistance and inflammation in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):5427.
[41] 刘如灿,金青哲,单良,等.山嵛酸低热量油脂的可用热量及安全性评价[J].中国粮油学报,2011,26(8):26-30.
[42] IWATA K, SAKAI H, TAKAHASHI D, et al. Myristic acid specifically stabilizes diacylglycerol kinase δ protein in C2C12 skeletal muscle cells. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2019;1864(7):1031-1038.
[43] SAKAI H, MATSUMOTO KI, URANO T, et al. Myristic acid selectively augments β-tubulin levels in C2C12 myotubes via diacylglycerol kinase δ. FEBS Open Bio. 2022;12(10):1788-1796.
[44] TREEDE I, BRAUN A, SPARLA R, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of phosphatidylcholine. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(37):27155-27164.
[45] LAGACE TA. Phosphatidylcholine: Greasing the Cholesterol Transport Machinery. Lipid Insights. 2016;8(Suppl 1):65-73.
[46] XIAO D, CHANG W. Phosphatidylserine in Diabetes Research. Mol Pharm. 2023; 20(1):82-89.
[47] TIAN S, ZHAO Y, QIAN L, et al. DHA-enriched phosphatidylserine alleviates high fat diet-induced jejunum injury in mice by modulating gut microbiota. Food Funct. 2023;14(3):1415-1429.
[48] WILLIS SJ, MILLET GP, BORRANI F. Insights for Blood Flow Restriction and Hypoxia in Leg Versus Arm Submaximal Exercise. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2020;15(5):714-719.
[49] 吴鹤云,张悦,蒋帅,等.木糖和葡萄糖共发酵生产L-组氨酸[J].食品与发酵工业,2020,46(16):115-120.
[50] BROSNAN ME, BROSNAN JT. Histidine Metabolism and Function. J Nutr. 2020; 150(Suppl 1):2570S-2575S.
[51] VICENT D, GARCIA-MARTINEZ JA, VILLANUEVA-PEÑACARRILLO ML, et al. Stimulation of insulin secretion and potentiation of glibenclamide-induced insulin release by the dimethyl ester of glutamic acid in anaesthetized rats. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1995;27(1):27-30.
[52] POORTMANS JR, CARPENTIER A, PEREIRA-LANCHA LO, et al. Protein turnover, amino acid requirements and recommendations for athletes and active populations. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2012;45(10):875-890.
[53] 李宝成,张怡,熊正英.补充酪氨酸对运动能力影响的可能机制[J].北京体育大学学报,2007(1):68-70.
[54] 贾青慧,陈莉,王珍,等.薏米及薏米糠氨基酸组成分析及营养评价[J].食品工业,2017,38(4):185-188.
[55] 李登光,倪伟,高伟.天门冬氨酸钾镁消除运动疲劳的作用机制[J].首都体育学院学报,2005(6):52-54. |