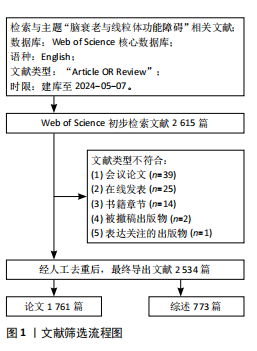
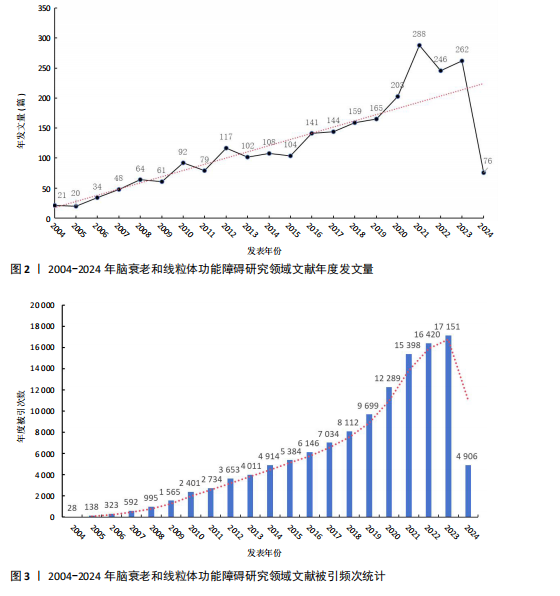
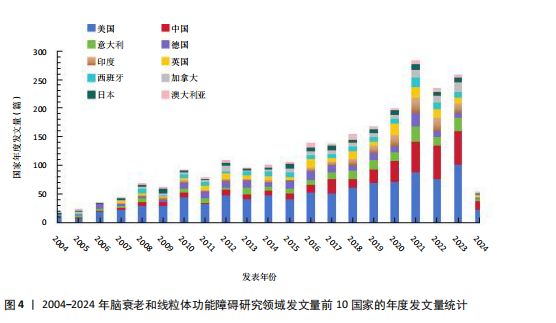
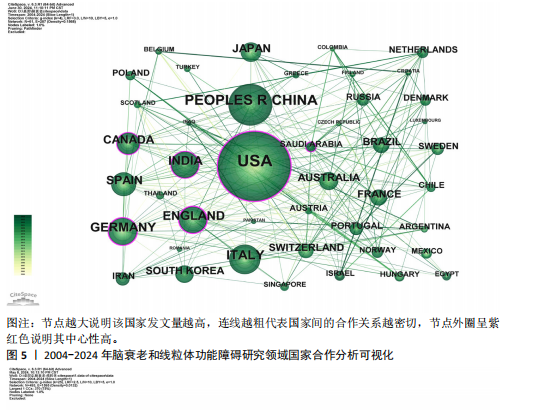
[1] CAI Y, SONG W, LI J, et al. The landscape of aging. Sci China Life Sci. 2022;65(12):2354-2454.
[2] KENNEDY BK, BERGER SL, BRUNET A, et al. Geroscience: linking aging to chronic disease. Cell. 2014;159(4):709-713.
[3] 原新,范文清.人口负增长与老龄化交汇时代的形势与应对[J].南开学报(哲学社会科学版),2022(6):1-10.
[4] 原新.全球人口负增长时间可能提前至2065年[J].人口与健康,2020(11):13-16.
[5] 郑真真.从全球人口变化看中国人口负增长[J].人口研究,2023,47(2):3-10.
[6] BLINKOUSKAYA Y, CAÇOILO A, GOLLAMUDI T, et al. Brain aging mechanisms with mechanical manifestations. Mech Ageing Dev. 2021;200:111575.
[7] HOU Y, DAN X, BABBAR M, et al. Ageing as a risk factor for neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019;15(10):565-581.
[8] CARDOSO AL, FERNANDES A, AGUILAR-PIMENTEL JA, et al. Towards frailty biomarkers: Candidates from genes and pathways regulated in aging and age-related diseases. Ageing Res Rev. 2018;47: 214-277.
[9] WANG H, LAUTRUP S, CAPONIO D, et al. DNA Damage-Induced Neurodegeneration in Accelerated Ageing and Alzheimer’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(13):6748.
[10] CHAN DC. Mitochondrial Dynamics and Its Involvement in Disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 2020;15:235-259.
[11] GRIMM A, ECKERT A. Brain aging and neurodegeneration: from a mitochondrial point of view. J Neurochem. 2017;143(4):418-431.
[12] FERNANDEZ-MARCOS PJ, AUWERX J. Regulation of PGC-1α, a nodal regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;93(4):884S-890S.
[13] GAO F, ZHANG J. Mitochondrial quality control and neurodegenerative diseases. Neuronal Signal. 2018;2(4):NS20180062.
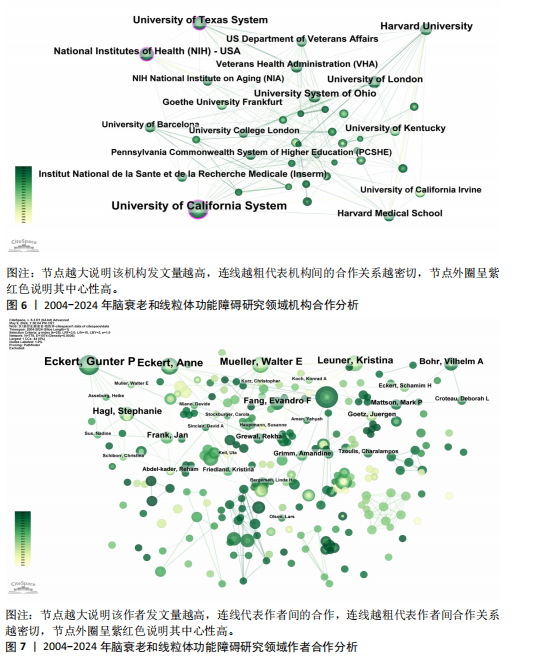
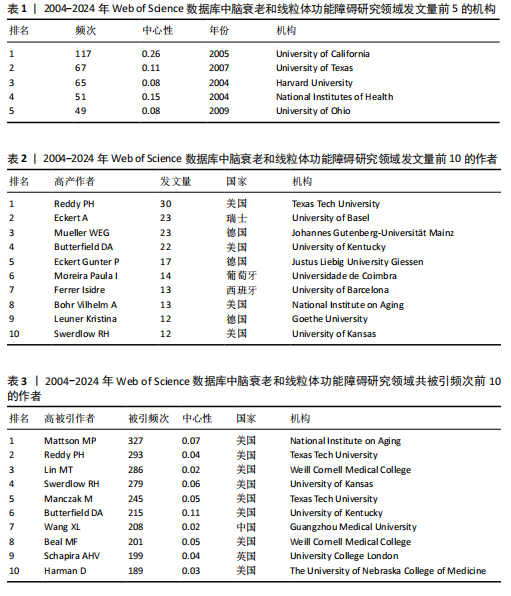
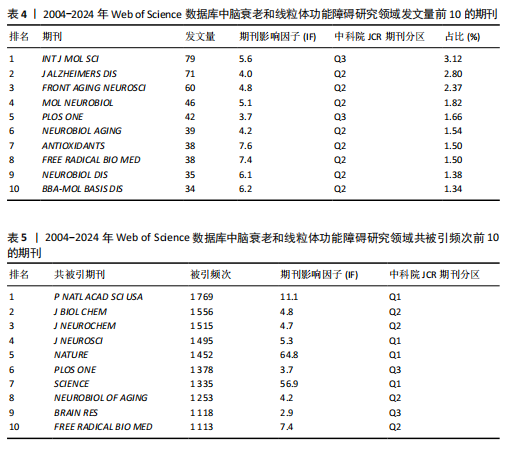
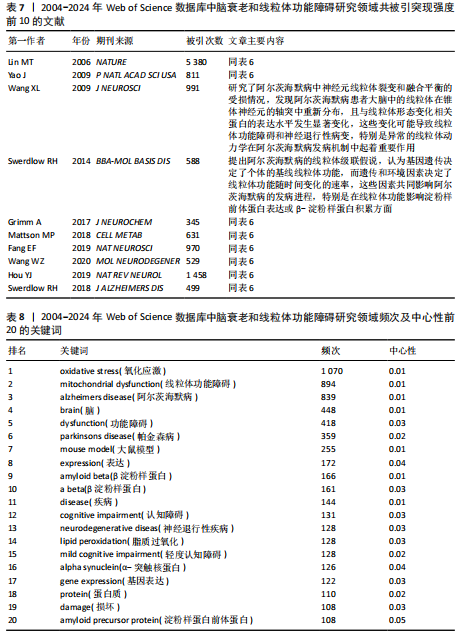
[14] CHEN C. Searching for intellectual turning points: progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):5303-5310.
[15] 陈挺, 李国鹏, 王小梅.优化科学知识图谱方法绘制全领域科学结构图谱[J].图书情报工作,2022,66(21):107-119.
[16] SYNNESTVEDT MB, CHEN C, HOLMES JH. CiteSpace II: visualization and knowledge discovery in bibliographic databases. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2005;2005:724-728.
[17] HIRSCH JE. An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(46):16569-16572.
[18] 唐晓娜,曾瑶,陈阳阳,等.基于Web of Science数据库中风病护理的文献计量学分析[J].广西医学,2020,42(7):908-913.
[19] 王东浩.文献计量学在图书情报与科技情报中的应用:评《文献计量学》(第二版)[J].领导科学,2022(10):153.
[20] AI Y, XING Y, YAN L, et al. Atrial Fibrillation and Depression: A Bibliometric Analysis From 2001 to 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:775329.
[21] 史海蛟,丁莉莉,杨珺涵,等.基于Cite Space研究中医药治疗冠心病合并高血压可视化分析[J].辽宁中医药大学学报, 2022,24(12):63-67.
[22] ZHOU W, KOU A, CHEN J, et al. A retrospective analysis with bibliometric of energy security in 2000-2017. Energy Reports. 2018;4:724-732.
[23] CHEN C, HU Z, LIU S, et al. Emerging trends in regenerative medicine: a scientometric analysis in CiteSpace. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12(5):593-608.
[24] 肖毅,陈晓萍,许潇丹,等.空间脑科学研究的回顾与展望[J].中国科学:生命科学,2024,54(2):325-337.
[25] 朱健椿,魏嘉昕,毛浚彬,等.深度学习在磁共振影像脑疾病诊断中的应用[J].工程科学学报,2024,46(2):306-316.
[26] MIWA S, KASHYAP S, CHINI E, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in cell senescence and aging. J Clin Invest. 2022; 132(13):e158447.
[27] PRADEEPKIRAN JA, BAIG J, SEMAN A, et al. Mitochondria in Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease: Focus on Mitophagy. Neuroscientist. 2024;30(4):440-457.
[28] REDDY PH, KSHIRSAGAR S, BOSE C, et al. Rlip overexpression reduces oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease: Mechanistic insights. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2023; 1869(7):166759.
[29] BOSE C, KSHIRSAGAR S, VIJAYAN M, et al. The role of RLIP76 in oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction: Evidence based on autopsy brains from Alzheimer’s disease patients. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2024;1870(2):166932.
[30] PERONE I, GHENA N, WANG J, et al. Mitochondrial SIRT3 Deficiency Results in Neuronal Network Hyperexcitability, Accelerates Age-Related Aβ Pathology, and Renders Neurons Vulnerable to Aβ Toxicity. Neuromolecular Med. 2023;25(1):27-39.
[31] YANG B, DAN X, HOU Y, et al. NAD+ supplementation prevents STING-induced senescence in ataxia telangiectasia by improving mitophagy. Aging Cell. 2021; 20(4):e13329.
[32] FARR SA, POON HF, DOGRUKOL-AK D, et al. The antioxidants alpha-lipoic acid and N-acetylcysteine reverse memory impairment and brain oxidative stress in aged SAMP8 mice. J Neurochem. 2003; 84(5):1173-1183.
[33] MIRSHAFA A, MOHAMMADI H, SHOKRZADEH M, et al. Tropisetron protects against brain aging via attenuating oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammation: The role of SIRT1 signaling. Life Sci. 2020;248: 117452.
[34] XU TT, LI H, DAI Z, et al. Spermidine and spermine delay brain aging by inducing autophagy in SAMP8 mice. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(7):6401-6414.
[35] RYAN KC, ASHKAVAND Z, NORMAN KR. The Role of Mitochondrial Calcium Homeostasis in Alzheimer’s and Related Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(23):9153.
[36] LIANG Y, CUI L, GAO J, et al. Gut Microbial Metabolites in Parkinson’s Disease: Implications of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Pathogenesis and Treatment. Mol Neurobiol. 2021;58(8):3745-3758.
[37] LEHMANN S, COSTA AC, CELARDO I, et al. Parp mutations protect against mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegeneration in a PARKIN model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell Death Dis. 2016; 7(3):e2166.
[38] 李政,易波,王国慧,等.基于CiteSpace的机器人结直肠手术临床应用现状与热点可视化分析[J].中国普通外科杂志, 2024,33(4):578-591.
[39] PICCA A, GUERRA F, CALVANI R, et al. Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Protein Misfolding and Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s Disease: Roads to Biomarker Discovery. Biomolecules. 2021;11(10):1508.
[40] DEOCARIS CC, KAUL SC, WADHWA R. From proliferative to neurological role of an hsp70 stress chaperone, mortalin. Biogerontology. 2008;9(6):391-403. |