中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (24): 5158-5170.doi: 10.12307/2025.702
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束调控机制:靶向转录因子及信号通路联合治疗策略
官镇洁1,2,李文媛1,2,耿 瑞1,王 莹1
- 1牡丹江医科大学神经组织工程研究所,黑龙江省牡丹江市 157011;2牡丹江市北药资源开发与应用协同创新中心,黑龙江省牡丹江市 157011
-
收稿日期:2024-08-14接受日期:2024-09-25出版日期:2025-08-28发布日期:2025-01-24 -
通讯作者:王莹,博士,教授,牡丹江医科大学神经组织工程研究所,黑龙江省牡丹江市 157011 -
作者简介:官镇洁,女,2000年生,四川省资中县人,汉族,牡丹江医科大学在读硕士,主要从事脊髓和周围神经损伤修复研究工作。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金面上项目(82371385),项目负责人:王莹;黑龙江省自然科学基金(SS2022H001),项目负责人:李文媛;牡丹江医学院科学基金火炬计划项目(2022-MYHJ-012),项目负责人:李文媛;牡丹江医学院博士科研启动基金(2021-MYBSKY-039),项目负责人:李文媛
Regulatory mechanisms of the corticospinal tract after spinal cord injury: combined therapeutic strategies targeting transcription factors and signaling pathways
Guan Zhenjie1, 2, Li Wenyuan1, 2, Geng Rui1, Wang Ying1
- 1Institute of Neural tissue Engineering, Mudanjiang Medical University, Mudanjiang 157011, Heilongjiang Province, China; 2Mudanjiang Collaborative Innovation Center for the Development and Application of Northern Medicinal Resources, Mudanjiang 157011, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Received:2024-08-14Accepted:2024-09-25Online:2025-08-28Published:2025-01-24 -
Contact:Wang Ying, PhD, Professor, Institute of Neural tissue Engineering, Mudanjiang Medical University, Mudanjiang 157011, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Guan Zhenjie, Master’s candidate, Institute of Neural tissue Engineering, Mudanjiang Medical University, Mudanjiang 157011, Heilongjiang Province, China; Mudanjiang Collaborative Innovation Center for the Development and Application of Northern Medicinal Resources, Mudanjiang 157011, Heilongjiang Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 82371385 (to WY); Heilongjiang Province Natural Science Foundation, No. SS2022H001 (to LWY); Torch Plan Project of Mudanjiang Medical University Science Foundation, No. 2022-MYHJ-012 (to LWY); Doctoral Scientific Research Foundation of Mudanjiang Medical University, No. 2021-MYBSKY-039 (to LWY)
摘要:
文题释义:
脊髓损伤:是一种破坏性的神经损伤疾病,会导致严重的运动、感觉和自主神经功能障碍。
轴突再生:轴突是一种特殊的细胞结构,使神经元之间相互联系,轴突损伤会导致严重的功能障碍。轴突再生是脊髓损伤后功能重建的第一步也是最重要的一步,对于治疗许多神经损伤和神经退行性疾病至关重要。
背景:目前治疗脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束策略主要聚焦于运动康复治疗、药物治疗、经颅磁电刺激、内源性调控如转录因子及特定信号通路介导,其中转录因子及其特定信号通路是调控脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突再生的关键因素,已有大量临床前研究证实转录因子及其信号通路相互协同对脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生具有显著调控效果。因此探索基于靶向转录因子及特定信号通路新的联合治疗脊髓损伤策略具有广阔的应用前景。
目的:归纳转录因子及其信号通路对脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生的调控作用及其介导的潜在分子机制,并探讨基于靶向转录因子及其信号通路为核心的联合治疗策略在脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经可塑性的应用,以期为治疗脊髓损伤提供新的联合治疗策略。
方法:以“脊髓损伤,轴突再生,转录因子,信号通路,皮质脊髓束,中枢神经系统,协同作用,神经保护”为中文检索词,以“spinal cord injury,axon regeneration,transcription factors,signaling pathway,Corticospinal tract,Central Nervous System,Synergistic system,Neuroprotective system”为英文检索词,检索万方数据知识服务平台、Web of Science及PubMed数据库建库时间至2024年9月期间的相关文献,最终纳入101篇文章进行分析和总结。
结果与结论:①概述了脊髓损伤后的皮质脊髓束轴突再生的生物特性及干预策略,解析了聚焦脊髓损伤后的皮质脊髓束的原因,阐明了脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束的反应以及再生的可能性。②研究中以Krüppel样因子6、Krüppel样因子7及神经元限制性沉默因子等为核心的转录因子联合调控策略能够显著促进脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生。③经磷脂酰肌醇3激酶-蛋白激酶 B-雷帕霉素靶蛋白信号通路、Wnt5a通路是转录因子调控皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生的经典信号通路,通过联合治疗策略更能够有效促进脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生及功能重建。④全面详细讨论了关于转录因子及特定信号通路的联合治疗策略,诸如Krüppel样因子6联合信号转导及转录激活因子3、Krüppel样因子7联合SOX11转录因子、联合抑制磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物及神经元限制性沉默因子等策略,发挥协同效应,促进脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生的效果均显著优于单独治疗,有效改善功能恢复,能够为未来治疗脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生提供可参考的方案;但其具体机制仍待进一步研究,而且目前联合策略仅在动物模型上广泛应用,未结合临床实际。⑤基于转录因子及特定信号通路联合治疗策略对脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生具有显著的治疗作用,未来需进一步精准探索联合调控分子机制,以期为脊髓损伤的康复和功能重建提供有效的联合治疗策略。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4075-781X(王莹)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
官镇洁, 李文媛, 耿 瑞, 王 莹. 脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束调控机制:靶向转录因子及信号通路联合治疗策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(24): 5158-5170.
Guan Zhenjie, Li Wenyuan, Geng Rui, Wang Ying. Regulatory mechanisms of the corticospinal tract after spinal cord injury: combined therapeutic strategies targeting transcription factors and signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5158-5170.
自那时起,人们普遍认为损伤后的皮质脊髓束神经束可以再生,这些再生的皮质脊髓束神经束没有穿过病变区域,而是在病变区域周围生长。在2001年,FOUAD等[12]发现皮质脊髓运动系统在解剖结构上展现出更大的适应损伤的潜力;2004年,BAREYRE等[13]初步揭示了脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突重塑的两个阶段,揭示了皮质表征的变化,证明了脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突具有重塑的能力。既然皮质脊髓束神经元轴突具有重塑的特性,那么脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生需要多长时间?又能重塑到什么程度?在2009年,YLERA等[14]发现脊髓损伤后神经元轴突再生的时间,并证实中枢神经系统在脊髓损伤后数月内同样具有轴突再生的能力。这表明皮质脊髓束神经元具有重新生长的内在机制,尽管这可能不足以产生长距离再生。在1981年,DAVID等[15]得出轴突与外在环境之间的相互作用在再生的成败中起着决定性作用的结论,这项研究激发了随后出现的再生研究,重点是识别干预外源性抑制线索。然而,中枢神经系统轴突在激光轴突切开术后不能再生,这与最小的外部抑制线索如免疫反应或瘢痕形成的存在有关。在2002年,GOLDBERG等[16]发现中和外源性抑制因子的临床前策略仅在神经元的亚群中适度增加轴突再生,这表明成年中枢神经系统中的轴突再生失败是由于固有再生能力降低和细胞外抑制因子的存在。脊髓损伤后存在实质性的组织损伤,这在细胞和分子水平上导致许多典型途径及其关键转录因子的改变。在取得一系列实验性成果后,在2024年,戴家峰等[17]通过建立小鼠C6脊髓背侧半切模型,解析了皮质脊髓束受损后初级运动皮质的功能重塑可能不仅依赖于受损皮质脊髓束神经元相关突触输入的改变,而更多地与受损神经元自身的转录调控变化有关,见图3。总之,内源性治疗策略在脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生中的应用是一个活跃的研究领域,近年来治疗脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生的技术已飞速发展,主要包括内源性神经营养因子的应用、干细胞移植及信号通路的激活等[18-19],文章主要关注转录因子及特定信号通路对脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生的治疗作用,因为转录因子是指导其他治疗技术发展的前驱,能够更好地为临床治疗、药理研究提供最基础的机制。
2.2 脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突反应 皮质脊髓束起源于大脑皮质V层锥体神经元,穿过内囊和脑脚,经腹侧到达脑干,在颈膨大和腰骶膨大处从白质进入灰质,最终将运动指令传递到前肢和后肢[20]。大多数皮质脊髓束轴突都是小直径(0.2-0.6 μm)无髓鞘轴突。而部分脊髓背外侧和腹侧的皮质脊髓束为大直径(1.5-5.0 μm)有髓鞘轴突,这些轴突与脊髓运动神经元形成突触连接。皮质脊髓束是支配脊髓运动神经元的唯一直接下行运动通路,也是支配脊髓运动神经元的主要通路,与脊髓损伤后肢体功能的恢复密切相关,见图4。


脊髓损伤后位于病变部位远端的皮质脊髓束轴突会迅速断裂并发生 Wallerian 变性,而位于病变近端的皮质脊髓束轴突则会出现缓慢而渐进的退行性改变。脊髓背侧半切模型会损伤大鼠脊髓背侧和背外侧皮质脊髓束轴突,但不会损伤小的腹侧皮质脊髓束轴突[21]。小鼠脊髓T8背侧半切术后病灶远端皮质脊髓束轴突会逐渐断裂并发生Wallerian变性,术后4周病变部位远端99.9%以上皮质脊髓束轴突消失,病变部位近端皮质脊髓束轴突继续逆行变性[22]。大鼠胸段脊髓全横断后,病变近侧皮质脊髓束轴突在脊髓损伤后1-8周内逐渐逆行变性,在脊髓损伤后慢性期8个月后,会出现少数皮质脊髓束轴突萌发,但未能重新支配损伤前靶部位,表明皮质脊髓束轴突可能具有重新生长的内在机制。
脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突再生对临床具有指导意义,在临床上不同时期的脊髓损伤患者有不同程度的症状体征。损伤后的症状体征主要集中于损伤运动功能和感觉功能,在运动功能上主要表现为损伤部位以下的运动功能受损,导致各种形式的瘫痪,如截瘫和四肢瘫等;在感觉功能上患者部分或完全丧失对疼痛、温度和触摸的知觉;此外患者还可能经历脊髓休克、自主神经功能紊乱、反射活动异常和膀胱功能异常等症状。促进脊髓损伤神经修复和运动功能恢复的一个重要目标是增强皮质脊髓束与脊髓运动回路的联系。通过转录因子调动内源性转录,促进皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生和恢复局部神经环路是脊髓损伤治疗方法的着手点。近年来研究者寻找到了多种治疗脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突再生的治疗策略,其中外源性策略包括移植、康复训练和电刺激等[23-25];内源性策略如提供促轴突再生微环境、抑制神经胶质瘢痕形成等[26-27]。目前研究重点聚焦于内源性策略如转录因子、信号通路通过靶向调控作用促进脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生。因此文章着眼于转录因子及特定信号通路促进脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生展开综述,旨在为今后临床研究提供新思路。
2.3 脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突再生治疗现状 目前,脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束的再生修复是再生医学领域的一个热点和难点,临床上缺乏有效的治疗和康复方法。脊髓损伤后,上升背柱轴突和下降皮质脊髓束轴突都会经历退化,随后是轴突枯死和回缩球的形成。当脊髓损伤后,会立即进入迅速发展期,此阶段轴突断裂,产生大量坏死神经元和神经胶质细胞,脊髓缺血,肿胀;接下来进入急性期,在这一阶段主要表现为血管破裂出血、各种免疫细胞活化;随后进入到慢性前期,在此阶段胶质瘢痕逐渐形成;最后进入到慢性期,表现为持续的瘢痕形成,Wallerian变性等;最终,病变重塑并导致囊性空化和神经胶质增生,使局部环境不利于再生。
研究表明,受损的中枢神经元细胞内在机制限制了轴突生长。轴突延伸需要受损神经元内的细胞状态表型发生重大变化。在轴突切开术之前,神经元的功能是在神经传导过程中维持细胞内通讯和结构稳态;在轴突切开术之后,再生需要大量细胞骨架和细胞膜物质的产生、运输和调节,需上调或下调大量基因才能重新启动轴突延伸,这对神经元内在生长状态构成了重大挑战。一种可能的解决方案是在受损神经元中调控潜在的转录因子,可以作为简单的杠杆来改变大量下游再生相关基因(regeneration-associated genes,RAG)的表达。大量研究证实调控包括Krüppel样因子、转录因子SOX11和信号转导及转录激活因子3在内的转录因子可以增强脊髓损伤后的再生轴突生长[28]。
近年来,人们对脊髓损伤的大型动物和非人灵长类动物模型产生了兴趣,以评估各种治疗方法。这些模型代表了在啮齿动物和人类之间的动物物种中介,使得新兴疗法具有进行临床前评估的机会,并且由于大型动物模型和人类之间的脊髓大小相当,因此具有很高的转化潜力。尽管在动物模型中进行了广泛的研究,但迄今为止还没有有效的治疗方法可以完全恢复或至少改善脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束的神经功能。在动物模型中,尽管已有潜在的治疗方法,但仍未成功应用到人。
在过去的20年中,皮质脊髓运动回路已经成为探索脊髓损伤后可塑性和功能恢复的治疗策略的主要目标。迄今为止,有效利用皮质脊髓运动回路可塑性的治疗策略包括神经调节、康复训练、干细胞和生物支架、神经再生/神经保护药物疗法。基于神经可塑性的方法依赖于运动皮质和脊髓内介导脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓回路恢复的可塑性[18,29-33],具体治疗方法见表1和图5。

2.4 转录因子对皮质脊髓束轴突再生的作用 转录因子作为一个强大的轴突再生调节因子,对脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突再生发挥重要调控作用。研究表明多种功能相同或相似的转录因子结合可以发挥更强的协同效应,而轴突生长完全恢复依赖于多个转录因子调控[34]。
2.4.1 Krüppel样因子6联合调控策略 尽管转录因子作为强大的再生调节因子,但仍需多个因子共同作用才能发挥强大的促再生作用,Krüppel样因子6作为Krüppel家族中的一员,参与调节内皮功能障碍、炎症和血管生成,

在增殖、代谢、炎症和损伤反应中发挥着至关重要的转录调控作用[35-36]。信号通路信号转导及转录激活因子3对皮质脊髓束神经束具有促进再生的作用,信号转导及转录激活因子3过表达显著增加脊髓损伤部位近端皮质脊髓束轴突萌芽,并在一定程度上促进损伤部位外周的轴突生长,同时信号转导及转录激活因子3过表达有助于前肢运动功能的改善。二者之间能够发挥相互作用的基础在于信号转导及转录激活因子3高度富含Krüppel样因子6反应基因的启动子序列,两种因子之间直接相互作用影响彼此的活性。此外,研究发现信号转导及转录激活因子3和Krüppel样因子6通过高度共同占据再生相关基因网络中的调控DNA协同促进皮质脊髓束神经元轴突生长[37]。
信号转导及转录激活因子3还可以通过转录交叉调节,直接靶向相关启动子提高“下游”Krüppel样因子6转录,启动额外促再生转录因子的二次级联[28]。
以Krüppel样因子6为核心结合其他转录因子或物理治疗组成新的联合治疗方法用以调节皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生,如Krüppel样因子6联合信号转导及转录激活因子3可以显著促进皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生但不足以改善前肢功能活动[37],但联合治疗促进皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生的效果显著优于单独治疗。因此针对运动功能的恢复,可以考虑除在转录因子联合的基础上再联合运动疗法共同改善损伤。此外,Krüppel样因子6和全能性先峰因子(nuclear receptor subfamily 5,group A,member 2,Nr5a2)也有同样的治疗效果,他们二者之间通过高度共同占据再生相关基因网络中的调控DNA协同促进皮质脊髓束神经元轴突生长。有趣的是,全能性先峰因子单独作用并不会增强皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生,但联合Krüppel样因子6却能够加强过表达Krüppel样因子6的作用,从而加强促进作用[34]。近年来,研究者将神经调节技术联合康复治疗进一步增强神经可塑性,故将转录因子联合康复训练也是另一有益治疗方法。可惜的是以Krüppel样因子6为核心的转录因子联合康复训练虽然促进了脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生的效果,但该联合疗法并没有展现出很好的前肢运动功能改善[38]。
综上所述,尽管Krüppel样因子6能够促进皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生,但无论是联合其他转录因子或物理治疗仍然不能促进前肢运动功能恢复。这可能归因于尽管Krüppel样因子6因子可以显著促进皮质脊髓束轴突的生长,但是并未达到触发前肢运动功能改善的阈值;亦可能由于Krüppel样因子6过度释放从而抑制皮质脊髓束轴突的生长。在未来,可以将联合转录因子叠加康复治疗这种多种治疗策略的联合或许能够产生更佳的治疗效果,这为研究者们在未来研究和应用转录因子治疗脊髓损伤提供更为丰富的理论依据。
2.4.2 Krüppel样因子7联合调控策略 Krüppel样因子7在中枢神经系统神经元轴突生长的发育期中表达,并随着神经元成熟而下调,主要参与调节神经系统的发育调控[39]。研究证实,Krüppel样因子7能够促进周围神经损伤后轴突再生[40]。与Krüppel样因子4相反,Krüppel样因子7在培养的神经元中过表达时增加轴突生长。除此之外Krüppel样因子7过表达后驱动下游再生相关基因对脊髓损伤后下行传导束中皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生具有显著的促进作用[41]。Krüppel样因子7过表达通过靶向下游基因p21阻断Rho蛋白(ras homolog family member,RhoA)信号传导进而刺激轴突生长,同时Krüppel样因子7通过激活再生相关基因的启动子显著促进脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生,且再生的轴突是由损伤的皮质脊髓束神经束诱发产生[42]。这表明联合疗法促再生效果大于单个转录因子的作用,进一步验证了联合疗法的可行性。
众所周知,脊髓损伤后损伤部位会形成神经胶质瘢痕,虽然它在一定程度上保护受损部位免受进一步伤害,但同时也会产生一些生长抑制因子,如硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖(chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan,CSPGs)。研究者证实硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖在中枢神经系统中抑制轴突生长,反之抑制硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖可促进轴突再生[43-44],因此抑制硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖联合高表达Krüppel样因子7被认为是另一个有效促进皮质脊髓束轴突再生的联合治疗策略。
研究显示,在小鼠身上将Krüppel样因子7联合抑制硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖能够有效促进损伤部位皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生,并且再生部位仅发生于损伤灶周围[45],再一次证实联合治疗强烈的目的性和高效性。此外,转录因子SOX11被普遍认为对神经再生有促进作用,SOX11在胚胎发生期间表达主要涉及神经发育过程[46],能够促进脊髓损伤后轴突再生,但对运动功能恢复并无显著效果[47]。这表明对SOX11的调控需要更加精确,以促进神经再生和功能恢复,同时需要避免不利影响。而Krüppel样因子7能够精确调控神经再生,因此将Krüppel样因子7和SOX11联合治疗脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生或许是一个有潜力的组合,这为皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生转录因子联合治疗策略提供了新的思路。
综上所述,Krüppel样因子7在脊髓损伤后的神经再生和功能恢复中发挥重要作用,Krüppel样因子7作为促脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生的一个核心因子,能够和许多其他转录因子组成新的组合放大促再生的作用,但这种联合治疗策略的核心在于是否能够找到合适且有效的转录因子组合,其在临床治疗中的应用潜力值得进一步研究和探索。
2.4.3 RE1敲除沉默转录因子/神经元限制性沉默因子联合治疗策略 神经元限制性沉默因子是一种在神经元和非神经元细胞中广泛表达的锌指转录因子,是神经元分化、多样性、可塑性和存活的基础。神经元限制性沉默因子可以与神经元限制性沉默元件结合,募集共阻遏蛋白通过表观遗传机制抑制元件下游基因的转录[48]。在神经发生中,神经元限制性沉默因子不仅作为一种转录沉默因子介导神经元特异性基因的转录抑制从而赋予神经元细胞特异性,而且还作为一种转录激活剂来诱导神经元分化[49]。神经元限制性沉默因子参与正常脑功能的多种生理过程。因此神经元限制性沉默因子的过表达、低表达、突变或异常分布可能导致脑功能障碍[50]。
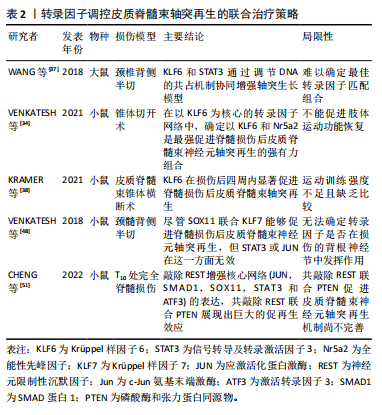
神经元限制性沉默因子是一种被广泛研究的调控神经发育和神经特异性基因表达的转录因子,已被证明具有抑制中枢神经系统神经再生的作用。在一组由c-Jun氨基末端激酶(c-Jun N-terminal kinase,Jun)、SMAD1、Sox11、信号转导及转录激活因3和激活转录因子3(activating transcription factor 3,ATF3)组成的核心调控网络中,神经元限制性沉默因子被证实是其上游阻遏因子,在脊髓损伤后高表达神经元限制性沉默因子阻碍神经元轴突再生,而破坏神经元限制性沉默因子则会启动在皮质神经元该调控网络促进脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生[51]。与此类似,磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物(phosphatase and tensin homolog,PTEN)被普遍认为是抑制再生的阻遏因子,抑制该因子能促进脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生。此外,研究表明抑制神经元限制性沉默因子比抑制磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物能够发挥更强的促再生作用,因此可以认为共抑制磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物联合神经元限制性沉默因子或许能够叠加促再生效应。最近的研究显示,含泛素类PHD环指1(Ubiquitinlike containing PHD ring finger 1,UHRF1)在启动子区域和DNA甲基转移酶(DNA methyltransferases,DNMTs)和H3K9me3相互作用,共抑制磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物和神经元限制性沉默因子的表达,从而促进轴突再生[52]。因此共抑制神经元限制性沉默因子联合磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物可以放大促进中枢神经系统神经再生,尤其关注脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突再生的作用,见表2。与中枢神经系统不同,神经元限制性沉默因子及其他内在生长抑制因子的表达在周围神经系统损伤的神经元中受到严格限制,因此周围神经具有内源性再生能力。
2.5 信号通路对皮质脊髓束轴突再生的影响 脊髓损伤后受损的皮质脊髓束修复受限,因为成熟的皮质脊髓束轴突无法再生。目前研究者聚焦于内源性信号通路对皮质脊髓束轴突再生的介导和调控能力。
2.5.1 经磷脂酰肌醇3激酶-蛋白激酶B-雷帕霉素靶蛋白信号通路 脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生需要许多关键的信号通路调控,其中之一是经磷脂酰肌醇3激酶-蛋白激酶B -雷帕霉素靶蛋白信号通路,它是由一系列抑制剂/活化剂分子组成。其中雷帕霉素靶蛋白与雷帕霉素靶蛋白C1和雷帕霉素靶蛋白C2亚基相互作用形成两个不同的复合体,雷帕霉素靶蛋白C1调控细胞的生长和代谢,而雷帕霉素靶蛋白C2主要调控细胞的存活和迁移[53]。经磷脂酰肌醇3激酶-蛋白激酶B信号通路的激活可抑制继发性创伤性脊髓损伤后亚急性期的炎症反应和细胞凋亡。在慢性期抑制雷帕霉素靶蛋白信号通路可以减少神经胶质瘢痕的形成[54]。近年来,人们普遍意识到了联合疗法的重要性,在促进脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生中尤其关注与雷帕霉素靶蛋白通路的联合治疗,诸如雷帕霉素靶蛋白通路联合Janus激酶信号转导/转录激活因子通路能够起到叠加效应,通过抑制两通路的上游靶基因磷酸酯酶与张力蛋白同源物和细胞因子信号抑制物3进而激活该通路提高脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突内源性再生能力[55]。研究显示,蛋白激酶B3和信号转导及转录激活因子3过表达脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突再生[56]。除此之外,还可通过物理治疗的方式激活雷帕霉素靶蛋白通路[57-58],前期研究中发现电针针刺足三里和内关穴位,能够通过激活该通路发挥神经保护作用[59]。ZHANG等[60]研究表明电针通过介导雷帕霉素靶蛋白通路激活皮质脊髓束与颈髓灰质运动神经元连接,促进脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突萌发。
除了对该通路的直接作用促进皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生外,还可以通过间接的方式激活此通路,达到促进皮质脊髓束轴突萌发的效果,如抑制通路的负调节因子磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物[61],磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物既具有双重特异性蛋白磷酸酶的功能,又具有脂质磷酸酶的功能。磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物独特的磷酸酶功能特征是通过磷脂酰肌醇-3,4,5-三磷酸去磷酸化为二磷酸来抵消经磷脂酰肌醇3激酶的活性,通过这种机制磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物充当经磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B通路的抑制因子。磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物失活会导致磷脂酰肌醇3,4,5-三磷酸积累和蛋白激酶B活化,活化的蛋白激酶B抑制TSC1/2复合物,从而激活雷帕霉素靶蛋白。磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物失活后通过激活下游的经磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B通路调控轴突生长的各个阶段及特征,包括轴突伸长、分支、口径、生长锥组成和极化[62]。最近的研究表明,抑制磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物能够加强雷帕霉素靶蛋白通路的激活促使脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生并改善前肢运动功能恢复[63]。
此外,在之前的表述中已经提到过抑制磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物联合抑制神经元限制性沉默因子具有促再生的叠加效应,因此考虑将抑制磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物联合其他因子或外源性措施对脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生或许具有类似的协同作用。事实上,通过内源性抑制磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物和敲除外源性因素Rho蛋白能共同促进脊髓损伤后连接大脑皮质、脊髓和后肢肌肉的皮质脊髓环路,共抑制Rho蛋白和磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物的组合具有诱导脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生的放大效果[64]。
与磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物一样,细胞因子信号抑制物3在脊髓损伤后也充当轴突生长抑制因子,细胞因子信号抑制物3是信号转导及转录激活因子3信号转导的直接靶标,通过拮抗Janus激酶信号转导/转录激活因子信号传导途径负调节信号转导及转录激活因子3功能[65]。磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物/细胞因子信号抑制物3能够协同上调雷帕霉素靶蛋白正向调节因子,包括Ras样小鸟苷三磷酸酶(a Ras-like small guanosine triphosphatase,Rheb)和胰岛素生长因子1(insulin-like growth factor 1,IGF1),这可能是一种“前馈”机制,进一步促进了雷帕霉素靶蛋白的激活和轴突生长。雷帕霉素靶蛋白的缺失导致的Krüppel样因子4表达减少,而Krüppel样因子4是一种已知阻碍轴突再生的转录因子[62]。磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物和细胞因子信号抑制物3协同机制体现在抑制磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物不会随着年龄增长增强皮质脊髓束轴突发芽,但敲除细胞因子信号抑制物3会随着年龄的增长而失去促进皮质脊髓束轴突发芽的作用。而共敲除磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物和细胞因子信号抑制物3对皮质脊髓束萌芽的协同作用会随着年龄的增长而迅速消失,这进一步说明了抑制磷酸酯酶与张力蛋白同源物对皮质脊髓束轴突萌发的重要性,并证实敲除磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物能够促进皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生且与年龄无关[66],虽然联合共敲除磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物和细胞因子信号抑制物3虽然能在一定程度上加强促脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生的作用,但联合治疗受年龄的制约,这为基础研究预测临床治疗提供了可参考的价值。此外,联合物理疗法也是一个可持续发展的策略,那么将康复训练联合共抑制磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物与细胞因子信号抑制物3对皮质脊髓束轴突再生是否具有叠加效应?之前的研究显示共抑制磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物与细胞因子信号抑制物3联合单丸抓取训练4周能够显著增强轴突再生并改善功能恢复[67],但这局限于脊髓损伤并未拓展至皮质脊髓束。然而,抑制磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物联合康复训练能够有效促进脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生[68]。因此可以认为康复治疗联合共抑制磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物与细胞因子信号抑制物3能够显著促进脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突再生,但再生效果如何还应做进一步的研究,这为指导今后的临床前实验提供了新的视角。
综上所述,通过雷帕霉素靶蛋白通路诱发皮质脊髓束轴突的生长,主要通过两种方式,一是通过直接作用,例如电针等刺激诱导雷帕霉素靶蛋白通路激活,进而促进皮质脊髓束轴突再生;二是通过抑制雷帕霉素靶蛋白通路上游的负向调节因子,达到相同的促进效果,使其皮质脊髓束轴突得以萌发;此外,可以考虑寻找雷帕霉素靶蛋白信号通路上游的正向调节因子,正向反馈mTOR信号通路,促进皮质脊髓束轴突萌芽,或者通过内源性激活皮质脊髓束神经元联合外源性康复运动治疗策略增强雷帕霉素靶蛋白信号通路,促进皮质脊髓束在脊髓损伤后轴突生长。
2.5.2 Wnt5a通路 Wnt信号通路调控大脑中神经祖细胞在中枢神经系统发育的不同阶段的自我更新、增殖和分化[69]。Wnt信号转导是一种细胞间协调机制,它对生物体的各种生理过程至关重要,包括干细胞再生、增殖、分裂、迁移、细胞极性、决定细胞命运、神经对称性和形态发生等[70]。研究表明,激活Wnt信号通路对于损伤后中枢神经系统再生反应、刺激神经发生、恢复认知脑功能具有重要的调控作用;还能调节神经干细胞增殖分化、神经元轴突再生、神经炎症和疼痛的生理和病理过程[71]。此外,Wnt通路调控着许多轴突的生长,对于新生儿脊髓背侧中线中皮质脊髓束神经元轴突的逆向生长至关重要[72]。
众所周知,Wnt信号通路主要包括两条途径,一是Wnt/β-连环蛋白(Wnt/β-catenin pathway,Wnt/β-catenin)经典通路,二是Wnt/Ca2+和Wnt/平面细胞极性通路(Wnt/planar cell polarity pathway,Wnt/PCP)非经典信号通路,已有研究表明Wnt/PCP信号通路能够促进轴突再生[73]。WNT通路包括19个配体,10个常规受体,4个非常规受体、2个共受体和14个可溶性调节剂组成,Wnt家族成员主要分为两种不同的类型[74],高转化Wnt成员包括:Wnt 1,Wnt 3,Wnt 3a和Wnt 7a。中间转化和非转化Wnt成员包括:Wnt 2,Wnt 4,Wnt 5a,Wnt 5b,Wnt 6,Wnt 7b和Wnt 11。前组Wnts成员激活β-catenin依赖性通路,在胚胎发育、组织再生和肿瘤发生中发挥关键作用。与之相反,后组Wnt成员激活β-catenin非依赖性通路,其中涉及小G蛋白,如Rac和Rho,以及蛋白激酶,如蛋白激酶C(Protein kinase C,PKC)和Ca2+/钙调蛋白依赖性激酶(Ca/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases,CaMK)[74-75]。Wnt 5a是Wnt家族中研究最广泛的Wnt蛋白之一,在多种器官的发育过程和出生后细胞功能中发挥调控作用。Wnt5a通过经典的卷曲受体和非典型酪氨酸激酶受体进行信号传导,促进皮质神经元轴突生长。此外,Wnt5a通过调控IP3受体的Ca2+释放和通过Trp通道的Ca2+内流,促进皮质脊髓束神经元轴突生长[75]。
在19个配体中Wnt5a和Wnt1是抑制性蛋白,能够发挥抑制脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突再生的作用。研究显示,脊髓损伤后Wnt5a能够迅速与酪氨酸激酶受体结合,富集于损伤灶附近以阻止脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生[76]。因此抑制Wnt5a通路或激活Wnt5a通路的抑制因子是促进脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突再生的潜在靶点。MIYASHITA等[77]进行了相关验证,在体外实验中,通过培养小脑颗粒神经元细胞发现Rho激酶作用于Wnt5a发挥神经突抑制作用;在体内实验应用鞘内导管渗透微型泵注入抗Ryk抗体,结果显示注射抗Ryk抗体治疗的大鼠显著促进皮质脊髓束轴突再生和运动功能恢复。这再一次证明了抑制Wnt-Ryk信号能够促进脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生,考虑到磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物同样作为抑制因子,联合共抑制Wnt-Ryk信号和磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物能够加强促进作用,然而最新的研究显示,共抑制Wnt5a和磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物的表达反而抑制了施万细胞增殖进而抑制轴突再生[78]。因此,共抑制Wnt5a和磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物的表达是否在皮质脊髓束上也有同样的抑制效果还需进一步研究,这为今后临床前研究提供了可参考的依据。联合治疗策略的另一可能性在于抑制Wnt5a通路联合过表达雷帕霉素靶蛋白促进神经元轴突再生,最新的研究证实了此观点能够实现神经元促再生的作用[79],然而还需进一步验证两者之间的具体关系并探讨促进皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生的效果。但不可否认的是该策略为临床治疗提供了一可行的想法。最近的研究发现Wnt5a不仅参与皮质脊髓束轴突再生过程,而且还能够降低神经元细胞密度、NG2+神经胶质前体积累和损伤部位的血清素能神经支配,以及抑制脊髓损伤后运动和膀胱功能恢复[80],见表3。在未来Wnt5a或许可以多方位的治疗脊髓损伤后的各种疾病,为临床治疗开启新的篇章。

2.6 转录因子及其特定信号通路临床转化现状的挑战和机遇 尽管基础研究取得了进展,但转录因子及其特定信号通路治疗脊髓损伤临床转化仍面临挑战,其临床应用难度主要有以下几个方面:①适应证选择问题:皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生主要适用于神经损伤和脊髓损伤等神经系统疾病的治疗,但其适用范围相对较小,而且临床试验需要严格选择适应证。②实验设计限制:动物实验模型主要通过调节转录因子的表达水平来影响轴突再生,但是人体神经系统的结构和功能与动物模型存在差异,因此实验结果可能不完全适用于人体。③临床转化难度:转录因子治疗神经损伤是一个新兴领域,其临床转化需要大量的研究和试验来验证其安全性和有效性。此外,还需要考虑伦理问题、费用问题、政策法规等问题。④适应人群限制:转录因子治疗需要针对个体化差异进行选择,不同个体对转录因子的反应程度和效果不同,因此需要更多的临床试验来验证其适应人群和禁忌人群。⑤安全性问题:转录因子治疗涉及人体试验,需要严格遵守伦理原则和法规要求,确保试验的安全性和可靠性。此外,还需要考虑长期使用转录因子的安全性问题,如免疫反应、药物相互作用等。
目前尚未有报道显示转录因子应用于临床治疗脊髓损伤的成功案例[81]。因此,转录因子调控皮质脊髓束轴突再生在临床转化方面存在一定的难度和挑战,需要更多的研究和临床试验来验证其安全性和有效性,同时也需要更多的政策法规和伦理问题的考虑。未来需要加强该领域的研发和临床试验工作,为神经系统疾病的治疗提供更多有效的治疗方法。
文章主要局限性在于临床实验结果主要来源于动物模型,联合策略仅在动物模型上广泛应用,未结合临床实际。在未来,将动物模型应用于临床治疗时,应对临床前实验结果进行验证复制,以确保实验的安全有效开展;在临床转化的过程中应考虑损伤模型是否可以应用至人体,因为单一的动物模型不足以概括人体损伤类型,应多加关注与人体结构相似的大型动物模型,诸如猕猴和猪等动物模型[82-83],以便更好地接近于人类脊髓损伤状况。



| [1] HACHMANN JT, YOUSAK A, WALLNER JJ, et al. Epidural spinal cord stimulation as an intervention for motor recovery after motor complete spinal cord injury. J Neurophysiol. 2021;126(6):1843-1859. [2] IZZY S. Traumatic spinal cord injury. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2024; 30(1):53-72. [3] JIANG B, SUN D, SUN H, et al. Prevalence, incidence, and external causes of traumatic spinal cord injury in china: a nationally representative cross-sectional survey. Front Neurol. 2021;12:784647. [4] HU X, XU W, REN Y, et al. Spinal cord injury: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):245. [5] 王淑影,王莹,李艺,等.脊髓损伤后神经元轴突内在再生能力调控策略的研究进展[J].医学综述,2024,30(8):897-901, 907. [6] WAGH K, STAVREVA DA, UPADHYAYA A, et al. Transcription factor dynamics: one molecule at a time. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2023;39:277-305. [7] FINKEL Z, CAI L. Transcription factors promote neural regeneration after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(11):2439-2440. [8] LU F, LIONNET T. Transcription factor dynamics. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2021;13(11):a040949. [9] WEIDEMÜLLER P, KHOLMATOV M, PETSALAKI E, et al. Transcription factors: bridge between cell signaling and gene regulation. Proteomics. 2021;21(23-24):e2000034. [10] GORDON MD, NUSSE R. Wnt signaling: multiple pathways, multiple receptors, and multiple transcription factors. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(32): 22429-22433. [11] MCCOUCH GP, AUSTIN GM, LIU CN, et al. Sprouting as a cause of spasticity. J Neurophysiol. 1958;21(3):205-216. [12] FOUAD K, PEDERSEN V, SCHWAB ME, et al. Cervical sprouting of corticospinal fibers after thoracic spinal cord injury accompanies shifts in evoked motor responses. Curr Biol. 2001;11(22):1766-1770. [13] BAREYRE FM, KERSCHENSTEINER M, RAINETEAU O, et al. The injured spinal cord spontaneously forms a new intraspinal circuit in adult rats. Nat Neurosci. 2004;7(3):269-277. [14] YLERA B, ERTüRK A, HELLAL F, et al. Chronically CNS-injured adult sensory neurons gain regenerative competence upon a lesion of their peripheral axon. Curr Biol. 2009;19(11):930-936. [15] DAVID S, AGUAYO AJ. Axonal elongation into peripheral nervous system “bridges” after central nervous system injury in adult rats. Science. 1981; 214(4523):931-933. [16] GOLDBERG JL, KLASSEN MP, HUA Y, et al. Amacrine-signaled loss of intrinsic axon growth ability by retinal ganglion cells. Science. 2002; 296(5574): 1860-1864. [17] 戴家峰,王丽昭,韩齐,等.脊髓损伤重塑皮质脊髓运动神经元突触输入的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(25):4054-4059. [18] HIROTA R, SASAKI M, KATAOKA-SASAKI Y, et al. Enhanced network in corticospinal tracts after infused mesenchymal stem cells in spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2022;39(23-24):1665-1677. [19] MA J, LI J, WANG X, et al. GDNF-loaded polydopamine nanoparticles-based anisotropic scaffolds promote spinal cord repair by modulating inhibitory microenvironment. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023; 12(8):e2202377. [20] HE J, ZHANG F, PAN Y, et al. Reconstructing the somatotopic organization of the corticospinal tract remains a challenge for modern tractography methods. Hum Brain Mapp. 2023;44(17):6055-6073. [21] Bareyre fm, kerschensteiner m, misgeld t, et al. Transgenic labeling of the corticospinal tract for monitoring axonal responses to spinal cord injury. Nat Med. 2005;11(12):1355-1360. [22] LIU K, LU Y, LEE JK, et al. PTEN deletion enhances the regenerative ability of adult corticospinal neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2010;13(9):1075-1081. [23] SAINI R, PAHWA B, AGRAWAL D, et al. Efficacy and outcome of bone marrow derived stem cells transplanted via intramedullary route in acute complete spinal cord injury - A randomized placebo controlled trial. J Clin Neurosci. 2022;100:7-14. [24] JO HJ, KIZZIAR E, SANGARI S, et al. Multisite hebbian plasticity restores function in humans with spinal cord injury. Ann Neurol. 2023;93(6):1198-1213. [25] ANDO M, TAMAKI T, MAIO K, et al. The muscle evoked potential after epidural electrical stimulation of the spinal cord as a monitor for the corticospinal tract: studies by collision technique and double train stimulation. J Clin Monit Comput. 2022;36(4):1053-1067. [26] PANG QM, CHEN SY, XU QJ, et al. Neuroinflammation and scarring after spinal cord injury: therapeutic roles of MSCs on inflammation and glial sca. Front Immunol. 2021;12:751021. [27] ZHANG C, KANG J, ZHANG X, et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of the cellular components involved in glial scar formation following spinal cord injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;153:113500. [28] VENKATESH I, BLACKMORE MG. Selecting optimal combinations of transcription factors to promote axon regeneration: Why mechanisms matter. Neurosci Lett. 2017;652:64-73. [29] LIN BS, ZHANG Z, PENG CW, et al. Effectiveness of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation combined with transspinal electrical stimulation on corticospinal excitability for individuals with incomplete spinal cord injury: a pilot study. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2023;31:4790-4800. [30] KANEKO N, SASAKI A, YOKOYAMA H, et al. Changes in corticospinal and spinal reflex excitability through functional electrical stimulation with and without observation and imagination of walking. Front Hum Neurosci. 2022;16:994138. [31] WOODHEAD A, RAINER C, HILL J, et al. Corticospinal and spinal responses following a single session of lower limb motor skill and resistance training. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2024;124(8):2401-2416. [32] LIU JL, WANG S, CHEN ZH, et al. The therapeutic mechanism of transcranial iTBS on nerve regeneration and functional recovery in rats with complete spinal cord transection. Front Immunol. 2023;14: 1153516. [33] MAYNARD G, KANNAN R, LIU J, et al. Soluble Nogo-Receptor-Fc decoy (AXER-204) in patients with chronic cervical spinal cord injury in the USA: a first-in-human and randomised clinical trial. Lancet Neurol. 2023;22(8): 672-684. [34] VENKATESH I, MEHRA V, WANG Z, et al. Co-occupancy identifies transcription factor co-operation for axon growth. Nat Commun. 2021; 12(1):2555. [35] SONG F, LI S, DAI X, et al. Activation of KLF6 by titanate nanofibers and regulatory roles of KLF6 on ATF3 in the endothelial monolayer and mouse aortas. Mol Omics. 2023;19(2):150-161. [36] LI J, YU D, HE C, et al. KLF6 alleviates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(7):393. [37] WANG Z, MEHRA V, SIMPSON M T, et al. KLF6 and STAT3 co-occupy regulatory DNA and functionally synergize to promote axon growth in CNS neurons. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):12565. [38] KRAMER AA, OLSON GM, CHAKRABORTY A, et al. Promotion of corticospinal tract growth by KLF6 requires an injury stimulus and occurs within four weeks of treatment. Exp Neurol. 2021;339:113644. [39] LIN T, CHEN Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Transcriptional control of chicken KLF7 promoter in preadipocytes. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021; 53(2):149-159. [40] LI WY, ZHU GY, YUE WJ, et al. KLF7 overexpression in bone marrow stromal stem cells graft transplantation promotes sciatic nerve regeneration. J Neural Eng. 2019;16(5):056011. [41] LI WY, WANG Y, ZHAI FG, et al. AAV-KLF7 Promotes descending propriospinal neuron axonal plasticity after spinal cord injury. Neural Plast. 2017;2017: 1621629. [42] TANAKA H, YAMASHITA T, YACHI K, et al. Cytoplasmic p21(Cip1/WAF1) enhances axonal regeneration and functional recovery after spinal cord injury in rats. Neuroscience. 2004;127(1):155-164. [43] PAN D, LI Y, YANG F, et al. Increasing toll-like receptor 2 on astrocytes induced by Schwann cell-derived exosomes promotes recovery by inhibiting CSPGs deposition after spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2021;18(1):172. [44] WEI Y, ANDREWS MR. Advances in chondroitinase delivery for spinal cord repair. J Integr Neurosci. 2022;21(4):118. [45] WANG Z, WINSOR K, NIENHAUS C, et al. Combined chondroitinase and KLF7 expression reduce net retraction of sensory and CST axons from sites of spinal injury. Neurobiol Dis. 2017;99:24-35. [46] TSANG SM, OLIEMULLER E, HOWARD BA. Regulatory roles for SOX11 in development, stem cells and cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020;67(Pt 1):3-11. [47] XU AK, GONG Z, HE YZ, et al. Comprehensive therapeutics targeting the corticospinal tract following spinal cord injury. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2019;20(3):205-218. [48] VENKATESH I, MEHRA V, WANG Z, et al. Developmental chromatin restriction of pro-growth gene networks acts as an epigenetic barrier to axon regeneration in cortical neurons. Dev Neurobiol. 2018;78(10):960-977. [49] NASSAR A, SATARKER S, GURRAM PC, et al. Repressor element-1 binding transcription factor (REST) as a possible epigenetic regulator of neurodegeneration and microRNA-based therapeutic strategies. Mol Neurobiol. 2023;60(10):5557-5577. [50] SU XJ, SHEN BD, WANG K, et al. Roles of the neuron-restrictive silencer factor in the pathophysiological process of the central nervous system. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:834620. [51] CHENG Y, YIN Y, ZHANG A, et al. Transcription factor network analysis identifies REST/NRSF as an intrinsic regulator of CNS regeneration in mice. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):4418. [52] OH YM, MAHAR M, EWAN EE, et al. Epigenetic regulator UHRF1 inactivates REST and growth suppressor gene expression via DNA methylation to promote axon regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(52):E12417-E12426. [53] WEI X, LUO L, CHEN J. Roles of mTOR signaling in tissue regeneration. Cells. 2019;8(9):1075. [54] YAO R, REN L, WANG S, et al. Euxanthone inhibits traumatic spinal cord injury via anti-oxidative stress and suppression of p38 and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in a rat model. Transl Neurosci. 2021;12(1):114-126. [55] 易凌荣,谭波涛,刘媛,等.联合激活mTOR和STAT信号通路对脊髓损伤小鼠轴突再生及运动功能的影响[J].解放军医学杂志, 2022,47(1): 12-19. [56] CAMPION TJ 3RD, SHEIKH IS, SMIT RD, et al. Viral expression of constitutively active AKT3 induces CST axonal sprouting and regeneration, but also promotes seizures. Exp Neurol. 2022;349:113961. [57] ZHANG Z, LIN BS, PENG CW, et al. Design of a novel paired associative nerve stimulation system and treatment strategy for incomplete spinal cord injury: a preliminary study. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2021;29:1341-1349. [58] CHEN Y, LI D, LI N, et al. Role of nerve signal transduction and neuroimmune crosstalk in mediating the analgesic effects of acupuncture for neuropathic pain. Front Neurol. 2023;14:1093849. [59] WANG MM, ZHANG M, FENG YS, et al. Electroacupuncture inhibits neuronal autophagy and apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT pathway following ischemic stroke. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:134. [60] ZHANG Y, YIN YL, JIN ZY, et al. Electroacupuncture activates neuroplasticity in the motor cortex and corticospinal tract via the mTOR pathway in a rat P-MCAO model. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022:3470685. [61] WAN L, WANG Y, LI J, et al. Inhibition of the AKT/mTOR pathway negatively regulates PTEN expression via miRNAs. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2022;54(11):1637-1647. [62] LUO X, PARK KK. Neuron-intrinsic inhibitors of axon regeneration: PTEN and SOCS3. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2012;105:141-173. [63] DANILOV CA, STEWARD O. Conditional genetic deletion of PTEN after a spinal cord injury enhances regenerative growth of CST axons and motor function recovery in mice. Exp Neurol. 2015;266:147-160. [64] NAKAMURA Y, UENO M, NIEHAUS JK, et al. Modulation of both intrinsic and extrinsic factors additively promotes rewiring of corticospinal circuits after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci. 2021;41(50):10247-10260. [65] WALKER EC, TRUONG K, MCGREGOR NE, et al. Cortical bone maturation in mice requires SOCS3 suppression of gp130/STAT3 signalling in osteocytes. Elife. 2020;9:e56666. [66] GEOFFROY CG, MEVES JM, KIM HJM, et al. Targeting PTEN but not SOCS3 resists an age-dependent decline in promoting axon sprouting. iScience. 2022;25(11):105383. [67] PAN L, YI L, LIU Y, et al. Effects of task-based rehabilitative training combined with PTEN/SOCS3 coinhibition promotes axon regeneration and upper extremity skilled motor function recovery after cervical spinal cord injury in adult mice. Neurosci Lett. 2023;800:137121. [68] PAN L, TAN B, TANG W, et al. Combining task-based rehabilitative training with PTEN inhibition promotes axon regeneration and upper extremity skilled motor function recovery after cervical spinal cord injury in adult mice. Behav Brain Res. 2021;405:113197. [69] BARZEGAR BEHROOZ A, TALAIE Z, JUSHEGHANI F, et al. Wnt and PI3K/Akt/mTOR survival pathways as therapeutic targets in glioblastoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1353. [70] KEREKES K, TREXLER M, BÁNYAI L, et al. Wnt inhibitory factor 1 binds to and inhibits the activity of sonic hedgehog. Cells. 2021;10(12):3496. [71] CHENG P, LIAO HY, ZHANG HH. The role of Wnt/mTOR signaling in spinal cord injury. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2022;25:101760. [72] LIU Y, SHI J, LU CC, et al. Ryk-mediated Wnt repulsion regulates posterior-directed growth of corticospinal tract. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8(9):1151-1159. [73] ZOU Y. Inter-growth cone communication mediated by planar cell polarity pathway in axon guidance. Dev Biol. 2022;490:50-52. [74] KIKUCHI A, YAMAMOTO H, SATO A, et al. Wnt5a: its signalling, functions and implication in diseases. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2012;204(1):17-33. [75] LI L, HUTCHINS BI, KALIL K. Wnt5a induces simultaneous cortical axon outgrowth and repulsive axon guidance through distinct signaling mechanisms. J Neurosci. 2009;29(18):5873-5883. [76] LIU Y, WANG X, LU CC, et al. Repulsive Wnt signaling inhibits axon regeneration after CNS injury. J Neurosci. 2008;28(33):8376-8382. [77] MIYASHITA T, KODA M, KITAJO K, et al. Wnt-Ryk signaling mediates axon growth inhibition and limits functional recovery after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2009;26(7):955-964. [78] YU F, WENG J, YUAN YS, et al. Wnt5a affects schwann cell proliferation and regeneration via Wnt/c-Jun and PTEN signaling pathway. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018;131(21):2623-2625. [79] YANG H, LIANG C, LUO J, et al. Transplantation of Wnt5a-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promotes recovery after spinal cord injury via the PI3K/AKT pathway. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. doi:10.1007/s12035-024-04248-8. [80] GONZÁLEZ P, GONZÁLEZ-FERNáNDEZ C, JAVIER RODRÍGUEZ F. Effects of Wnt5a overexpression in spinal cord injury. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(11): 5150-5163. [81] GRIFFIN JM, BRADKE F. Therapeutic repair for spinal cord injury: combinatory approaches to address a multifaceted problem. EMBO Mol Med. 2020;12(3):e11505. [82] WATHEN CA, GHENBOT YG, OZTURK AK, et al. Porcine models of spinal cord injury. Biomedicines. 2023;11(8):2202. [83] SAWADA M, YOSHINO-SAITO K, NINOMIYA T, et al. Reorganization of corticospinal projections after prominent recovery of finger dexterity from partial spinal cord injury in macaque monkeys. eNeuro. 2023;10(8): ENEURO.0209-23.2023. [84] RAZA SHA, KHAN R, CHENG G, et al. RNA-Seq reveals the potential molecular mechanisms of bovine KLF6 gene in the regulation of adipogenesis. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;195:198-206. [85] MAO Y, CHEN Y, ZHANG Z. Molecular function of Krüppel-like factor 7 in biology. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2023;55(5):713-725. [86] LI T, ZHAO X, DUAN J, et al. Targeted inhibition of STAT3 in neural stem cells promotes neuronal differentiation and functional recovery in rats with spinal cord injury. Exp Ther Med. 2021;22(1):711. [87] AL-JAWAHIRI R, STOKES L, SMITH H, et al. Short report: behavioural characterisation of SOX11 syndrome. Res Dev Disabil. 2023;143:104623. [88] VEVERKA P, BROM T, JANOVIČ T, et al. Electron microscopy reveals toroidal shape of master neuronal cell differentiator REST - RE1-silencing transcription factor. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023;21:731-741. [89] SUN X, HUANG L Y, PAN H X, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and exercise restore motor function following spinal cord injury by activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(5):1067-1075. [90] MANNING BD, TOKER A. AKT/PKB Signaling: navigating the network. Cell. 2017;169(3):381-405. [91] PHILIPPE L, VAN DEN ELZEN AMG, WATSON MJ, et al. Global analysis of LARP1 translation targets reveals tunable and dynamic features of 5’ TOP motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(10):5319-5328. [92] BLANCO DB, CHAPMAN NM, RAYNOR JL, et al. PTEN directs developmental and metabolic signaling for innate-like T cell fate and tissue homeostasis. Nat Cell Biol. 2022;24(11):1642-1654. [93] MILLER KM, MARFULL-OROMí P, ZOU Y. Characterization of axon guidance phenotypes in Wnt/PCP mutant mice. Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2438:277-286. [94] BOIDO M, VERCELLI A. Genes and miRNAs as hurdles and promoters of corticospinal tract regeneration in spinal cord injury. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:748911. [95] KARAMIAN BA, SIEGEL N, NOURIE B, et al. The role of electrical stimulation for rehabilitation and regeneration after spinal cord injury. J Orthop Traumatol. 2022;23(1):2. [96] ZIPSER CM, CRAGG JJ, GUEST JD, et al. Cell-based and stem-cell-based treatments for spinal cord injury: evidence from clinical trials. Lancet Neurol. 2022;21(7):659-670. [97] ZHU B, GU G, REN J, et al. Schwann cell-derived exosomes and methylprednisolone composite patch for spinal cord injury repair. ACS Nano. 2023;17(22):22928-22943. [98] KISS BIMBOVA K, BACOVA M, KISUCKA A, et al. Activation of three major signaling pathways after endurance training and spinal cord injury. Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59(2):950-967. [99] TEDESCHI A, POPOVICH PG. The Application of omics technologies to study axon regeneration and CNS repair. F1000Res. 2019;8:F1000 Faculty Rev-311. [100] FENG T, ZHAO C, RAO JS, et al. Different macaque brain network remodeling after spinal cord injury and NT3 treatment. iScience. 2023;26(6):106784. [101] WANG Z, DUAN H, HAO F, et al. Circuit reconstruction of newborn neurons after spinal cord injury in adult rats via an NT3-chitosan scaffold. Prog Neurobiol. 2023;220:102375. |
| [1] | 陈伊娴, 陈 晨, 卢立恒, 汤锦鹏, 于晓巍. 雷公藤甲素治疗骨关节炎的网络药理学分析与实验验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(4): 805-815. |
| [2] | 尹 路, 蒋川锋, 陈俊杰, 易 明, 王子赫, 石厚银, 汪国友, 沈骅睿. 沙苑子苷A对关节软骨细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [3] | 王秋月, 靳 攀, 蒲 锐. 运动干预与细胞焦亡在骨关节炎中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [4] | 艾克帕尔·艾尔肯, 陈晓涛, 吾凡别克·巴合提. 成骨诱导人牙周膜干细胞来源外泌体促进炎症微环境下人牙周膜干细胞成骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [5] | 张昊军, 李泓毅, 张 辉, 陈浩然, 张力中, 耿 杰, 侯传东, 于 琦, 贺培凤, 贾金鹏, 卢学春. 间充质细胞源性骨肉瘤中关键分子标志物鉴定及药物敏感性分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1448-1456. |
| [6] | 吕丽婷, 于 霞, 张金梅, 高巧婧, 刘仁凡, 李 梦, 王 璐. 脑衰老与外泌体研究进程及现状的文献计量学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1457-1465. |
| [7] | 孙玉婷, 吴家媛, 张 剑. 影响牙髓干细胞成骨及成牙本质分化的相关物理因素及作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1531-1540. |
| [8] | 喻 婷, 吕冬梅, 邓 浩, 孙 涛, 程 钎. 淫羊藿苷预处理增强人牙周膜干细胞对M1型巨噬细胞的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1328-1335. |
| [9] | 赵瑞华, 陈思娴, 郭 杨, 石 磊, 吴承杰, 吴 毛, 杨光露, 张昊恒, 马 勇. 温肾通督方促进小鼠脊髓损伤的修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1118-1126. |
| [10] | 郑 琳, 靳文君, 罗珊珊, 黄 芮, 王 杰, 程余婷, 安哲庆, 熊 玥, 巩仔鹏, 廖 健. 杜仲促进去势大鼠牙槽骨成骨的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1159-1167. |
| [11] | 张德宝, 王 鹏, 李 琨, 张少杰, 李志军, 李树文, 吴一民. 自体黄韧带干预下兔硬膜外纤维瘢痕的形成[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1168-1175. |
| [12] | 姬慧慧, 蒋 旭, 张志敏, 邢运虹, 王亮亮, 李 娜, 宋雨庭, 罗旭光, 崔慧林, 曹锡梅. SR9009联合吲哚丙酸通过核因子κB信号通路减轻C2C12成肌细胞的炎症反应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1220-1229. |
| [13] | 何 波, 陈 文, 马岁录, 何志军, 宋 渊, 李金鹏, 刘 涛, 魏晓涛, 王威威, 谢 婧. 皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤的发病机制及治疗进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1230-1238. |
| [14] | 陈伊琳, 蒋晓波, 屈红林, 刘瑞莲. GSK3/Nrf2调控的生物节律在机体衰老中的规律[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1257-1264. |
| [15] | 张文华, 李 荀, 张伟超, 李欣颖, 马帼澳, 王孝强. SphK1/S1P/S1PR2信号通路促进肌生成:运动改善骨骼肌健康的新视角[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1265-1275. |
脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束断裂和神经元死亡导致下行运动传导通路的功能障碍,皮质脊髓束轴突几乎没有再生和重新连接的先天能力,因此调控皮质脊髓束轴突再生是脊髓损伤功能重建的重要治疗策略[4]。现如今,调控脊髓损伤后神经元轴突再生机制主要基于转录因子调控、细胞骨架动力学、轴突运输和表观遗传修饰4大方面[5],其中转录因子及特定信号通路对脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突再生具有重要调控作用。
转录因子是细胞发生过程的关键调节因子[6]。既包括内源性的过程如细胞发育和细胞分化,也包括外源性的过程如对外部信号的反应。转录因子可以通过调节转录、翻译、转录后调节或调节位点结合的可及性促使其他因子结合或阻止其结合,并激活或抑制基因的转录[7-8]。信号通路常导致转录因子的激活或失活,转录因子是信号通路和基因调控之间的纽带。重编程过程通常由一组转录因子的转录诱导驱动,然后驱动所需的基因调控程序。相比之下,对外部刺激的反应通常由受体激活和信号通路启动,这些信号通路通过翻译后修饰的级联,然后导致一组转录因子的调控[9]。不同转录因子之间基于信号通路的交叉调节可能是转录因子联合治疗的一个重要机制。因此,深入了解受转录因子调控影响的信号通路对于再生神经科学非常重要,因为它可以指导转录因子联合治疗策略的合理开发[10]。文章着眼于转录因子及特定信号通路促进脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突再生展开综述,旨在为今后临床研究提供新思路。
文章将从以下转录因子和信号通路进行详细叙述:Krüppel样因子6(Krüppel-like factor 6,KLF6),在神经系统中Krüppel样因子6的作用涉及多种生物学过程,包括神经元的成熟和轴突再生;Krüppel样因子7(Krüppel-like factor 7,KLF7),也称为B-细胞特异性抗原2属抗体(B-cell specific antigen 2,BAS2),在神经系统的发育中扮演着重要角色,它影响神经发生和神经元迁移;SOX11(SRY-related high-mobility group box 11),属于SOX家族,对神经系统的发育具有重要作用,SOX11的表达对于胚胎神经系统以及组织重构都至关重要,对于神经突的生长和神经元的存在都是必须的;信号转导及转录激活因子3(Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3,STAT3 ),它在细胞信号传导中起着核心作用,信号转导及转录激活因子3的激活通常涉及在酪氨酸残基上的磷酸化,此过程通常由Janus激酶(Janus kinases,JAK)家族成员催化。激活后的信号转导及转录激活因子3会形成二聚体,转移到细胞核内,调控多种基因的表达;随后是RE1敲除沉默转录因子/神经元限制性沉默因子(RE1-Silencing Transcription Factor,REST/Neuron-Restrictive Silencer Factor,NRSF),神经元限制性沉默因子在多种神经生物学过程中发挥作用,包括神经元的生存、分化、突触可塑性和神经保护。研究表明,神经元限制性沉默因子在神经发育过程中起到抑制某些基因表达的作用,而在成熟的神经系统中,神经元限制性沉默因子可能参与维持神经元功能和响应环境变化。
信号通路主要包括磷脂酰肌醇3激酶-蛋白激酶B-雷帕霉素靶蛋白(phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-protein kinase B-mammalian target of rapamycin,PI3K-AKT-mTOR)信号通路,该通路在细胞外生长因子与受体酪氨酸激酶(receptor tyrosine kinase,RTK)结合后,会激活磷脂酰肌醇3激酶,进而产生第二信使磷脂酰肌醇3,4,5-三磷酸(phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate,PIP3),招募并激活蛋白激酶B。活化的蛋白激酶B通过磷酸化多种酶、激酶和转录因子等下游因子,进而调节细胞的功能。雷帕霉素靶蛋白是磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B下游的一种重要的丝氨酸-苏氨酸蛋白激酶,它通过激活核糖体激酶来调节肿瘤细胞的增殖、存活和侵袭转移。Wnt5a通路(Wnt family member 5A,Wnt5a),该通路是Wnt家族的成员之一,它通过激活非典型Wnt信号通路在多种生物学过程中发挥作用。它参与神经发育、神经元存活、突触可塑性和神经再生等过程。此外,Wnt5a还参与调节轴突再生和神经保护,这为神经系统损伤的治疗提供了新的策略。
因此,此综述从转录因子及其特定信号通路对脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生的作用出发。讨论Krüppel样因子6、Krüppel样因子7、神经元限制性沉默因子、经磷脂酰肌醇3激酶-蛋白激酶B-雷帕霉素靶蛋白信号通路及Wnt5a信号通路在脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突再生过程的作用机制,并探讨基于相关转录因子及其特定信号通路的联合治疗策略靶向治疗皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生的相关研究进展,旨在为脊髓损伤临床治疗提供新的治疗策略。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
1.1 资料来源
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在2023年6月至2024年9月检索。
1.1.2 检索时限 各数据库建库时间至2024年9月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 万方数据知识服务平台、Web of Science、PubMed数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“脊髓损伤,轴突再生,转录因子,信号通路,皮质脊髓束,中枢神经系统,协同作用,神经保护”,英文检索词为“spinal cord injury,axon regeneration,transcription factors,signaling pathway,corticospinal tract,Central Nervous System,Synergistic system,Neuroprotective system”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 综述、实验文章、系统评价、学位论文和荟萃分析等。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 手工检索引用文献中价值较高的参考文献,阅读评估是否符合纳入标准。
1.1.7 检索策略 以PubMed数据库和万方数据知识服务平台检索策略为例,见图1。
1.1.8 检索文献量 计算机初步检索到3 579篇文献。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 入选标准 转录因子及其信号通路对脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突再生相关研究。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①文献内容与主题无关的文章和重复性研究;②低质量文献。
1.3 文献质量评估和数据的提取 严格剔除与研究目的相关度不高以及陈旧重复的文献,随后再次筛选出新颖、研究内容密切相关、可参考价值高的文章,最终纳入101篇文献进行综述,文献筛选流程见图2。
3.1 既往他人在该领域的贡献和存在的问题 综上所述,上述转录因子及其信号通路与脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突再生密切相关[84-93],见表4。
尽管针对许多相似同质的内源性轴突调控转录因子和信号通路,但仅有少数如Krüppel样因子6、Krüppel样因子7、神经元限制性沉默因子等转录因子以及经磷脂酰肌醇3激酶-蛋白激酶B-雷帕霉素靶蛋白信号通路、Wnt5a信号通路等信号通路能够促进脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突再生,有利于脊髓损伤后的功能恢复,基于上述转录因子及其信号通路的靶向联合治疗策略为临床治疗脊髓损伤提供新的治疗思路。见图6。
虽然当前对相关转录因子和信号通路的研究取得了一定的成果,但仍存在不足之处:①生物体内的转录因子及信号通路互相联系、错综复杂,对目的转录因子自身同其他信号通路的交互作用网络、各通路之间的互相作用关系仍需深入研究;②既往大多数实验为动物实验,后期研究应探索将动物模型的实验结果应用到人体临床研究的可行性及生物安全性;③尽管已发现多种转录因子及其信号通路可调控脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突的再生,但有关其下游信号机制的阐述仍不清晰。④仍需进一步探索其他转录因子及其信号通路对脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生的作用功效及机制,这将更好地为脊髓损伤患者提供更全面更有效的基因治疗选择。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 在文献检索过程中作者发现,相关转录因子、信号通路被国内外大量学者广泛应用于脑出血、癌症和神经科学等领域,但在脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突再生领域中的研究尚无全面、系统的文章将转录因子及其信号通路联合脊髓损伤、皮质脊髓束轴突再生领域的研究成果进行综合分析。
此外,该综述全面讨论了转录因子及其信号通路在脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突再生中的治疗作用,深入探讨了它们的作用机制,通过对这些关键通路的荟萃分析,为寻求新的治疗方法提供了重要的参考。此外,这些深入分析有助于揭示Krüppel样因子6、Krüppel样因子7、神经元限制性沉默因子和经磷脂酰肌醇3激酶-蛋白激酶B-雷帕霉素靶蛋白信号通路、Wnt5a信号通路治疗脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突再生的内源性分子机制,为未来的研究提供了方向。
3D模式图目的是为了更加直观地了解到相关转录因子的蛋白结构与功能之间的联系,以便更立体地认识转录因子直接相互作用的协同机制,这对于理解转录因子的功能以及开发针对特定转录因子的药物具有重要意义。虽然这并不直接涉及脊髓损伤的治疗,但它们展示了3D蛋白结构图在生物医学领域的广泛应用潜力,具体结构见表4。
3.3 综述的局限性 ①尽管内源性转录因子及其信号通路在脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突再生领域已表现出较好的治疗效果,但该方法仍然处于初步探索阶段,需要更深入的研究和验证;②在此综述中,可能由于综述时不同实验方法和不同样本群体造成结果偏差;③缺乏跨物种的比较和临床研究,限制了从动物模型到人体临床研究的转换。
3.4 综述的重要意义 脊髓损伤后轴突无法完全连接严重影响了神经元连接,造成严重的功能障碍,对于脊髓损伤患者回归家庭和社会产生了不可逆转的伤害。现如今仍然缺乏治疗脊髓损伤的有效方法,目前的临床方法主要基于早期脊柱稳定、药物治疗、干细胞移植和康复计划[94-97]。基于动物模型的临床前研究[98],文章推测将转录因子及其信号通路组合治疗,通过物理相互作用、转录交叉调节、基于信号传递的交叉调节和调节DNA的共占据等协同作用机制[34],能够有效地促进皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生。不同转录因子和信号通路的相互作用在皮质脊髓束轴突的再生过程中发挥重要的作用[31],如信号转导及转录激活因子3和Krüppel样因子6可以直接相互结合,并直接影响活性。而磷酸酯酶与张力蛋白同源物和细胞因子信号抑制物3通过下游效应物的交叉协同激活特定轴突再生相关蛋白翻译和基因转录。信号转导及转录激活因子3通过转录交叉调节,直接靶向相关启动子提高“下游”Krüppel样因子6转录,启动额外促再生转录因子的二次级联。Krüppel样因子6和全能性先峰因子通过高度共同占据再生相关基因网络中的调控DNA协同促进皮质脊髓束神经元轴突生长[2]。未来的研究应进一步探索这些转录因子和信号通路之间的相互作用,以及它们如何共同影响皮质脊髓束神经元轴突的再生过程。
尽管促进皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生还有许多阻碍,但现今的技术可以为此提供新的解决途径,例如多组学包括表观遗传学、转录组学和蛋白质组学等结合神经示踪将明确特定神经元及其亚群轴突再生能力。有助于精准研究转录因子调控脊髓损伤后轴突再生分子机制[99];基因重编程亦能调控皮质脊髓束轴突再生;神经环路特异性遗传技术、特定药物激活受体技术、病毒神经示踪等可用于评估脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突再生和功能连接。转录因子联合治疗策略能够有效恢复中枢神经损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生的能力。因此,如何明确最佳转录因子治疗组合,以及明确后如何以最佳方式提供这些因素,是今后治疗皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生策略的核心问题。而基于CRISPR技术的基因编辑为上述问题的解决提供了有效的技术手段,当前已经在制备人类疾病动物模型中得到广泛应用。未来应考虑如何利用CRISPR技术来加速设计有效的基于转录因子联合治疗的干预措施,以促进中枢神经系统损伤的恢复。
此外,前期研究发现,相对调控皮质脊髓束的轴突投射,其他下行轴突通路的调控策略亦能发挥功能重建作用[100-101],如红核脊髓束(红核)、前庭脊髓束(前庭复合体)和网状脊髓束(网状结构),以及去甲肾上腺素能轴突(小脑室)、多巴胺能轴突(间脑)和5-羟色胺轴突(脑干)的投射通路,因为成年后哺乳动物的前庭复合体、中缝核和红核比皮质脊髓束更具神经可塑性。未来可以利用相关神经调控技术提高皮质脊髓束轴突再生的能力,或通过物理治疗结合药理治疗的方法,如康复治疗结合药物治疗进行干预,进一步促进脊髓损伤的功能恢复,有望为脊髓损伤患者带来新的治疗选择。
3.5 课题组专家的意见和建议 文章系统综述了转录因子及特定信号通路对脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生的影响。作者认为联合治疗策略对于脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生的治疗效果优于单独疗法,这显示出联合疗法治疗疾病的前景。在临床应用方面,文章讨论的转录因子及特定信号通路在脊髓损伤后能够促进皮质脊髓束神经元轴突再生可以为开发新的治疗方法提供理论基础,为临床脊髓损伤患者提供新的治疗靶点。预期应用药物干预来模拟它们的生物学效应;使用基因疗法来增强转录因子活性等。在药物开发和疾病模型研究中,动物模型是不可或缺的工具,动物模型是研究疾病机制和评估治疗方法的重要工具,但动物模型并不能完全模拟人类疾病的复杂性,它们在预测人类反应方面存在局限性。因此在将研究成果转化为临床应用时需要谨慎,如社会伦理问题、确保治疗的安全性、有效性和最小化潜在的不良反应等。因此动物模型始终不能替代临床作用。而当前正在开发的新的模型和方法如类器官和基于CRISPR技术的基因编辑技术能够提高转录因子及其与其他特定信号通路联合促进皮质脊髓束轴突再生研究的准确性和临床相关性。这些新方法有望在未来减少对动物模型的依赖,并加速从临床前到临床的转化过程。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||