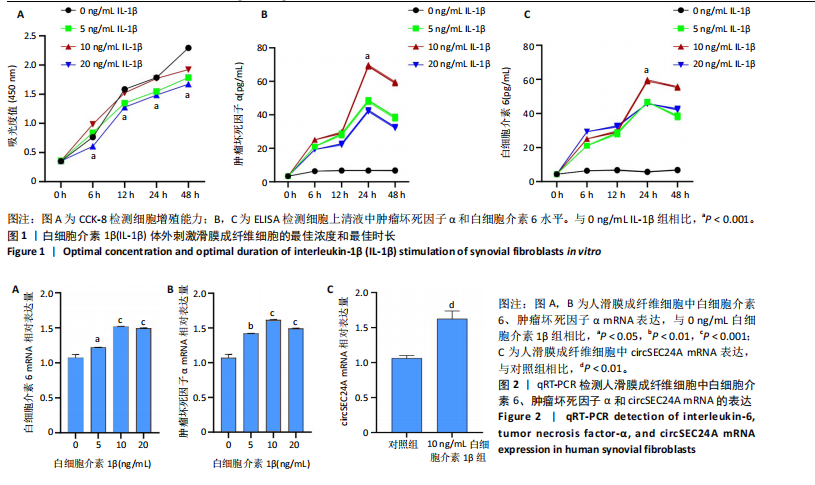
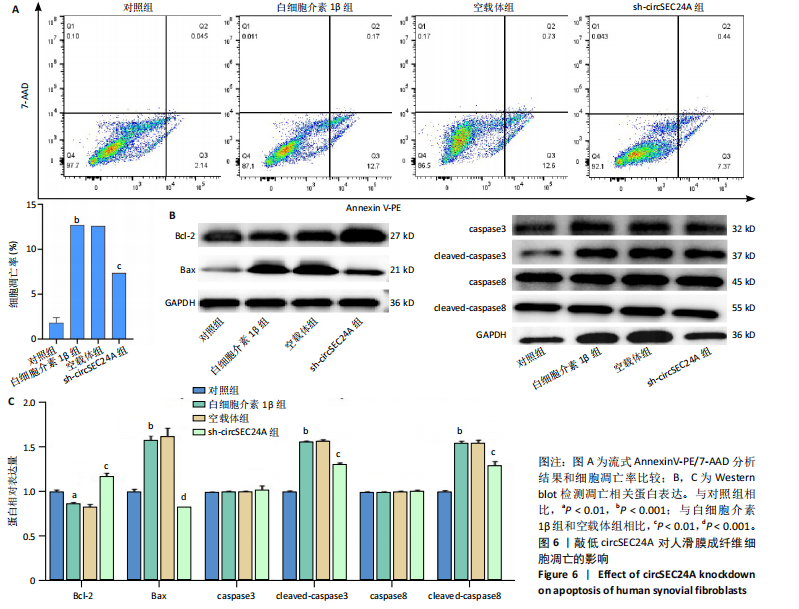
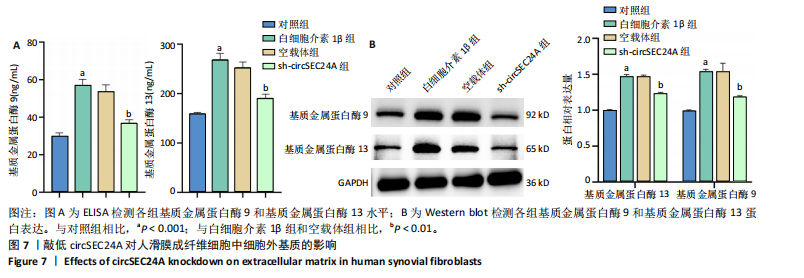
[1] PHILPOTT HT, BIRMINGHAM TB, CARTER MM, et al. Association between synovial tissue damage and pain in late-stage knee osteoarthritis: A cross-sectional study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2024;32(11):1503-1512.
[2] 何至,许凯,裴新武,等.沉默miR-126对关节软骨细胞增殖、凋亡和炎症反应的影响及其机制[J].山东医药,2024,64(25):40-43.
[3] 宋亚丽,秦凯丽,公慧萍,等.姜黄素对LPS诱导小鼠滑膜成纤维细胞炎症和纤维化的影响[J].中成药,2024,46(4):1356-1359.
[4] SCANZELLO CR, GOLDRING SR. The role of synovitis in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Bone. 2012;51(2):249-257.
[5] OEHLER S, NEUREITER D, MEYER-SCHOLTEN C, et al. Subtyping of osteoarthritic synoviopathy. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2002;20(5):633-640.
[6] CHEN R, TONG Y, HU X, et al. circSLTM knockdown attenuates chondrocyte inflammation, apoptosis and ECM degradation in osteoarthritis by regulating the miR-515-5p/VAPB axis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024;138:112435.
[7] HUANG K, LIU X, QIN H, et al. FGF18 encoding circular mRNA-LNP based on glycerolipid engineering of mesenchymal stem cells for efficient amelioration of osteoarthritis. Biomater Sci. 2024;12(17):4427-4439.
[8] WANG X, XUE Q, DUAN Q, et al. Circ_0011058 alleviates RA pathology through the circ_0011058/miR-335-5p/CUL4B signal axis. Autoimmunity. 2024;57(1): 2299587.
[9] WANG R, LI H, HAN Y, et al. Knockdown of circ_0025908 inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion, and inflammation while stimulates apoptosis in fibroblast-like synoviocytes by regulating miR-650-dependent SCUBE2. Autoimmunity. 2022;55(7):473-484.
[10] WU Y, ZHANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. CircRNA hsa_circ_0005105 upregulates NAMPT expression and promotes chondrocyte extracellular matrix degradation by sponging miR-26a. Cell Biol Int. 2017;41(12):1283-1289.
[11] ZHANG B, ZHOU J. CircSEC24A (hsa_circ_0003528) interference suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via miR-421/MMP3 axis. Bioengineered. 2022;13(4):9049-9062.
[12] JASIM SA, SALAHDIN OD, MALATHI H, et al. Targeting Hepatic Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) and Related Drug Resistance by Small Interfering RNA (siRNA). Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024;82(4):3031-3051.
[13] LIAO Y, YANG D, LUO H, et al. CircSEC24A promotes tumor progression through sequestering miR-455-3p in hepatocellular carcinoma. Neoplasma. 2021: 210305N285. doi: 10.4149/neo_2021_210305N285.
[14] CHEN Y, XU S, LIU X, et al. CircSEC24A upregulates TGFBR2 expression to accelerate pancreatic cancer proliferation and migration via sponging to miR-606. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21(1):671.
[15] LU X, GAN Q, GAN C. Circular RNA circSEC24A Promotes Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression by Regulating miR-1193/MAP3K9 Axis. Onco Targets Ther. 2021;14:653-666.
[16] DADIHANC T, ZHANG Y, LI GQ, et al. CircRNA SEC24A promotes osteoarthritis through miR-107-5p/CASP3 axis. Regen Ther. 2024;26:60-70.
[17] LI N, XU Q, LIU Q, et al. Leonurine attenuates fibroblast-like synoviocyte-mediated synovial inflammation and joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2017;56(8):1417-1427.
[18] LEE K, NIKU S, KOO SJ, et al. Molecular imaging for evaluation of synovitis associated with osteoarthritis: a narrative review. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024;26(1):25.
[19] MOTTA F, BARONE E, SICA A, et al. Inflammaging and Osteoarthritis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2023;64(2):222-238.
[20] ZENG N, YAN ZP, CHEN XY, et al. Infrapatellar Fat Pad and Knee Osteoarthritis. Aging Dis. 2020;11(5):1317-1328.
[21] 凌晖,袁涛,韩杰,等.原发性膝骨关节炎患者滑膜组织中与炎症相关circRNA的筛选和生物学功能分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(23):3683-3690.
[22] MATHIESSEN A, CONAGHAN PG. Synovitis in osteoarthritis: current understanding with therapeutic implications. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):18.
[23] REMST DF, BLANEY DAVIDSON EN, VAN DER KRAAN PM. Unravelling osteoarthritis-related synovial fibrosis: a step closer to solving joint stiffness. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015;54(11):1954-1963.
[24] SHI L, ZHANG H, SUN J, et al. CircSEC24A promotes IL-1β-induced apoptosis and inflammation in chondrocytes by regulating miR-142-5p/SOX5 axis. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2022;69(2):701-713.
[25] 于瑞.CXCL2对骨关节炎滑膜细胞增殖凋亡影响的研究[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2022.
[26] CHEN B, SUN Y, XU G, et al. Role of crosstalk between synovial cells and chondrocytes in osteoarthritis (Review). Exp Ther Med. 2024;27(5):201.
[27] JIANG T, WENG Q, LIU K, et al. Bidirectional association identified between synovitis and knee and hand osteoarthritis: a general population-based study. Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2024;50:101169.
[28] 周丽君,张克远,王茜,等.环状RNA通过细胞内机制参与骨关节炎的发病[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(35):5716-5722.
[29] ZHANG J, ZHAO X, ZHANG J, et al. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0023404 exerts an oncogenic role in cervical cancer through regulating miR-136/TFCP2/YAP pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;501(2):428-433.
[30] MAO X, CAO Y, GUO Z, et al. Biological roles and therapeutic potential of circular RNAs in osteoarthritis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021;24:856-867.
[31] WENG PW, YADAV VK, PIKATAN NW, et al. Novel NFκB Inhibitor SC75741 Mitigates Chondrocyte Degradation and Prevents Activated Fibroblast Transformation by Modulating miR-21/GDF-5/SOX5 Signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(20):11082.
[32] RAMIREZ MLG, SALVESEN GS. A primer on caspase mechanisms. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018;82:79-85.
[33] SEYREK K, IVANISENKO NV, RICHTER M, et al. Controlling Cell Death through Post-translational Modifications of DED Proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 2020;30(5):354-369.
[34] THOMAS CM, FULLER CJ, WHITTLES CE, et al. Chondrocyte death by apoptosis is associated with cartilage matrix degradation. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007; 15(1):27-34.
[35] MCILWAIN DR, BERGER T, MAK TW. Caspase functions in cell death and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015;7(4):a026716.
[36] ZHANG J, LI Q, CHANG S. The effects of particle density in moxa smoke on the ultrastructure of knee cartilage and expressions of TNF-α, IL-1b, BAX, and Bcl-2 mRNA in a rat model for osteoarthritis. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(4):6589-6595. |