[1] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249.
[2] AHADI A. Dysregulation of miRNAs as a signature for diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer and their involvement in the mechanism underlying gastric carcinogenesis and progression. Iubmb Life. 2020;72(5):884-898.
[3] JELSKI W, MROCZKO B. Potential diagnostic utility of microRNAs in gastrointestinal cancers. Cancer Manag Res. 2023;15:863-871.
[4] TANG XH, GUO T, GAO XY, et al. Exosome-derived noncoding RNAs in gastric cancer: functions and clinical applications. Mol Cancer. 2021;20(1):99.
[5] OUYANG J, XIE Z, LEI X, et al. Clinical crosstalk between microRNAs and gastric cancer. Int J Oncol. 2021;58(4):7.
[6] TAN S, XIA L, YI P, et al. Exosomal miRNAs in tumor microenvironment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39(1):67.
[7] SANTOS P, ALMEDIA F. Role of exosomal miRNAs and the tumor microenvironment in drug resistance. Cells. 2020;9(6):1450.
[8] WANG J, GUAN X, ZHANG Y, et al. Exosomal miR-27a derived from gastric cancer cells regulates the transformation of fibroblasts into cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;49(3):869-883.
[9] JEPPESEN DK, ZHANG Q, FRANKLIN JL, et al. Extracellular vesicles and nanoparticles: emerging complexities. Trends Cell Biol. 2023;33(8):667-681.
[10] AGARWAL P, ANEES A, HARSIDDHARAY RK, et al. A comprehensive review on exosome: Recent progress and outlook. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2023. doi: 10.2174/2211738511666230523114311.
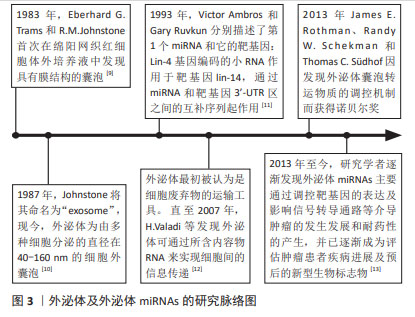
[11] LEE RC, FEINBAUM RL, AMBROS V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993; 75(5):843-854.
[12] VALADI H, EKSTROM K, BOSSIOS A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654-659.
[13] NAIL HM, CHIU CC, LEUNG CH, et al. Exosomal miRNA-mediated intercellular communications and immunomodulatory effects in tumor microenvironments. J Biomed Sci. 2023;30(1):69.
[14] WORTZEL I, DROR S, KENIFIC CM, et al. Exosome-mediated metastasis: communication from a distance. Dev Cell. 2019;49(3):347-360.
[15] ALOI N, DRAGO G, RUGGIERI S, et al. Extracellular vesicles and immunity: at the crossroads of cell communication. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(2):1205.
[16] MISHRA LC, PANDEY U, GUPTA A, et al. Alternating exosomes and their mimetics as an emergent strategy for targeted cancer therapy. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9:939050.
[17] PREETHI KA, SELVAKUMAR SC, ROSS K, et al. Liquid biopsy: Exosomal microRNAs as novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2022;21(1):54.
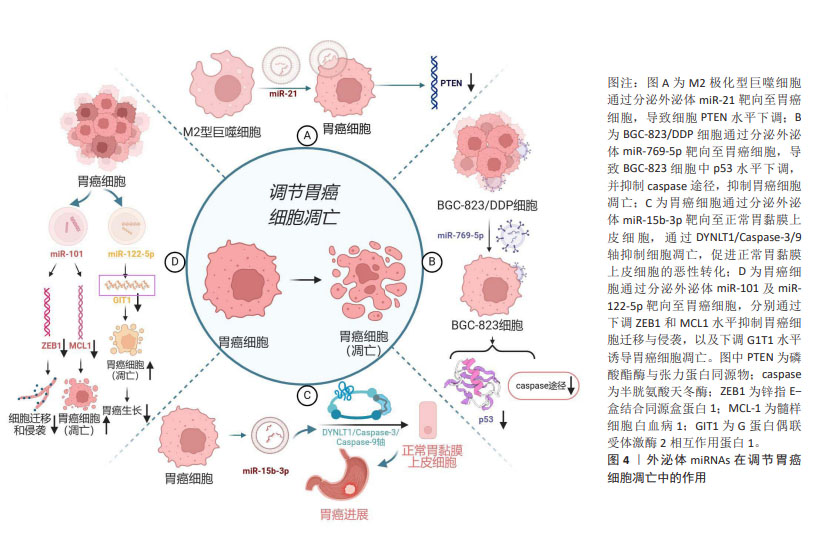
[18] ZHENG P, CHEN L, YUAN X, et al. Exosomal transfer of tumor-associated macrophage-derived miR-21 confers cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017;36(1):53.
[19] WEI S, PENG L, YANG J, et al. Exosomal transfer of miR-15b-3p enhances tumorigenesis and malignant transformation through the DYNLT1/Caspase-3/Caspase-9 signaling pathway in gastric cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39(1):32.
[20] JIAO Y, ZHANG L, LI J, et al. Exosomal miR-122-5p inhibits tumorigenicity of gastric cancer by downregulating GIT1. Int J Biol Marker. 2021;36(1):36-46.
[21] IMAMURA T, KOMATSU S, ICHIKAWA D, et al. Low plasma levels of miR-101 are associated with tumor progression in gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(63):106538-106550.
[22] GIUPPI M, LA SALVIA A, EVANGELISTA J, et al. The role and expression of angiogenesis-related miRNAs in gastric cancer. Biology(Basel). 2021;10(2):146.
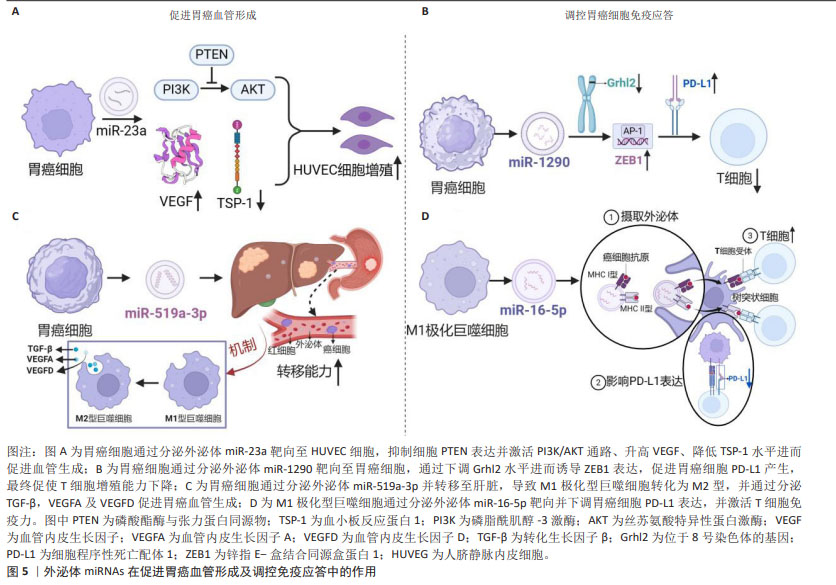
[23] DU J, LIANG Y, LI J, et al. Gastric cancer cell-derived exosomal microRNA-23a promotes angiogenesis by targeting PTEN. Front Oncol. 2020;10:326.
[24] LIN S, QUE Y, QUE C, et al. Exosome miR-3184-5p inhibits gastric cancer growth by targeting XBP1 to regulate the AKT, STAT3 and IRE1 signalling pathways. Asia-Pac J Clin Onco. 2022;19(2):e27-e38.
[25] 任志俭.外泌体miR-1273g-3p在胃癌中的作用及机制研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2022.
[26] QIU S, XIE L, LU C, et al. Gastric cancer-derived exosomal miR-519a-3p promotes liver metastasis by inducing intrahepatic M2-like macrophage-mediated angiogenesis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022;41(1):296.
[27] XU L, XIE X, LUO Y. The role of macrophage in regulating tumour microenvironment and the strategies for reprogramming tumour-associated macrophages in antitumour therapy. Eur J Cell Biol. 2021;100(2):151153.
[28] ZHU L, ZHANG S, CHEN S, et al. Exosomal miR-552-5p promotes tumorigenesis and disease progression via the PTEN/TOB1 axis in gastric cancer. J Cancer. 2022;13(3):890-905.
[29] XIA X, WANG S, NI B, et al. Hypoxic gastric cancer-derived exosomes promote progression and metastasis via MiR-301a-3p/PHD3/HIF-1α positive feedback loop. Oncogene. 2020;39(39):6231-6244.
[30] FENG C, SHE J, CHEN X, et al. Exosomal miR-196a-1 promotes gastric cancer cell invasion and metastasis by targeting SFRP1. Nanomedicine. 2019; 14(19):2579-2593.
[31] 朱萌,张宁,卢新兰,等. 肿瘤源性外泌体miR-106a调控间皮细胞Smad7表达影响胃癌腹膜转移[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2020, 41(3):340-346.
[32] WEI R, LIU S, ZHANG S, et al. Cellular and extracellular components in tumor microenvironment and their application in early diagnosis of cancers. Anal Cell Pathol. 2020;2020:6283796.
[33] LIANG Y, LIU Y, ZHANG Q, et al. Corrigendum to tumor-derived extracellular vesicles containing microRNA-1290 promote immune escape of cancer cells through the Grhl2/ZEB1/PD-L1 axis in gastric cancer. Transl Res. 2021;231:102-112.
[34] 李军涛.胃癌外泌体miR-135b-5p调控γδT细胞免疫功能的作用和机制研究[D].苏州:苏州大学,2021.
[35] LIU F, BU Z, ZHAO F, et al. Increased T-helper 17 cell differentiation mediated by exosome-mediated microRNA-451 redistribution in gastric cancer infiltrated T cells. Cancer Sci. 2018;109:65-73.
[36] ZHOU, J, TANG, Z, GAO, S, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages: recent insights and therapies. Front Oncol. 2020;10:188.
[37] LI Z, SUO B, LONG G, et al. Exosomal miRNA-16-5p derived from M1 macrophages enhances T cell-dependent immune response by regulating PD-L1 in gastric cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:572689.
[38] RAUE R, FRANK AC, SYED SN, et al. Therapeutic targeting of microRNAs in the tumor microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):2210.
[39] MOWLA M, HASHEMI A. Functional roles of exosomal miRNAs in multi-drug resistance in cancer chemotherapeutics. Exp Mol Pathol. 2020;118:9104592.
[40] GUO QR, WANG H, YAN YD, et al. The role of exosomal microRNA in cancer drug resistance. Front Oncol. 2020;10:472.
[41] LIN H, ZHANG L, ZHANG C, et al. Exosomal miR-500a-3p promotes cisplatin resistance and stemness via negatively regulating FBXW7 in gastric cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(16):8930-8941.
[42] JING X, XIE M, DING K, et al. Exosome-transmitted miR-769-5p confers cisplatin resistance and progression in gastric cancer by targeting CASP9 and promoting the ubiquitination degradation of p53. Clin Transl Med. 2022;12(5):e780.
[43] ZHANG X, WANG S, WANG H, et al. Circular RNA circNRIP1 acts as a microRNA-149-5p sponge to promote gastric cancer progression via the AKT1/mTOR pathway. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):20.
[44] SANG H, ZHANG W, PENG L, et al. Exosomal circRELL1 serves as a miR-637 sponge to modulate gastric cancer progression via regulating autophagy activation. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(1):56.
[45] CHEN Y, LIU H, ZOU J, et al. Exosomal circ_0091741 promotes gastric cancer cell autophagy and chemoresistance via the miR-330-3p/TRIM14/Dvl2/Wnt/β-catenin axis. Hum Cell. 2022;36(1):258-275.
[46] ZHANG H, DENG T, LIU R, et al. CAF secreted miR-522 suppresses ferroptosis and promotes acquired chemo-resistance in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):43.
[47] GAO H, MA J, CHENG Y, et al. Exosomal transfer of macrophage-derived miR-223 confers doxorubicin resistance in gastric cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:12169-12179.
[48] JI R, ZHANG X, GU H, et al. MiR-374a-5p: a new target for diagnosis and drug Resistance therapy in gastric cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;18: 320-331.
[49] ZHOU M, DONG J, HUANG J, et al. Chitosan-gelatin-EGCG nanoparticle-meditated LncRNA TMEM44-AS1 silencing to activate the P53 signaling pathway for the synergistic reversal of 5-FU resistance in gastric cancer. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(22):e2105077.
[50] JIN L, MA X, ZHANG N, et al. Targeting oncogenic miR-181a-2-3p inhibits growth and suppresses cisplatin resistance of gastric cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2021;13:8599-8609.
[51] 唐德平,邢梦洁,宋文涛,等. MicroRNA治疗在癌症及其他疾病中的研究进展[J].中国生物工程杂志,2021,41(11):64-73.
[52] YANG J, LI X, WEI S, et al. Evaluation of the diagnostic potential of a plasma exosomal miRNAs panel for gastric cancer. Front Oncol. 2021;11:683465.
[53] LIU X, CHU K. Abstract 2765: Exosomal miRNAs as circulating biomarkers for prediction of metastasis in stage II/III gastric cancer Cancer Res. 2019; 79(13):2765-2765.
[54] ZHENG GD, XU ZY, HU C, et al. Exosomal miR-590-5p in serum as a biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:636566.
[55] OHZAWA H, SAITO A, KUMAGAI Y, et al. Reduced expression of exosomal miR29s in peritoneal fluid is a useful predictor of peritoneal recurrence after curative resection of gastric cancer with serosal involvement. Oncol Rep. 2020;43(4):1081-1088.
[56] LU X, LU J, WANG S, et al. Circulating serum exosomal miR-92a-3p as a novel biomarker for early diagnosis of gastric cancer. Future Oncol. 2021; 17(8):907-919.
[57] ZHAO G, ZHOU A, LI X, et al. The significance of exosomal RNAs in the development, diagnosis, and treatment of gastric cancer. Genes (Basel). 2021;12(1):73.
[58] ZHANG Z, WU H, CHONG W, et al. Liquid biopsy in gastric cancer: predictive and prognostic biomarkers. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(10):903.
[59] KOH, HB, KIM, HJ, KANG, SW, et al. Exosome-based drug delivery: translation from bench to clinic. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(8):2042.
[60] LIU X, ABRAHAM JM, CHENG Y, et al. Synthetic circular RNA functions as a miR-21 sponge to suppress gastric carcinoma cell proliferation. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018;13:312-321.
[61] GU J, CHU X, HUO Y, et al. Gastric cancer-derived exosomes facilitate pulmonary metastasis by activating ERK-mediated immunosuppressive macrophage polarization. J Cell Biochem. 2023;124(4):557-572.
[62] 石亮.胃癌细胞源性外泌体miR-431-5p通过诱导铁死亡对胃癌的抑制作用及其机制研究[D].石家庄:河北大学,2023.
[63] REN W, ZHANG X, LI W, et al. Exosomal miRNA-107 induces myeloid-derived suppressor cell expansion in gastric cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:4023-4040.
[64] HUANG J, SHEN M, YAN M, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of miR-1290 promotes cell proliferation and invasion in gastric cancer via NKD1. Acta Bioch Bioph Sin. 2019;51(9):900-907.
[65] XU G, ZHANG B, YE J, et al. Exosomal miRNA-139 in cancer-associated fibroblasts inhibits gastric cancer progression by repressing MMP11 expression. Int J Biol Sci. 2019;15(11):2320-2329.
[66] LIN XM, WANG ZJ, LIN YX, et al. Decreased exosome-delivered miR-486-5p is responsible for the peritoneal metastasis of gastric cancer cells by promoting EMT progress. World J Surg Oncol. 2021;19(1):312.
[67] JI R, LIN J, GU H, et al. Gastric cancer derived mesenchymal stem cells promote the migration of gastric cancer cells through miR-374a-5p. Curr Stem Cell Rest. 2023;18(6):853-863.
[68] YANG H, FU H, WANG B, et al. Exosomal miR-423-5p targets SUFU to promote cancer growth and metastasis and serves as a novel marker for gastric cancer. Mol Carcinogen. 2018;57(9):1223-1236.
[69] HE J, WU J, DONG S, et al. Exosome-encapsulated miR-31, miR-192, and miR-375 serve as clinical biomarkers of gastric cancer. J Oncol. 2023; 2023:7335456.
[70] ZHANG Y, HAN T, FENG D, et al. Screening of non-invasive miRNA biomarker candidates for metastasis of gastric cancer by small RNA sequencing of plasma exosomes. Carcinogenesis. 2020;41(5):582-590.
[71] OHZAWA H, KUMAGAI Y, YAMAGUCHI H, et al. Exosomal microRNA in peritoneal fluid as a biomarker of peritoneal metastases from gastric cancer. Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2019;4(1):84-93.
[72] SHI Y, WANG Z, ZHU X, et al. Exosomal miR-1246 in serum as a potential biomarker for early diagnosis of gastric cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 2019; 25(1):89-99.
[73] YUN J, HAN SB, KIM HJ, et al. Exosomal miR-181b-5p downregulation in ascites serves as a potential diagnostic biomarker for gastric cancer-associated malignant ascites. J Gastric Cancer. 2019;19(3):301-314.
[74] SOEDA N, IINUMA H, SUZUKI Y, et al. Plasma exosome-encapsulated microRNA-21 and microRNA-92a are promising biomarkers for the prediction of peritoneal recurrence in patients with gastric cancer. Oncol Lett. 2019;18(5):4467-4480.
[75] 李金昌,王俊壹,张其德,等. MiR-494-3p在胃癌患者血清外泌体中的表达及价值[J].临床检验杂志,2023,41(7):508-511.
[76] 孙婧悦,王啸.血清外泌体miRNAs联合CA72-4在胃癌诊断中的价值分析[J].中国肿瘤临床,2022,49(12):636-641.
[77] KUMATA Y, IINUMA H, SUZUKI Y, et al. Exosomeencapsulated microRNA23b as a minimally invasive liquid biomarker for the prediction of recurrence and prognosis of gastric cancer patients in each tumor stage. Oncol Rep. 2018;40(1):319-330. |