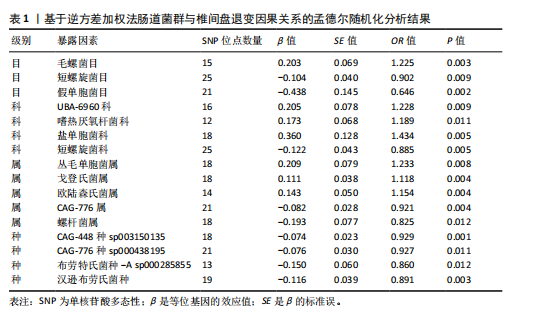
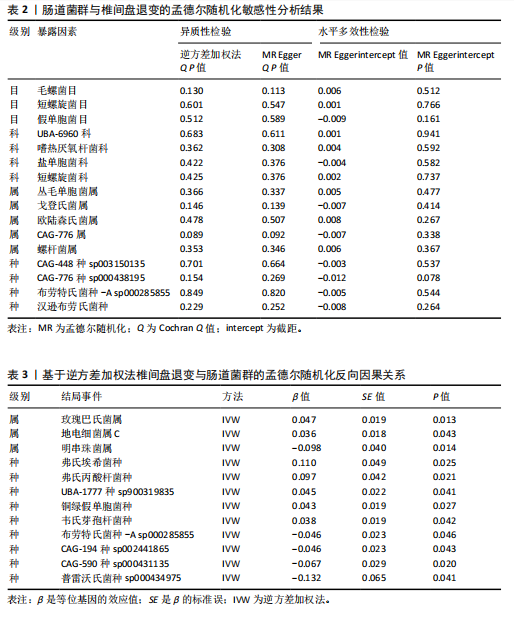
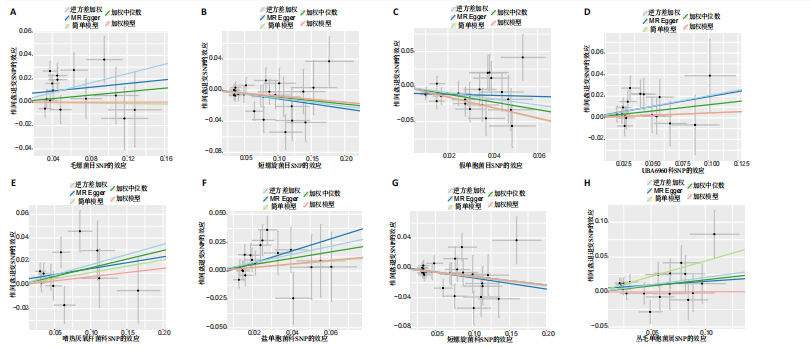
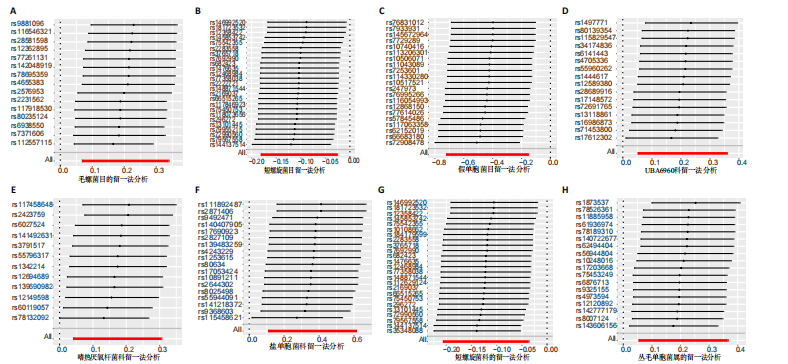
[1] QIN C, CHEN M, YU Q, et al. Causal relationship between the blood immune cells and intervertebral disc degeneration: univariable, bidirectional and multivariable Mendelian randomization. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1321295.
[2] GAO B, JIANG B, XING W, et al. Discovery and application of postnatal nucleus pulposus progenitors essential for intervertebral disc homeostasis and degeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(13):e2104888.
[3] KANG L, ZHANG H, JIA C, et al. Epigenetic modifications of inflammation in intervertebral disc degeneration. Ageing Res Rev. 2023;87:101902.
[4] 卢世浩,张子凡,孙柏峰,等.间充质干细胞移植治疗椎间盘退变植入途径的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2023, 33(11):1052-1056.
[5] XU J, SHAO T, LOU J, et al. Aging, cell senescence, the pathogenesis and targeted therapies of intervertebral disc degeneration. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14: 1172920.
[6] DING SL, ZHANG TW, ZHANG QC, et al. Excessive mechanical strain accelerates intervertebral disc degeneration by disrupting intrinsic circadian rhythm. Exp Mol Med. 2021;53(12):1911-1923.
[7] MARFIA G, GUARNACCIA L, NAVONE SE, et al. Microgravity and the intervertebral disc: the impact of space conditions on the biomechanics of the spine. Front Physiol. 2023;14:1124991.
[8] CHEN HH, HSU HT, LIAO MH, et al. Effects of sex and obesity on LEP variant and leptin level associations in intervertebral disc degeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(20): 12275.
[9] OU-YANG DC, KLECK CJ, ACKERT-BICKNELL CL. Genetics of intervertebral disc degeneration. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2023; 21(1):56-64.
[10] XIA Q, ZHAO Y, DONG H, et al. Progress in the study of molecular mechanisms of intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;174:116593.
[11] 马玮玮,陈虹谷,李彤彤,等.基于孟德尔随机化分析肠道菌群与骨密度的因果关系[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(12): 1780-1785.
[12] MA PJ, WANG MM, WANG Y. Gut microbiota: a new insight into lung diseases. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;155:113810.
[13] FAN Y, PEDERSEN O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021;19(1):55-71.
[14] RAJASEKARAN S, SOUNDARARAJAN DCR, TANGAVEL C, et al. Human intervertebral discs harbour a unique microbiome and dysbiosis determines health and disease. Eur Spine J. 2020;29(7):1621-1640.
[15] NI S, HUANG X, LI X, et al. METTL3 promotes nucleus pulposus cell senescence in intervertebral disc degeneration by regulating TLR2 m6A methylation and gut microbiota. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2024;79(8):glae150.
[16] BIRNEY E. Mendelian Randomization. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2022;12(4): 4913-4924.
[17] GILL D, WALKER VM, MARTIN RM, et al. Comparison with randomized controlled trials as a strategy for evaluating instruments in Mendelian randomization. Int J Epidemiol. 2020;49(4):1404-1406.
[18] 柴金莲,李树栋,李威,等.肠道菌群与药物相关性骨坏死:两样本双向孟德尔随机化分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2024,28(27):4325-4331.
[19] LEVIN M G, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization as a tool for cardiovascular research: a review. JAMA Cardiol. 2024; 9(1):79-89.
[20] QIN Y, HAVULINNA AS, LIU Y, et al. Combined effects of host genetics and diet on human gut microbiota and incident disease in a single population cohort. Nat Genet. 2022;54(2):134-142.
[21] XU J, ZHANG S, TIAN Y, et al. Genetic causal association between iron status and osteoarthritis: a two-sample mendelian randomization. Nutrients. 2022; 14(18):3683.
[22] MOUNIER N, KUTALIK Z. Bias correction for inverse variance weighting Mendelian randomization. Genet Epidemiol. 2023; 47(4):314-331.
[23] XIAO G, HE Q, LIU L, et al. Causality of genetically determined metabolites on anxiety disorders: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. J Transl Med. 2022; 20(1):475.
[24] DENG Y, WONG MCS. Association between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporosis in japanese populations: a mendelian randomization study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023;75(8):1334-1343.
[25] LIU Z, WANG H, YANG Z, et al. Causal associations between type 1 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular diseases: a Mendelian randomization study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023;22(1):236.
[26] ZHANG GZ, DENG YJ, XIE QQ, et al. Sirtuins and intervertebral disc degeneration: roles in inflammation, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial function. Clin Chim Acta. 2020;508:33-42.
[27] LIN J, ZHENG X, XIONG Z, et al. DJ-1- mediated p62 degradation delays intervertebral disc degeneration by inhibiting apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells. Apoptosis. 2023;28(9-10):1357-1371.
[28] WANG D, SHANG Q, MAO J, et al. Phosphorylation of KRT8 (keratin 8) by excessive mechanical load-activated PKN (protein kinase N) impairs autophagosome initiation and contributes to disc degeneration. Autophagy. 2023;19(9): 2485-2503.
[29] YAO B, CAI Y, WANG W, et al. The effect of gut microbiota on the progression of intervertebral disc degeneration. Orthop Surg. 2023;15(3):858-867.
[30] LYU FJ, CUI H, PAN H, et al. Painful intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation: from laboratory evidence to clinical interventions. Bone Res. 2021;9(1):7.
[31] LIN B, WANG Y, ZHANG P, et al. Gut microbiota regulates neuropathic pain: potential mechanisms and therapeutic strategy. J Headache Pain. 2020;21(1):103.
[32] WANG J, ZHU N, SU X, et al. Gut-microbiota-derived metabolites maintain gut and systemic immune homeostasis. Cells. 2023; 12(5):793.
[33] ZHENG D, LIWINSKI T, ELINAV E. Interaction between microbiota and immunity in health and disease. Cell Res. 2020;30(6):492-506.
[34] SONG C, ZHOU Y, CHENG K, et al. Cellular senescence - Molecular mechanisms of intervertebral disc degeneration from an immune perspective. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;162:114711.
[35] SUN Y, CHEN Q, LIN P, et al. Characteristics of Gut microbiota in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Shanghai, China. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019;9:369.
[36] KRITSCHIL R, SCOTT M, SOWA G, et al. Role of autophagy in intervertebral disc degeneration. J Cell Physiol. 2022; 237(2):1266-1284.
[37] FAN C, CHU G, YU Z, et al. The role of ferroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;11: 1219840.
[38] HODGKINSON K, EL ABBAR F, DOBRANOWSKI P, et al. Butyrate’s role in human health and the current progress towards its clinical application to treat gastrointestinal disease. Clin Nutr. 2023; 42(2):61-75.
[39] GENG Z, WANG J, CHEN G, et al. Gut microbiota and intervertebral disc degeneration: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):601.
[40] MOHAMMAD S, THIEMERMANN C. Role of metabolic endotoxemia in systemic inflammation and potential interventions. Front Immunol. 2020;11:594150.
[41] D’AMICO D, OLMER M, FOUASSIER AM, et al. Urolithin A improves mitochondrial health, reduces cartilage degeneration, and alleviates pain in osteoarthritis. Aging Cell. 2022;21(8):e13662.
[42] GARCIA-VILLALBA R, BELTRAN D, FRUTOS MD, et al. Metabolism of different dietary phenolic compounds by the urolithin-producing human-gut bacteria Gordonibacter urolithinfaciens and Ellagibacter isourolithinifaciens. Food Funct. 2020;11(8):7012-7022.
[43] LIN J, ZHUGE J, ZHENG X, et al. Urolithin A-induced mitophagy suppresses apoptosis and attenuates intervertebral disc degeneration via the AMPK signaling pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;150: 109-119.
[44] SHI PZ, WANG JW, WANG PC, et al. Urolithin a alleviates oxidative stress-induced senescence in nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells through SIRT1/PGC-1alpha pathway. World J Stem Cells. 2021;13(12):1928-1946.
[45] MA L, NI Y, WANG Z, et al. Spermidine improves gut barrier integrity and gut microbiota function in diet-induced obese mice. Gut Microbes. 2020;12(1):1-19.
[46] ZHENG D, WU Z, LI L, et al. Genetic analysis of the causal relationship between gut microbiota and intervertebral disc degeneration: a two-sample Mendelian randomized study. Eur Spine J. 2024;33(5): 1986-1998.
[47] SHAHI SK, FREEDMAN SN, Murra AC, et al. Prevotella histicola, a human gut commensal, is as potent as COPAXONE® in an animal model of multiple sclerosis. Front Immunol. 2019;10:462.
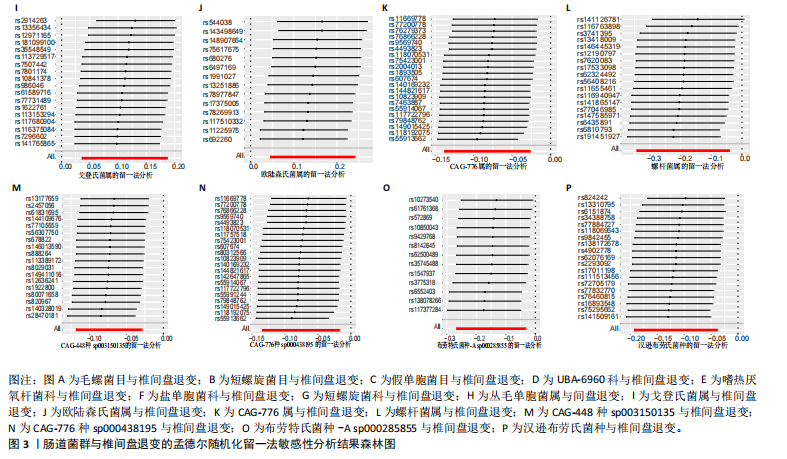
|