1.1 设计 体外细胞培养实验。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2022年10月至2023年12月在南华大学附属第一医院综合楼实验室完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 实验动物 8周龄雄性C57BL/6小鼠,体质量22 g左右,购买自南华大学医学院实验动物中心,动物许可证号:SYXK(湘)2020-002,小鼠分笼饲养,人工控制光照(12 h∶12 h光/暗周期),环境温度(22±2) ℃,相对湿度(55±10)%,自由给水和饵料,实验前适应环境1周。
此次实验严格遵守中华人民共和国科技部[2006]398号文件《关于善待实验动物的指导性意见》要求。实验方案经南华大学附属第一医院动物实验医学伦理委员会批准。
1.3.2 主要试剂及仪器 Ⅳ型胶原酶、PBS、Accutase 细胞消化液(美国Innovative Cell Technologies公司);抗小鼠抗体CD29、CD31、CD45、CD63、CD81、CD90(美国BD公司);α-MEM培养基、体积分数10%新生牛血清、成软骨诱导培养基、成脂肪诱导培养基、Alcian Blue、EdU试剂盒(上海Invitrogen 公司);油红O、PKH26荧光细胞标记试剂盒(美国Sigma 公司);α-平滑肌肌动蛋白抗体、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白抗体(德国Santa Cruz 公司);70 μm孔径细胞筛(BD Biosciences公司);RNA试剂盒(北京艾德莱生物科技有限公司);全外泌体分离试剂盒(上海Invitrogen公司);mRFP-GFP-LC3质粒(上海汉恒生物);SYBR®Premix Ex TaqTM II试剂盒(大连TaKaRa公司)。细胞超净工作台(苏州安泰科技有限公司);CO2培养箱(赛默飞世尔科技);细胞培养皿及孔板(NEST);光学显微镜(XDS-1A);倒置相差显微镜(奥林巴斯,IX71);透射电镜(日本日立);低速离心机(上海卢湘仪,TDZ4B-WS);超高速离心机(日本日立);Real-time检测仪(ABI-7500);摇床(其林贝尔,TS-1000);流式细胞仪(美国BD公司);荧光显微镜(日本基恩士公司)。
1.4 实验方法
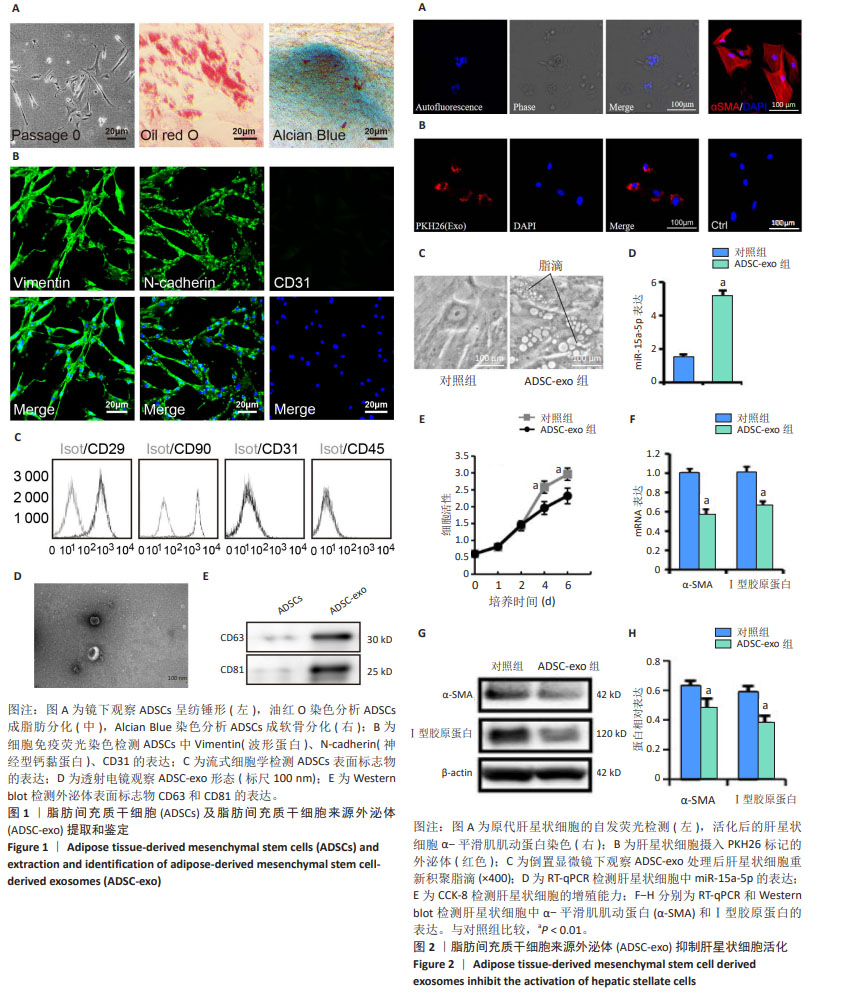
1.4.1 肝星状细胞、脂肪间充质干细胞培养及外泌体的提取和鉴定
(1)肝星状细胞分离培养:采用胶原酶灌注消化法和密度梯度离心法收集肝星状细胞。取小鼠肝脏组织,肝脏离体后,门静脉插管,Hank’s液灌洗,38 ℃ Ⅰ型胶原酶灌洗消化肝组织,有齿镊分离去除肝包膜,200 μm孔径细胞筛过滤,回收细胞悬液50×g低速离心3 min,回收上清,离心、回收反复循环3次,150×g离心10 min,吸弃上清液,用15% iodixanol溶液(ρ=1.084 g/mL)悬浮离心管底部的细胞团,上层缓慢添加8% iodixanol溶液(ρ=1.050 g/mL),再在上层缓慢添加5 mL Hank’s液,1 400×g离心15 min,收集位于8% iodixanol和15% iodixanol溶液交界液面处的肝星状细胞,用含体积分数为10%胎牛血清的α-MEM培养基培养,每2 d换液1次,待细胞融合度约70%时消化传代处理。显微镜下观察细胞形态,328 nm波长紫外光激发细胞自发荧光,细胞免疫荧光染色法检测肝星状细胞中α-平滑肌肌动蛋白的表达
情况。
(2)脂肪间充质干细胞分离培养:取小鼠腹股沟区皮下脂肪组织,PBS冲洗3遍,剪碎后加入1 mg/mL Ⅳ型胶原酶混匀消化1 h,70 μm孔径细胞筛过滤后离心,以2×105/cm2密度接种于含体积分数为10%胎牛血清的α-MEM培养基的25 cm2培养瓶中,每2 d换液1次,待细胞融合度达70%-80%时消化传代处理,取第3代细胞进行鉴定和使用。
细胞表型检测:细胞用Accutase消化酶消化后分别加入CD29及CD45抗体各10 μL,同型对照管分别加入IgG-FITC或者IgG-PE作阴性对照,4 ℃遮光反应30 min,400×g离心5 min后流式细胞仪上机检测。
细胞免疫荧光染色:细胞固定后透化,封闭,分别加一抗Vimentin(1∶500)、N-cadherin(1∶500)、CD31 (1∶1 000)于湿盒4 ℃孵育过夜,清洗后加FITC标记二抗(1∶1 000),室温下孵育2 h,清洗后DAPI染色。
细胞分化能力检测:细胞以1×105/孔密度接种于6孔板,待达到80%汇合后,分别用成软骨诱导培养基及成脂肪诱导培养基培养。成脂诱导培养7 d后行油红O染色;成软骨诱导培养14 d后行Alcian Blue染色。
(3)外泌体分离鉴定:第3代脂肪间充质干细胞培养72 h后,收集细胞上清液,3 000×g离心15 min,弃去细胞和细胞碎片,参照外泌体提取试剂说明书按1∶4比例加入外泌体提取试剂,混匀后4 ℃过夜,1 500×g离心30 min,弃上清,再1 500×g离心5 min,小心吸弃上清,沉淀即为外泌体,纯化后的外泌体以PBS重悬分装,-80 ℃保存。透射电子显微镜观察外泌体形态;通过BCA法蛋白定量后用Western blot鉴定外泌体表面标记物CD63和CD81表达量。
(4)肝星状细胞摄取外泌体示踪:用0.5 mL稀释液C悬浮ADSC-Exo,加入PKH26荧光染料应用液,吹打混匀,孵育后加α-MEM完全培养基终止反应,离心并洗涤,将PKH26荧光标记后的ADSC-Exo与肝星状细胞避光共培养48 h,PBS洗涤,DAPI染色,荧光显微镜观察。
1.4.2 CCK-8检测 采用CCK-8法测定ADSC-exo对肝星状细胞增殖能力的影响。按照1×105/孔的密度将肝星状细胞接种于96孔板中,培养24 h后,外泌体组加入ADSC-exo(20 μL/mL),对照组常规培养,每组每个时间点4个复孔,分别在第1,2,4,6天,每孔加入20 μL CCK-8溶液,37 ℃孵育3 h,酶标仪测定450 nm处吸光度值。
1.4.3 实验分组 实验分2组:对照组和外泌体组。肝星状细胞接种于24孔板中,每孔1×105个细胞,培养24 h后更换培养基,外泌体组加入ADSC-exo(20 μL/mL)共培养48 h,对照组常规培养48 h,无特殊处理。
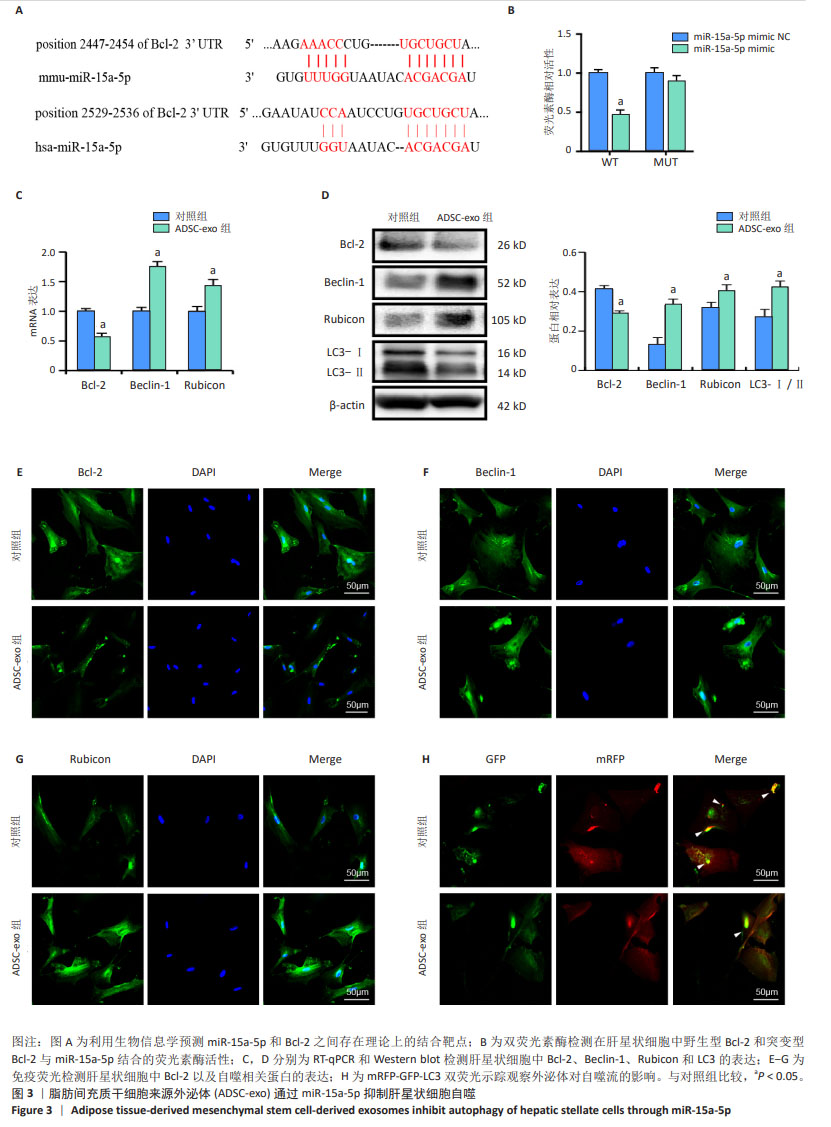
1.4.4 Western blot检测各组肝星状细胞中α-平滑肌肌动蛋白、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、LC3、Bcl-2、Beclin-1和Rubicon蛋白表达水平 RIPA裂解液分别提取各组肝星状细胞总蛋白,BCA法检测蛋白浓度,SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳分离蛋白,PVDF转膜并室温下封闭1 h,清洗后加入一抗4 ℃孵育过夜,一抗分别为α-平滑肌肌动蛋白抗体(1∶1 000)、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白抗体(1∶500)、LC3抗体(1∶1 000)、Bcl-2抗体(1∶500)、Beclin-1抗体(1∶500)、Rubicon抗体(1∶1 000)、GAPDH抗体(1∶1 000),清洗3次,每次5 min,室温下孵育二抗1 h,二抗为Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody, HRP(1∶5 000)、Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody, HRP(1∶5 000),清洗3次,每次5 min,最后用Bio-Rad图像系统曝光拍照和Image J软件行定量分析。
1.4.5 RT-qPCR检测各组肝星状细胞中α-平滑肌肌动蛋白、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、miR-15a-5p、Bcl-2、Beclin-1和Rubicon mRNA表达水平 TRIzol提取各组肝星状细胞总RNA,反转录成cDNA,按照系列反应条件进行荧光定量PCR反应:95 ℃10 min;95 ℃ 15 s,60 ℃ 30 s,40个循环,操作按照SYBR®Premix Ex TaqTM II试剂盒说明书进行。引物序列见表1。

1.4.6 免疫荧光法 两组肝星状细胞固定后透化处理,封闭,滴加Bcl-2(1∶500)、Beclin-1(1∶500)、Rubicon一抗(1∶1 000)于湿盒4 ℃孵育过夜,清洗3遍,加FITC标记二抗(1∶1 000),室温下孵育2 h,清洗后DAPI染色,荧光显微镜下观察。
1.4.7 双荧光mRFP-eGFP-LC3 质粒转染示踪法 按1×105/孔的密度将两组肝星状细胞接种于24孔板,融合度达60%-70%时加入自噬双标慢病毒RFP-eGFP-LC3质粒转染24 h,荧光显微镜下观察肝星状细胞中自噬小体和自噬溶酶体的形成情况,评估ADSC-exo对自噬流的影响。
1.4.8 生物信息学分析 通过Entrez Nucleotide数据库(www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore)找到小鼠源性和人源性Bcl-2 3’非编码区的序列,通过TargetScanHuman 7.2(www.targetscan.org)和(www.micorrna.org)数据库对miR-15a-5p和Bcl-2 3’非编码区结合位点进行预测。
1.5 主要观察指标 ①ADSC-exo对小鼠肝星状细胞自噬的影响;②验证miR-15a-5p和Bcl-2之间的靶向关系;③ADSC-exo中miR-15a-5p靶向Bcl-2对自噬基因Beclin-1和Rubicon及相关蛋白表达的影响。
1.6 统计学分析 采用SPSS 19.0统计软件进行统计分析。图表均采用GraphPad PRISM Version 6.0软件进行绘制。数据以x±s表示,分别进行组间独立t 检验,多样本均数比较采用方差分析。P < 0.01为差异有显著性意义。文章统计学方法已经通过南华大学衡阳医学院生物统计学专家审核。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程