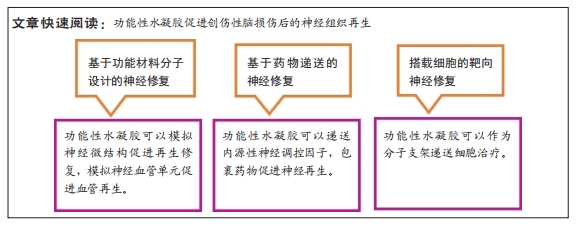
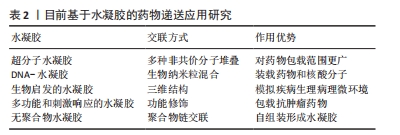
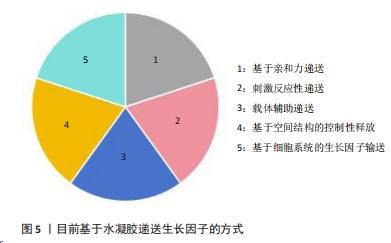
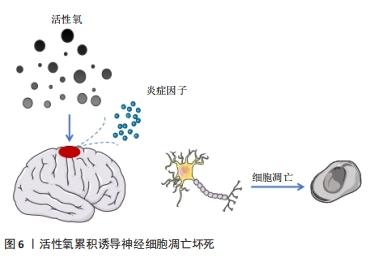
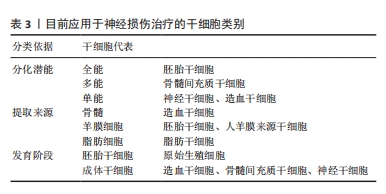
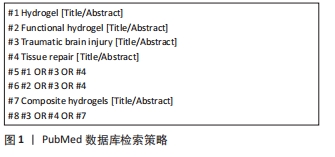
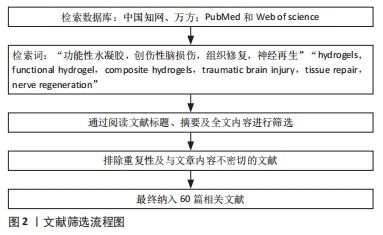
[1] 陈一豪. CS-HEC-HA/GP温敏水凝胶的制备及其联合hUC-MSCs在TBI神经修复中的作用[D].郑州.郑州大学.2019.
[2] BURDA JE, BERNSTEIN AM, SOFRONIEW MV. Astrocyte roles in traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol. 2016;275 Pt 3(03):305-315.
[3] SHAHROR RA, WU CC, CHIANG YH, et al. Genetically Modified Mesenchymal Stem Cells: The Next Generation of Stem Cell-Based Therapy for TBI. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(11):4051.
[4] THAL SC, HEINEMANN M, LUH C, et al. Pioglitazone reduces secondary brain damage after experimental brain trauma by PPAR-γ-independent mechanisms. J Neurotrauma. 2011;28(6):983-993.
[5] SICA A, MANTOVANI A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(3):787-795.
[6] HU X, LEAK RK, SHI Y, et al. Microglial and macrophage polarization—new prospects for brain repair. Nat Nat Rev Neurol. 2015;11(1):56-64.
[7] WANG G, ZHANG J, HU X, et al. Microglia/macrophage polarization dynamics in white matter after traumatic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013;33(12):1864-1874.
[8] MANGANAS LN, ZHANG X, LI Y, et al. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy identifies neural progenitor cells in the live human brain. Science. 2007;318(5852):980-985.
[9] KADRY H, NOORANI B, CUCULLO L. A blood-brain barrier overview on structure, function, impairment, and biomarkers of integrity. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2020;17(1):69.
[10] BAGCHI S, CHHIBBER T, LAHOOTI B, et al. In-vitro blood-brain barrier models for drug screening and permeation studies: an overview. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13:3591-3605.
[11] RUMON MMH, AKIB AA, SULTANAF, et al. Self-Healing Hydrogels: Development, Biomedical Applications, and Challenges. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(21):4539.
[12] 王朝翔. ECM-SA复合水凝胶的制备及其在TBI后血管化的应用研究[D].南通:南通大学.2021.
[13] XU J, HSU SH. Self-healing hydrogel as an injectable implant: translation in brain diseases. J Biomed Sci. 2023;30(1):43.
[14] WANG L, JIAN Y, LE X, et al. Actuating and memorizing bilayer hydrogels for a self-deformed shape memory function. Chem Commun (Camb). 2018;54(10):1229-1232.
[15] PRADHAN K, DAS G, KHAN J, et al. Neuro-Regenerative Choline-Functionalized Injectable Graphene Oxide Hydrogel Repairs Focal Brain Injury. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2019;10(3):1535-1543.
[16] YAO M, GAO F, XU R, et al. A dual-enzymatically cross-linked injectable gelatin hydrogel loaded with BMSC improves neurological function recovery of traumatic brain injury in rats. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(10): 4088-4098.
[17] ROWLAND MJ, PARKINS CC, MCABEE JH, et al. An adherent tissue-inspired hydrogel delivery vehicle utilised in primary human glioma models. Biomaterials. 2018:179:199-208.
[18] MA X, WANG M, RAN Y, et al. Design and Fabrication of Polymeric Hydrogel Carrier for Nerve Repair. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(8):1549.
[19] GRAÇA MFP, MIGUEL SP, CABRAL CSD, et al. Hyaluronic acid-Based wound dressings: A review. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;241:116364.
[20] CORTES H, CABALLERO-FLORÁN IH, MENDOZA-MUñOZ N, et al. Hyaluronic acid in wound dressings. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2020;66(4):191-198.
[21] TIAN WM, HOU SP, MA J, et al. Hyaluronic acid-poly-D-lysine-based three-dimensional hydrogel for traumatic brain injury. Tissue Eng. 2005;11(3-4):513-525.
[22] YE Q, ZHANG Y, DAI K, et al. Three dimensional printed bioglass/gelatin/alginate composite scaffolds with promoted mechanical strength, biomineralization, cell responses and osteogenesis. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2020;31(9):77.
[23] YOO J, PARK JH, KWON Y W, et al. Augmented peripheral nerve regeneration through elastic nerve guidance conduits prepared using a porous PLCL membrane with a 3D printed collagen hydrogel. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(22):6261-6271.
[24] SALEHI M, NASERI-NOSAR M, EBRAHIMI-BAROUGH S, et al. Regeneration of sciatic nerve crush injury by a hydroxyapatite nanoparticle-containing collagen type I hydrogel. J Physiol Sci. 2018; 68(5):579-587.
[25] LI J, ZHANG D, GUO S, et al. Dual-enzymatically cross-linked gelatin hydrogel promotes neural differentiation and neurotrophin secretion of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of moderate traumatic brain injury. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021:187:200-213.
[26] GUO H, ZHOU H, LU J, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor: an attractive target in the treatment of hypoxic/ischemic brain injury. Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(1):174-179.
[27] SAVIC I. Sex differences in the human brain, their underpinnings and implications. Preface. Prog Brain Res. 2010:186:vii-ix.
[28] LIU X, WANG J, WANG P, et al. Hypoxia-pretreated mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes-loaded low-temperature extrusion 3D-printed implants for neural regeneration after traumatic brain injury in canines. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022:10:1025138.
[29] ELLIOTT DONAGHUE I, TAM R, SEFTON MV, et al. Cell and biomolecule delivery for tissue repair and regeneration in the central nervous system. J Control Release. 2014;190:219-227.
[30] LEE RJ, SPRINGER ML, BLANCO-BOSE WE, et al. VEGF gene delivery to myocardium: deleterious effects of unregulated expression. Circulation. 2000;102(8):898-901.
[31] NAGAHARA AH, TUSZYNSKI MH. Potential therapeutic uses of BDNF in neurological and psychiatric disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011; 10(3):209-219.
[32] MARSHALL J, SZMYDYNGER-CHODOBSKA J, RIOULT-PEDOTTI MS, et al. TrkB-enhancer facilitates functional recovery after traumatic brain injury. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):10995.
[33] EDELBROCK AN, ÀLVAREZ Z, SIMKIN D, et al. Supramolecular Nanostructure Activates TrkB Receptor Signaling of Neuronal Cells by Mimicking Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor. Nano Lett. 2018; 18(10):6237-6247.
[34] CHEN X, HUANG X, LIU C, et al. Surface-fill H(2)S-releasing silk fibroin hydrogel for brain repair through the repression of neuronal pyroptosis. Acta Biomater. 2022:154:259-274.
[35] WANG L, ZHANG D, REN Y, et al. Injectable hyaluronic acid hydrogel loaded with BMSC and NGF for traumatic brain injury treatment. Mater Today Bio. 2021:13:100201.
[36] KHATRI N, THAKUR M, PAREEK V, et al. Oxidative Stress: Major Threat in Traumatic Brain Injury. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2018;17(9):689-695.
[37] CHUANG JY, KAO TJ, LIN SH, et al. Specificity protein 1-zinc finger protein 179 pathway is involved in the attenuation of oxidative stress following brain injury. Redox Biol. 2017:11:135-143.
[38] HUANG X, YE Y, ZHANG J, et al. Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging Functional Hydrogel Delivers Procyanidins for the Treatment of Traumatic Brain Injury in Mice. A CS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022. doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c04930.
[39] BAI J, ZHANG Y, TANG C, et al. Gallic acid: Pharmacological activities and molecular mechanisms involved in inflammation-related diseases. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;133:110985.
[40] ZHANG D, CHANG R, REN Y, et al. Injectable and reactive oxygen species-scavenging gelatin hydrogel promotes neural repair in experimental traumatic brain injury. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;219: 844-863.
[41] BERTZ A, WÖHL-BRUHN S, MIETHE S, et al. Encapsulation of proteins in hydrogel carrier systems for controlled drug delivery: influence of network structure and drug size on release rate. J Biotechnol. 2013; 163(2):243-249.
[42] CARTER P J. Potent antibody therapeutics by design. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6(5):343-357.
[43] SCHIRRMANN T, MENZEL C, HUST M, et al. Oligomeric forms of single chain immunoglobulin (scIgG). MAbs. 2010;2(1):73-76.
[44] YOO J, KIM HS, HWANG DY. Stem cells as promising therapeutic options for neurological disorders. J Cell Biochem. 2013;114(4):743-753.
[45] HSIEH FY, HSU SH. 3D bioprinting: A new insight into the therapeutic strategy of neural tissue regeneration. Organogenesis. 2015;11(4):153-158.
[46] WU KH, MO XM, HAN ZC, et al. Stem cell engraftment and survival in the ischemic heart. Ann Thorac Surg. 2011;92(5):1917-1925.
[47] ENGLER AJ, SEN S, SWEENEY HL, et al. Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell. 2006;126(4):677-689.
[48] FAN L, LIU C, CHEN X, et al. Directing Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Derived Neural Stem Cell Fate with a Three-Dimensional Biomimetic Hydrogel for Spinal Cord Injury Repair. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(21):17742-17755.
[49] WANG LS, BOULAIRE J, CHAN PP, et al. The role of stiffness of gelatin-hydroxyphenylpropionic acid hydrogels formed by enzyme-mediated crosslinking on the differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cell. Biomaterials. 2010;31(33):8608-8616.
[50] DAS M, MAYILSAMY K, MOHAPATRA SS, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for the treatment of traumatic brain injury: progress and prospects. Rev Neurosci. 2019;30(8):839-855.
[51] LIU X, WU C, ZHANG Y, et al. Hyaluronan-based hydrogel integrating exosomes for traumatic brain injury repair by promoting angiogenesis and neurogenesis. Carbohydr Polym. 2023:306:120578.
[52] MA S, ZHOU J, HUANG T, et al. Sodium alginate/collagen/stromal cell-derived factor-1 neural scaffold loaded with BMSCs promotes neurological function recovery after traumatic brain injury. Acta Biomater. 2021;131:185-197.
[53] SHI W, HUANG CJ, XU XD, et al. Transplantation of RADA16-BDNF peptide scaffold with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells forced with CXCR4 and activated astrocytes for repair of traumatic brain injury. Acta Biomater. 2016:45:247-261.
[54] LU P, WANG Y, GRAHAM L, et al. Long-distance growth and connectivity of neural stem cells after severe spinal cord injury. Cell. 2012;150(6):1264-1273.
[55] LI X, TZENG SY, LIU X, et al. Nanoparticle-mediated transcriptional modification enhances neuronal differentiation of human neural stem cells following transplantation in rat brain. Biomaterials. 2016:84:157-166.
[56] ZHENG Y, WU G, CHEN L, et al. Neuro-regenerative imidazole-functionalized GelMA hydrogel loaded with hAMSC and SDF-1α promote stem cell differentiation and repair focal brain injury. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(3):627-637.
[57] ZHONG Q, LACO F, LIAO MC, et al. Influencing the Fate of Cardiac and Neural Stem Cell Differentiation Using Small Molecule Inhibitors of ALK5. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2018;7(10):709-720.
[58] GAO Z, YU Y, DAI K, et al. Engineering Neutrophil Immunomodulatory Hydrogels Promoted Angiogenesis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022; 14(35):39746-39758.
[59] LIU Y, HSU YH, HUANG AP, et al. Semi-Interpenetrating Polymer Network of Hyaluronan and Chitosan Self-Healing Hydrogels for Central Nervous System Repair. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(36): 40108-40120.
[60] WANG L, WEI X, HE X, et al. Osteoinductive Dental Pulp Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicle-Loaded Multifunctional Hydrogel for Bone Regeneration. ACS Nano. 2024;18(12):8777-8797.
|