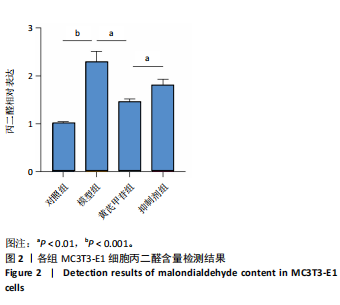
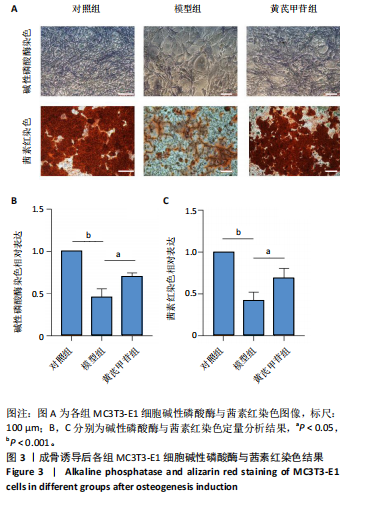
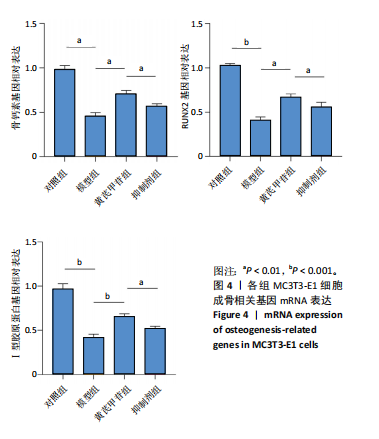
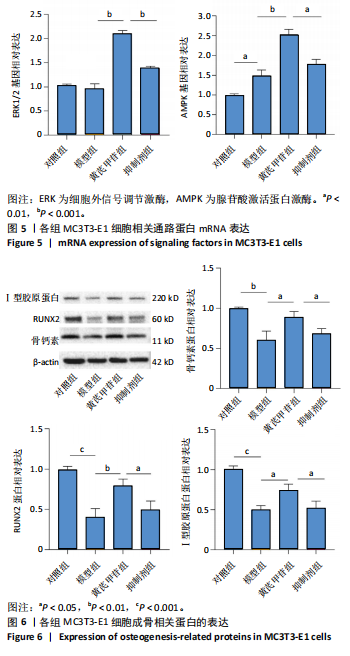
[1] ENSRUD KE, CRANDALL CJ. Osteoporosis. Ann Intern Med. 2017;167(3): ITC17-ITC32.
[2] LANGDAHL BL. Overview of treatment approaches to osteoporosis. Br J Pharmacol. 2021;178(9):1891-1906.
[3] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)[J].中国全科医学,2023,26(14):1671-1691.
[4] KIMBALL JS, JOHNSON JP, CARLSON DA. Oxidative Stress and Osteoporosis. J Bone Joint Surg. 2021;103(15):1451-1461.
[5] ZHANG C, LI H, LI J, et al. Oxidative stress: A common pathological state in a high-risk population for osteoporosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023; 163:114834.
[6] RIEGGER J, SCHOPPA A, RUTHS L, et al. Oxidative stress as a key modulator of cell fate decision in osteoarthritis and osteoporosis: a narrative review. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023;28(1): 76.
[7] 曹志威,武晓蓉,邵国,等.MC3T3-E1细胞成骨模型的应用及研究进展[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2023,20(5):86-89,93.
[8] 蒋微,蒋式骊,刘平.黄芪甲苷的药理作用研究进展[J].中华中医药学刊,2019,37(9):2121-2124.
[9] 王嵩,黄思捷,郤庆.含黄芪中药复方制剂中黄芪甲苷含量测定的研究进展[J].上海医药,2021,42(5): 64-68.
[10] SUN NY, LIU XL, GAO J, et al. Astragaloside-IV modulates NGF-induced osteoblast differentiation via the GSK3β/β-catenin signalling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(1):19.
[11] WANG F, QIAN H, KONG L, et al. Accelerated Bone Regeneration by Astragaloside IV through Stimulating the Coupling of Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(7):1821-1836.
[12] SUGIURA R, SATOH R, TAKASAKI T. ERK: A Double-Edged Sword in Cancer. ERK-Dependent Apoptosis as a Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Cancer. Cells. 2021;10(10):2509.
[13] KIM JM, YANG YS, PARK KH, et al. The ERK MAPK Pathway Is Essential for Skeletal Development and Homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(8):1803.
[14] LIU X, ZHANG J, WANG S, et al. Astragaloside IV attenuates the H2O2-induced apoptosis of neuronal cells by inhibiting α-synuclein expression via the p38 MAPK pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40(6):1772-1780.
[15] LIU Y, CHONG L, LI X, et al. Astragaloside IV rescues MPP+-induced mitochondrial dysfunction through upregulation of methionine sulfoxide reductase A. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(3):2650-2656.
[16] 刘海萌,付冠.黄芪甲苷增强骨髓间充质干细胞修复大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤的实验研究[J].中国免疫学杂志,2020,36(11):1313-1317.
[17] JIN H, DU J, REN H, et al. Astragaloside IV protects against iron loading-induced abnormal differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs). FEBS Open Bio. 2021;11(4):1223-1236.
[18] BLAKE JF, BURKARD M, CHAN J, et al. Discovery of (S)-1-(1-(4-Chloro-3-fluorophenyl)-2-hydroxyethyl)-4-(2-((1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)amino)pyrimidin-4-yl)pyridin-2(1H)-one (GDC-0994), an Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) Inhibitor in Early Clinical Development. J Med Chem. 2016;59(12):5650-5660.
[19] ROSKOSKI R. Targeting ERK1/2 protein-serine/threonine kinases in human cancers. Pharmacol Res. 2019;142:151-168.
[20] FILAIRE E, TOUMI H. Reactive oxygen species and exercise on bone metabolism: friend or enemy? Joint Bone Spine. 2012;79(4):341-346.
[21] YANG K, CAO F, QIU S, et al. Metformin Promotes Differentiation and Attenuates H2O2-Induced Oxidative Damage of Osteoblasts via the PI3K/AKT/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:829830.
[22] ZHAO X, LIN S, LI H, et al. Myeloperoxidase Controls Bone Turnover by Suppressing Osteoclast Differentiation Through Modulating Reactive Oxygen Species Level. J Bone Miner Res. 2021;36(3):591-603.
[23] DOMAZETOVIC V, MARCUCCI G, FALSETTI I, et al. Blueberry Juice Antioxidants Protect Osteogenic Activity against Oxidative Stress and Improve Long-Term Activation of the Mineralization Process in Human Osteoblast-Like SaOS-2 Cells: Involvement of SIRT1. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(2):125.
[24] AUSTERMANN K, BAECKER N, STEHLE P, et al. Putative Effects of Nutritive Polyphenols on Bone Metabolism In Vivo-Evidence from Human Studies. Nutrients. 2019;11(4):871.
[25] MARCUCCI G, DOMAZETOVIC V, NEDIANI C, et al. Oxidative Stress and Natural Antioxidants in Osteoporosis: Novel Preventive and Therapeutic Approaches. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023;12(2):373.
[26] FONTANI F, MARCUCCI G, IANTOMASI T, et al. Glutathione, N-acetylcysteine and lipoic acid down-regulate starvation-induced apoptosis, RANKL/OPG ratio and sclerostin in osteocytes: involvement of JNK and ERK1/2 signalling. Calcif Tissue Int. 2015;96(4):335-346.
[27] LEÓN-REYES G, ARGOTY-PANTOJA AD, BECERRA-CERVERA A, et al. Oxidative-Stress-Related Genes in Osteoporosis: A Systematic Review. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023;12(4):915.
[28] LIU Y, YU X, HUANG A, et al. INTS7-ABCD3 Interaction Stimulates the Proliferation and Osteoblastic Differentiation of Mouse Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Suppressing Oxidative Stress. Front. Physiol. 2021;12:758607.
[29] SHEN Y, WANG H, XIE H, et al. l-arginine promotes angio-osteogenesis to enhance oxidative stress-inhibited bone formation by ameliorating mitophagy. J Orthop Translat. 2024;46:53-64.
[30] 梁伟乔,钟诚,李宇明.骨质疏松症的中医病因病机认识与治疗进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020, 26(1):135-139.
[31] 闵甦,关永林,周广超,等.基于气血理论探讨补气补血中药防治骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].中医临床研究,2021,13(9):118-121,139.
[32] 刘路,李凯,胡阳,等.黄芪有效成分抗骨质疏松症作用机制的研究进展[J].中草药,2023,54(4): 1321-1328.
[33] ZOU Y, LI S, CHEN T, et al. Astragaloside IV ameliorates peripheral immunosuppression induced by cerebral ischemia through inhibiting HPA axis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;105:108569.
[34] YANG K, XIE Q, TANG T, et al. Astragaloside IV as a novel CXCR4 antagonist alleviates osteoarthritis in the knee of monosodium iodoacetate-induced rats. Phytomedicine. 2023;108:154506.
[35] ZHUANG Z, WANG ZH, DENG LH, et al. Astragaloside IV Exerts Cardioprotection in Animal Models of Viral Myocarditis: A Preclinical Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:1388.
[36] CAI B, ZHANG AG, ZHANG X, et al. Promoting Effects on Proliferation and Chondrogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Four “Kidney-Tonifying” Traditional Chinese Herbs. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:792161.
[37] ESSAWY AE, ABD ELKADER HAE, KHAMISS OA, et al. Therapeutic effects of astragaloside IV and Astragalus spinosus saponins against bisphenol A-induced neurotoxicity and DNA damage in rats. PeerJ. 2021;9:e11930.
[38] 邵帅,鲁美丽,高秀秋,等.黄芪甲苷对脂多糖诱导的巨噬细胞炎症反应及核因子κB受体活化因子配体/骨保护素系统表达的影响[J].中国医科大学学报,2022,51(4):294-300.
[39] 成鹏,白银亮,胡彩莉,等.黄芪甲苷通过调控FoxO3a/Wnt2/β-catenin通路抑制去卵巢大鼠骨质疏松的作用[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2018,24(15):161-166.
[40] ROSKOSKI R. ERK1/2 MAP kinases: structure, function, and regulation. Pharmacol Res. 2012;66(2):105-143.
[41] LEE DW, KIM KM, PARK S, et al. Eucalyptol induces osteoblast differentiation through ERK phosphorylation in vitro and in vivo. J Mol Med. 2023;101(9): 1083-1095.
[42] YUH D Y, MAEKAWA T, LI X, et al. The secreted protein DEL-1 activates a β3 integrin-FAK-ERK1/2-RUNX2 pathway and promotes osteogenic differentiation and bone regeneration. J Biol Chem. 2020;295(21):7261-7273.
[43] CHUNXIA R, XINQING H, LU W, et al. Metformin Carbon Dots for Promoting Periodontal Bone Regeneration via Activation of ERK/AMPK Pathway. Adv Healthcare Mater. 2021;10(12):e2100196.
[44] YUE H, LENG Z, BO Y, et al. Novel Peptides from Sea Cucumber Intestinal Enzyme Hydrolysates Promote Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells via Phosphorylation of PPARγ at Serine 112. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2023;67(9):e2200451. |