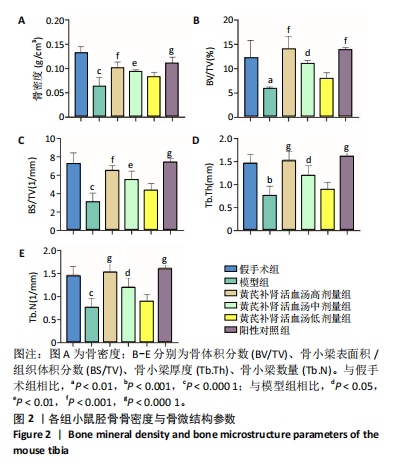
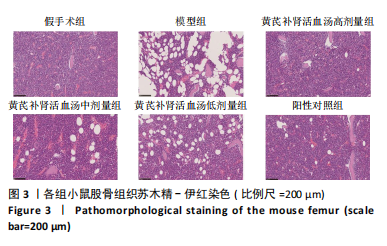
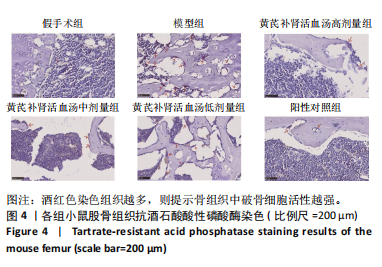
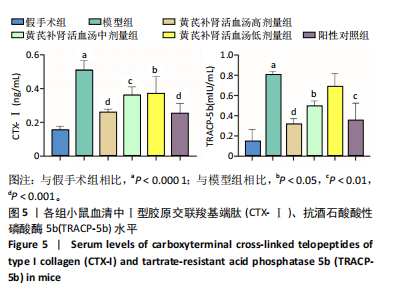
[1] TRAPANI D, GINSBURG O, FADELU T, et al. Global challenges and policy solutions in breast cancer control. Cancer Treat Rev. 2022;104:102339.
[2] LIN YT, LIN J, LIU YE, et al. Nafamostat mesylate overcomes endocrine resistance of breast cancer through epigenetic regulation of CDK4 and CDK6 expression. Transl Oncol. 2022;15(1):101302.
[3] 中国抗癌协会乳腺癌专业委员会.中国抗癌协会乳腺癌诊治指南与规范(2021年版)[J].中国癌症杂志,2021,31(10):954-1040.
[4] 孟慧.益肾健骨方通过RANKL/RANK/OPG轴调控阿那曲唑相关骨丢失的机制探讨[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2022.
[5] MATSUMOTO T, ENDO I. RANKL as a target for the treatment of osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39(1):91-105.
[6] YASUDA H. Discovery of the RANKL/RANK/OPG system. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39(1):2-11.
[7] 卢雯平,王笑民,马飞.乳腺癌中西医结合诊疗指南[J].北京中医药,2024,43(1):7-16.
[8] 梁丽春,莫春生,李娟娟,等.补肾法对乳腺癌芳香化酶抑制剂治疗所致骨丢失的疗效观察[J].广州中医药大学学报,2019,36(3):344-349.
[9] 殷玉莲,张卫红,周悦,等.补肾壮骨方防治芳香化酶抑制剂引起的骨代谢异常的临床研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(9):1195-1200.
[10] 梁鸿艺,刘志勇,刘晓菲,等.基于PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α信号通路探讨补肾活血汤干预乳腺癌内分泌治疗相关骨质疏松的作用机制[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2022,28(17):164-172.
[11] 李海洋,桂新景,岳佑凇,等.中药汤剂煎煮工艺标准化与个性化结合方法探索[J].医药导报,2021,40(11):1561-1567.
[12] ABDURAHMAN A, LI X, LI J, et al. Loading-driven PI3K/Akt signaling and erythropoiesis enhanced angiogenesis and osteogenesis in a postmenopausal osteoporosis mouse model. Bone. 2022;157:116346.
[13] JAYARAMAN S, HOU X, KUFFEL MJ, et al. Antitumor activity of Z-endoxifen in aromatase inhibitor-sensitive and aromatase inhibitor-resistant estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2020;22(1):51.
[14] SCHECH A, YU S, GOLOUBEVA O, et al. A nude mouse model of obesity to study the mechanisms of resistance to aromatase inhibitors. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2015;22(4):645-656.
[15] 胡立冬.阿仑膦酸钠通过调节miR-133a的表达改善糖尿病性骨质疏松症[D].兰州:甘肃中医药大学,2018.
[16] 何佳,祁珊珊,李鑫鑫.抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶染色方法的改良[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2019,35(7):864-866.
[17] 李丽,陈菲,包春娟,等.TRAP染色与免疫组化套染技术在骨组织损伤修复染色中的应用[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2021,37(5):622-623.
[18] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会.乳腺癌诊疗指南(2022年版)[J].中国合理用药探索,2022,19(10):1-26.
[19] BURSTEIN HJ, SOMERFIELD MR, BARTON DL, et al. Endocrine Treatment and Targeted Therapy for Hormone Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer: ASCO Guideline Update. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(35):3959-3977.
[20] HOWELL SJ, CASBARD A, CARUCCI M, et al. Fulvestrant plus capivasertib versus placebo after relapse or progression on an aromatase inhibitor in metastatic, oestrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer (FAKTION): overall survival, updated progression-free survival, and expanded biomarker analysis from a randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022;23(7):851-864.
[21] ANDRIKOPOULOU A, FISTE O, LIONTOS M, et al. Aromatase and CDK4/6 Inhibitor-Induced Musculoskeletal Symptoms: A Systematic Review. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(3):465.
[22] YU Q, XU Y, YU E, et al. Risk of cardiovascular disease in breast cancer patients receiving aromatase inhibitors vs. tamoxifen: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022;47(5):575-587.
[23] 刘炳蔚,王静,乔雪,等.雌激素受体阳性乳腺癌患者内分泌治疗期高脂血症的临床特征及中药用药分析:基于真实世界研究[J].中国全科医学,2023,26(36):4558-4564.
[24] EBELING PR, NGUYEN HH, ALEKSOVA J, et al. Secondary Osteoporosis. Endocr Rev. 2022;43(2):240-313.
[25] KELLOFF GJ, LUBET RA, LIEBERMAN R, et al. Aromatase inhibitors as potential cancer chemopreventives. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1998;7(1):65-78.
[26] GNANT M, PFEILER G, STEGER GG, et al. Adjuvant denosumab in postmenopausal patients with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer (ABCSG-18): disease-free survival results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(3):339-351.
[27] LESLIE WD, MORIN SN, LIX LM, et al. Performance of FRAX in Women with Breast Cancer Initiating Aromatase Inhibitor Therapy: A Registry-Based Cohort Study. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34(8):1428-1435.
[28] WAQAS K, LIMA FERREIRA J, TSOURDI E, et al. Updated guidance on the management of cancer treatment-induced bone loss (CTIBL) in pre- and postmenopausal women with early-stage breast cancer. J Bone Oncol. 2021;28:100355.
[29] REID DM, DOUGHTY J, EASTELL R, et al. Guidance for the management of breast cancer treatment-induced bone loss: a consensus position statement from a UK Expert Group. Cancer Treat Rev. 2008;34 Suppl 1: S3-18.
[30] D’ORONZO S, SILVESTRIS E, PARADISO A, et al. Role of Bone Targeting Agents in the Prevention of Bone Metastases from Breast Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(8):3022.
[31] ABU EL-ASRAR AM, STRUYF S, VAN DAMME J, et al. Circulating fibrocytes contribute to the myofibroblast population in proliferative vitreoretinopathy epiretinal membranes. Br J Ophthalmol. 2008;92(5): 699-704.
[32] 林寒秋,陈武进.乳腺癌的中医研究进展[J].中医药通报,2024, 23(1):67-69.
[33] 孟慧.益肾健骨方通过RANKL/RANK/OPG轴调控阿那曲唑相关骨丢失的机制探讨[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2022.
[34] 王慧达,孙小桐,毕蓝,等.黄芪多糖在正畸骨改建中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(32):5214-5218.
[35] 王选阳,高原,唐进法,等.黄芪及其药对研究进展[J/OL].中华中医药学刊,1-13[2024-04-30].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1546.R.20240611.1535.002.html.
[36] 何嘉郡,秦晨,贺廉清,等.黄芪黄酮类成分及其药理作用研究[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2024,26(1):112-119.
[37] 范志梁,田兴中,顾春松,等.黄芪调节维生素D介导OPG/RANKL/RANK信号通路对维甲酸诱导骨质疏松C57BL/6J小鼠股骨的影响[J].时珍国医国药,2023,34(4):831-834.
[38] 蒋佳豪,彭兴宁,吴官保,等.基于Klotho、PI3K、Akt蛋白表达水平探讨补肾活血汤对绝经后骨质疏松大鼠骨骼、血管及肾脏功能的影响[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2024,44(1):9-15.
[39] DA W, TAO L, ZHU Y. The Role of Osteoclast Energy Metabolism in the Occurrence and Development of Osteoporosis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:675385.
[40] LI Y, ZHUANG Q, TAO L, et al. Urolithin B suppressed osteoclast activation and reduced bone loss of osteoporosis via inhibiting ERK/NF-κB pathway. Cell Prolif. 2022;55(10):e13291.
[41] FISCHER V, HAFFNER-LUNTZER M. Interaction between bone and immune cells: Implications for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022;123:14-21.
[42] YAO Z, GETTING SJ, LOCKE IC. Regulation of TNF-Induced Osteoclast Differentiation. Cells. 2021;11(1):132. |