中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (13): 2849-2860.doi: 10.12307/2025.035
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇
NLRP3炎性小体在脊髓损伤后小胶质细胞中的作用
周文洋,廖烨晖,田明昊,何宝强,钟德君
- 西南医科大学附属医院骨科,四川省泸州市 646000
-
收稿日期:2023-12-16接受日期:2024-02-29出版日期:2025-05-08发布日期:2024-09-12 -
通讯作者:钟德君,博士,主任医师,西南医科大学附属医院骨科,四川省泸州市 646000 -
作者简介:周文洋,男,2000年生,四川省资阳市人,汉族,西南医科大学在读硕士,主要从事脊髓损伤方面的研究。 -
基金资助:四川省医学会科研课题计划(S17075),项目负责人:钟德君;泸州市人民政府——西南医科大学科技战略合作项目(2020LZXNYDJ22),项目负责人:钟德君
Effect of NLRP3 inflammasome in microglia after spinal cord injury
Zhou Wenyang, Liao Yehui, Tian Minghao, He Baoqiang, Zhong Dejun
- Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2023-12-16Accepted:2024-02-29Online:2025-05-08Published:2024-09-12 -
Contact:Zhong Dejun, MD, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Zhou Wenyang, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:Sichuan Medical Association Research Project, No. S17075 (to ZDJ); Science and Technology Strategic Cooperation Project of Luzhou Municipal People’s Government—Southwest Medical University, No. 2020LZXNYDJ22 (to ZDJ)
摘要:
文题释义:
NLRP3炎性小体:是先天性免疫系统的重要组成成分,由NLRP3,ASC和Caspase-1所构成。NLRP3可检测外源性致病性侵袭和内源性细胞损伤,从而促进NLRP3炎性小体形成,进而调控炎症反应。脊髓损伤:是一种急性疾病,主要导致损伤平面以下不同程度的部分或永久性的感觉和运动功能的丧失,给患者和社会造成严重负担。脊髓损伤常见于高空坠落伤以及交通事故,尽管治疗费用逐年递增,但仍没有有效的疗法来明显促进脊髓损伤后的神经功能恢复。
摘要
背景:NOD样受体热蛋白结构域相关蛋白3(NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain associated protein 3,NLRP3)炎性小体与脊髓损伤后的神经炎症密切相关,小胶质细胞极化和焦亡在其中发挥关键作用,靶向调控NLRP3有利于诱导小胶质细胞从M1促炎表型向M2抗炎表型极化和调节小胶质细胞焦亡,是一个有前景的治疗策略。
目的:归纳NLRP3炎性小体在脊髓损伤后小胶质细胞中作用的分子机制以及治疗策略的研究进展。
方法:检索PubMed、Web of Science和中国知网数据库,英文检索词为“spinal cord injury,NLRP3,microglia,polarization,pyroptosis”,中文检索词为“脊髓损伤,NLRP3,小胶质细胞,极化,焦亡,炎症”,按纳入和排除标准共纳入79篇文献进行总结。
结果与结论:①目前,关于脊髓损伤复杂的发病机制尚未有统一定论,大量研究表明脊髓损伤与炎症因子和信号通路关系密切,以NLRP3炎性小体作为其发病机制和治疗突破口的相关研究也是当前的热点。②NLRP3炎性小体在脊髓损伤后的炎症反应、氧化应激和神经元恢复等起到关键作用。③小胶质细胞是脑和脊髓中的免疫细胞,是继发性脊髓损伤最重要的调节因子,脊髓损伤后小胶质细胞对内部环境作出调整,主要表现为极化及焦亡,产生大量炎症因子,阻碍脊髓损伤的神经再生和功能恢复,通过调控小胶质细胞表型变化,是治疗脊髓损伤的另一个关键因素。④NLRP3炎性小体与小胶质细胞密切相关,脊髓损伤后NLRP3炎性小体主要在小胶质细胞中表达,其会促进小胶质细胞向M1极化和促进促裂解蛋白D的产生,进一步破坏神经稳态,从而加重脊髓损伤的进展。⑤许多分子参与NLRP3炎性小体调控小胶质细胞,其中核转录因子κB及MAPK信号通路促进NLRP3炎性小体表达,其他信号通路抑制该炎性小体表达。⑥目前有大量的外源性分子及药物调控NLRP3炎性小体,临床应用前景广泛,已有相关药物处于临床试验阶段并取得良好疗效,如NLRP3特异性抑制剂MCC950,但如何精准控制靶向递送、减少对其他组织器官影响等关键问题亟需解决,随着研究的深入,未来有望在脊髓损伤治疗方式上作出新的突破。
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-6849-3275 (周文洋)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
周文洋, 廖烨晖, 田明昊, 何宝强, 钟德君. NLRP3炎性小体在脊髓损伤后小胶质细胞中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(13): 2849-2860.
Zhou Wenyang, Liao Yehui, Tian Minghao, He Baoqiang, Zhong Dejun. Effect of NLRP3 inflammasome in microglia after spinal cord injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2849-2860.
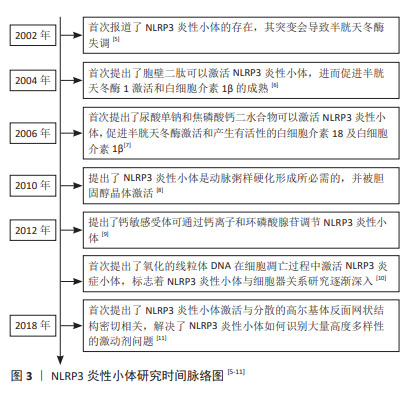
到目前为止,随着对NLRP3炎性小体的研究逐渐深入,国内外研究大部分集中于对其激活和疾病中的作用[12]。NLRP3炎性小体的激活分为经典活化和非经典活化,目前大部分都在对其经典通路激活进行研究,其受多种因素所激活,主要包括离子通道、线粒体、溶酶体、高尔基复合体及内质网损伤等所导致[4]。NLRP3炎性小体在脊髓损伤中的作用主要集中于炎症和焦亡两方面,脊髓损伤后引发氧化应激和各种炎症因子的激活,通过调控NLRP3炎性小体,有助于改善脊髓损伤后微环境,从而治疗脊髓损伤。近年来,焦亡已经成为一个热点话题,大量的研究表明NLRP3炎性小体与焦亡紧密联系,焦亡是一种程序性细胞死亡,其在神经元、小胶质细胞、星形胶质细胞及少突胶质细胞中均有大量研究,通过调控NLRP3炎性小体依赖性焦亡,降低相关炎症因子的释放,有助于促进脊髓损伤后的神经元恢复,治疗脊髓损伤。
2.1.1 NLRP3炎性小体的组成结构 NLRP3炎性小体由3个主要组分构成:NLRP3、ASC和caspase-1,这3种主要组分具有不同的作用,NLRP3主要功能为捕获危险信号并募集下游分子;caspase-1参与细胞因子白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18的成熟以及促裂解蛋白D(gasderminD,GSDMD)的加工以介导细胞因子释放和焦亡;ASC承担连接NLRP3和caspase-1的作用。NLRP3由3部分组成:氨基(N)-末端pyrin结构域(PYD)、羧基(C)-末端LRR和核苷酸结合寡聚化结构域(NOD或NACHT)[13]。位于中心的腺苷三磷酸(ATP)酶结构域,称为NACHT,包括核苷酸结合结构域(NBD)、螺旋结构域1(HD1)、翼螺旋结构域(WHD)和螺旋结构域2(HD2)以及由12个重复序列组成的富含亮氨酸序列(LRR)结构域[4]。衔接子ASC含有N-末端PYD和C-末端胱天蛋白酶募集结构域(CARD)。Caspase-1由N末端CARD、称为p20的大催化亚基和称为p10的C末端小催化亚基组成[14]。ASC敲除小鼠脊髓损伤后运动功能恢复明显优于野生型小鼠,其NLRP3炎性小体相关蛋白表达降低[15]。在小鼠巨噬细胞中,与NLRP3相互作用的有丝分裂激酶NIMA相关激酶7(NEK7)是炎性小体活化所必需的[16]。NEK7敲除并不会明显改善小鼠脊髓损伤后的运动功能,但能减弱局部炎症反应并抑制受损脊髓的小胶质细胞/巨噬细胞中NLRP3炎性小体的活化[17]。上述研究表明,ASC,NEK7在NLRP3炎性小体中扮演不可或缺的角色。NLRP3炎性小体已成为炎症过程的关键要素,并被视为脊髓损伤中的潜在靶标,见图4。
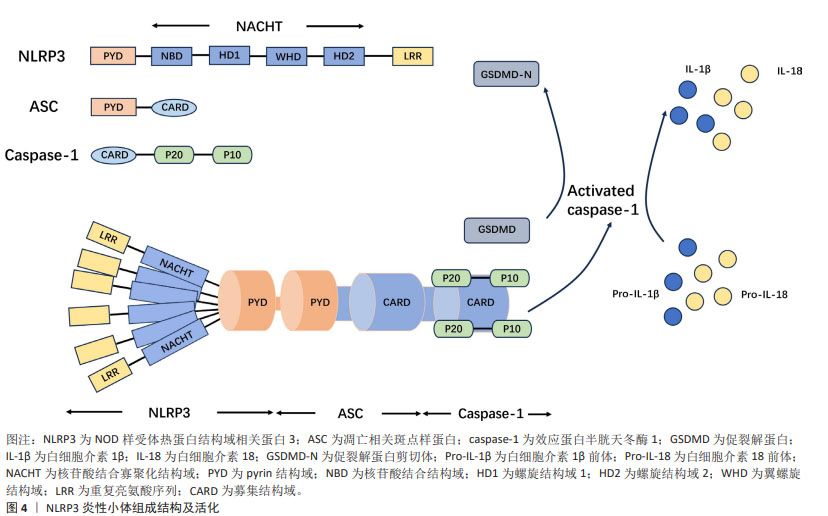
2.1.2 NLRP3炎性小体活化 NLRP3炎性小体的活化分为典型NLRP3炎性小体活化和非典型NLRP3炎性小体活化,文章主要陈述典型NLRP3炎性小体的活化。典型的NLRP3炎性小体活化需要2个步骤:启动步骤和激活步骤。首先,NLRP3表达可以在识别病原体相关分子模式或损伤相关分子模式时由模式识别受体或由参与免疫和炎症反应的细胞因子所引发。在相关因子活化后,NLRP3和其他炎性小体组分的表达在转录水平上上调。NLRP3的翻译后修饰,包括泛素化、磷酸化和类小泛素化,使得NLRP3活化,同时仍使NLRP3保持在自我抑制状态[4,18]。在第二步中,NLRP3被多种微生物和无菌刺激物激活,这些刺激包括细胞外ATP、尼日利亚菌素、短杆菌肽、细菌毒素和颗粒物质,如二氧化硅晶体、氢氧化铝、尿酸单钠和焦磷酸钙二水合物。在活化后,NLRP3组装并募集下游组分以形成炎性小体复合物,将白细胞介素1家族中的促细胞因子转化为调节免疫应答所必需的成熟促炎细胞因子白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18[19]。NLRP3炎性小体活化是一个复杂的过程,其中涉及到各种各样的分子对其进行调节,研究这些分子是治疗疾病的关键。
2.2 小胶质细胞极化与焦亡 中枢神经系统由神经元和神经胶质细胞所组成,神经胶质细胞主要包括小胶质细胞、少突胶质细胞以及星形胶质细胞,其中小胶质细胞是大脑及脊髓的常驻免疫细胞[20]。小胶质细胞能够精确地识别凋亡细胞及其碎片,避免吞噬相邻的正常神经元[21]。除此之外,其还可以促进神经元发育以及轴突再生[22]。然而,小胶质细胞容易受到外界环境的干扰,作为炎症效应器,小胶质细胞在脊髓损伤后会被多种物质所激活,释放大量的细菌毒素以及炎症因子,导致神经元死亡,从而加重脊髓损伤,而炎性小体所介导的神经炎症是导致脊髓损伤炎症的不良后果之一。炎性小体主要包括NLRP3、Nod样受体蛋白1(Nod-like receptor protein 1,NLRP1)及黑色素瘤缺乏因子2 (absent in melanoma 2,AIM2)炎性小体等,调控这些炎性小体,有助于促进神经元的恢复。研究表明,血红素加氧酶1可以通过下调脊髓损伤后神经元NLRP1的表达来促进神经元存活[23],经雷帕霉素预处理后的小胶质细胞可以通过AIM2信号通路抑制脊髓损伤后的神经元损伤[24],NLRP1及AIM炎性小体在脊髓损伤后发挥重要作用,但截至目前,NLRP1及AIM2炎性小体在脊髓损伤中的研究文献数量有所欠缺,暂未形成统一的观点,未来可以增加这方面的研究。NLRP3炎性小体是在脊髓损伤中研究最多的炎性小体,其主要在小胶质细胞中表达,通过调控NLRP3炎性小体,有利于减轻小胶质细胞中炎症因子的释放,从而促进神经元再生修复及脊髓损伤后功能恢复。
2.2.1 小胶质细胞极化 小胶质细胞和巨噬细胞是第一批响应脊髓损伤的细胞,是继发性脊髓损伤最重要的调节因子。位于脊髓的小胶质细胞在正常生理条件下以静息状态存在,并执行免疫监视功能[25]。当脊髓损伤时,静息状态下的小胶质细胞可极化为M1型和M2型,M1表型识别有害刺激,从而产生炎性细胞因子,如白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α,M2型为抗炎状态,清除细胞碎片,促进细胞外基质的形成和血管生成[26]。研究表明,M1型小胶质细胞在炎症早期释放大量炎症因子及氧自由基等有害物质,破坏神经元结构,影响神经元正常功能;M2型小胶质细胞在炎症晚期分泌一些神经营养物质,清除坏死或凋亡的神经元碎片,促进组织胶质瘢痕的形成。M2型小胶质细胞由多种抗炎递质调节驱动,并对抗M1型诱导的炎症,最终实现免疫抑制和神经元保护[27]。此外,M1型小胶质细胞促进损伤区域中硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖的沉积,从而抑制损伤区域的轴突再生[28],而M2型小胶质细胞在免疫调节中起重要作用,促进脊髓损伤后的神经再生和修复[29]。通过调节M1/M2的极化平衡以及由此产生的炎症因子,有可能减轻神经炎症反应,对保护神经系统免受继发性损伤具有重要意义,为脊髓损伤的诊断和治疗提供重要的临床依据。
2.2.2 小胶质细胞焦亡 细胞焦亡是一种程序性细胞死亡的促炎形式,其发生与NLRP3炎性小体密切相关。与其他程序性细胞死亡不同,焦亡的特征在于质膜破裂形成孔隙,细胞的通透性增加以及炎性细胞因子的释放。焦亡的发生依赖于caspase-1的形成,刺激物激活NLRP3炎性小体,诱导caspase-1裂解为有活性的caspase-1,有活性的caspase-1将白细胞介素1β与白细胞介素18前体切割成成熟形式的白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18,还可以切割GSDMD,暴露氨基酸结合位点,促进GSDMD-N结构域募集到细胞膜上,形成细胞膜孔,从而释放白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18,导致级联炎症反应和炎症细胞聚集[4]。几乎所有中枢神经系统细胞都可发生焦亡,如神经元、少突胶质细胞、星形胶质细胞以及小胶质细胞,目前国内外研究大部分聚焦于小胶质细胞焦亡的研究。轴突再生障碍是脊髓损伤恢复的主要障碍,抑制小胶质细胞电压门控质子通道减轻活性氧的产生,抑制焦亡从而促进轴突再生[30]。采用大鼠肾上腺嗜铬细胞瘤细胞与小胶质细胞共培养结果显示,通过抑制小胶质细胞焦亡有助于轴突再生[31]。通过靶向调控NLRP3炎性小体,可以抑制小胶质细胞焦亡,有助于缓解脊髓损伤后的神经炎症,促进神经元再生,促进脊髓损伤后功能恢复。

2.3 参与脊髓损伤后NLRP3炎性小体调控小胶质细胞的信号通路
2.3.1 核转录因子κB信号通路 核转录因子κB是一组转录因子,其中的通路可被不同种类的促炎细胞因子激活。核转录因子κB在哺乳动物细胞的炎症、分化、增殖和存活中发挥关键作用[32]。核转录因子κB家族包含5个成员:RelA/p65、RelB、c-Rel、核转录因子κB1/p50(p105)和核转录因子κB2/p52(p100),脊髓损伤后其主要在损伤部位的小胶质细胞和巨噬细胞被激活[33]。小胶质细胞活化后,会激活核转录因子κB信号通路,诱导星形胶质细胞的激活并放大炎症和神经毒性作用,导致神经元及少突胶质细胞死亡,促进神经胶质瘢痕的形成,最终进一步加重脊髓损伤[34]。除此之外,核转录因子κB激活可以促进NLRP3炎性小体的活化,进一步加重神经炎症反应[35]。通过拮抗核转录因子κB信号通路,有助于减轻继发性脊髓损伤的炎症环境,促进脊髓损伤后神经功能的恢复。
2.3.2 MAPK和AMPK信号通路 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶 (mitogen-activated protein kinases,MAPKs)家族包括细胞外调节蛋白激酶(exracellular signal-regulated kinase,ERK)、p38 MAPK和c-Jun氨基末端激酶(C-JUN N-terminal kinase,JNK),是一组在促炎细胞因子表达中起重要作用的信号分子。腺苷酸激活蛋白激酶(adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase,AMPK)和p38 MAPK通路是调节活化的小胶质细胞中的炎症反应的关键信号通路[36]。活性氧和MAPK信号通路可激活核转录因子κB,这在脊髓损伤后活化的小胶质细胞介导的神经炎症反应中起重要作用[37]。过表达范可尼贫血互补群 C(FANCC)可以抑制p38 MAPK磷酸化,降低NLRP3炎性小体及其相关蛋白表达,抑制小胶质细胞焦亡[37]。
NADPH氧化酶(NOX)是包括NOX1、NOX2、NOX3和NOX4以及DUOX2的酶复合物家族,其中NOX2和NOX4主要表达于脊髓小胶质细胞,并在中枢神经系统损伤时上调。NOX4增加活性氧的产生,进而促进p38 MAPK和JNK的磷酸化,从而激活核转录因子κB信号通路,进而促进NLRP3炎性小体相关蛋白的表达[38]。晚期氧化蛋白产物包括二酪氨酸和交联蛋白产物,是氧化应激的新标志物,脊髓损伤大鼠晚期氧化蛋白产物和氧化应激水平升高,晚期氧化蛋白产物通过NOX4-活性氧-NLRP3-GSDMD信号通路引发小胶质细胞焦亡[39]。除此之外,AMPK的激活可以抑制炎症起始中的NLRP3炎性小体合成,通过激活AMPK,可以减少NLRP3/caspase-1/白细胞介素1β轴来减轻小胶质细胞炎症,减轻脊髓损伤后的组织炎症反应,从而促进小鼠运动功能恢复[40]。MAPK与AMPK是许多分子相互作用的“中转站”,通过调控其表达,有助于修复损伤,显著减轻对细胞的有害作用。
2.3.3 PI3K/AKT信号通路 磷酸肌醇-3-激酶/蛋白激酶B(phosphoinositide 3-kinases/proteinkinase B,PI3K/AKT)信号通路在小胶质细胞中起关键作用, PI3K/AKT激活后可以将小胶质细胞极化从促炎M1表型转变为抗炎 M2 表型,从而增加白细胞介素10表达,显著降低促炎细胞因子释放[41]。通过PI3K/AKT信号通路可调节脊髓损伤后的小胶质细胞的NLRP3炎性小体活化。胞外5′核苷酸酶
(Ecto-5′-nucleotidase,CD73)是一种糖基化蛋白,存在于外质膜层上,其功能是将细胞外AMP水解成腺苷和磷酸盐。CD73通过A2B腺苷受体(A2BAR)促进M2型小胶质细胞极化以及抑制M1小胶质细胞极化,从而减少脊髓损伤后的神经炎症[42]。在动物实验中,A2BAR会降低CD73敲低导致的NLRP3表达上调。FOXO1是促裂解蛋白D的转录激活因子,CD73通过A2BAR/PI3K/AKT/FOXO1途径减轻NLRP3炎性小体,从而抑制小胶质细胞焦亡,促进脊髓损伤功能恢复。缺氧诱导因子是由缺氧诱导因子1α和缺氧诱导因子1β亚基组成的异二聚体转录因子,是氧稳态的主要调节因子,其上调小胶质细胞CD73表达,与CD73协同促进小胶质细胞焦亡[43]。基于此,通过调控信号通路及其上下游靶标,有助于脊髓损伤后的神经功能恢复。
2.3.4 JAK/STAT信号通路 Janus激酶/信号转导和转录激活蛋白(Janus kinase/sigal transducer and activator of transcripation,JAK/STAT)信号通路是响应许多炎症调节物而触发的最重要的级联反应之一。小胶质细胞在脊髓损伤后被激活,M1型小胶质细胞在干扰素γ+脂多糖/肿瘤坏死因子α刺激后上调STAT1,以促进炎症的产生,白细胞介素4 和 白细胞介素13 诱导的 M2 型细胞上调STAT6表达,从而发挥抗炎作用,促进细胞增殖、迁移、生长和髓鞘再生[44]。Toll样受体4(Toll-like receptor4,TLR4)是一种重要的先天免疫受体,其可引发对各种疾病的炎症反应,其作为损伤相关分子模式和病原体相关分子模式的重要模式识别受体,在引发焦亡中起着重要的作用。细胞及动物实验共同证明脊髓损伤后死盒解螺旋3X连锁(DEAD-box helicase 3X-linked,DDX3X)表达增加,但当TLR4缺乏时表达减少。此外,DDX3X低表达在体外减轻了NLRP3炎性小体和小胶质细胞的焦亡,而DDX3X过表达有效地逆转TLR4缺乏的抗焦亡作用。同时,荧光素酶实验和免疫共沉淀实验共同证实STAT1是DDX3X的转录激活因子,TLR4会导致JAK2/STAT1通路激活,并且JAK2抑制剂减轻DDX3X/NLRP3介导的小胶质细胞焦亡。这进一步说明TLR4在脊髓损伤后通过激活JAK2/STAT1/DDX3X/NLRP3信号传导轴来促进小胶质细胞焦亡。
除此之外,双糖链蛋白聚糖(biglycan,BGN)与TLR4相互作用共同促进脂多糖/ ATP诱导的小胶质细胞中STAT1/DDX3X/NLRP3轴介导的焦亡[45]。JAK和STAT 之间的分子相互作用介导细胞反应,在神经稳态和神经炎症中都起着重要作用,干扰这些相互作用的分子,特别是靶向 JAK和STAT的小分子,在治疗脊髓损伤的动物研究中显示出良好的疗效和安全性。
2.3.5 自噬信号通路 除此之外,自噬是一种清除机制,其将受损的细胞器以及过量的蛋白质递送到溶酶体。首先具有双层膜结构的囊泡构成原始自噬囊泡,随后外膜与溶酶体融合,形成功能降解的自噬囊泡,通常称为自噬溶酶体[46]。溶酶体中的酶降解自噬囊泡和内膜的内容物,以执行自噬效应。自噬参与生物体的许多生理活动,包括抑制炎性趋化因子释放[47]。研究表明,NLRP3炎性小体的积累会诱导自噬体形成,从而反过来抑制炎性小体的活化[48]。活化的小胶质细胞产生内源性大麻素并表达抑制神经炎症的大麻素受体亚型,在小胶质细胞实验中,应用大麻素受体2(cannabinoid type 2 receptor,CB2R)激活剂下调脂多糖诱导后M1小胶质细胞比例,上调M2小胶质细胞的比例,降低白细胞介素6和白细胞介素1β的表达,促进白细胞介素10的表达,CB2R通过AMPK/UNC-51样激酶(UNC-51-like kinase 1,ULK1)自噬信号通路,增加微管关联蛋白A/B(microtubule-associated protein A/B,LCB/A)的比例,从而促进NLRP3的降解和泛素化,减弱神经炎症反应和逆转小胶质细胞极化,促进脊髓损伤后运动功能的恢复。动物实验与细胞实验相一致,除此之外,CB2R还可以改善脊髓损伤后神经元损伤的扩大、胶质瘢痕形成、继发性神经元凋亡和脱髓鞘[49]。自噬是细胞的一种自我保护机制,是细胞为应对压力而激活的细胞保护反应,通过调控自噬,有助于减轻炎症因子的产生,修复脊髓损伤后的微环境。
2.3.6 其他受体分子 小胶质细胞上有许多受体可以调节脊髓损伤的NLRP3炎性小体,从而缓解神经炎症。电压门控质子通道会选择性地在中枢神经系统中的小胶质细胞中表达,电压门控质子通道会诱导NADPH氧化酶介导活性氧的生成[50];其敲低会将小胶质细胞极化状态从M1型转变为M2型,阻碍NOX活性,显著导致活性氧减 少[51]。研究表明抑制小胶质细胞的电压门控质子通道通过调节活性氧的生成从而减少NLRP3炎性小体诱导的神经元焦亡,促进脊髓损伤后轴突再生和运动功能恢复[30]。P2X7R是嘌呤能受体P2X家族的独特亚型,是由595个氨基酸组成的ATP门控非选择性阳离子通道。在中枢神经系统中,P2X7R主要在小胶质细胞上表达,小胶质细胞上P2X7R通过NLRP3炎性小体调节脊髓损伤后的神经炎症,揭示P2X7R可能是治疗脊髓损伤的有效靶点[52]。趋化因子受体4(C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4,CXCR4)是多功能G蛋白偶联受体,其通常由天然配体CXCL12激活并在各种组织中表达,包括神经元、星形胶质细胞和小胶质细胞。小胶质细胞表达CXCL12受体CXCR4,CXCL12通过与CXCR4受体结合,减弱小胶质细胞中的NLRP3炎性小体活化来抑制神经炎症[53],见图5。
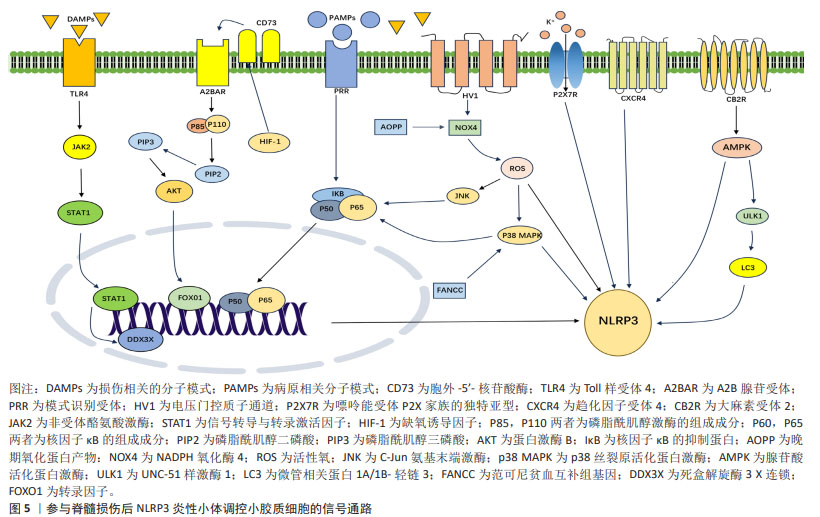
信号通路是指细胞内外的信号分子通过受体、效应器和转录因子等一系列分子的相互作用,传递和调节细胞的生理功能的过程。信号通路在脊髓损伤的发生、发展和修复中发挥着重要作用,不同的信号通路可以影响神经元的存活、死亡、分化和再生,以及胶质细胞、血管细胞和炎症细胞的活化、增殖以及迁移等。NLRP3炎性小体与这些信号通路密切相关,通过调控这些分子,可以抑制NLRP3炎性小体激活,从而缓解小胶质焦亡和促进小胶质细胞向M2极化,减轻脊髓损伤后的神经炎症和维持内环境稳态,促进神经通路的建立。未来可以增加靶向这些分子药物的研究,为脊髓损伤患者带来治疗的希望。
2.4 外源性分子调控脊髓损伤后小胶质细胞中NLRP3炎性小体
2.4.1 非编码RNA 非编码RNA是不编码蛋白质的RNA,如微小RNA(microRNA,miRNA)、长链非编码RNA(long non-coding RNA,lncRNA)及环状RNA(circular RNA,circRNA),均可参与NLRP3炎性小体激活的调节。miRNA是一类长度为22-24个核苷酸的非编码单链RNA分子,广泛参与DNA的转录后调控,其通过上调或下调脊髓损伤后改变的靶基因来调节相关蛋白质的表达。荧光素酶实验证明NLRP3是miR-423-5p的直接分子靶点。miR-423-5p通过抑制NLRP3的表达,从而抑制小胶质细胞M1极化,促进小胶质细胞M2极化,减少神经炎症,促进脊髓损伤恢复[54]。NLRP3也是是miR-223的靶标,NLRP3上调可减弱miR-223的作用,加重小胶质细胞炎症反应,脊髓损伤后从大鼠尾静脉注射Lv-miR-223,促进神经元增加、减轻脊髓中央灰质和背侧白质损伤[55]。MiR-451靶向NLRP3的3′-UTR,负向调控NLRP3表达,从而减轻小胶质细胞炎症因子释放[56]。
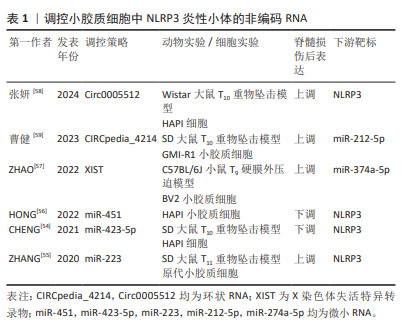
长链非编码RNA是长度超过200个核苷酸的非编码RNA,其从外显子、启动子和基因间区域转录而来,转录产生不同种类的长链非编码RNA。X染色体失活特异转录物(X-inactive specific transcript,XIST)是一种广泛报道的长链非编码RNA,其敲低可引起miR-374a-5p上调,从而抑制小胶质细胞自噬,进而抑制小胶质细胞中NLRP3炎性小体活化,减轻脊髓的充血、水肿和结构损伤,锌通过沉默XIST,从而促进小鼠运动功能恢复[57]。环状RNA是另一种具有稳定环状结构的非编码RNA,与终止于5′帽和3′尾的线性RNA相反,其基于3′和5′末端的共价结合形成闭环。Circ0005512敲低可以抑制NLRP3炎性小体及其相关蛋白的表达,从而减少细胞焦亡[58]。除此之外,另一种Circpedia_4214也可以促进NLRP3炎性小体及其相关蛋白表达,双荧光素酶实验显示,CIRCpedia_4214可直接靶向结合 miR-212-5p,从而调控Myd88表达,激活NLRP3炎性小体,加重脊髓损伤的炎症反应。敲低CIRCpedia_4214后可以减少小胶质细胞焦亡和神经元丢失,改善大鼠的运动功能[59]。非编码RNA在脊髓损伤中扮演越来越重要的角色,通过靶向调控非编码RNA,有利于减轻NLRP3的生成,进而调控小胶质细胞极化和焦亡,减轻脊髓损伤后的神经炎症反应,促进脊髓损伤后的功能恢复。见表1。
2.4.2 中药活性成分 中药活性成分可通过拮抗NLRP3炎性小体,从而介导小胶质细胞极化和焦亡,进而减轻神经炎症,达到治疗脊髓损伤效果。花旗松素是一种天然类黄酮,大量存在于柑橘类水果、葡萄、洋葱和橄榄油中。花旗松素抑制小胶质细胞活化介导的氧化应激。花旗松素通过PI3K/AKT/NLRP3信号传导途径抑制小胶质细胞焦亡,从而促进轴突再生和髓鞘恢复,改善大鼠的运动功能[31]。
甘草甜素一种三萜糖苷复合物,是从药用植物甘草根茎中提取出来的一种具有多种生理功能的有效活性成分,口服甘草酸抑制创伤性脊髓损伤后NLRP3炎性小体活化并促进小胶质细胞M2极化从而改善创伤性脊髓损伤后的功能恢复,可抑制神经活性因子的释放和神经元凋亡,促进脊髓损伤后神经元存活和功能恢复[60]。
松果菊苷是从肉苁蓉中分离出来的一种苯乙醇苷,在中国已用作草药数百年,其通过抑制核转录因子κB通路的激活,从而降低NLRP3炎性小体,减轻神经炎症;除此之外,其可抑制小胶质细胞活性氧的产生,保护线粒体免受损伤及逆转NEK7的表达,从而有效促进脊髓损伤后后肢运动功能的恢复,减少神经元丢失,改善脊髓严重的纹理紊乱及异常的组织排列[35]。山奈酚是一种具有良好特征的天然多酚,也是最常见的膳食类黄酮之一,富含于大多数植物性食物中,包括茶、西兰花、葡萄柚、羽衣甘蓝和卷心菜。山奈酚通过抑制NOX4减少活性氧的产生,抑制p38 MAPK和JNK的磷酸化,从而抑制核转录因子κB信号通路,进而抑制NLRP3炎性小体的形成,促进脊髓损伤后前肢功能恢复,改善脊髓损伤后脊髓结构紊乱,促进脊髓灰质和白质外侧索恢复[38]。丹皮酚、雷公藤红素、马钱素和虎杖苷均通过核转录因子κB通路靶向调控NLRP3炎性小体,抑制小胶质细胞焦亡和促进小胶质细胞向M2极化,从而促进脊髓损伤大鼠后肢运动功能恢复和保护神经元[61-63]。
中药作为天然药物的丰富来源,其活性成分在脊髓损伤后的抗炎、抗焦亡及抗应激扮演重要角色,其作为一种重要的辅助治疗方法,有助于修复受损的脊髓,见表2。

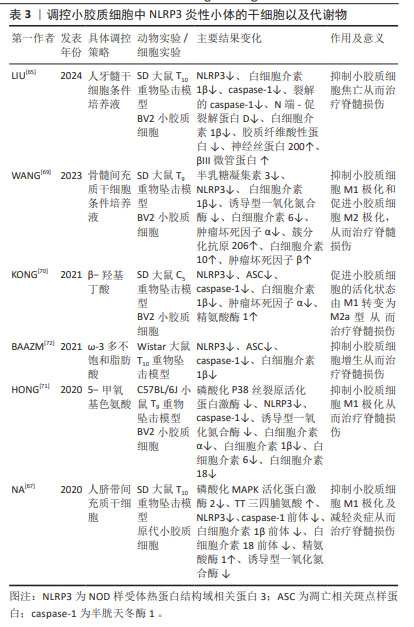
2.4.3 干细胞疗法 干细胞可以在损伤组织区域释放许多有益因子,从而具有治疗脊髓损伤潜力,其可通过多种机制改善脊髓损伤的功能恢复,例如神经保护、免疫调节和轴突的发芽及再生。干细胞可以抑制小胶质细胞极化及焦亡从而为治疗脊髓损伤提供了可行性方法,例如人脐带间充质干细胞、骨髓间充质干细胞和人牙髓干细胞等。人牙髓干细胞是来源于颅神经嵴的干细胞,并且就其胚胎起源而言与脊髓相似,其培养液通过抑制NLRP3来减轻小胶质细胞焦亡,从而促进脊髓损伤后的轴突再生和髓鞘恢复,减少胶质瘢痕形成,促进诱发电位恢复[65]。MAPK活化蛋白激酶2(MAPK activated protein kinase 2,MK2)作为p38 MAPK的底物参与细胞周期、细胞迁移、肌动蛋白重塑和炎症的调节。三四脯氨酸(Tristetraprolin,TTP)是NLRP3炎性小体的负调节因子,通过靶向结合NLRP3的3′-UTR区域抑制NLRP3的表达[66]。脊髓损伤后MK2过度表达,抑制TTP活性,从而上调NLRP3及其相关炎症因子水平,小胶质细胞极化状态也会被破坏,引起细胞极化至M1状态。人脐带间充质干细胞移植联合超声波治疗可通过抑制MK2的磷酸化来下调NLRP3表达水平,从而减少炎症反应,改善免疫微环境,挽救脊髓损伤[67]。研究表明,活化的小胶质细胞会分泌半乳糖凝集素3(Gal-3),通过活性氧/硫氧还蛋白互作蛋白(thioredoxin-interacting protein,TXNIP)/NLRP3轴调节神经炎症[68]。骨髓间充质干细胞培养液通过限制Gal-3/NLPR3的表达,从而抑制M1小胶质细胞/巨噬细胞极化,促进M2小胶质细胞/巨噬细胞极化来减少炎症反应,减轻大鼠的脊髓损伤后的出血和水肿,改善脊髓损伤后的运动功能[69]。
干细胞是近几年来研究的热点,临床前研究带来了令人鼓舞的前景,但临床试验的结果却很弱且相互矛盾,通过干细胞移植及干细胞所产生的培养液可以减轻脊髓损伤后的小胶质细胞炎症,挽救脊髓损伤[70-72],见表3。
2.4.4 代谢物 生物在进行生命活动后会产生各种各样的代谢物,其有利也有弊,通过调控代谢产物从而调控NLRP3炎性小体,有助于缓解脊髓损伤。酮代谢物β-羟基丁酸可抑制NLRP3炎性小体活化,并促进脊髓损伤后巨噬细胞/小胶质细胞从促炎性活化状态M1向更具保护性的活化状态M2极化,减轻神经炎症,从而改善脊髓损伤后的运动功能和促进其电生理恢复[70]。5-甲氧基色氨酸是色氨酸的代谢物,通过对p38-MAPK信号通路和NLRP3/caspase-1表达的负调节,降低M1小胶质细胞活化,并减少炎症细胞因子的产生。在动物实验中,其能降低脊髓损伤小鼠神经胶质瘢痕相关的神经炎症水平,在给药后可调节神经完整性和神经元存活以及改善运动功能[71]。ω-3多不饱和脂肪酸可以显著减弱脊髓损伤抑制NLRP3炎性小体及抑制脊髓小胶质细胞增生,从而减轻炎症因子的释放,其还可减轻脱髓鞘,从而改善脊髓损伤大鼠运动能力[72]。饮食治疗在脊髓损伤治疗中扮演越来越重要的角色,通过调控不同种类的食物摄入,可以调节代谢产物,进而缓解脊髓损伤的炎症,见表3。
2.4.5 特异性抑制剂 近年来,已经研究出许多NLRP3抑制剂来抑制NLRP3炎性小体及其相关上下信号分子。MCC950是研究最多且特异性的NLRP3炎性小体抑制剂,其不抑制NLRP1和AIM2炎性小体。MCC950与NLRP3中的NACHT结构域结合,阻断其水解ATP的能力,从而抑制ASC的募集和caspase-1的裂解。除此之外,其可减少小胶质细胞促炎细胞因子分泌,增加小胶质细胞抗炎细胞因子的产生,并将小胶质细胞的表型转变为抗炎状态[73]。MCC950可显著增强脊髓损伤后小鼠运动功能的恢复和减轻神经元的损伤[74]。小分子CY-09也可以特异性抑制NLRP3与ATP结合从而阻断ATP酶活性,其通过抑制3′-O-(4-苯甲酰苯甲酰基)腺苷-5′-三磷酸(3′-O-(4-benzoylbenzoyl) adenosine 5′-triphosphate,BzATP),进而上调P2X7受体来调节NLRP3炎性小体,最终抑制脊髓损伤后的神经炎症[75]。BAY11-7082是一种磺酸衍生物,具有多种药理活性,与CY-09的作用类似,其可抑制小胶质细胞活化和中性粒细胞浸润,从而减少神经胶质形成和改善线粒体功能障碍,进而减少神经元死亡和促进脊髓损伤小鼠的运动恢复[76]。越来越多的特异性抑制剂用于脊髓损伤的治疗,这些特异性抑制剂大部分在脊髓损伤中表现出良好的效果,但尚未得到批准用于治疗脊髓损伤,未来的工作需要过渡到临床试验,以测试其安全性和治疗效果。
2.4.6 其他外源性分子 除此之外,还有许多因素可以调控小胶质细胞中的NLRP3炎性小体,离子稳态紊乱是脊髓损伤过程的一部分,在脊髓损伤的早期阶段起着不可或缺的作用,通过拮抗离子通道有利于保护内环境稳态平衡,促进脊髓损伤后的恢复。利鲁唑是一种钠通道阻滞剂和谷氨酸能神经传导抑制剂,利鲁唑通过抑制NLRP3炎性小体活化,从而减少小胶质细胞焦亡,降低炎症反应,减轻脊髓实质破坏,促进脊髓损伤大鼠功能恢复[77]。3,4-二氢萘-1(2H)-酮衍生物抑制脂多糖刺激的小胶质细胞中的氧化应激活性氧的产生、核转录因子κB信号通路以及NLRP3炎性小体相关蛋白的表达;除此之外,其还可以抑制小胶质细胞M1极化,但不会影响M2型小胶质细胞[78]。亚甲蓝是线粒体靶向细胞毒性试剂,亚甲蓝通过减少ASC与NLRP3的结合以抑制小胶质细胞中活性氧产生。体内及体外实验均表明亚甲蓝通过抑制小胶质细胞NLRP3炎症小体活化减轻脊髓损伤后急性神经炎症[79]。总之,越来越多的策略可用于调控NLRP3炎性小体,从而调节小胶质细胞的极化和焦亡,为脊髓损伤患者带来治疗的希望。
总之,大量策略可以调控脊髓损伤后小胶质细胞中NLRP3炎性小体。首先,非编码RNA,如miRNA、lncRNA和circRNA可以参与NLRP3炎性小体的激活调节。其次,中药活性成分,如花旗松素、丹皮酚和甘草甜素等,可以通过拮抗NLRP3炎性小体,减轻神经炎症,促进神经元再生,恢复神经稳态,从而治疗脊髓损伤。此外,干细胞可以释放许多有益因子,改善脊髓损伤的功能恢复,生命活动会产生各种各样的代谢物,如β-羟基丁酸、5-甲氧基色氨酸和ω-3多不饱和脂肪酸,其可以调控NLRP3炎性小体,通过抑制这些代谢物的产生,有助于神经通路的再次建立。最后,相关的特异性抑制剂如MCC950和CY-09,它们可以抑制NLRP3炎性小体及其相关上下信号分子。近年来,干细胞外泌体广泛应用于脊髓损伤的治疗,其主要依赖于非编码RNA发挥功能,但与NLRP3炎性小体之间的研究较少,未来可以增加这方面的研究,NLRP3炎性小体调控是一个复制且深入的领域,需要更多的研究来深入理解这些机制并开发出有效的治疗方法。
| [1] JIANG B, SUN D, SUN H, et al. Prevalence, incidence, and external causes of traumatic spinal cord injury in china: a nationally representative cross-sectional survey. Front Neurol. 2021;12:784647. [2] HU X, XU W, REN Y, et al. Spinal cord injury: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):245. [3] HUNG WL, HO CT, PAN MH. Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome in neuroinflammation: health promoting effects of dietary phytochemicals in neurological disorders. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2020;64(4):e1900550. [4] XU J, NÚÑEZ G. The NLRP3 inflammasome: activation and regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 2023;48(4):331-344. [5] MARTINON F, BURNS K, TSCHOPP J. The inflammasome: a molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta. Mol Cell. 2002;10(2):417-426. [6] MARTINON F, PÉTRILLI V, MAYOR A, et al. Gout-associated uric acid crystals activate the NALP3 inflammasome. Nature. 2006;440(7081): 237-241. [7] DUEWELL P, KONO H, RAYNER KJ, et al. NLRP3 inflammasomes are required for atherogenesis and activated by cholesterol crystals. Nature. 2010;464(7293):1357-1361. [8] MARTINON F, AGOSTINI L, MEYLAN E, et al. Identification of bacterial muramyl dipeptide as activator of the NALP3/cryopyrin inflammasome. Curr Biol. 2004;14(21):1929-1934. [9] LEE GS, SUBRAMANIAN N, KIM AI, et al. The calcium-sensing receptor regulates the NLRP3 inflammasome through Ca2+ and cAMP. Nature. 2012;492(7427):123-127. [10] SHIMADA K, CROTHER TR, KARLIN J, et al. Oxidized mitochondrial DNA activates the NLRP3 inflammasome during apoptosis. Immunity. 2012;36(3):401-414. [11] CHEN J, CHEN ZJ. PtdIns4P on dispersed trans-Golgi network mediates NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nature. 2018;564(7734):71-76. [12] MARTINON F, BURNS K, TSCHOPP J. The inflammasome: a molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta. Mol Cell. 2002;10(2):417-426. [13] SWANSON KV, DENG M, TING JPY. The NLRP3 inflammasome: molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019;19(8):477-489. [14] BOUCHER D, MONTELEONE M, COLL R C, et al. Caspase-1 self-cleavage is an intrinsic mechanism to terminate inflammasome activity. J Exp Med. 2018;215(3):827-840. [15] SHIRAISHI Y, KIMURA A, KIMURA H, et al. Deletion of inflammasome adaptor protein ASC enhances functional recovery after spinal cord injury in mice. J Orthop Sci. 2021;26(3):487-493. [16] HE Y, ZENG MY, YANG D, et al. NEK7 is an essential mediator of NLRP3 activation downstream of potassium efflux. Nature. 2016; 530(7590):354-357. [17] JI X, SONG Z, HE J, et al. NIMA-related kinase 7 amplifies NLRP3 inflammasome pro-inflammatory signaling in microglia/macrophages and mice models of spinal cord injury. Experimental Cell Research. 2021;398(2):112418. [18] SHARMA M, DE ALBA E. Structure, activation and regulation of NLRP3 and AIM2 inflammasomes. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(2):872. [19] FU J, WU H. Structural mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2023;41:301-316. [20] SINGH D. Astrocytic and microglial cells as the modulators of neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflammation. 2022;19(1):206. [21] NORRIS GT, SMIRNOV I, FILIANO AJ, et al. Neuronal integrity and complement control synaptic material clearance by microglia after CNS injury. J Exp Med. 2018;215(7):1789-1801. [22] CSERÉP C, PÓSFAI B, DÉNES Á. Shaping neuronal fate: functional heterogeneity of direct microglia-neuron interactions. Neuron. 2021; 109(2):222-240. [23] LIN WP, XIONG GP, LIN Q, et al. Heme oxygenase-1 promotes neuron survival through down-regulation of neuronal NLRP1 expression after spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2016;13(1):52. [24] XIAO X, CHEN XY, DONG YH, et al. Pre-treatment of rapamycin transformed M2 microglia alleviates traumatic cervical spinal cord injury via AIM2 signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;121:110394. [25] CROTTI A, RANSOHOFF RM. Microglial physiology and pathophysiology: insights from genome-wide transcriptional profiling. Immunity. 2016; 44(3):505-515. [26] TANG Y, LE W. Differential roles of M1 and M2 microglia in neurodegenerative diseases. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53(2):1181-1194. [27] YU SS, LI ZY, XU XZ, et al. M1-type microglia can induce astrocytes to deposit chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(5):1072-1079. [28] FANG YP, QIN ZH, ZHANG Y, et al. Implications of microglial heterogeneity in spinal cord injury progression and therapy. Exp Neurol. 2023;359:114239. [29] LI X, YU Z, ZONG W, et al. Deficiency of the microglial Hv1 proton channel attenuates neuronal pyroptosis and inhibits inflammatory reaction after spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):263. [30] HU Z, XUAN L, WU T, et al. Taxifolin attenuates neuroinflammation and microglial pyroptosis via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway after spinal cord injury. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;114:109616. [31] CHEN S, WU X, LAI Y, et al. Kindlin-2 inhibits Nlrp3 inflammasome activation in nucleus pulposus to maintain homeostasis of the intervertebral disc. Bone Res. 2022;10(1):5. [32] DING Y, CHEN Q. The NF-κB pathway: a focus on inflammatory responses in spinal cord injury. Mol Neurobiol. 2023;60(9):5292-5308. [33] WANG X, ZHANG Z, ZHU Z, et al. Photobiomodulation promotes repair following spinal cord injury by regulating the transformation of A1/A2 reactive astrocytes. Front Neurosci. 2021;15:768262. [34] GAO S, XU T, GUO H, et al. Ameliorative effects of echinacoside against spinal cord injury via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2019;237:116978. [35] SONG C, HEPING H, SHEN Y, et al. AMPK/p38/Nrf2 activation as a protective feedback to restrain oxidative stress and inflammation in microglia stimulated with sodium fluoride. Chemosphere. 2020;244:125495. [36] LIU Z, YAO X, JIANG W, et al. Advanced oxidation protein products induce microglia-mediated neuroinflammation via MAPKs-NF-κB signaling pathway and pyroptosis after secondary spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):90. [37] XIA M, LI X, YE S, et al. FANCC deficiency mediates microglial pyroptosis and secondary neuronal apoptosis in spinal cord contusion. Cell Biosci. 2022;12(1):82. [38] LIU Z, YAO X, SUN B, et al. Pretreatment with kaempferol attenuates microglia-mediate neuroinflammation by inhibiting MAPKs–NF–κB signaling pathway and pyroptosis after secondary spinal cord injury. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;168:142-154. [39] LIU Z, YAO X, JIANG W, et al. Advanced oxidation protein products induce microglia-mediated neuroinflammation via MAPKs-NF-κB signaling pathway and pyroptosis after secondary spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):90. [40] SUN P, ZHAO T, ZHOU J, et al. Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor roflupram suppresses inflammatory responses using reducing inflammasome in microglia after spinal cord injury. Altern Ther Health Med. 2023; 29(7):340-347. [41] HE X, LI Y, DENG B, et al. The PI3K /AKT signalling pathway in inflammation, cell death and glial scar formation after traumatic spinal cord injury: Mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Proliferation. 2022;55(9):e13275. [42] XU S, ZHU W, SHAO M, et al. Ecto-5’-nucleotidase (CD73) attenuates inflammation after spinal cord injury by promoting macrophages/microglia M2 polarization in mice. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15(1): 155. [43] XU S, SHAO M, MA X, et al. CD73 alleviates GSDMD-mediated microglia pyroptosis in spinal cord injury through PI3K/AKT/Foxo1 signaling. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11(1):e269. [44] GUO X, JIANG C, CHEN Z, et al. Regulation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway in spinal cord injury: an updated review. Front Immunol. 2023; 14:1276445. [45] WANG J, ZHANG F, XU H, et al. TLR4 aggravates microglial pyroptosis by promoting DDX3X‐mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation via JAK2/STAT1 pathway after spinal cord injury. Clin Transl Med. 2022; 12(6):e894. [46] HERNANDEZ-DIAZ S, SOUKUP SF. The role of lipids in autophagy and its implication in neurodegeneration. Cell Stress. 2020;4(7):167-186. [47] WU AG, ZHOU XG, QIAO G, et al. Targeting microglial autophagic degradation in NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;65:101202. [48] CAI B, ZHAO J, ZHANG Y, et al. USP5 attenuates NLRP3 inflammasome activation by promoting autophagic degradation of NLRP3. Autophagy. 2022;18(5):990-1004. [49] JIANG F, XIA M, ZHANG Y, et al. Cannabinoid receptor-2 attenuates neuroinflammation by promoting autophagy-mediated degradation of the NLRP3 inflammasome post spinal cord injury. Front Immunol. 2022;13:993168. [50] SHEN Y, LUO Y, LIAO P, et al. Role of the voltage-gated proton channel Hv1 in nervous systems. Neurosci Bull. 2023;39(7):1157-1172. [51] ZHENG J, MURUGAN M, WANG L, et al. Microglial voltage-gated proton channel Hv1 in spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2022; 17(6):1183. [52] FAN X, MA W, ZHANG Y, et al. P2X7 receptor (P2X7R) of microglia mediates neuroinflammation by regulating (NOD)-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome-dependent inflammation after spinal cord injury. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e925491. [53] ROOSEN K, SCHELD M, MANDZHALOVA M, et al. CXCL12 inhibits inflammasome activation in LPS-stimulated BV2 cells. Brain Res. 2021; 1763:147446. [54] CHENG J, HAO J, JIANG X, et al. Ameliorative effects of miR-423-5p against polarization of microglial cells of the M1 phenotype by targeting a NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;99:108006. [55] ZHANG M, WANG L, HUANG S, et al. MicroRNA-223 targets NLRP3 to relieve inflammation and alleviate spinal cord injury. Life Sci. 2020; 254:117796. [56] HONG Z, ChENG J, YE Y, et al. MicroRNA-451 attenuates the inflammatory response of activated microglia by downregulating nucleotide binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3. World Neurosurg. 2022;167:e1128-e1137. [57] ZHAO X, SUN J, YUAN Y, et al. Zinc promotes microglial autophagy through NLRP3 inflammasome inactivation via XIST/miR-374a-5p axis in spinal cord injury. Neurochem Res. 2022;47(2):372-381. [58] 张妍,张文凯,张雯秀,等.Circ0005512促进雌性大鼠脊髓损伤后小胶质细胞/巨噬细胞焦亡[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(31): 5029-5035. [59] 曹健.CIRCpedia_4214通过miR-212-5p/Myd88轴调控脊髓损伤后小胶质细胞焦亡的机制研究[D].南昌:南昌大学,2023. [60] SU XQ, WANG XY, GONG FT, et al. Oral treatment with glycyrrhizin inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and promotes microglial M2 polarization after traumatic spinal cord injury. Brain Res Bull. 2020; 158:1-8. [61] DAI W, WANG X, TENG H, et al. Celastrol inhibits microglial pyroptosis and attenuates inflammatory reaction in acute spinal cord injury rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;66:215-223. [62] LV R, DU L, LIU X, et al. Polydatin alleviates traumatic spinal cord injury by reducing microglial inflammation via regulation of iNOS and NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019; 70:28-36. [63] HUANG X, CHEN X, LI Q, et al. Loganin reduces neuroinflammation and promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury through inhibiting NF-κB/NLRP3 signalling. Toxicon. 2023;232:107202. [64] ZHAO H, WANG X, LIU S, et al. Paeonol regulates NLRP3 inflammasomes and pyroptosis to alleviate spinal cord injury of rat. BMC Neurosci. 2022;23(1):16. [65] LIU T, MA Z, LIU L, et al. Conditioned medium from human dental pulp stem cells treats spinal cord injury by inhibiting microglial pyroptosis. Neural Regen Res. 2024;19(5):1105-1111. [66] HANEKLAUS M, O’NEIL JD, CLARK AR, et al. The RNA-binding protein Tristetraprolin (TTP) is a critical negative regulator of the NLRP3 inflammasome. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(17):6869-6881. [67] NA L, WANG S, LIU T, et al. Ultrashort wave combined with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell (HUC-MSC) transplantation inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome and improves spinal cord injury via MK2/TTP signalling pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:1-13. [68] REN Z, LIANG W, SHENG J, et al. Gal-3 is a potential biomarker for spinal cord injury and Gal-3 deficiency attenuates neuroinflammation through ROS/TXNIP/NLRP3 signaling pathway. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(12): BSR20192368. [69] WANG Y, WANG X, ZOU Z, et al. Conditioned medium from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells relieves spinal cord injury through suppression of Gal-3/NLRP3 and M1 microglia/macrophage polarization. Pathol Res Pract. 2023;243:154331. [70] KONG G, LIU J, LI R, et al. Ketone metabolite β-hydroxybutyrate ameliorates inflammation after spinal cord injury by inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome. Neurochem Res. 2021;46(2):213-229. [71] HONG X, JIANG F, LI Y, et al. Treatment with 5-methoxytryptophan attenuates microglia-induced neuroinflammation in spinal cord trauma. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;88:106988. [72] BAAZM M, BEHRENS V, BEYER C, et al. Regulation of inflammasomes by application of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in a spinal cord injury model. Cells. 2021;10(11):3147. [73] REN H, KONG Y, LIU Z, et al. Selective NLRP3 (pyrin domain–containing protein 3) inflammasome inhibitor reduces brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 2018;49(1):184-192. [74] JIAO J, ZHAO G, WANG Y, et al. MCC950, a selective inhibitor of NLRP3 inflammasome, reduces the inflammatory response and improves neurological outcomes in mice model of spinal cord injury. Front Mol Biosci. 2020;7:37. [75] FAN X, MA W, ZHANG Y, et al. P2X7 receptor (P2X7R) of microglia mediates neuroinflammation by regulating (NOD)-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome-dependent inflammation after spinal cord injury. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e925491. [76] JIANG W, LI M, HE F, et al. Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome to attenuate spinal cord injury in mice. J Neuroinflammation. 2017;14(1): 207. [77] 刘涛,张文凯,马子谦,等.利鲁唑干预脊髓损伤大鼠小胶质细胞中NLRP3炎性小体的活化[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(7): 1036-1042. [78] SUN Y, ZHOU YQ, LIU YK, et al. Potential anti-neuroinflammatory NF-кB inhibitors based on 3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1 (2H)-one derivatives. J of Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2020;35(1):1631-1640. [79] LIN ZH, WANG SY, CHEN LL, et al. Methylene blue mitigates acute neuroinflammation after spinal cord injury through inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation in microglia. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017; 11:391. |
| [1] | 张艺博, 卢健棋, 毛美玲, 庞 延, 董 礼, 杨尚冰, 肖 湘. 类风湿关节炎与冠状动脉粥样硬化的因果关系:GWAS数据库血清代谢物和炎症因子数据[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | 余 帅, 刘家伟, 朱 彬, 潘 檀, 李兴龙, 孙广峰, 于海洋, 丁 亚, 王宏亮. 小分子药物治疗骨关节炎的热点问题及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [3] | 王文涛, 侯振扬, 王熠军, 徐耀增. Apelin-13抑制巨噬细胞M1极化缓解全身炎症性骨丢失[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1548-1555. |
| [4] | 陈 帅, 金 杰, 韩化伟, 田宁晟, 李志伟. 两样本孟德尔随机化分析循环炎症细胞因子与骨密度的因果关联[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [5] | 李开颖, 魏晓歌, 宋 斐, 杨 楠, 赵振宁, 王 燕, 穆 静, 马惠昇. 理筋手法调控兔骨骼肌损伤修复中瘢痕形成的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1600-1608. |
| [6] | 于经邦, 吴亚云. 非编码RNA在肺纤维化过程中的调控作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1659-1666. |
| [7] | 王秋月, 靳 攀, 蒲 锐. 运动干预与细胞焦亡在骨关节炎中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [8] | 袁维勃, 刘 婵, 余丽梅. 肝脏类器官在肝脏疾病模型与移植治疗中的应用潜力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1684-1692. |
| [9] | 胡涛涛, 刘 兵, 陈 诚, 殷宗银, 阚道洪, 倪 杰, 叶凌霄, 郑祥兵, 严 敏, 邹 勇. 过表达神经调节蛋白1的人羊膜间充质干细胞促进小鼠皮肤创面愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1343-1349. |
| [10] | 金 凯, 唐 婷, 李美乐, 谢裕安. 人脐带间充质干细胞条件培养基及外泌体对肝癌细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭和凋亡的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [11] | 李帝均, 酒精卫, 刘海峰, 闫 磊, 李松岩, 王 斌. 明胶三维微球装载人脐带间充质干细胞修复慢性肌腱病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1356-1362. |
| [12] | 娄 国, 张 敏, 付常喜. 8周运动预适应增强脂肪干细胞治疗心肌梗死大鼠的效果[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1363-1370. |
| [13] | 刘 琪, 李林臻, 李玉生, 焦泓焯, 杨 程, 张君涛. 淫羊藿苷含药血清促进3种细胞共培养体系中软骨细胞增殖和干细胞成软骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
| [14] | 艾克帕尔·艾尔肯, 陈晓涛, 吾凡别克·巴合提. 成骨诱导人牙周膜干细胞来源外泌体促进炎症微环境下人牙周膜干细胞成骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [15] | 何龙才, 宋文学, 明 江, 陈光唐, 王军浩, 廖益东, 崔君拴, 徐卡娅. SD大鼠乳鼠原代皮质神经元和小胶质细胞同时提取并培养的实验方法[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1395-1400. |
脊髓损伤可分为原发性损伤和继发性损伤,前者是指机械性损伤,后者是细胞和生物反应对原发性损伤的结果,其涉及免疫系统、神经系统和血管系统,主要包括出血、缺血、氧化应激、炎症反应、神经细胞死亡、脱髓鞘和瘢痕形成等[2]。神经炎症在脊髓损伤中起重要作用,主要由中枢神经系统中的小胶质细胞介导。脊髓损伤诱导的炎症反应涉及NOD样受体热蛋白结构域相关蛋白3(NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain associated protein 3,NLRP3)炎性小体的激活,其与小胶质细胞活化密切相关[3]。NLRP3炎性小体是一种多蛋白复合物,由NLRP3、凋亡相关斑点样蛋白(apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing,ASC)和效应蛋白半胱天冬酶1(caspase-1)3部分组成,可以识别多种激活信号,并激活caspase-1,从而促进白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18等促炎细胞因子的成熟和释放[4]。近20年来,NLRP3炎性小体已经成为大家关注的焦点,其与焦亡和炎症的发生发展密切相关,可以通过NLRP3炎性小体对刺激和相关分子等激活信号作出反应,促使小胶质细胞向M1型极化和焦亡,进一步加大脊髓损伤的炎症反应。因此调控NLRP3炎性小体,有助于调节脊髓损伤诱导的炎症反应,恢复神经稳态,促进脊髓损伤后神经功能恢复。
目前,关于靶向调控NLRP3炎性小体取得了一系列重要进展,且研究热度呈持续上升趋势,以往综述往往研究拮抗NLRP3炎性小体从而治疗脊髓损伤,未单独对某一细胞进行总结,但国内外对于脊髓损伤后NLRP3炎性小体的研究集中于小胶质细胞,因此文章在以往研究基础上重点探讨NLRP3炎性小体在脊髓损伤后小胶质细胞中的作用,主要从小胶质细胞极化以及焦亡两方面进行调节,详细阐述了脊髓损伤后NLRP3炎性小体调控小胶质细胞的信号通路,从非编码RNA、中药活性成分、干细胞、特异性抑制剂和代谢物等多个方面总结了最新靶向调控NLRP3炎性小体的治疗策略。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2023年12月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 2013年1月至2023年12月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed、Web of Science和中国知网数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 英文检索词为“spinal cord injury,NLRP3,microglia,polarization,pyroptosis,inflammation”,中文检索词为“脊髓损伤,NLRP3,小胶质细胞,极化,焦亡,炎症” 。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著和综述。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 有部分文献为所检索文献的参考文献延伸阅读所获取。
1.1.7 检索策略 以PubMed与中国知网数据库检索策略为例,见图1。
1.1.8 检索文献量 共检索到文献3 157篇,其中PubMed数据库1 459篇,Web of Science数据库1 668篇,中国知网数据库30篇。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①介绍脊髓损伤相关的文献;②介绍小胶质细胞与NLRP3炎性小体相关的文献;③介绍小胶质细胞极化与焦亡相关的文献;④同一领域的相关研究选择近年发表的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①研究目的及内容与此研究无关的文献;②重复性研究;③逻辑不严谨及可信度差的文献。
1.3 文献质量评估及数据提取 共检索到文献3 157篇,排除与研究目的相关性差及陈旧、文献质量不高及重复文献3 078篇,最终纳入79篇相关度文献进行综述,最终选取PubMed数据库和Web of Science数据库共76篇(由于两个数据库绝大部分为重复文章,故将英文文献数量合并去重后统计),中国知网数据库3篇,见图2。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 以往的综述关于调节NLRP3炎性小体从而治疗脊髓损伤大部分是总结所有细胞层面上进行的系统性研究,没有深入总结探讨在某一细胞的作用,而且主要集中于细胞焦亡,文章在此基础上特别对小胶质细胞进行研究,从小胶质细胞焦亡以及极化方面进行研究NLRP3炎性小体,重点探讨如何调控NLRP3炎性小体,进而拮抗小胶质细胞焦亡和促进小胶质细胞向M2极化,从而缓解神经炎症,促进脊髓损伤后运动功能恢复。
3.3 综述的局限性、重要意义和展望 近年来,关于NLRP3炎性小体在炎症性疾病的作用越来越熟为人知,关于NLRP3炎性小体在脊髓损伤中的作用机制研究仍然较少,内容还不够深入,文章未能概括全面并列举论述,且在检索过程中发现有许多文章集中发于单一杂志。文章将国内外NLRP3炎性小体在脊髓损伤后小胶质细胞中的作用进行详细阐述,详细阐述了NLRP3炎性小体调控小胶质细胞的机制,通过拮抗NLRP3炎性小体有助于脊髓损伤的恢复,如何在体内精确控制NLRP3炎性小体的激活可能是未来脊髓损伤的潜在治疗靶点。伴随大数据时代的到来,纳米工程、人工智能及水凝胶等新方法、新技术的涌现,有望在未来打破技术壁垒,使在多途径、多靶点拮抗NLRP3炎性小体成为可能,为将来脊髓损伤诊疗提供新的技术支撑,接下来可以围绕这些调节因素进行实质性的临床研究。
3.4 课题专家组对未来的建议 调控NLRP3炎性小体为脊髓损伤的治疗提供一种新的思路。目前关于NLRP3炎性小体在脊髓损伤中的研究处于起步阶段,未来可以从以下几方面入手:①NLRP3炎性小体在脊髓损伤中的调控大部分集中于对小胶质细胞的研究,未来可增加对神经元、星形胶质细胞等的研究。②除了NLRP3炎性小体外,还在AIM及NLRP1等与炎症密切相关的炎性小体,可加大对它们的研究。③NLRP3炎性小体在小胶质细胞的极化和焦亡中发挥重要作用,大部分都集中与小胶质细胞焦亡,未来可增加与小胶质细胞极化和其他表型的研究。④尽管上述策略及设想有广泛的研究和应用前景,但将其用于临床实践甚至研制出作为治疗脊髓损伤的普遍药物之前,仍有大量的实验要做,探究在临床上脊髓损伤患者是否具有一致的变化。⑤增加组合疗法研究,将有助于阐明各个策略调控NLRP3炎性小体的作用机制,以实现更加精控地调节小胶质细胞极化和焦亡,使其更好地应用于脊髓损伤治疗。⑥充分发挥中医药优势,开发有希望的中药复方。总之,调节NLRP3炎性小体治疗脊髓损伤值得深入研究,目前的实验药物有很大的应用潜力,这为脊髓损伤患者的治疗提供了有前景的方案。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
文题释义:
NLRP3炎性小体:是先天性免疫系统的重要组成成分,由NLRP3,ASC和Caspase-1所构成。NLRP3可检测外源性致病性侵袭和内源性细胞损伤,从而促进NLRP3炎性小体形成,进而调控炎症反应。#br#脊髓损伤:是一种急性疾病,主要导致损伤平面以下不同程度的部分或永久性的感觉和运动功能的丧失,给患者和社会造成严重负担。脊髓损伤常见于高空坠落伤以及交通事故,尽管治疗费用逐年递增,但仍没有有效的疗法来明显促进脊髓损伤后的神经功能恢复。
#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
文章将NLRP3在脊髓损伤后小胶质细胞的作用进行总结,与以往综述不同的是文章主要聚焦于NLRP3炎性小体对小胶质细胞的调控。NLRP3炎性小体是近几年的研究热点,其在炎症激活中扮演重要角色。小胶质细胞是脊髓的免疫细胞,其与炎症密切相关,通过靶向调控NLRP3炎性小体可以抑制小胶质细胞焦亡和向M1型极化。文章将参与其调控的分子及信号通路进行了详细阐述,并对调控其的外源性分子进行总结,有利于大家认识脊髓损伤后NLRP3炎性小体在小胶质细胞中扮演的角色,为进一步了解脊髓损伤后的炎症反应提供帮助。
#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||