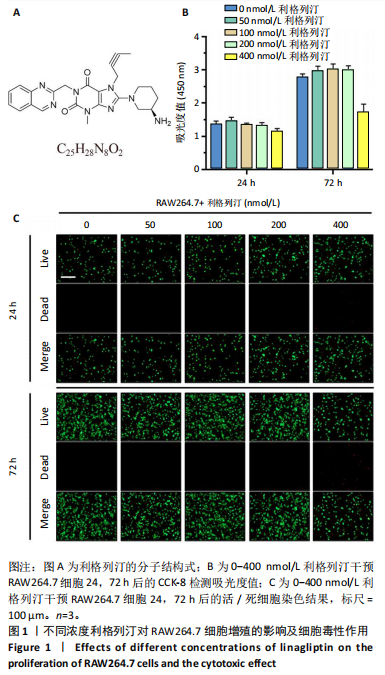
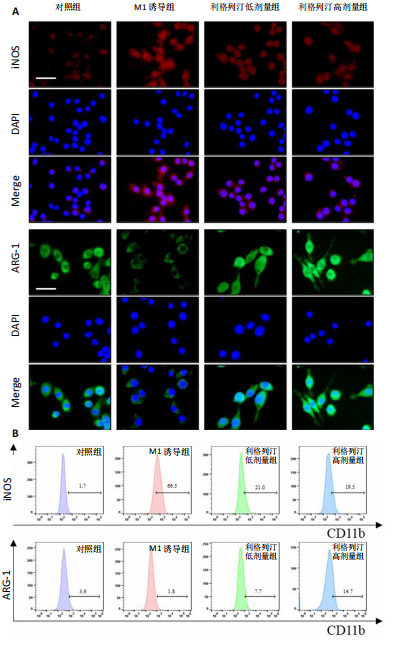
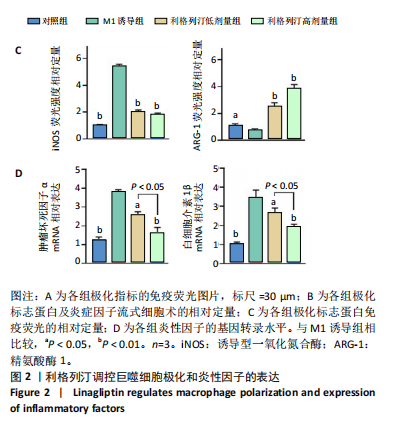
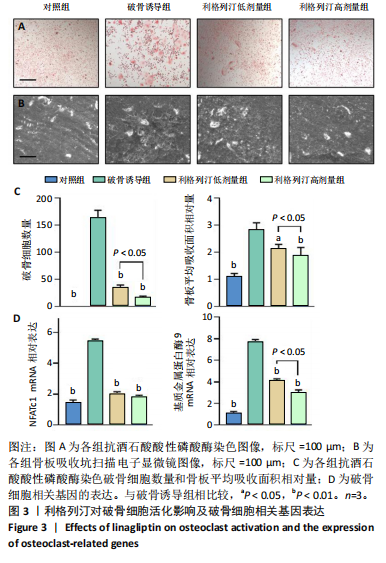
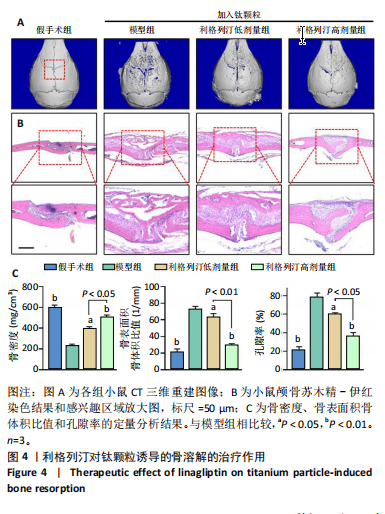
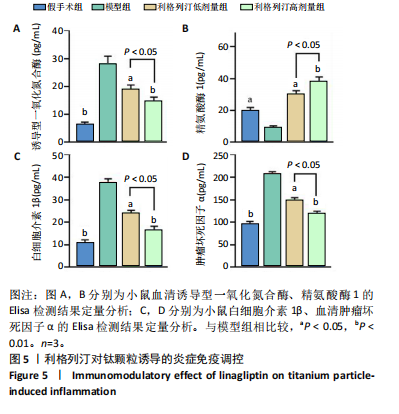
[1] KATZ JN, ARANT KR, LOESER RF. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review. JAMA. 2021;325(6):568-578.
[2] CONNOLLY P, COOMBS S, SCHWARZKOPF R. Mechanical complications after total knee arthroplasty. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2023;20(12): 1105-1117.
[3] RODRÍGUEZ-MERCHÁN EC, GÓMEZ-CARDERO P, ENCINAS-ULLÁN CA. Management of bone loss in revision total knee arthroplasty: therapeutic options and results. EFORT Open Rev. 2021;6(11):1073-1086.
[4] HODGES NA, SUSSMAN EM, STEGEMANN JP. Aseptic and septic prosthetic joint loosening: Impact of biomaterial wear on immune cell function, inflammation, and infection. Biomaterials. 2021;278:121127.
[5] MAZZELLA FM, ZHANG Y, BAUER TW. Update on the role of pathology and laboratory medicine in diagnosing periprosthetic infection. Hum Pathol. 2024;147:5-14.
[6] MA TL, CHEN JX, KE ZR, et al. Targeting regulation of stem cell exosomes: Exploring novel strategies for aseptic loosening of joint prosthesis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:925841.
[7] NIRWAN N, VOHORA D. Linagliptin in Combination With Metformin Ameliorates Diabetic Osteoporosis Through Modulating BMP-2 and Sclerostin in the High-Fat Diet Fed C57BL/6 Mice. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:944323.
[8] LIU J, LIU Z, LU M, et al. The combination of linagliptin and metformin rescues bone loss in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis. J Drug Target. 2023; 31(6):646-654.
[9] WANG SC, WANG XY, LIU CT, et al. The Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Linagliptin Ameliorates Endothelial Inflammation and Microvascular Thrombosis in a Sepsis Mouse Model. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(6):3065.
[10] SINGH TP, VANGAVETI VN, MALABU UH. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and their potential role in the management of atherosclerosis--A review. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2015;9(4):223-229.
[11] PUIJK R, SIEREVELT IN, PIJLS BGCW, et al. Increased risk of aseptic loosening for posterior stabilized compared with posterior cruciate-retaining uncemented total knee replacements: a cohort study of 13,667 knees from the Dutch Arthroplasty Registry. Acta Orthop. 2023;94:600-606.
[12] SUN Z, KANG J, YANG S, et al. CD73 inhibits titanium particle-associated aseptic loosening by alternating activation of macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;122:110561.
[13] BAO S, YU D, TANG Z, et al. Conformationally regulated “nanozyme-like” cerium oxide with multiple free radical scavenging activities for osteoimmunology modulation and vascularized osseointegration. Bioact Mater. 2023;34:64-79.
[14] MA T, CHEN S, WANG J, et al. Enhanced Osteolysis Targeted Therapy through Fusion of Exosomes Derived from M2 Macrophages and Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Modulating Macrophage Polarization. Small. 2024;20(7):e2303506.
[15] OUYANG Z, XU J, LIU T, et al. STING/TBK1 Regulates Inflammation in Macrophages and Titanium Particles-Induced Osteolysis. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(6):3273-3284.
[16] WANG Z, TAO H, CHU M, et al. Byakangelicol suppresses TiPs-stimulated osteoclastogenesis and bone destruction via COX-2/NF-κB signaling pathway. Regen Biomater. 2023;11:rbad092.
[17] VASCONCELOS DP, JABANGWE C, LAMGHARI M, et al. The Neuroimmune Interplay in Joint Pain: The Role of Macrophages. Front Immunol. 2022;13:812962.
[18] SONG B, JIANG C, LUO H, et al. Macrophage M1 Plays a Positive Role in Aseptic Inflammation-Related Graft Loosening After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Surgery. Inflammation. 2017;40(6):1815-1824.
[19] LI F, HUANG K, WANG J, et al. A dual functional Ti-Ga alloy: inhibiting biofilm formation and osteoclastogenesis differentiation via disturbing iron metabolism. Biomater Res. 2023;27(1):24.
[20] YU X, WU Q, REN Z, et al. Kaempferol attenuates wear particle-induced inflammatory osteolysis via JNK and p38-MAPK signaling pathways. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024;318(Pt B):117019.
[21] CHAN KL, POLLER WC, SWIRSKI FK, et al. Central regulation of stress-evoked peripheral immune responses. Nat Rev Neurosci.2023;24(10): 591-604.
[22] XIONG Y, MI BB, LIN Z, et al. The role of the immune microenvironment in bone, cartilage, and soft tissue regeneration: from mechanism to therapeutic opportunity. Mil Med Res. 2022;9(1):65.
[23] ZREIQAT H, KUMAR RK, MARKOVIC B, et al. Macrophages at the skeletal tissue-device interface of loosened prosthetic devices express bone-related genes and their products. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2003; 65(1):109-117.
[24] PENG X, LI Y, CHENG C, et al. Research on the inhibition for aseptic loosening of artificial joints by Sr-doped calcium polyphosphate (SCPP)in vivo. Biomed Mater. 2021;16(6). doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/ac2492.
[25] LIU X, DIAO L, ZHANG Y, et al. Piperlongumine Inhibits Titanium Particles-Induced Osteolysis, Osteoclast Formation, and RANKL-Induced Signaling Pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(5):2868.
[26] GU M, PAN B, CHEN W, et al. SPHK Inhibitors and Zoledronic Acid Suppress Osteoclastogenesis and Wear Particle-Induced Osteolysis. Front Pharmacol. 2022;12:794429.
[27] NAPOLI N, CHANDRAN M, PIERROZ DD, et al. Mechanisms of diabetes mellitus-induced bone fragility. Nature reviews. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017;13(4):208-219.
[28] JOSSE RG, MAJUMDAR SR, ZHENG Y, et al. Sitagliptin and risk of fractures in type 2 diabetes: Results from the TECOS trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017;19(1):78-86.
[29] KOHLER S, KASPERS S, SALSALI A, et al. Analysis of Fractures in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Treated With Empagliflozin in Pooled Data From Placebo-Controlled Trials and a Head-to-Head Study Versus Glimepiride. Diabetes Care. 2018;41(8):1809-1816.
[30] YUAN S, WAN ZH, CHENG SL,et al. Insulin-like Growth Factor-1, Bone Mineral Density, and Fracture: A Mendelian Randomization Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021;106(4):e1552-e1558.
[31] ZHUGE F, NI Y, NAGASHIMADA M, et al. DPP-4 Inhibition by Linagliptin Attenuates Obesity-Related Inflammation and Insulin Resistance by Regulating M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization. Diabetes. 2016;65(10):2966-2979.
[32] ISHIDA M, SHEN WR, KIMURA K, et al. DPP-4 inhibitor impedes lipopolysaccharide-induced osteoclast formation and bone resorption in vivo. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109:242-253.
[33] OHLENDIECK K, SWANDULLA D. Complexity of skeletal muscle degeneration: multi-systems pathophysiology and organ crosstalk in dystrophinopathy. Pflugers Arch. 2021;473(12):1813-1839.
[34] YAMADERA S, NAKAMURA Y, INAGAKI M, et al. Linagliptin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in human U937 monocytes.Inflamm Regen. 2018;38:13. |