1.1 设计 随机对照动物实验+细胞体外实验,两组间比较采用独立样本t检验,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2021年7-12月在承德医学院动物实验中心完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 实验动物 36只健康雄性Wistar大鼠,SPF级,8周龄,体质量160-180 g,购自河北医科大学实验动物公共服务平台,动物合格证号:SCXK(冀)2020-001。饲养于温度22-25 ℃、湿度50%、明暗周期12 h/12 h的SPF房内,允许大鼠自由摄食饮水,适应性饲养1周后进行实验。实验中的所有操作均在动物实验伦理指导守则指导下进行。实验方案已获得河北省眼科医院伦理委员会批准,伦理批号:HBEH20210316004。
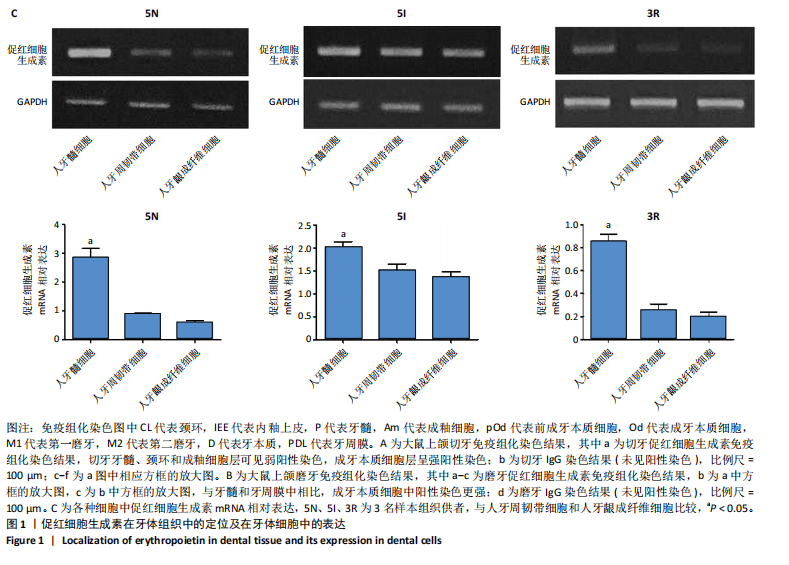
1.3.2 人体组织样本 收集河北省眼科医院3例患者完整拔除的健康智齿,每例患者2颗,3例患者的智齿样本分别记为5N、5I、3R。患者均自愿提供组织样本并签署知情同意书。实验方案已获得河北省眼科医院伦理委员会批准,伦理批号:HBEH20211012001。
1.3.3 主要试剂 胶原蛋白海绵(货号003)购自迈帝医疗科技实业有限公司;EPO(货号epo-01)购自上海赛迈生物科技有限公司;RIPA试剂(货号R0278)购自美国Sigma公司;Ketac Cem Easymix玻璃离子水门汀(国械注进20153172743)购自美国3M公司;兔EPO抗体(货号ab273070)、兔巢蛋白抗体(货号ab105389)、兔骨形态发生蛋白2抗体(货号ab214821)购自英国Abcam公司;苏木精-伊红染色试剂盒(货号C0105S)购自上海碧云天生物技术有限公司;DMEM培养基(货号11965092)、胎牛血清(货号16140063)、TRIzol试剂(货号15596018)、High-Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kit(货号4368813)购自美国Thermo Fisher公司;LipofectamineTM 2000(货号11668-027)购自上海信帆生物科技有限公司;PCR引物与内参购自上海生工生物工程股份有限公司;siRNA载体的构建与验证由上海英拜生物科技有限公司完成;茜素红S染色液(货号SH-0594)购自北京凯诗源生物科技有限公司。其他试剂均为市售分析纯。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 建立大鼠直接盖髓模型与分组干预 将60 mmol/L EPO溶液与30 mL胶原蛋白溶液混合均匀,调整EPO的终浓度为1 μmol/L,将混合液倒入6孔板中,置于-80 ℃环境冷冻12 h,使用冷冻干燥机真空冷冻干燥24 h,得到的复合物分割成约0.5 mm3的小块,经60Co辐照灭菌处理后置于4 ℃环境保存待用。
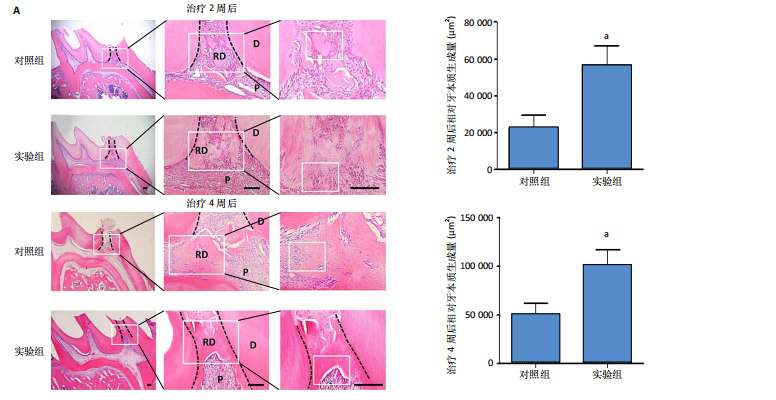
采用随机数字表法将32只大鼠随机分为对照组与实验组,每组16只。所有大鼠腹腔注射50 mg/kg戊巴比妥钠麻醉,使用2%碘伏消毒口腔及周围组织,用1/4球钻在上颌第一磨牙牙合面中央窝处间断钻磨至透粉,用探针穿髓,生理盐水冲洗、无菌棉球止血,实验组露髓处放入含100 ng EPO的胶原蛋白海绵直接盖髓,对照组露髓处放入含PBS的胶原蛋白海绵直接盖髓,用玻璃离子粘固剂封闭窝洞。治疗2,4周后,各组随机取8只大鼠,腹腔注射戊巴比妥钠麻醉后经心脏注入PBS与40 g/L多聚甲醛,分离上颌骨,置入40 g/L多聚甲醛中固定24 h,4 ℃下用10%乙二胺四乙酸脱钙1个月,石蜡包埋后制成厚度5 μm的石蜡切片。
苏木精-伊红染色:石蜡切片依次经过常规脱蜡至水、苏木精染色、冲洗、返蓝、伊红染色、梯度乙醇脱水、二甲苯透明、中性树胶封固处理后,置于光学显微镜下观察修复性牙本质生成情况并拍照。每张切片随机选择3个不同视野,使用Image J软件对修复性牙本质面积进行定量分析。
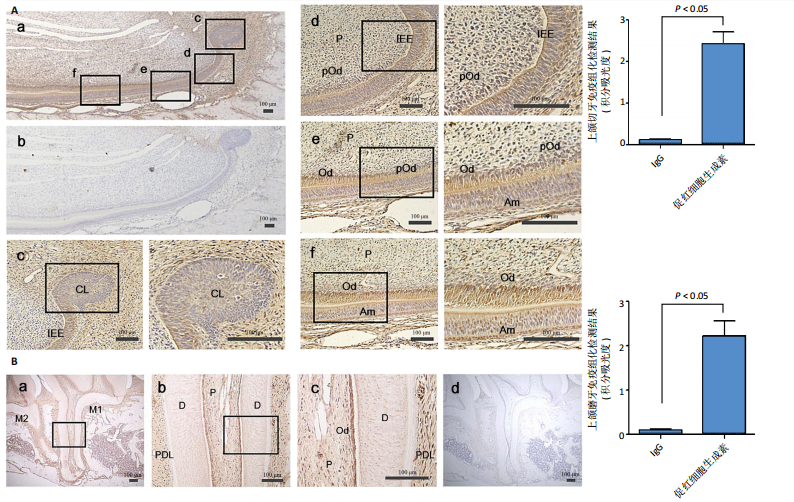
巢蛋白免疫组化染色:石蜡切片脱蜡后置入2%牛血清白蛋白中室温封闭1 h,加入巢蛋白抗体(1∶100)后置入4 ℃环境过夜,次日加入亲和素-过氧化物酶结合物室温孵育30 min,加入DAB显色液,依次经苏木精复染,经流水冲洗、返蓝、梯度乙醇脱水、二甲苯透明、中性树胶封固处理后,置于倒置显微镜下观察拍照。每张切片随机选择5个不同视野,使用Image J软件分析巢蛋白表达积分吸光度值。
1.4.2 EPO在牙体组织中的定位 取4只SD大鼠,腹腔注射50 mg/kg戊巴比妥钠麻醉后,经心脏注入PBS与40 g/L多聚甲醛,分离上颌骨,置入40 g/L多聚甲醛中固定24 h,4 ℃下用10%乙二胺四乙酸脱钙1个月,石蜡包埋后制成厚度5 μm的石蜡切片,进行EPO或IgG免疫组化染色,抗体稀释比均为1∶100,染色步骤同上,分析磨牙与切牙中EPO表达情况。使用Image J软件分析EPO表达积分吸光度值。
1.4.3 细胞获取、培养与分组 通过组织块培养从每例患者的牙髓组织、牙周韧带组织及牙龈组织中分别分离获取人牙髓细胞、人牙周韧带细胞和人牙龈成纤维细胞。在无菌条件下用拔髓针取出牙髓组织(剪弃根尖1/3部分),从牙根中部1/3处分离牙周韧带组织,分离牙龈组织,均分割为约1 mm3的小块,分散接种于6孔板中,加入含体积分数10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养基,置于37 ℃、体积分数5% CO2饱和湿度的电热恒温培养箱中培养3 d,观察到各细胞从组织块中爬出,每隔3 d换液1次。待细胞融合达到70%-80%时进行传代,取第3代细胞进行实验。
1.4.4 EPO基因在细胞中的表达 收集普通培养的人牙髓细胞、人牙周韧带细胞和人牙龈成纤维细胞,使用TRIzol试剂提取细胞总RNA,用反转录试剂盒转录成cDNA第一链,引物序列见表1。反应条件:94 ℃预变性5 min,94 ℃变性30 s,55 ℃退火30 s,72 ℃延伸30 s,循环35次;72 ℃延伸7 min。PCR产物接受1.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳,在凝胶成像系统上拍照,并用FluorChem 8900分析软件计算出EPO mRNA相对表达水平。

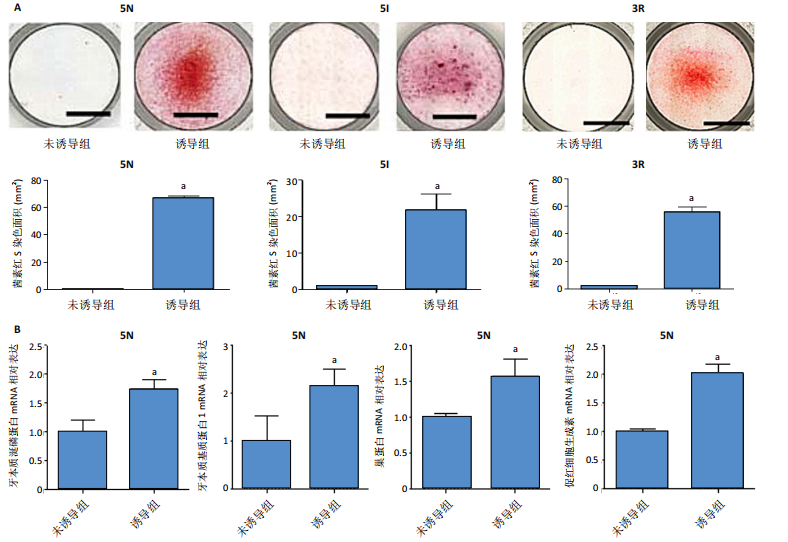
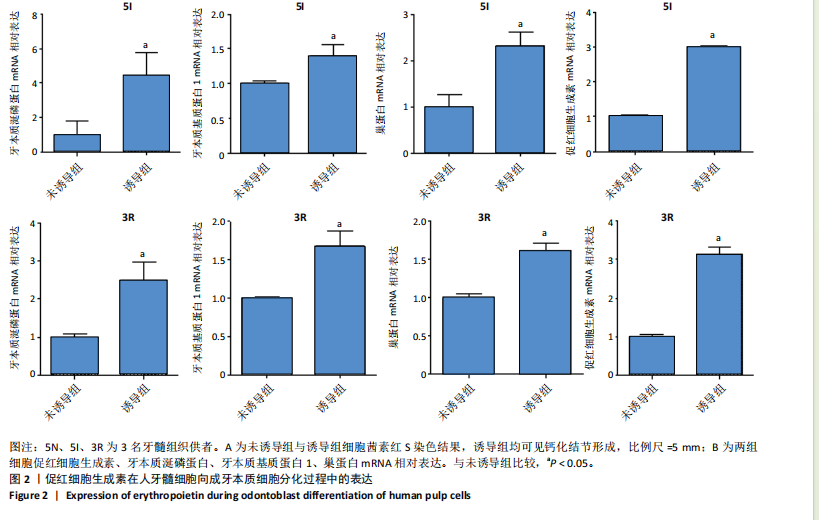
1.4.5 EPO在人牙髓细胞向成牙本质细胞分化中的表达 将人牙髓细胞接种于24孔板中,每孔加入1 mL含体积分数10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养基,细胞密度为3×104/孔,分2组培养:未诱导组不加入任何试剂,诱导组加入2 mmol/L氯化钙诱导细胞分化为成牙本质细胞[13],置于37 ℃、体积分数5% CO2饱和湿度的电热恒温培养箱中培养。
茜素红S染色:培养5 d后,吸除培养基,加入体积分数10%甲醛室温固定1 h,去离子水冲洗后加入1%茜素红S染色液(pH=4.2)室温孵育1 h,去离子水冲洗后于倒置显微镜下观察拍照,观察矿化结节的形成。每孔随机选择4个不同视野,使用Image J软件对茜素红S染色阳性面积进行定量分析。
RT-PCR检测:培养5 d后,采用RT-PCR检测EPO、牙本质涎磷蛋白、牙本质基质蛋白1、巢蛋白mRNA相对表达,检测方法同上。引物序列见表2。

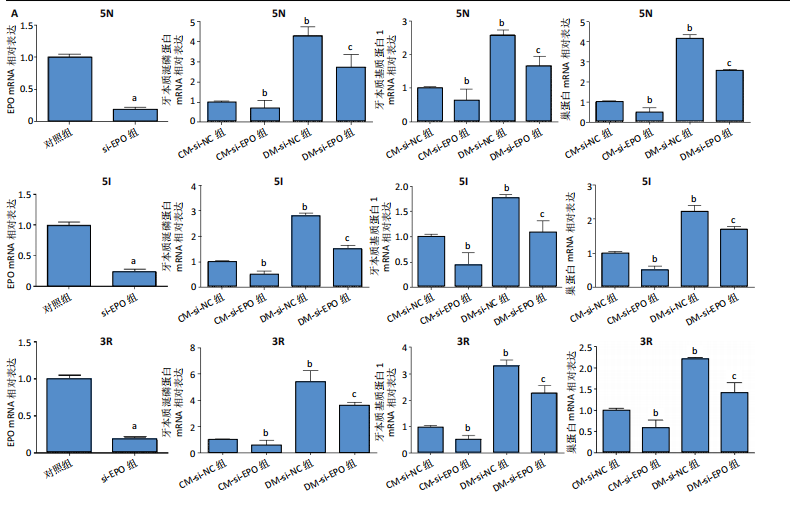
1.4.6 EPO下调对人牙髓细胞向牙本质细胞分化的影响 将人牙髓细胞接种于24孔板中,每孔加入1 mL含体积分数10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养基,细胞密度为3×104/孔,分2组转染,分别转染si-NC与si-EPO,分别记为si-NC组、si-EPO组。转染72 h后,采用RT-PCR检测EPO mRNA相对表达(引物序列见表2)。
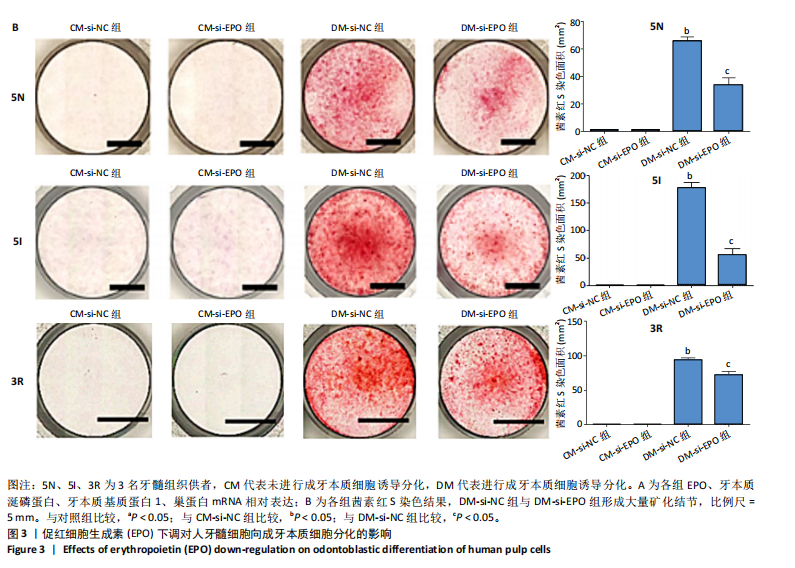
将人牙髓细胞接种于24孔板中,每孔加入1 mL含体积分数10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养基,细胞密度为3×104/孔,分4组培养:①CM-si-NC组:转染si-NC 72 h后不进行成牙本质细胞诱导分化,继续培养5 d;②DM-si-NC组:转染si-NC 72 h后加入2 mmol/L氯化钙诱导细胞分化为成牙本质细胞,继续培养5 d;③CM-si-EPO组:转染si-EPO 72 h后不进行成牙本质细胞诱导分化,继续培养5 d;④DM-si-EPO组:转染si-EPO 72 h后加入2 mmol/L氯化钙诱导细胞分化为成牙本质细胞,继续培养5 d。培养结束后,采用RT-PCR检测EPO、牙本质涎磷蛋白、牙本质基质蛋白1 mRNA相对表达(引物序列见表2),茜素红S染色检测矿化结节形成。
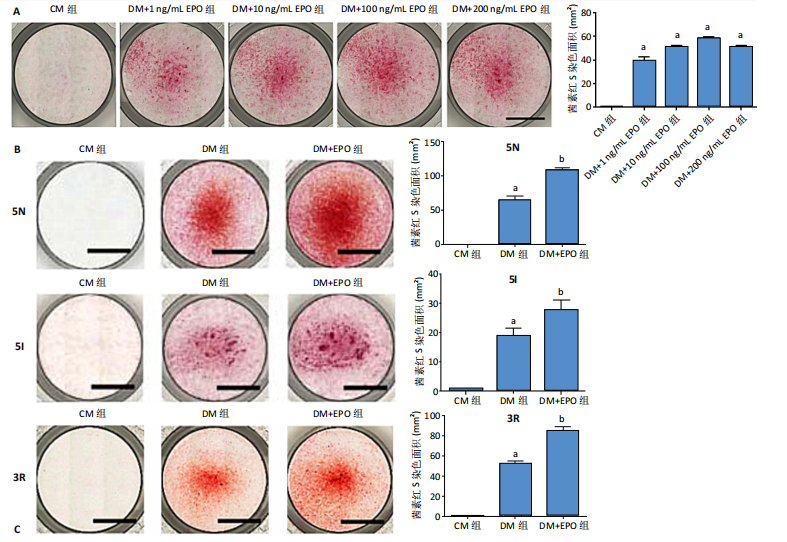
1.4.7 EPO对人牙髓细胞向成牙本质细胞分化的影响 将人牙髓细胞(5I供者)接种于24孔板中,每孔加入1 mL含体积分数10%胎牛血清+2 mmol/L氯化钙的DMEM培养基,细胞密度为3×104/孔,分别加入不同质量浓度(1,10,100,200 ng/mL)EPO干预5 d,对照组未加入氯化钙与EPO。干预结束后进行茜素红S染色,筛选矿化结节形成最多的质量浓度进行后续实验。
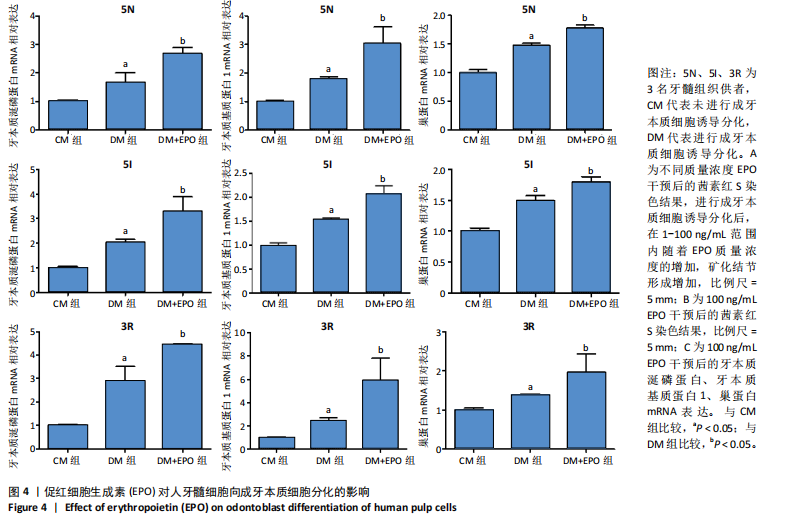
将人牙髓细胞接种于24孔板中,每孔加入1 mL含体积分数10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养基,细胞密度为3×104/孔,分3组培养:CM组不加入任何试剂,DM组加入2 mmol/L氯化钙诱导细胞分化为成牙本质细胞,DM+EPO组加入2 mmol/L氯化钙+100 ng/mL EPO。培养5 d后,采用RT-PCR检测EPO、牙本质涎磷蛋白、牙本质基质蛋白1的mRNA相对表达(引物序列见表2),茜素红S染色检测矿化结节形成。
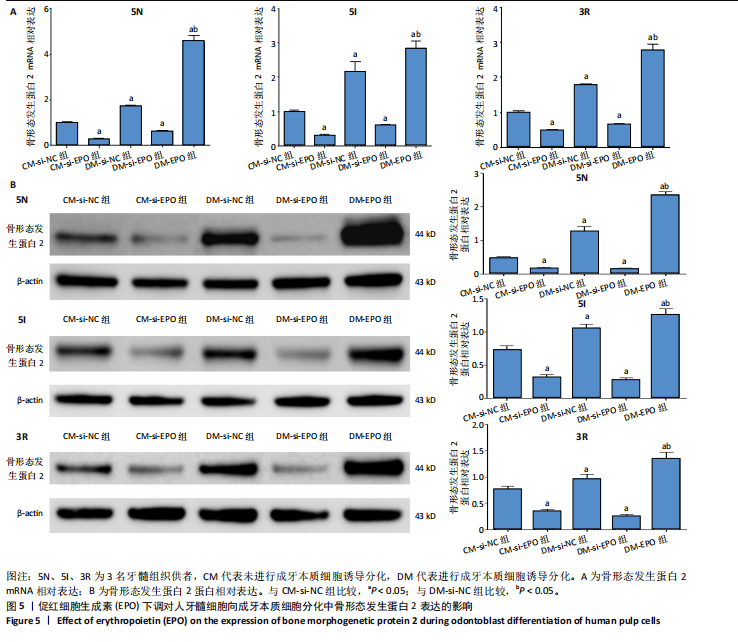
1.4.8 EPO对人牙髓细胞向成牙本质细胞分化中骨形成发生蛋白2表达的影响 将人牙髓细胞接种于24孔板中,每孔加入1 mL含体积分数10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养基,细胞密度为3×104/孔,分5组培养:①CM-si-NC组转染si-NC 72 h后继续培养5 d;②CM-si-EPO组转染si-EPO 72 h后继续培养5 d;③DM-si-NC组转染si-NC 72 h后加入2 mmol/L氯化钙诱导细胞分化为成牙本质细胞,继续培养5 d;④DM-si-EPO组转染si-EPO 72 h后加入2 mmol/L氯化钙诱导细胞分化为成牙本质细胞,继续培养5 d;⑤DM+EPO组加入2 mmol/L氯化钙诱导细胞分化为成牙本质细胞,同时加入100 ng/mL EPO,培养5 d。培养结束后,采用RT-PCR检测骨形态发生蛋白2 mRNA相对表达(引物序列见表2),Western blotting骨形态发生蛋白2蛋白相对表达。
Western blotting检测骨形态发生蛋白2表达:收集各组细胞,加入适量预冷RIPA,充分混匀后冰上孵育30 min。4 ℃下10 000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液,BCA定量后制样。凝胶电泳分离样品蛋白,转膜,截取目的条带浸于5%脱脂奶粉制成的封闭液中,置于摇床上室温封闭1 h。封闭液稀释骨形态发生蛋白2、β-actin抗体制成孵育液(稀释比例均为1∶500),充分摇匀后置于4 ℃环境下过夜。洗膜,加入稀释比例为1∶5 000的对应二抗孵育液室温孵育2 h,洗膜后加入ECL化学发光液避光反应5 min,用定量成像仪采集结果。
1.5 主要观察指标 EPO在牙体组织中的定位及在牙体细胞中的表达,EPO在人牙髓细胞向成牙本质细胞分化过程中的表达, EPO对人牙髓细胞向成牙本质细胞分化的影响,EPO下调对人牙髓细胞向成牙本质细胞分化及骨形态发生蛋白2表达的影响,EPO对直接盖髓治疗后修复性牙本质形成的影响。
1.6 统计学分析 使用SPSS 22.0统计软件处理收集到的数据,计量资料用x±s来表示,两组间比较采用独立样本t检验,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析。P < 0.05表示差异有显著性意义。该文统计学方法已经河北省眼科医院生物统计学专家审核。