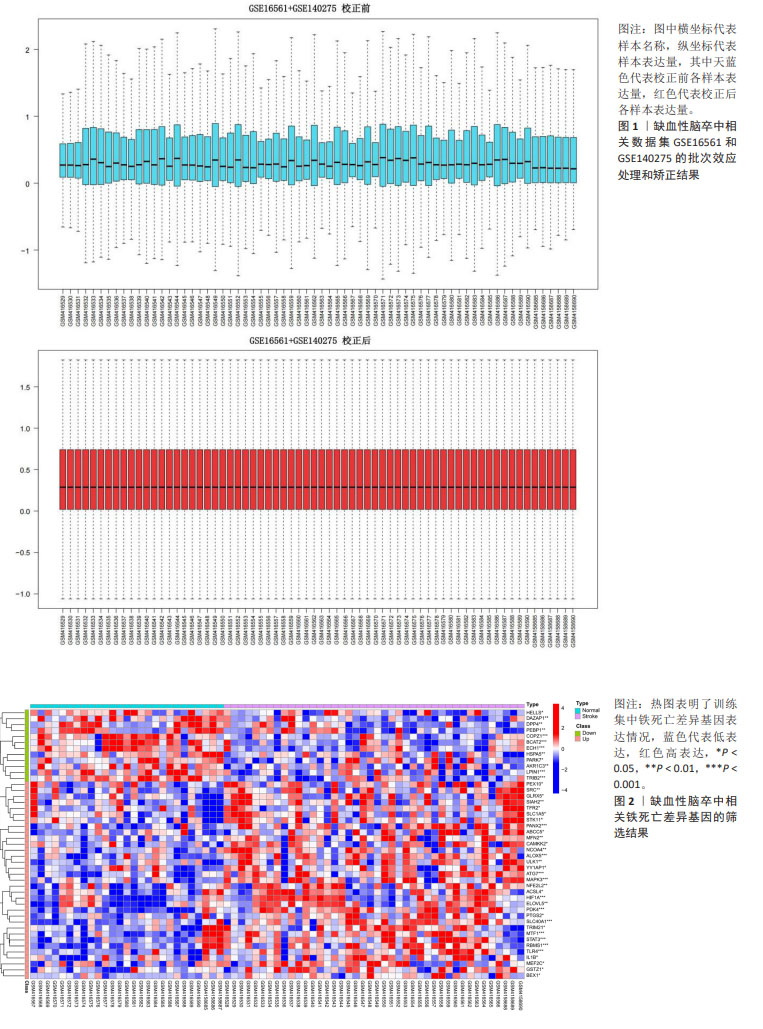
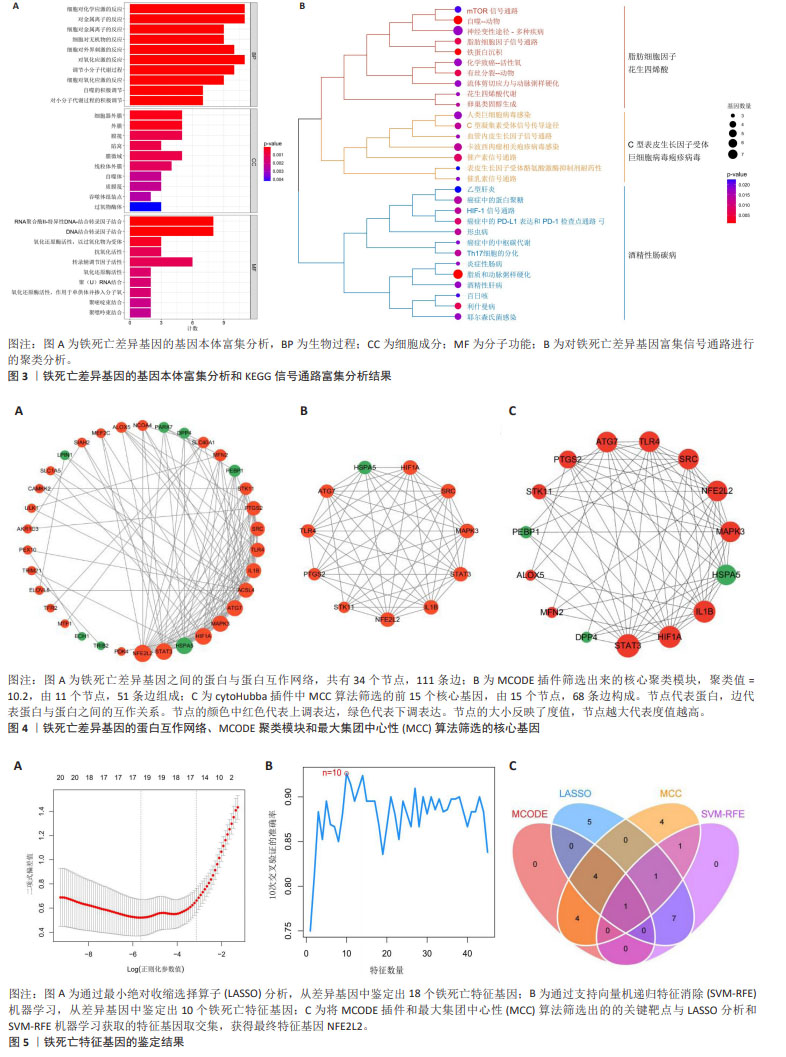
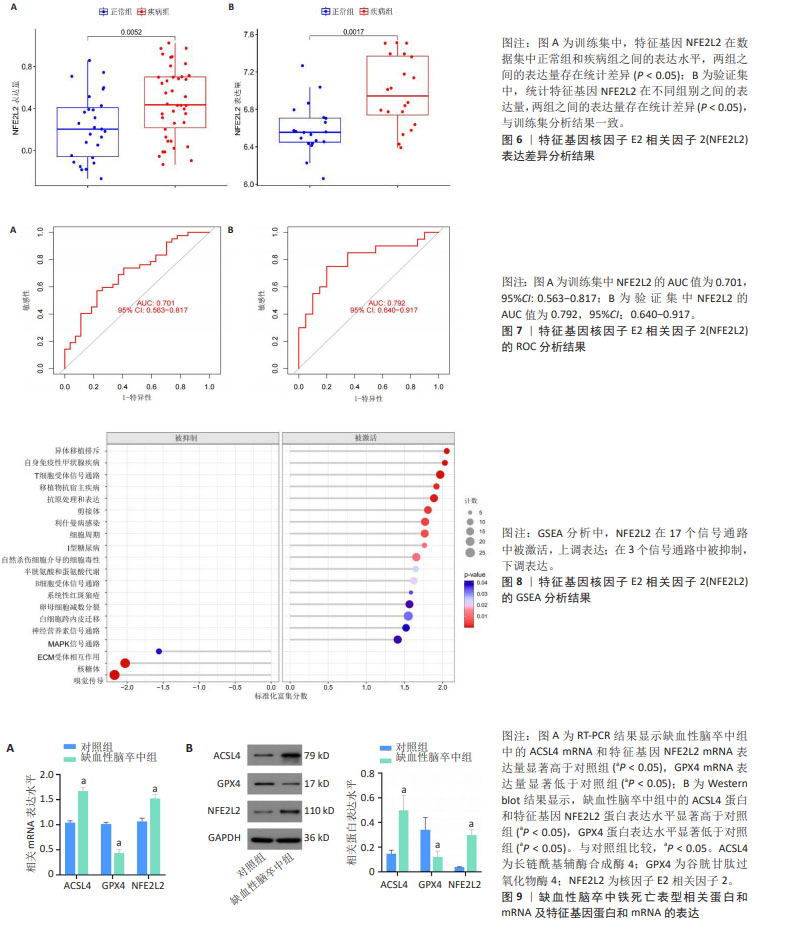
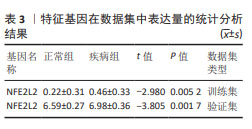
[1] ANDRABI SS, PARVEZ S, TABASSUM H. Ischemic stroke and mitochondria: mechanisms and targets. Protoplasma. 2020;257(2):335-343.
[2] TUO QZ, ZHANG ST, LEI P. Mechanisms of neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke and their therapeutic implications. Med Res Rev. 2022;42(1):259-305.
[3] GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018; 392(10159):1789-1858.
[4] GBD 2019 STROKE COLLABORATORS. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021;20(10):795-820.
[5] REN J X, LI C, YAN XL, et al. Crosstalk between oxidative stress and ferroptosis/oxytosis in ischemic stroke: possible targets and molecular mechanisms. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:6643382.
[6] WEILAND A, WANG Y, WU W, et al. Ferroptosis and its role in diverse brain diseases. Mol Neurobiol. 2019;56(7):4880-4893.
[7] WEI Z, XIE Y, WEI M, et al. New insights in ferroptosis: potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of ischemic stroke. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1020918.
[8] ZHANG Y, LU X, TAI B, et al. Ferroptosis and its multifaceted roles in cerebral stroke. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021;15: 615372.
[9] TUO QZ, LEI P, JACKMAN KA, et al. Tau-mediated iron export prevents ferroptotic damage after ischemic stroke. Mol Psychiatry. 2017;22(11):1520-1530.
[10] LIU J, GUO ZN, YAN XL, et al. Crosstalk between autophagy and ferroptosis and its putative role in ischemic stroke. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:577403.
[11] FABRIS F, PALMER D, DE MAGALHÃES JP, et al. Comparing enrichment analysis and machine learning for identifying gene properties that discriminate between gene classes. Brief Bioinform. 2020;21(3): 803-814.
[12] AUSLANDER N, GUSSOW AB, KOONIN EV. Incorporating machine learning into established bioinformatics frameworks. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(6):2903.
[13] MANN M, KUMAR C, ZENG WF, et al. Artificial intelligence for proteomics and biomarker discovery. Cell Syst. 2021;12(8): 759-770.
[14] PENG C, AI Q, ZHAO F, et al. Quercetin attenuates cerebral ischemic injury by inhibiting ferroptosis via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023; 963:176264.
[15] LIVAK KJ, SCHMITTGEN TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25(4): 402-408.
[16] ZHAO Y, ZHANG X, CHEN X, et al. Neuronal injuries in cerebral infarction and ischemic stroke:From mechanisms to treatment (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2022;49(2):15.
[17] TUO QZ, ZHANG ST, LEI P. Mechanisms of neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke and their therapeutic implications. Med Res Rev. 2022;42(1):259-305.
[18] YAO MY, LIU T, ZHANG L, et al. Role of ferroptosis in neurological diseases. Neurosci Lett. 2021;747:135614.
[19] LI Y, LI M, FENG S, et al. Ferroptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress in ischemic stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2024;19(3): 611-618.
[20] LAN B, GE JW, CHENG SW, et al. Extract of Naotaifang, a compound Chinese herbal medicine, protects neuron ferroptosis induced by acute cerebral ischemia in rats. J Integr Med. 2020;18(4):344-350.
[21] GUO H, ZHU L, TANG P, et al. Carthamin yellow improves cerebral ischemia‑reperfusion injury by attenuating inflammation and ferroptosis in rats. Int J Mol Med. 2021;47(4):52.
[22] 于瑜,王钟兴.基于生物信息学途径筛选缺血性脑卒中关键基因及药物预测[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版),2021,42(1): 42-50.
[23] 周嫱,柏娜,刘生刚,等.基于生物信息学和机器学习方法探索缺血性脑卒中关键风险基因[J].中国神经精神疾病杂志, 2022,48(9):525-532.
[24] GUO Y, ZHOU P, QIAO L, et al. Maternal protein deficiency impairs peroxisome biogenesis and leads to oxidative stress and ferroptosis in liver of fetal growth restriction offspring. J Nutr Biochem. 2023; 121:109432.
[25] CHEN X, KANG R, KROEMER G, et al. Organelle-specific regulation of ferroptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2021;28(10):2843-2856.
[26] SHE R, LIU D, LIAO J, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunctions induce PANoptosis and ferroptosis in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury: from pathology to therapeutic potential. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023;17: 1191629.
[27] ZHENG D, LIU J, PIAO H, et al. ROS-triggered endothelial cell death mechanisms: focus on pyroptosis, parthanatos, and ferroptosis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1039241.
[28] YANG K, ZENG L, YUAN X, et al. The mechanism of ferroptosis regulating oxidative stress in ischemic stroke and the regulation mechanism of natural pharmacological active components. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;154:113611.
[29] TANG D, CHEN X, KANG R, et al. Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res. 2021;31(2):107-125.
[30] ROJO DE LA VEGA M, CHAPMAN E, ZHANG DD. NRF2 and the hallmarks of cancer. Cancer cell. 2018;34(1):21-43.
[31] CONRAD M, KAGAN VE, BAYIR H, et al. Regulation of lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis in diverse species. Genes Dev. 2018;32(9-10):602-619.
[32] NISHIZAWA H, YAMANAKA M, IGARASHI K. Ferroptosis: regulation by competition between NRF2 and BACH1 and propagation of the death signal. FEBS J. 2023;290(7): 1688-1704.
[33] BERSUKER K, HENDRICKS JM, LI Z, et al. The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit ferroptosis. Nature. 2019;575(7784):688-692.
[34] JIANG X, STOCKWELL BR, CONRAD M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021; 22(4):266-282.
[35] LIU Z, LV X, SONG E, et al. Fostered Nrf2 expression antagonizes iron overload and glutathione depletion to promote resistance of neuron-like cells to ferroptosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020;407:115241.
[36] DENG X, CHU W, ZHANG H, et al. Nrf2 and ferroptosis: a new research direction for ischemic stroke. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023;43(8):3885-3896.
[37] SONG X, LONG D. Nrf2 and ferroptosis: a new research direction for neurodegenerative diseases. Front Neurosci. 2020;14:267.
[38] CUI Y, ZHANG Y, ZHAO X, et al. ACSL4 exacerbates ischemic stroke by promoting ferroptosis-induced brain injury and neuroinflammation. Brain Behav Immun. 2021;93:312-321.
[39] FAN GB, LI Y, XU GS, et al. Propofol inhibits ferroptotic cell death through the Nrf2/Gpx4 signaling pathway in the mouse model of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Neurochem Res. 2023;48(3):956-966. |