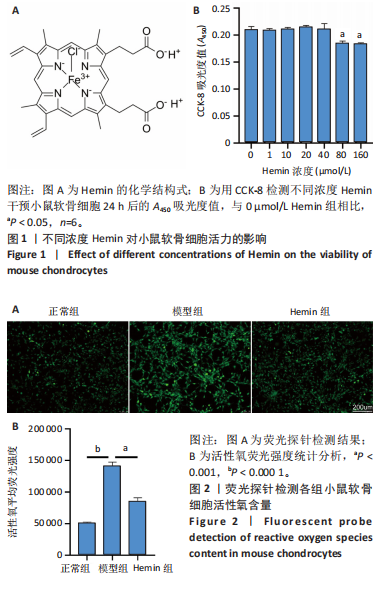
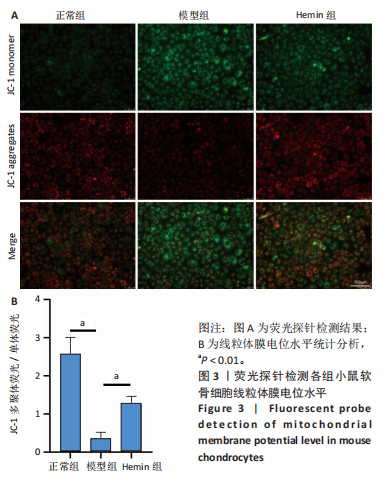
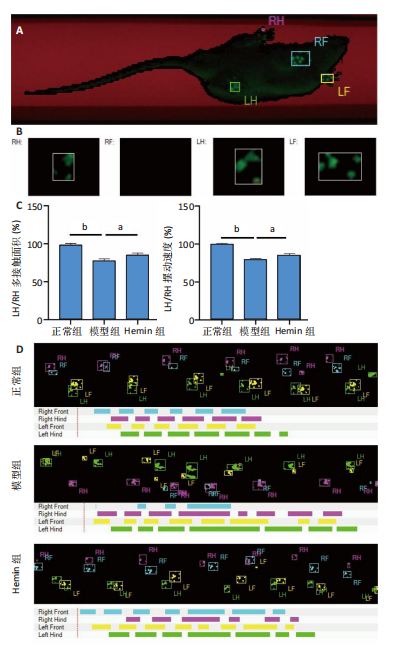
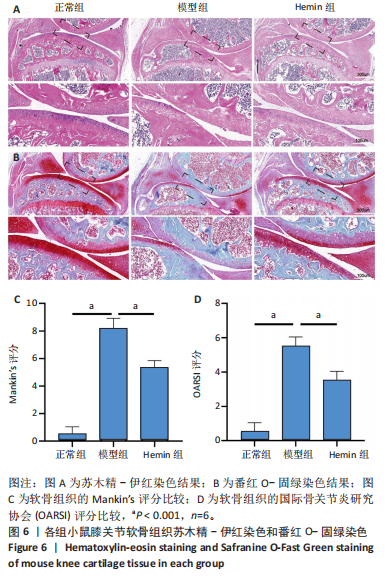
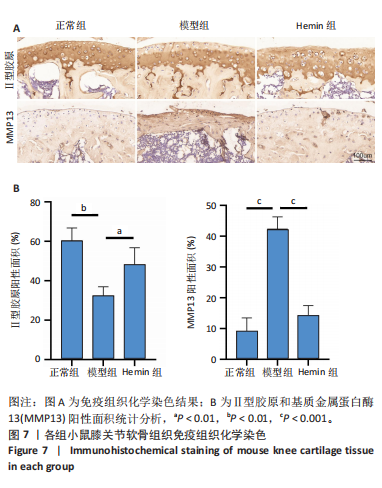
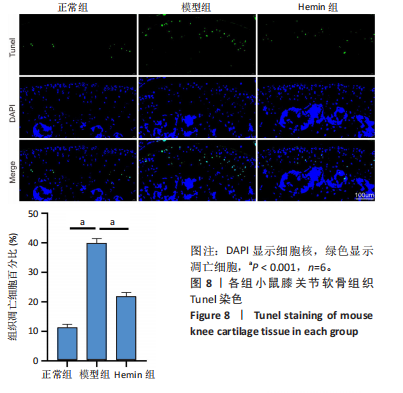
[1] LIU Q, WANG S, LIN J, et al. The burden for knee osteoarthritis among Chinese elderly: estimates from a nationally representative study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(12):1636-1642.
[2] KATZ JN, ARANT KR, LOESER RF. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review. JAMA. 2021;325(6):568-578.
[3] Hunter DJ, Bierma-Zeinstra S. Osteoarthritis. The Lancet. 2019; 393(10182):1745-1759.
[4] 赵彦萍, 林志国, 林书典, 等. 骨关节炎诊疗规范[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2022,61(10):1136-1143.
[5] ROBINSON WH, LEPUS CM, WANG Q, et al. Low-grade inflammation as a key mediator of the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(10):580-592.
[6] PEAT G, THOMAS MJ. Osteoarthritis year in review 2020: epidemiology & therapy. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(2):180-189.
[7] RIEGGER J, SCHOPPA A, RUTHS L, et al. Oxidative stress as a key modulator of cell fate decision in osteoarthritis and osteoporosis: a narrative review. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023;28(1):76.
[8] LIU X, LI Y, ZHAO J, et al. Pyroptosis of chondrocytes activated by synovial inflammation accelerates TMJ osteoarthritis cartilage degeneration via ROS/NLRP3 signaling. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023; 124(Pt A):110781.
[9] LEPETSOS P, PAPAVASSILIOU AG. ROS/oxidative stress signaling in osteoarthritis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1862(4):576-591.
[10] BISSELL DM, LONGO DL, ANDERSON KE, et al. Porphyria. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(9):862-872.
[11] KUMAR D, JENA GR, RAM M, et al. Hemin attenuated oxidative stress and inflammation to improve wound healing in diabetic rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2019;392(11):1435-1445.
[12] WANG YJ, PENG QY, DENG SY, et al. Hemin protects against oxygen–glucose deprivation-induced apoptosis activation via neuroglobin in SH-SY5Y cells. Neurochem Res. 2017;42(8):2208-2217.
[13] WU B, WU Y, FAN C, et al. Heme supplementation ameliorates lupus nephritis through rectifying the disorder of splenocytes and alleviating renal inflammation and oxidative damage. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;94:107482.
[14] MANKIN HJ, LIPPIELLO L. Biochemical and metabolic abnormalities in articular cartilage from osteo-arthritic human hips. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970;52(3):424-34.
[15] GLASSON SS, CHAMBERS MG, VAN DEN BERG WB, et al. The OARSI histopathology initiative – recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in the mouse. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010:18 Suppl 3:S17-S23.
[16] KLOPPENBURG M, BERENBAUM F. Osteoarthritis year in review 2019: epidemiology and therapy. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(3):242-248.
[17] Abdel-Rahman R, Alsharif I, Abd-Elsalam R, et al. Crataegus sinaica defatted methanolic extract ameliorated monosodium iodoacetate-induced oxidative stress andinhibited inflammation in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Res Pharm Sci. 2022;17(5):493-507.
[18] WAN C, LIU W, JIANG L, et al. Knockdown of MKL1 ameliorates oxidative stress-induced chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage matrix degeneration by activating TWIST1-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in rats. Autoimmunity 2022;55(8):559-566.
[19] WANG S, DENG Z, MA Y, et al. The Role of Autophagy and Mitophagy in Bone Metabolic Disorders. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(14):2675-2691.
[20] OH J, SON YS, KIM WH, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells genetically engineered to express platelet-derived growth factor and heme oxygenase-1 ameliorate osteoarthritis in a canine model. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):43.
[21] PAN Z, HE Q, ZENG J, et al. Naringenin protects against iron overload-induced osteoarthritis by suppressing oxidative stress. Phytomedicine. 2022;105:154330.
[22] COLLINO M, PINI A, MUGELLI N, et al. Beneficial effect of prolonged heme oxygenase 1 activation in a rat model of chronic heart failure. Dis Model Mech. 2013;6(4):1012-1020.
[23] VAAMONDE-GARCIA C, COURTIES A, PIGENET A, et al. The nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor/heme oxygenase-1 axis is critical for the inflammatory features of type 2 diabetes–associated osteoarthritis. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(35):14505-14515.
[24] SHENG W, YANG H, NIU Z, et al. Anti-apoptosis effect of heme oxygenase-1 on lung injury after cardiopulmonary bypass. J Thorac Dis. 2020;12(4):1393-1403.
[25] TAKADA T, MIYAKI S, ISHITOBI H, et al. Bach1 deficiency reduces severity of osteoarthritis through upregulation of heme oxygenase-1. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:285.
[26] SANADA Y, TAN SJO, ADACHI N, et al. Pharmacological Targeting of Heme Oxygenase-1 in Osteoarthritis. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021; 10(3):419.
[27] BAI F, FAN C, LIN X, et al. Hemin protects UVB-induced skin damage through inhibiting keratinocytes apoptosis and reducing neutrophil infiltration. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2023;238:112604.
[28] HASHIMOTO M, NAKASA T, HIKATA T, et al. Molecular network of cartilage homeostasis and osteoarthritis. Med Res Rev. 2008;28(3): 464-481.
[29] 宋永周, 关健, 李明, 等.Nrf2介导姜黄素对软骨细胞氧化应激损伤的保护作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(51):8218-8222.
[30] TAN Z, ZHANG B. Echinacoside alleviates osteoarthritis in rats by activating the Nrf2-HO-1 signaling pathway. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2022;44(6):850-859.
[31] SHIN HJ, PARK H, SHIN N, et al. p47phox siRNA-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles Suppress ROS/Oxidative Stress-Induced Chondrocyte Damage in Osteoarthritis. Polymers (Basel). 2020;12(2):443.
[32] PARK C, JEONG JW, LEE DS, et al. Sargassum serratifolium Extract Attenuates Interleukin-1β-Induc ed Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response in Chondrocytes by Suppr essing the Activation of NF-κB, p38 MAPK, and PI3K/Akt. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(8):2308.
[33] LIU L, ZHANG W, LIU T, et al. The physiological metabolite α-ketoglutarate ameliorates osteoarthritis by regulating mitophagy and oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2023;62:102663.
[34] MAWATARI T, NAKAMICHI I, SUENAGA E, et al. Effects of heme oxygenase‐1 on bacterial antigen‐induced articular chondrocyte catabolism in vitro. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(12):1943-1949.
[35] ZHOU Y, WANG T, HAMILTON JL, et al. Wnt/β-catenin Signaling in Osteoarthritis and in Other Forms of Arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2017;19(9):53.
[36] DING Y, WANG L, ZHAO Q, et al. MicroRNA‑93 inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammation in osteoar thritis by targeting the TLR4/NF‑κB signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med.2019;43(2):779-790.
[37] HE Z, LI H, HAN X, et al. Irisin inhibits osteocyte apoptosis by activating the Erk signaling pa thway in vitro and attenuates ALCT-induced osteoarthritis in mice. Bone. 2020;141:115573.
[38] CAI D, FENG W, LIU J, et al. 7,8‑Dihydroxyflavone activates Nrf2/HO‑1 signaling pathways and protects against osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2019;18(3):1677-1684.
[39] KENSLER TW, WAKABAYASHI N, BISWAL S. Cell survival responses to environmental stresses via the Keap1-Nrf2-A. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2007;47:89-116.
[40] LOBODA A, DAMULEWICZ M, PYZA E, et al. Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative stress response and diseases: an evolutionarily conserved mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73(17):3221-3247.
[41] PAN X, CHEN T, ZHANG Z, et al. Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signal with Myricetin for attenuating ECM degr adation in human chondrocytes and ameliorating the murine osteoarthrit is. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;75:105742. |