中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (30): 4904-4911.doi: 10.12307/2023.552
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
制备脱细胞基质生物墨水在心血管疾病领域中的应用
蒋鸿辉,孔媛媛,刘 婧,王志红
- 中国医学科学院生物医学工程研究所,天津市 300192
-
收稿日期:2022-08-12接受日期:2022-10-10出版日期:2023-10-28发布日期:2023-04-03 -
通讯作者:王志红,副研究员,中国医学科学院生物医学工程研究所,天津市 300192 刘婧,副研究员,中国医学科学院生物医学工程研究所,天津市 300192 -
作者简介:蒋鸿辉,男,1997年生,广西壮族自治区桂林市人,汉族,北京协和医学院在读硕士,中国医学科学院生物医学工程研究所,主要从事生物瓣膜体外模拟测试方面的研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金面上项目(32071356),项目负责人:王志红;国家自然科学基金面上项目(82272158),项目负责人:刘婧;中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金(3332022069),项目负责人:刘婧;中国医学科学院医学与健康科技创新工程(2022-I2M-1-023),项目负责人:王志红
Preparation and applications of decellularized extracellular matrix bioink in cardiovascular fields
Jiang Honghui, Kong Yuanyuan, Liu Jing, Wang Zhihong
- Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Tianjin 300192, China
-
Received:2022-08-12Accepted:2022-10-10Online:2023-10-28Published:2023-04-03 -
Contact:Wang Zhihong, Associate researcher, Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Tianjin 300192, China Liu Jing, Associate researcher, Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Tianjin 300192, China -
About author:Jiang Honghui, Master candidate, Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Tianjin 300192, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 32071356 (to WZH); National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 82272158 (to LJ); the Special Fund of Central University Basic Research Funds, No. 3332022069 (to LJ); Medical and Health Science and Technology Innovation Project of Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, No. 2022-I2M-1-023 (to WZH)
摘要:
文题释义:
脱细胞基质:生物组织或器官经过脱细胞处理去除细胞成分,降低免疫原性,同时保留细胞外基质成分与结构,最终获得的脱细胞基质材料。生物墨水:用于打印活细胞或生物活性分子的生物材料,可为细胞的生存提供合适的微环境。水凝胶材料是最为常用的生物墨水,主要包括胶原蛋白、明胶和海藻酸盐等。
背景:借助计算机辅助,3D生物打印技术利用负载活细胞的生物墨水实现组织器官的构建,这种技术设计自由度高、可个性化定制且制造灵活,为心血管组织工程构建带来了新希望。生物墨水是3D生物打印技术的关键,是生物材料与组织再生领域近年来的研究热点。脱细胞基质材料具有低免疫原性、维持原有细胞外基质组分与纤维结构以及利于组织特异性细胞的存活与扩增的特点,是一种具有潜力的生物墨水。
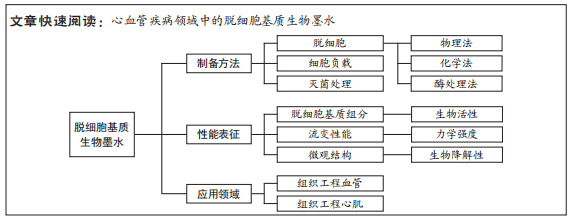
目的:总结了脱细胞基质生物墨水的制备与性能表征方法及其在心血管领域中的应用,为脱细胞基质生物墨水在心血管领域中的应用研究提供重要参考。
方法:在中国知网和PubMed数据库中进行相关文献检索,中文检索词为“3D打印、脱细胞、生物墨水、血管、心脏”,英文检索词为“decellularization,bioink,3D print,vessel,cardiac”,最终纳入82篇文献进行分析。
结果与结论:①脱细胞基质生物墨水的基本制备步骤包括生物材料脱细胞处理获得脱细胞基质,酶解消化脱细胞基质,调节消化液pH值和渗透压以及脱细胞基质混合细胞;②脱细胞基质生物墨水的基本性能表征主要包括脱细胞基质组分、流变性能、微观结构、生物活性、力学性能以及生物降解性;③在血管方面,研究者们通过使用先进打印技术、材料复合以及牺牲层等策略,制备出的脱细胞基质血管的力学性能可得到提升,并得到多层小口径血管,但这些打印过程较复杂,血管性能缺乏动物实验验证,多层血管的培养条件未经优化,且未进行缝合强度和爆破压等重要测试,无法满足医疗器械所需的性能;④在心肌修复方面,研究者证实与胶原及GelMA等相比,脱细胞基质生物墨水在心肌修复中更有优势。同时研究者集中于通过提升材料力学强度和导电性能,并构建微血管网络,进行脱细胞基质心肌补片的设计,这些补片在治疗心肌梗死方面表现出一定优势。然而种子细胞的参数(类型、区域密度和数量等)对于心肌补片的影响问题以及心肌补片与宿主组织之间的电耦合问题等均未取得突破,无法满足医疗器械所需的性能;⑤因此,脱细胞基质生物墨水虽然在构造心血管结构方面展现出了一定潜力,但以脱细胞基质为基础打印的血管和心肌补片目前仍处于实验室阶段,距离进入临床应用还需克服一系列问题。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5661-9983(蒋鸿辉);https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7341-0201(王志红);https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8306-7611(刘婧)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
蒋鸿辉, 孔媛媛, 刘 婧, 王志红. 制备脱细胞基质生物墨水在心血管疾病领域中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(30): 4904-4911.
Jiang Honghui, Kong Yuanyuan, Liu Jing, Wang Zhihong. Preparation and applications of decellularized extracellular matrix bioink in cardiovascular fields[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(30): 4904-4911.
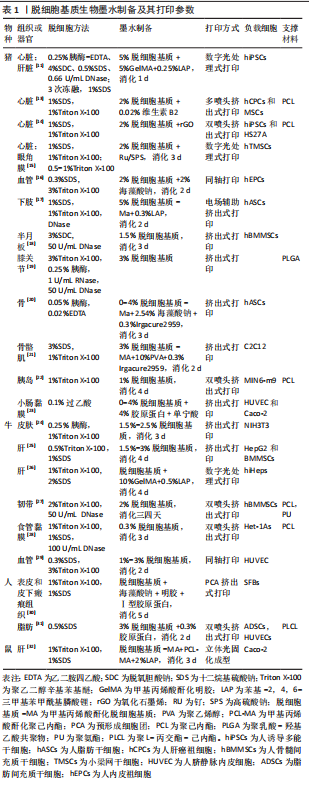
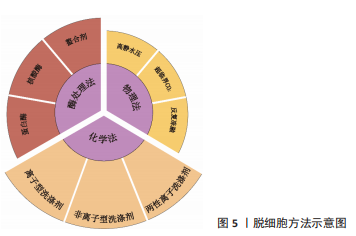
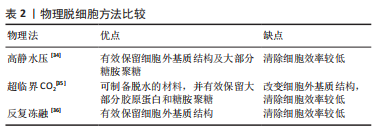
2.1.1 脱细胞方法 脱细胞过程,去除组织或器官中的细胞成分,保留ECM组分和微观组织结构。不同组织或器官的细胞数量、细胞外基质的紧密度、厚度和脂质含量等各有差异。特定组织或器官来源的脱细胞基质制备,需使用不同的脱细胞方法。脱细胞方法主要包括物理法、化学法和酶处理法,见图5。
物理方法:如表2所示,常用物理脱细胞方法有高静水压法、超临界CO2法、反复冻融法以及超声破碎法等,其基本原理为通过物理方法破坏细胞膜,释放细胞内容物[34-36]。①高静水压法,当液体静水压超过600 MPa时[34],细胞破碎。②CO2的临界点为:31 ℃,7.38 MPa,超临界CO2是温度和压力处于临界温度和临界压力以上的CO2,可破坏组织的极性基团,并制备干态的脱细胞基质材料[35]。③反复冻融方法通常需对材料进行循环低温冷冻(-20 ℃,-80 ℃或-196 ℃)与室温/生理温度解冻,从而破坏细胞膜,并在膜内形成冰晶导致细胞裂解[36]。整体上,物理脱细胞法可保持更好的ECM结构完整性,但细胞清除效率较低。
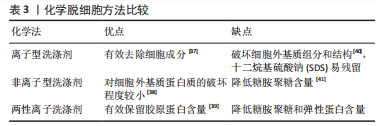
化学方法:通过洗脱试剂破坏细胞膜,从而达到去除细胞的目的。如表3所示,常用的化学试剂为洗涤剂[37-41],主要包括离子型洗涤剂、非离子型洗涤剂和两性离子洗涤剂。离子型洗涤剂如十二烷基硫酸钠(sodium dodecyl sulfate,SDS)和脱氧胆酸钠(sodium deoxycholate,SDC)可破坏脂质-脂质、脂质-蛋白质、DNA-蛋白质和蛋白质-蛋白质的相互作用,释放细胞成分和DNA,被广泛用于各种组织如软骨和心肌等[37]。聚乙二醇辛基苯基醚(Triton X-100)是常用的非离子型洗涤剂,可温和破坏脂质-脂质、脂质-蛋白质和DNA-蛋白质的相互作用,但不影响蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用[38]。3-[3-(胆酰胺丙基)二甲氨基]丙磺酸内盐(3-[(3-Cholanidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-1-propanesulfonate,Chaps)是一种非变性两性离子洗涤剂,可破坏蛋白质之间的非共价键并溶解膜蛋白[39]。整体上,化学脱细胞法细胞去除率高,但对细胞外基质结构破坏较大。不同的脱细胞试剂的效果也不尽相同,需根据所处理组织/器官的大小、厚度、紧密度以及所保留物质的组分不同,选取不同的脱细胞配方。
酶处理方法:作为物理法与化学法的后处理方法,酶处理可去除DNA、RNA以及其他引起免疫原性的抗原物质,常用酶包括蛋白酶和核酸酶等。经化学试剂处理后,组织孔隙率会增大,进一步利用酶处理可去除残余的核酸成分。蛋白酶如胰酶可破坏蛋白质肽链,导致蛋白质水解并破坏细胞与细胞外基质的黏附。核酸酶如DNase与RNase能分别催化DNA和RNA发生裂解。研究显示长时间使用酶处理可能降低组织的胶原蛋白和糖胺聚糖含量,影响细胞外基质结构稳定性[42]。
2.1.2 灌注洗脱与浸泡搅拌法 对于较大尺寸的组织/器官,如心脏、肺和肝脏等,简单的组织浸泡洗脱,难以让洗脱液浸入组织器官的深部,脱细胞去除效果较差,此类组织器官脱细胞基质的制备,更适合利用灌注洗脱法制备。灌注方法通过注射泵向脏器内注入液体,脏器的血管网络作为液体流通的管道,并通过压力传感器控制流速,主要针对大型脏器如心脏、肾脏等该方法可提高大型脏器的脱细胞效率并保留血管网络结构,但需额外的注射/抽吸泵等装置,对流速控制要求较高[43]。浸泡搅拌可保证材料有更大面积暴露于液体中,主要针对小型组织,其效果取决于试剂、组织大小和搅拌速率等[44]。
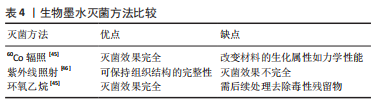
2.1.3 脱细胞基质材料的灭菌方法 灭菌处理对于脱细胞基质生物墨水的保存与使用至关重要,常用的灭菌方法包括:60Co辐照、紫外线灭菌、环氧乙烷和抗生素处理等。
各灭菌方法各具优缺点。60Co辐照利用强穿透性的电子束破坏微生物的核酸、蛋白质和酶[45]。紫外线灭菌是实验室材料常用的灭菌方法之一,其可引发胸腺嘧啶分子间交联,形成共价二聚体,从而破坏微生物的DNA结构[46]。环氧乙烷可导致微生物蛋白质和核酸中的氨基和羧基烷基化[45],见表4。
动物组织/器官的脱细胞方法发展几十年,技术已较为成熟。研究人员在具体研究工作中,应根据组织器官的不同来源、结构特点以及脱细胞基质的未来用途,针对性地选择合适的脱细胞方法。脱细胞方法选择是脱细胞基质制备的首要步骤,也是决定脱细胞基质质量的关键环节。制备过程中,除要考察细胞去除效率之外,需兼顾活性物质保留、细胞外基质天然组织结构的维持完整性以及试剂残余等问题。
2.2 脱细胞基质生物墨水性能表征 脱细胞基质生物墨水制备的质量以及组分信息、流变性能,对于其后续应用具有重要指导作用。一般利用DNA和ECM蛋白定量可判断脱细胞效果达标与否;流变性能检测可辅助判断脱细胞基质生物墨水的打印性;微观结构、生物相容性、力学强度和生物降解性测试可用于评估脱细胞基质生物墨水的功能性。
2.2.1 脱细胞基质组分 脱细胞充分与否直接决定生物墨水的免疫排斥作用,目前临床可使用标准为dsDNA含量低于50 ng/mg(干质量状态)[42];同时可辅助DNA凝胶电泳实验,DNA残余片段长度低于200 bp;组织切片苏木精-伊红染色,验证无明显可见的细胞核残余。除猿类和人类外,哺乳动物细胞的细胞膜上存在α-gal抗原表位[47],该表位是造成异种器官移植时出现免疫排斥的主要原因,需进行去除和检测。为掌握特定组织来源的脱细胞基质理化特性与生物活性,对其组成成分如胶原蛋白和弹性蛋白等含量进行测定。利用SDS-PAGE可分析肽链信息[48],液相二级质谱(LC-MS/MS)定量分析蛋白质组成信息[40]。VISSCHER等[49]利用LC-MS/MS方法比较了猪软骨脱细胞前后的蛋白质组成,发现683种蛋白质仅存在于新鲜猪软骨中,21种蛋白质仅存在于脱细胞猪软骨中,412种蛋白质在猪软骨脱细胞前后均存在。
2.2.2 流变性能 流变性能指示材料的可成胶性能,决定材料的可打印性,测试方法包括黏度-剪切速率测试、温度扫描测试和频率振动测试等。挤出式打印的生物墨水黏度通常要求为30-6×107 mPa s-1,其精度范围为200-1 000 μm[50]。黏度-剪切速率测试可确定材料的黏度及其是否具有剪切变稀性,保证打印细胞的活力大于90%。研究发现,在剪切速率为2 s-1时,软骨、脂肪和心脏来源的墨水的黏度分别为2.8 Pa s-1,6.13 Pa s-1和23.6 Pa s-1[11]。温度扫描测试可检测在固定振动频率下,墨水在升温过程中储能模量G’与损耗模量G’’的大小变化,这种变化源于胶原蛋白单体的自组装,从而分析脱细胞基质生物墨水由预凝胶(G’ < G’’)转变为凝胶(G’ > G’’)的过程,判断最佳成胶温度与成胶时间。频率振动测试可测试不同的振动频率范围内G’与G’’的大小关系。
2.2.3 微观结构 生物墨水的微观结构,包括拓扑结构、支架纤维的直径、孔径大小和纤维取向等会影响细胞排列和成熟分化[48]。扫描电镜可用于观察凝胶的纤维结构,脱细胞基质水凝胶浓度越高,其内部孔径大小会逐渐降低[51]。不同动物或者组织来源的脱细胞基质纤维直径各有不同,例如猪膀胱脱细胞基质凝胶的纤维直径约为74 nm[52],而猪心肌、猪小肠和人脂肪组织脱细胞基质凝胶的纤维直径约为100 nm[53-55]。
2.2.4 生物活性 脱细胞基质生物墨水因其在组织来源等方面存在差异,因此对细胞活力、增殖、迁移、形貌、分化和表型等具有不同影响。WOLF等[52]发现在猪真皮脱细胞基质凝胶表面培养的C2C12成肌细胞会融合形成大直径的多核肌管状结构,而在猪膀胱脱细胞基质凝胶表面细胞融合的程度较小。AGUADO等[56]对比了具有不同储能模量(0.33-58.10 Pa)的脱细胞基质凝胶对于其负载的细胞影响,发现G’为29.6 Pa的脱细胞基质凝胶的细胞活力最高。
2.2.5 力学强度 生物墨水的力学强度对于其后续应用至关重要,对其基本的机械特性进行研究有助于后续材料的优化。力学性能主要包括压缩模量、软硬度、弹性模量等。压缩测试用于获得材料的压缩模量;超声波法、磁共振弹性成像法和原子力显微镜用于检测硬度[57-58];纳米压痕仪则用于纳米尺度上测量力学性质和硬度[59]。研究发现软骨和椎间盘脱细胞基质凝胶的压缩模量强度基本低于20 kPa[60]。
2.2.6 生物降解性 将冻干的材料放入酶溶液或植入动物模型体内,通过测量材料随着时间变化的质量损失情况,可表征材料的生物降解性。植入物的降解速率由浓度、交联剂、墨水来源的组织类型及体内外环境等因素共同决定[61]。材料的降解会影响其力学性能以及细胞的伸展和迁移[62],理想植入物的降解速率应匹配组织细胞外基质再生速率,且降解产物无副作用。GILBERT等[63]发现猪小肠黏膜脱细胞基质植入体内后在1个月内降解了50%,在3个月内完全降解。
脱细胞基质生物墨水的性能表征,是判断脱细胞基质生物墨水3D打印性、以及3D打印条件参数设置的重要前提。因此,在具体研究中,对所制备的脱细胞基质的组分信息、流变性能、降解特性、形貌结构以及生物降解性等基本理化性能进行全面详细评估,是必不可少的环节。
2.3 脱细胞基质生物墨水在心血管领域中的应用 在20世纪80年代,VACANTI和LANGER提出组织工程概念,即通过结合生物学、材料学和工程学等方法用以修复及再造组织或器官[64]。之后,由SHINOKA,ZIMMERMANN和NEREM分别率先开展了工程化心脏瓣膜、心肌组织和血管的研究[65-67]。但至今为止,仅有少量进入临床试验的心血管组织工程产品,比如源于猪小肠黏膜下层脱细胞基质的CorMatrix、源于猪心肌脱细胞基质的VentriGel和海藻酸钠凝胶材料Algisyl-LVR?,其中CorMatrix作为心肌补片已进入临床试验阶段。3D生物打印技术具有设计自由度高和制造灵活的特点,其通过计算机辅助技术有望构建具有复杂几何功能结构的心血管组织器官。
2.3.1 脱细胞基质生物墨水在组织工程血管中的应用 天然血管主要由3层结构构成,包括内膜、中膜和外膜,分别由内皮细胞、平滑肌细胞和成纤维细胞组成。内皮层在血管抗凝过程起关键作用,而平滑肌细胞构成的中膜层可起到收缩舒张作用。
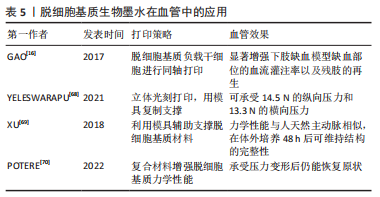
组织工程策略构建血管作为人工血管开发的前沿性技术。随着生物3D打印技术的发展,通过生物墨水负载内皮细胞或内皮祖细胞、以及平滑肌细胞,体外仿生构建由内皮细胞与平滑肌细胞构成的功能血管成为可能。GAO等[16]利用同轴打印,将负载人内皮祖细胞的猪降主动脉脱细胞基质生物墨水与海藻酸钠溶液作为外壳,泊洛沙姆 (Pluronic F-127)溶液作为内部牺牲层,构建了人工血管。这种3D打印血管治疗裸鼠下肢缺血模型,植入28 d后,其3D打印血管内腔形成了内皮层,并且缺血部位的血流灌注率获得显著提升,该研究证明了3D打印血管的可行性,但该血管力学强度较弱,手术吻合性较差,需进一步优化改进。
针对上述脱细胞基质生物墨水打印结构力学强度弱的问题,YELESWARAPU等[68]使用立体光刻3D打印技术,先打印出同心圆柱模具,再向模具内部灌注羊食管肌肉脱细胞基质生物墨水得到由脱细胞基质组成的管状结构,该结构可承受14.5 N的纵向压力和13.3 N的横向压力。此外,XU等[69]使用F127溶液和一种有机硅溶液(SE1700)构建了中空管状结构,并向中空部位灌注负载人主动脉平滑肌细胞的猪软骨脱细胞基质墨水,再向内层灌注负载人脐静脉内皮细胞的猪软骨脱细胞基质墨水,最后将上述结构浸入负载人皮肤成纤维细胞的猪软骨脱细胞基质墨水池中,得到了三层小口径血管,这种血管的力学性能与人天然主动脉相似,在体外培养48 h后仍能维持完整结构,见图6。
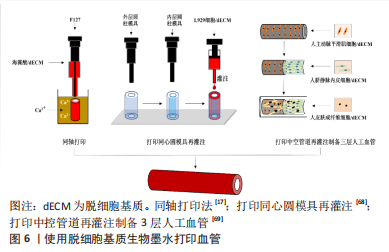
此外,有研究团队通过将脱细胞基质与其他材料混合,从而增强打印结构的力学性能。例如,POTERE等[70]将猪主动脉脱细胞基质、明胶和海藻酸混合,打印出高度为9 mm的大血管,该血管在承受外界压力变形后仍能回复原状。
脱细胞基质生物墨水在组织工程血管构建中的应用总结见表5。通过使用先进打印技术与材料复合,脱细胞基质血管的力学性能可得到提升,然而现有研究工作打印过程较为复杂,且缺乏动物实验验证。再者,对于多层血管培养条件优化,以及各层之间的相互作用尚缺乏考虑。更为重要的,脱细胞基质生物墨水构造血管的缝合强度、爆破压等重要性能还需进行详细测试,为其作为医疗器械应用于临床治疗提供充分证据。因此,现有脱细胞基质生物墨水打印的血管主要用于基础研究,如病理学、药理学和毒理学研究。
由“蓝光英诺”公司开发的首款干细胞3D生物打印产品REVOVAS在恒河猴和五指山小型猪身上进行了实验,结果表明植入的血管在短期内可实现完整血管组织再生,具备正常血管的功能,目前该产品已获得临床试验批准,临床试验结果还有待验证。
2.3.2 脱细胞基质生物墨水在组织工程心肌中的应用 心室壁由3层结构组成,由外到内分别是心外膜、心肌层和心内膜,其中心肌层是构成心室壁的主要成分,由各向异性心肌细胞和胶原纤维组成[71]。心肌梗死发生时,冠状动脉被部分或全部阻塞,导致局部心肌缺血缺氧,造成大量心肌细胞死亡并被成纤维细胞替代,形成瘢痕组织。组织工程心肌通过负载细胞或活性分子构建具有天然心肌组织结构的仿生支架,使其具有诱导修复损伤心肌组织的能力,最终恢复心肌功能。
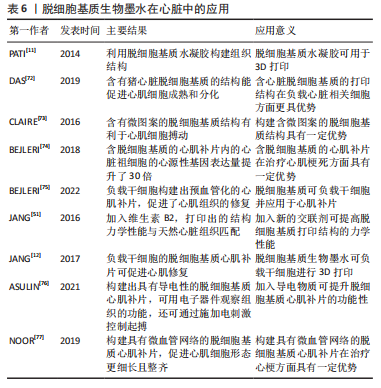
研究表明,利用脱细胞基质构建心肌补片可促进缺血部位的血管新生、提升心肌细胞的活力及改善心肌的收缩功能等。例如,PATI等[11]首次使用猪心脏脱细胞基质生物墨水进行打印,与胶原蛋白组相比,含脱细胞基质的打印组织结构中的小鼠心肌细胞的心肌特异性基因Myh6(Myosin Heavy Chain 6)和Actn1(Alpha-Sarcomeric Actinin)表达水平更高。DAS等[72]先打印聚乙烯-醋酸乙烯酯支架,再将猪心脏脱细胞基质墨水打印至支架上,结果表明与胶原蛋白组相比,含有猪心脏脱细胞基质的结构更能促进心肌细胞成熟和分化。有研究将猪左心室脱细胞基质与GelMA混合,并负载心肌细胞,通过控制紫外光照的路径打印出具有平行线条微图案的心肌结构[73]。体外培养1 d后,脱细胞基质-GelMA心肌结构中的心肌细胞与微图案的线条相平行;体外培养3 d后,在无外部刺激的情况下,脱细胞基质-GelMA心肌结构中的心肌细胞可观察到搏动现象;体外培养7 d后,与胶原蛋白-GelMA组相比,脱细胞基质-GelMA组中在平行于线条的区域中可观察到更密集的细胞,同时该组出现更多同步收缩区。BEJLERI等[74]将GelMA与猪心室脱细胞基质混合打印出心脏补片,与GelMA组相比,该补片内的心脏祖细胞的心源性基因表达量提升了30倍;GelMA-脱细胞基质补片贴附在小鼠心外膜表面14 d后出现明显的血管化。之后该团队利用小鼠右心室衰竭模型发现该补片可促进血管形成、降低心肌肥大程度和提高右心室的功能性,表明加入脱细胞基质可提升治疗效果[75]。由此可见,与胶原和GelMA等相比,脱细胞基质生物墨水在心肌修复中更有优势。
组织工程心肌修复材料的设计,主要集中于提升材料力学强度、导电性能以及构建微血管网络3个方面。其中为了打印出力学性能与心脏组织相匹配的结构,JANG等[51]将维生素B2加入猪心脏脱细胞基质生物墨水中,所打印的结构经过紫外交联后再进行热孵育,其硬度提高了33倍,力学性能接近于天然心脏组织,且能促进心脏祖细胞分化。进一步地,JANG等[12]利用猪心脏脱细胞基质分别负载人间充质干细胞和心脏祖细胞,同时加入血管内皮生长因子,构建出预血管化的心肌补片,该补片可增强心肌功能、降低心肌肥大和纤维化程度,促进了心肌组织的修复效果。
心脏通过传导系统将电信号传导到心脏的各个部位而产生收缩舒张功能,心肌电活动的紊乱是心肌梗死后心肌功能受损的主要原因之一。构建导电性组织工程心肌对于心功能恢复具有至关重要的意义。ASULIN等[76]将猪视网膜脱细胞基质、导电石墨桨和表面活性剂混合,打印出嵌含柔性、可伸展的电子器件的心肌补片,该补片可经受类似于心肌收缩的持续形变,并且电子器件可用于观察组织功能,还可通过电刺激控制起搏。
心肌存活需要充足的血供进行氧气扩散和营养物质运输,如何打印具有微血管网络的结构是该心肌组织打印的难题之一。预血管化是一个重要的策略。基于此,NOOR等[77]利用负载心肌细胞的脱细胞基质生物墨水打印出2层网格结构,而在第三层利用不负载细胞的脱细胞基质生物墨水打印出支撑壁结构,同时在该层内部打印负载内皮细胞的明胶墨水;最后,再利用负载内皮细胞的脱细胞基质生物墨水打印出2层网格结构作为顶层,从而形成心肌补片。该补片在37 ℃孵育30 min可去除液化后的明胶,形成具有血管网络的心肌补片;该补片在体外培养至第7天时,内皮细胞形成了一层连续的管状结构;植入小鼠大网膜内7 d后,补片内的心肌细胞形态更为细长且整齐,同时具有大量肌动蛋白条纹,说明该补片已具有一定的收缩性。
脱细胞基质生物墨水在组织工程心肌中的应用总结见表6。
尽管已有研究在心肌补片和心肌组织的力学性能、心肌补片的电传导性、促血管再生、促细胞生长和收缩性等方面取得了一定进展,然而种子细胞的参数(类型、区域密度和数量等)对于心肌补片的影响问题和导电心肌补片与宿主组织之间的电耦合问题等尚未取得突破。
脱细胞基质作为生物墨水在3D打印心血管组织工程领域的应用潜力,近年来取得较大进展,但现有研究大多处于概念性验证阶段,距离临床应用还有较远的距离。从概念性验证到实现临床应用仍面临巨大挑战:①脱细胞基质材料的力学强度还有待进一步提升;②如何实现大尺寸组织或器官的组织结构稳定性以及营养代谢长期稳定性维持;③未来作为产品应用,如何保持脱细胞基质成分与批次稳定性;④以及储存与运输问题如何解决等,未来仍需要开展大量研究工作。

| [1] 吴永健. 2020年中国心血管健康与疾病报告[J].心肺心血管杂志,2020, 40(10):1005-1009. [2] MCCRARY MW, BOUSALIS D, MOBINI S, et al. Decellularized tissues as platforms for in vitro modeling of healthy and diseased tissues. Acta Biomater. 2020;111:1-19. [3] GOPINATHAN J, NOH I. Recent trends in bioinks for 3D printing. Biomater Res. 2018:22(11):1-15. [4] E.POEL W. Preparation of Acellular Homogenates From Muscle Samples. Science. 1948;108:390-391. [5] HJELLE JT, CARLSON EC, BRENDEL K, et al. Biosynthesis of basement membrane matrix by isolated rat renal glomeruli. Kidney Int. 1979;15(1):20-32. [6] KREJCI NC, CUONO CB, LANGDON RC, et al. In vitro reconstitution of skin: fibroblasts facilitate keratinocyte growth and differentiation on acellular reticular dermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1991;97(5):843-848. [7] SCHMIDT CE, BAIER JM. Acellular vascular tissues: Natural biomaterials for tissue repair and tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2000;21(22):2215-2231. [8] ELKINS RC, DAWSON PE, GOLDSTEIN S, et al. Decellularized human valve allografts. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001;71(5):S428-S432. [9] LANDERS R, HÜBNER U, SCHMELZEISEN R, et al. Rapid prototyping of scaffolds derived from thermoreversible hydrogels and tailored for applications in tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2002;23(23):4437-4447. [10] OTT HC, MATTHIESEN TS, GOH SK, et al. Perfusion-decellularized matrix: using nature’s platform to engineer a bioartificial heart. Nat Med. 2008;14(2):213-221. [11] PATI F, JANG J, HA DH, et al. Printing three-dimensional tissue analogues with decellularized extracellular matrix bioink. Nat Commun. 2014;5:1-11. [12] JANG J, PARK HJ, KIM SW, et al. 3D printed complex tissue construct using stem cell-laden decellularized extracellular matrix bioinks for cardiac repair. Biomaterials. 2017;112:264-274. [13] KIM BS, KWON YW, KONG JS, et al. 3D cell printing of in vitro stabilized skin model and in vivo pre-vascularized skin patch using tissue-specific extracellular matrix bioink: a step towards advanced skin tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2018;168:38-53. [14] TSUI JH, LEONARD A, CAMP ND, et al. Tunable electroconductive decellularized extracellular matrix hydrogels for engineering human cardiac microphysiological systems. Biomaterials. 2021;272-287. [15] KIM H, KANG B, CUI X, et al. Light-activated decellularized extracellular matrix-based bioinks for volumetric tissue analogs at the centimeter scale. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31(32):2011252-2011261. [16] GAO G, LEE JH, JANG J, et al. Tissue engineered bio-blood-vessels constructed using a tissue-specific bioink and 3D coaxial cell printing technique: a novel therapy for ischemic disease. Adv Funct Mater. 2017;27(33):1-12. [17] KIM WJ, LEE H, LEE CK, et al. A bioprinting process supplemented with in situ electrical stimulation directly induces significant myotube formation and myogenesis. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;2105170:1-16. [18] CHAE S, LEE SS, CHOI YJ, et al. 3D cell-printing of biocompatible and functional meniscus constructs using meniscus‐derived bioink. Biomaterials. 2021;267: 120466-120507. [19] 张彬,沈师,鲜海,等.3D打印制备PLGA / 脱细胞软骨细胞外基质支架材料及其理化特性研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2019,8(8):1011-1018. [20] LEE J, HONG J, KIM WJ, et al. Bone-derived dECM/alginate bioink for fabricating a 3D cell-laden mesh structure for bone tissue engineering. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;250:116914-116923. [21] KIM WJ, LEE H, LEE JU, et al. Efficient myotube formation in 3D bioprinted tissue construct by biochemical and topographical cues. Biomaterials. 2020;230: 116914-116923. [22] SCIENCE PS, FUSION C, MOHIUDDIN TMG, et al. A 3D bioprinted hybrid encapsulation system for delivery of human pluripotent stem cell-derived pancreatic islet-like aggregates. Mater Des. 2021;11(20):5035-5040. [23] KIM WJ, KIM GH. An intestinal model with a finger-like villus structure fabricated using a bioprinting process and collagen/SIS-based cell-laden bioink. Theranostics. 2020;10(6):2495-2508. [24] AHN G, MIN KH, KIM C, et al. Precise stacking of decellularized extracellular matrix based 3D cell-laden constructs by a 3D cell printing system equipped with heating modules. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):1-11. [25] LEE H, HAN W, KIM H, et al. Development of liver decellularized extracellular matrix bioink for three-dimensionalcell printing-based liver tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules. 2017;18(4):1229-1237. [26] MAO Q, WANG Y, LI Y, et al. Fabrication of liver microtissue with liver decellularized extracellular matrix (dECM) bioink by digital light processing (DLP) bioprinting. Mater Sci Eng C. 2020;109:110625-110634. [27] CHAE S, SUN Y, CHOI YJ, et al. 3D cell-printing of tendon-bone interface using tissue-derived extracellular matrix bioinks for chronic rotator cuff repair. Biofabrication. 2021;13(3):035005-035021. [28] HA DH, CHAE S, LEE JY, et al. Therapeutic effect of decellularized extracellular matrix-based hydrogel for radiation esophagitis by 3D printed esophageal stent. Biomaterials. 2021;266:120477-120488. [29] CHOI YJ, JUN YJ, KIM DY, et al. A 3D cell printed muscle construct with tissue-derived bioink for the treatment of volumetric muscle loss. Biomaterials. 2019; 206:160-169. [30] BIN Y, DONGZHEN Z, XIAOLI C, et al. Modeling human hypertrophic scars with 3D preformed cellular aggregates bioprinting. Bioact Mater. 2022;10:247-254. [31] LEE S, LEE HS, CHUNG JJ, et al. Enhanced regeneration of vascularized adipose tissue with dual 3D‐printed elastic polymer/dECM hydrogel complex. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(6):1-22. [32] ELOMAA L, KESHI E, SAUER IM, et al. Development of GelMA/PCL and dECM/PCL resins for 3D printing of acellular in vitro tissue scaffolds by stereolithography. Mater Sci Eng C. 2020;112:110958-110967. [33] DEFOREST CA, ANSETH KS. Advances in bioactive hydrogels to probe and direct cell fate. Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng. 2012;3:421-444. [34] HASHIMOTO Y, FUNAMOTO S, SASAKI S, et al. Preparation and characterization of decellularized cornea using high-hydrostatic pressurization for corneal tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2010;31(14):3941-3948. [35] ZAMBON A, VETRALLA M, URBANI L, et al. Dry acellular oesophageal matrix prepared by supercritical carbon dioxide. J Supercrit Fluids. 2016;115:33-41. [36] PLANT CD, PLANT GW. Viral transduction of Schwann cells for peripheral nerve repair. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1739:455-466. [37] SAFARI F, FANI N, EGLIN D, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res - Part A. 2019;107(8):1793-1802. [38] SIMSA R, PADMA AM, HEHER P, et al. Systematic in vitro comparison of decellularization protocols for blood vessels. PLoS One. 2018;13(12): 1-19. [39] LOSTUTTER TW, LEWIS MA, CONCRONCE JM, et al. Decellularization of human and porcine lung tissues for pulmonary tissue engineering. Bone. 2014;23(1):1-7. [40] GAETANI R, AUDE S, DEMADDALENA LL, et al. Evaluation of different decellularization protocols on the generation of pancreas-derived hydrogels. Tissue Eng - Part C Methods. 2018;24(12):697-708. [41] LUO Z, BIAN Y, SU W, et al. Comparison of various reagents for preparing a decellularized porcine cartilage scaffold. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(3):1417-1427. [42] PETER M, CRAPOTHOMAS W, GILBERT, et al. An overview of tissue and whole organ decellularization processes. Biomaterials. 2012;32(12):3233-3243. [43] MATUSKA AM, MCFETRIDGE PS. Laser micro-ablation of fibrocartilage tissue: Effects of tissue processing on porosity modification and mechanics. J Biomed Mater Res - Part B Appl Biomater. 2018;106(5):1858-1868. [44] TCHOUKALOVA YD, HINTZE JM, HAYDEN RE, et al. Tracheal decellularization using a combination of chemical, physical and bioreactor methods. Int J Artif Organs. 2018;41(2):100-107. [45] QIU S, RAO Z, HE F, et al. Decellularized nerve matrix hydrogel and glial-derived neurotrophic factor modifications assisted nerve repair with decellularized nerve matrix scaffolds. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2020;14(7):931-943. [46] 苑龙,李森,卞继超,等.3d 生物打印生物墨水灭菌技术的合理选择与应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(6):2914–2921. [47] BADYLAK SF, GILBERT TW. Immune response to biologic scaffold materials. Semin Immunol. 2008;20(2):109-116. [48] JEFFORDS ME, WU J, SHAH M, et al. Tailoring material properties of cardiac matrix hydrogels to induce endothelial differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells Cells. Physiol Behav. 2017;176(12):139-148. [49] VISSCHER DO, LEE H, VAN ZUIJLEN PPM, et al. A photo-crosslinkable cartilage-derived extracellular matrix (ECM) bioink for auricular cartilage tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2021;121:193-203. [50] HÖLZL K, LIN S, TYTGAT L, et al. Bioink properties before, during and after 3D bioprinting. Biofabrication. 2016;8(3):032002-032021. [51] JANG J, KIM TG, KIM BS, et al. Tailoring mechanical properties of decellularized extracellular matrix bioink by vitamin B2-induced photo-crosslinking. Acta Biomater. 2016;33:88-95. [52] WOLF MT, DALY KA, Brennan-Pierce EP, et al. A hydrogel derived from decellularized dermal extracellular matrix. Biomaterials. 2012;33(29):7028-7038. [53] JOHNSON TD, LIN SY, CHRISTMAN KL. Tailoring material properties of a nanofibrous extracellular matrix derived hydrogel. Nanotechnology. 2011;22(49): 494015-494025. [54] LIANG R, YANG G, KIM KE, et al. Positive effects of an extracellular matrix hydrogel on rat anterior cruciate ligament fibroblast proliferation and collagen mRNA expression. J Orthop Transl. 2015;3(3):114-122. [55] YOUNG DA, IBRAHIM DO, HU D, et al. Injectable hydrogel scaffold from decellularized human lipoaspirate. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(3):1040-1049. [56] AGUADO BA, MULYASASMITA W, SU J, et al. Improving viability of stem cells during syringe needle flow through the design of hydrogel cell carriers. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(7-8):806-815. [57] MUELLER S. Introduction to liver stiffness: a novel parameter for the diagnosis of liver disease. Liver Elastography Clin Use Interpret. 2020:3-9. [58] CURTIS ET, ZHANG S, KHALILZAD-SHARGHI V, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography methodology for the evaluation of tissue engineered construct growth. J Vis Exp. 2012;(60):1-7. [59] GEFEN A, MARGULIES SS. Are in vivo and in situ brain tissues mechanically similar? J Biomech. 2004;37(9):1339-1352. [60] CHEN W, XU Y, LI Y, et al. 3D printing electrospinning fiber-reinforced decellularized extracellular matrix for cartilage regeneration. Chem Eng J. 2020; 382:122986. [61] BADYLAK SF, FREYTES DO, GILBERT TW. Reprint of: Extracellular matrix as a biological scaffold material: Structure and function. Acta Biomater. 2015;23(S):S17-S26. [62] KHETAN S, GUVENDIREN M, LEGANT WR, et al. Degradation-mediated cellular traction directs stem cell fate in covalently crosslinked three-dimensional hydrogels. Nat Mater. 2013;12(5):458-465. [63] GILBERT TW, STEWART-AKERS AM, SIMMONS-BYRD A, et al. Degradation and remodeling of small intestinal submucosa in canine Achilles tendon repair. J Bone Jt Surg Ser A. 2007;89(3):621-630. [64] VACANTI CA, LANGER R, SCHLOO B, et al. Synthetic polymers seeded with chondrocytes provide a template for new cartilage formation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1991;88(5):753-759. [65] SHINOKA T, BREUER CK, TANEL RE, et al. Heart valves: valve in a lamb model leaflet. Ann Thorac Surg. 1995;60(6S):S513-S516. [66] ZIMMERMANN WH, MELNYCHENKO I, WASMEIER G, et al. Engineered heart tissue grafts improve systolic and diastolic function in infarcted rat hearts. Nat Med. 2006;12(4):452-458. [67] NEREM RM. Cellular engineering. Ann Biomed Eng. 1991;19(5):529-545. [68] YELESWARAPU S, CHAMEETTACHAL S, PATI F. Integrated 3D printing-based framework - a strategy to fabricate tubular structures with mechanocompromised hydrogels. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2021;4(9):6982-6992. [69] XU Y, HU Y, LIU C, et al. A novel strategy for creating tissue-engineered biomimetic blood vessels using 3D bioprinting technology. Materials (Basel). 2018;11(9):1581-1595. [70] POTERE F, BELGIO B, CROCI GA, et al. 3D bioprinting of multi-layered segments of a vessel-like structure with ECM and novel derived bioink. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:1-13. [71] GARDIN C, FERRONI L, LATREMOUILLE C, et al. Recent applications of three dimensional printing in cardiovascular medicine. Cells. 2020;9(3):742-774. [72] DAS S, KIM SW, CHOI YJ, et al. Decellularized extracellular matrix bioinks and the external stimuli to enhance cardiac tissue development in vitro. Acta Biomater. 2019;95:188-200. [73] YU C, MA X, WANG P, et al. Scanningless and continuous 3D bioprinting of human tissues with decellularized extracellular matrix. Physiol Behav. 2016;176(1):139-148. [74] BEJLERI D, STREETER BW, NACHLAS ALY, et al. A bioprinted cardiac patch composed of cardiac-specific extracellular matrix and progenitor cells for heart repair. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018;7(23):1-13. [75] BEJLERI D, ROBESON MJ, BROWN ME, et al. In vivo evaluation of bioprinted cardiac patches composed of cardiac-specific extracellular matrix and progenitor cells in a model of pediatric heart failure. Biomater Sci. 2022;10(2):444-456. [76] ASULIN M, MICHAEL I, SHAPIRA A, et al. One-step 3D printing of heart patches with built-in electronics for performance regulation. Adv Sci. 2021;8(9):1-8. [77] NOOR N, SHAPIRA A, EDRI R, et al. 3D printing of personalized thick and perfusable cardiac patches and hearts. Adv Sci. 2019;6(11):1900344-1900355. [78] VERNENGO AJ, GRAD S, EGLIN D, et al. Bioprinting tissue analogues with decellularized extracellular matrix bioink for regeneration and tissue models of cartilage and intervertebral discs. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30(44):1909044-1909088. [79] BAIGUERA S, DEL GAUDIO C, DI NARDO P, et al. 3D printing decellularized extracellular matrix to design biomimetic scaffolds for skeletal muscle tissue engineering. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:2689701-2689714. [80] CHOUDHURY D, TUN HW, WANG T, et al. Organ-derived decellularized extracellular matrix: a game changer for bioink manufacturing? Trends Biotechnol. 2018;36(8):787-805. [81] PRICE D. Decellularized extracellular matrix materials for cardiac repair and regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;8(5):19-39. [82] 闫伽宁,胥义.脱细胞基质生物墨水制备方法及应用进展[J].生物工程学报, 2021,37(11):4024-4035. |
| [1] | 黎梓楷, 张程程, 熊嘉颖, 杨曦瑞, 阳 晶, 石海山. 奥硝唑药物对牙髓再生根管内血管化的潜在影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | 赖鹏宇, 梁 冉, 沈 山. 组织工程技术修复颞下颌关节:问题与挑战[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [3] | 娄 国, 张 敏, 付常喜. 8周运动预适应增强脂肪干细胞治疗心肌梗死大鼠的效果[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1363-1370. |
| [4] | 赵楠楠, 李彦杰, 秦合伟, 朱博超, 丁慧敏, 徐振华. 通脉开窍丸治疗血管性痴呆模型大鼠海马区神经元的铁死亡变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1401-1407. |
| [5] | 万玲玲, 吴梦滢, 张宇骄, 罗青清. 炎性因子干扰素γ以焦亡途径影响人血管平滑肌细胞的迁移和凋亡[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1422-1428. |
| [6] | 德 吉, 索朗达, 魏宇辰, 王 斌, 阿旺措吉, 仁青措姆, 崔久增, 张 磊, 巴 贵. 藏西北绒山羊子宫内膜容受性相关基因和可变剪接事件的综合分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1429-1436. |
| [7] | 陈玉宁, 蒋 颖, 廖翔宇, 陈琼君, 熊 亮, 刘 悦, 刘 通. 补气活血合剂干预脑缺血再灌注模型大鼠相关因子及自噬蛋白的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1152-1158. |
| [8] | 高 洋, 秦合伟, 刘丹丹. ACSL4介导铁死亡及在动脉粥样硬化性心血管病中的潜在作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1239-1247. |
| [9] | 徐 飞, 闫金强, 柴守栋. 机械应力调控血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(5): 1064-1072. |
| [10] | 王荣荣, 黄玉珊, 李湘淼, 白金柱. 创伤性脊髓损伤急性期前列腺素E1对血管相关因子的调节和微循环功能的保护[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(5): 958-967. |
| [11] | 韩海慧, 孟晓辉, 徐 博, 冉 磊, 施 杞, 肖涟波. 成纤维细胞生长因子受体1抑制剂对胶原诱导关节炎模型大鼠骨破坏的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(5): 968-977. |
| [12] | 熊波涵, 王国梁, 余 洋, 薛文强, 余 鸿, 刘津瑞, 阮朝晖, 李雅娟, 刘昊龙, 董开颜, 龙 丹, 陈 钊. 内减张技术辅助前交叉韧带重建促进滇南小耳猪跟腱移植物韧带化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(4): 713-720. |
| [13] | 孙现娟, 王秋花, 张锦艺, 杨杨杨, 王文双, 张晓晴. 不同静电纺丝膜上骨髓间充质干细胞的黏附、增殖与成血管平滑肌分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(4): 661-669. |
| [14] | 彭 永, 胡江平, 朱 欢. 低负荷血流限制和高强度抗阻运动对男性运动青年大腿微循环功能的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(2): 393-401. |
| [15] | 付常喜, 何瑞波, 马 刚, 朱 政, 马文超 .
不同运动模式影响心肌梗死致心力衰竭大鼠骨骼肌重塑的机制
[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(2): 221-230. |
组织工程策略通过仿生构建组织替代物,修复与治疗缺损或病变的器官组织,解决现有器官移植存在的供体不足以及体外研究模型短缺等问题[2]。生物3D打印技术通过生物墨水负载活细胞,可构建具有高精度、仿生结构和具有生理功能的组织支架,有望解决临床器官移植供体不足和研究模型缺乏的问题。
目前,常用生物墨水有琼脂糖、壳聚糖、丝素蛋白、胶原蛋白和海藻酸盐等,但这些材料各有优缺点。例如:海藻酸钠生物相容性良好,但稳定性差;高分子材料如聚己内酯、聚L-丙交酯-己内酯等,虽然力学性能优良,但细胞黏附性差[3]。脱细胞基质(decellularized extracellular matrix,dECM)生物墨水是一种具有低免疫原性、保留大部分原始组织结构、由细胞外基质(extracellular matrix,ECM)组分组成的材料,目前该类材料已被应用于制备组织工程支架、干细胞递送以及药物筛选领域。脱细胞基质材料最早可追溯到1948年,POEL等[4]首次通过脱细胞方法,将肌肉组织剁碎并均质化,将细胞外基质与细胞分离。尽管该研究中所采用的方法较为粗糙,但为后续脱细胞技术的发展奠定了重要基础。随后,从二十世纪七八十年代开始,脱细胞基质开始受到关注并蓬勃发展。1979年,HJELLE等[5]首次制备获得具有组织特异性的大鼠肾小球基底膜脱细胞基质。1991年,KREJCI等[6]报告了第一个利用脱细胞基质进行损伤组织修复的研究,利用动物实验证明皮肤来源的脱细胞基质可修复小鼠皮肤伤口。之后,研究者对心血管组织,如血管和心脏瓣膜进行了脱细胞处理获得心血管组织来源的脱细胞基质[7-8],并证明了支架在心血管疾病治疗中的应用潜力。2002年,LANDERS等[9]首次使用温敏性水凝胶进行打印,为后续研究者在制备生物墨水方面提供了重要参考信息。2008年,OTT等[10]利用灌注的方式制备了完整的大鼠心脏脱细胞基质支架,在去除细胞成分的同时保留了其内部结构特征,标志着全器官脱细胞技术的开端,同时为后续的器官脱细胞基质支架再细胞化奠定了基础。2014年,PATI等[11]首次使用脱细胞基质水凝胶进行3D打印,构建了具有一定复杂度的支架结构,该结构用于培养干细胞,结果证明脱细胞基质生物墨水可支持干细胞分化。2017年JANG等[12]利用脱细胞基质生物墨水首次负载干细胞进行3D打印,拓展了脱细胞基质生物墨水在组织工程领域中的应用,见图1。
 脱细胞基质生物墨水的制备及其可打印性是决定其在生物3D打印中应用的两个关键要点。该综述总结对比了目前常用动物组织或器官的脱细胞方法,并详细介绍了从脱细胞基质到脱细胞基质生物墨水所需满足的条件,同时介绍了脱细胞基质生物墨水研究的关键理化特性、表征方法及关键性能指标,最后,总结概括了脱细胞基质生物墨水在人工血管、心肌补片和心肌组织构建中的应用。该综述将对未来从事脱细胞基质生物墨水及组织工程相关研究的人员,提供该领域的研究进展以及相关重要测试方法,有助于其快速了解领域发展。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
脱细胞基质生物墨水的制备及其可打印性是决定其在生物3D打印中应用的两个关键要点。该综述总结对比了目前常用动物组织或器官的脱细胞方法,并详细介绍了从脱细胞基质到脱细胞基质生物墨水所需满足的条件,同时介绍了脱细胞基质生物墨水研究的关键理化特性、表征方法及关键性能指标,最后,总结概括了脱细胞基质生物墨水在人工血管、心肌补片和心肌组织构建中的应用。该综述将对未来从事脱细胞基质生物墨水及组织工程相关研究的人员,提供该领域的研究进展以及相关重要测试方法,有助于其快速了解领域发展。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 主要由第一作者在2022年5月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 检索重点时限为2005-01-01/2022-05-01。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中国知网和PubMed数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“3D打印、脱细胞、生物墨水、血管、心脏”,英文检索词为“decellularization,bioink,3D print,vessel,cardiac”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著和综述。
1.1.6 检索策略 以PubMed数据库为例,检索策略见图2。

1.2.1 纳入标准 ①有关脱细胞基质材料介绍的文献;②有关脱细胞基质生物墨水介绍的文献;③有关脱细胞基质生物墨水在血管或心肌补片领域中应用的文献;④同一领域中论点和论据可靠的文献;⑤近期发表的较高质量的综述文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①重复性研究且与研究目的相关性差的文章;②发表时间过于陈旧、资料无法获得的文章。
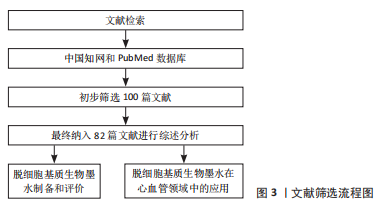
1.3 文献质量评估及数据的提取 通过阅读文章题目和摘要初检得到98篇文献,通过阅读全文排除重复性和与研究目的相关性差的文献,最后纳入82篇文献进行综述,其中中文4篇,英文78篇,见图3。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 相较于其他相关类型文献,该综述对于脱细胞基质生物墨水的制备过程、原理和评价进行了详细的总结,且对于目前脱细胞基质生物墨水在心血管领域中的应用进行了总结。
3.3 综述的局限性 该综述虽对脱细胞基质生物墨水在心血管领域中的应用进行了讨论,主要集中于基础研究,对于临床中的应用研究还缺乏全面总结。
3.4 综述的重要意义 该综述以脱细胞基质生物墨水的制备过程作为切入点,详细比较了目前生物材料的脱细胞方法,并在酶解消化、负载细胞上详细介绍了从脱细胞基质到脱细胞基质生物墨水所需要的条件。同时,该综述从脱细胞基质成分、流变性能、微观纤维结构、对细胞的影响、力学强度和生物降解性上总结了脱细胞基质生物墨水制备后所需要进行的评价方法及相关参数,有助于有意从事该领域研究的人员对该领域的研究进展以及关键测试方法获得基本认识与了解。最后,该综述总结了脱细胞基质生物墨水在人工血管、心肌补片和心肌组织上的应用,突出了脱细胞基质生物墨水应用于心血管领域的优势,有助于优化在心血管领域中的生物墨水设计。
3.5 课题专家对未来的建议 目前脱细胞基质生物墨水距离实现临床转化还有一定距离。在基础研究方面,对于脱细胞基质生物墨水有以下建议:①提升脱细胞基质生物墨水的力学强度以及力学可控性,寻找新的方法加强其力学强度及力学可控性;②对不同来源的脱细胞基质生物墨水的蛋白质组学信息,以及脱细胞基质生物墨水与宿主细胞之间相互作用机制进行深入研究,优化组织特异性的生物墨水。
在心血管应用研究方面,对于脱细胞基质生物墨水有以下建议:①利用脱细胞基质生物墨水打印的血管进行与血液有关的病理研究,以及体外构建相关的病理模型(如血栓模型),从而进行药理学和毒理学研究;②对种子细胞的参数(类型、区域密度和数量等)对于心肌补片的影响问题进行研究,对种子细胞的选取进行优化;③对导电心肌补片与宿主组织之间的电耦合问题进行研究,为导电的心肌补片的临床应用提供基础。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
脱细胞基质:生物组织或器官经过脱细胞处理去除细胞成分,降低免疫原性,同时保留细胞外基质成分与结构,最终获得的脱细胞基质材料。生物墨水:用于打印活细胞或生物活性分子的生物材料,可为细胞的生存提供合适的微环境。水凝胶材料是最为常用的生物墨水,主要包括胶原蛋白、明胶和海藻酸盐等。
据《中国心血管健康与疾病报告2020》报道,目前中国心血管病患者约为3.3亿,心血管疾病占中国居民死亡原因的40%以上,仅2018年用于缺血性心脏病的住院总费用高达1119.82亿元,造成重大国民经济负担。流行病学研究显示,缺血性心血管疾病患者人数呈明显上升趋势,急需开发新的有效治疗方法与技术。以人工血管为例,以Gore-Tex®和Dacron®为代表的人造血管产品作为大动脉导管使用,技术相对成熟,但其作为小口径血管(内径<6 mm)时,血管发生血栓、狭窄和感染等风险提高,使用失败率高,临床亟待解决。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||